
List of plant morphology terms
Encyclopedia
Biologists that study plant morphology
use a number of different terms to describe plant organs and parts that can be observed with the human eye using no more than a hand held magnifying lens. These terms are used to identify and classify plants.
Plant habit
Root
Roots generally do not offer many characters used in plant identification and classification but are important in determining plant duration though in some groups they very important for proper identification including the grasses.
Bud
Leaves
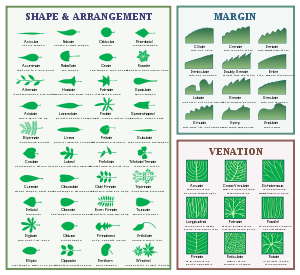 Leaf Parts: – A complete leaf is composed of a blade, petiole and stipules and in many plants one or more might be lacking or highly modified.
Leaf Parts: – A complete leaf is composed of a blade, petiole and stipules and in many plants one or more might be lacking or highly modified.
Duration of leaves:
Venation:
Leaf Arrangement or Phyllotaxy:
Leaf Type:
Leaf Blade Shape:
Leaf Base Shape:
Leaf Blade Apex:
Leaf Blade Margins:
Leaf Modifications:
Basic flower
Pollination
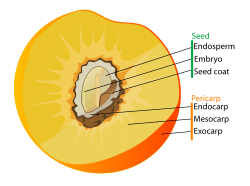
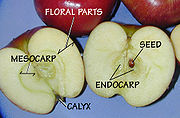 Fruits are divided into different types depending on how they form, were or how they open and what parts they are composed of.
Fruits are divided into different types depending on how they form, were or how they open and what parts they are composed of.
Pteridophyte sporangium
Bryophyte sporangium
Plant morphology
Plant morphology or phytomorphology is the study of the physical form and external structure of plants. This is usually considered distinct from plant anatomy, which is the study of the internal structure of plants, especially at the microscopic level...
use a number of different terms to describe plant organs and parts that can be observed with the human eye using no more than a hand held magnifying lens. These terms are used to identify and classify plants.
General plant terms
- Abaxial – located on the side facing away from the axis.
- Adaxial – located on the side facing towards the axis.
- Dehiscent – opening at maturity
- GallGallGalls or cecidia are outgrowths on the surface of lifeforms caused by invasion by other lifeforms, such as parasites or bacterial infection. Plant galls are abnormal outgrowths of plant tissues and can be caused by various parasites, from fungi and bacteria, to insects and mites...
– outgrowth on the surface caused by invasion by other lifeforms, such as parasites - Indehiscent – not opening at maturity
- Reticulate – web-like or network-like
- Striated – marked by a series of lines, grooves, or ridges
- Tesselate – marked by a pattern of polygons, usually rectangles
- Wing (plant) – any flat surfaced structure emerging from the side or summit of an organ; seeds, stems.
Plant habitHabit (biology)Habit, when used in the context of biology, refers to the instinctive actions of animals and the natural tendencies of plants.In zoology, this term most often refers to specific behavioral characteristics, even when directly related to physiology...
- Acaulescent – the leaves and inflorescence rise from the ground, appearing to have no stem.
- Acid plant – plants with acid saps, normally due to the production of ammonium salts (malicMalic acidMalic acid is an organic compound with the formula HO2CCH2CHOHCO2H. It is a dicarboxylic acid which is made by all living organisms, contributes to the pleasantly sour taste of fruits, and is used as a food additive. Malic acid has two stereoisomeric forms , though only the L-isomer exists...
and oxalic acidOxalic acidOxalic acid is an organic compound with the formula H2C2O4. This colourless solid is a dicarboxylic acid. In terms of acid strength, it is about 3,000 times stronger than acetic acid. Oxalic acid is a reducing agent and its conjugate base, known as oxalate , is a chelating agent for metal cations...
) - Acme – the period when the plant or population is at its maximum vigor.
- Actinomorphic – parts of plants that are radially symmetrical in arrangement.
- ArborescentArborescentArborescent is a term used by the French thinkers Deleuze and Guattari to characterize thinking marked by insistence on totalizing principles, binarism and dualism...
– growing into a treeTreeA tree is a perennial woody plant. It is most often defined as a woody plant that has many secondary branches supported clear of the ground on a single main stem or trunk with clear apical dominance. A minimum height specification at maturity is cited by some authors, varying from 3 m to...
-like habit, normally with a single woody stem. - AscendingAscendingAscending is a science fiction novel by the Canadian writer James Alan Gardner, published in 2001 by HarperCollins Publishers under its various imprints. It is the fifth novel in Gardner's "League of Peoples" series...
– growing uprightly, in an upward direction, heading in the direction of the top. - Assurgent – growth ascending.
- Branching – dividing into multiple smaller segments.
- Caducous – falling away early.
- Caulescent – with a well-developed stem above ground.
- Cespitose – forming dense tufts, normally applied to small plants typically growing into mats, tufts or clumps.
- Creeping – growing along the ground and producing roots at intervals along surface.
- DeciduousDeciduousDeciduous means "falling off at maturity" or "tending to fall off", and is typically used in reference to trees or shrubs that lose their leaves seasonally, and to the shedding of other plant structures such as petals after flowering or fruit when ripe...
– falling away after its function is completed. - Decumbent – growth starts off prostrate and the ends become upright.
- Deflexed – bending downward.
- Determinate growth – Growing for a limited time, floral formation and leaves.
- DimorphicPolymorphism (biology)Polymorphism in biology occurs when two or more clearly different phenotypes exist in the same population of a species — in other words, the occurrence of more than one form or morph...
– of two different forms. - Ecad – a plant assumed to be adapted to a specific habitat.
- EcotoneEcotoneAn ecotone is a transition area between two biomes but different patches of the landscape, such as forest and grassland. It may be narrow or wide, and it may be local or regional...
– the boundary that separates two plant communities, generally of major rank – trees in woods and grasses in savanna for example. - EctogenesisEctogenesisEctogenesis is the growth of an organism in an artificial environment outside the body in which it would normally be found, such as the growth of an embryo or fetus outside the mother's body, or the growth of bacteria outside the body of a host.-Human embryos and fetuses:Ectogenesis of human...
– variation in plants due to conditions out side of the plants. - Ectoparasite – a parasitic plant that has most of its mass outside of the host, the body and reproductive organs of the plant lives outside of the host.
- EpigealEpigealEpigeal, epigean, epigeic and epigeous are biological terms describing an organism's activity above the soil surface.In botany, a seed is described as epigeal when the cotyledons of the germinating seed expand, throw off the seed shell and become photosynthetic above the ground...
– living on the surface of the ground. See also terms for seeds.- Epigean – occurring on the ground.
- Epigeic – plants with stolons on the surface of the ground.
- Epigeous – on the ground. Used for leaf fungus that live on the surface of the leaf.
- Epilithic – growing on the surface of rocks.
- Epiphloedal – growing on the bark of trees.
- Epiphloedic – an organism that grows on the bark of trees.
- Epiphyllous – growing on the leaves. For example, HelwingiaHelwingiaThe genus Helwingia consists of 2-5 species of shrubs native to Asia. It is the only genus in the family Helwingiaceae.The plants have alternate leaves and small inflorescences which are epiphyllous...
japonica has epiphyllous flowers (ones that form on the leaves). - EpiphyteEpiphyteAn epiphyte is a plant that grows upon another plant non-parasitically or sometimes upon some other object , derives its moisture and nutrients from the air and rain and sometimes from debris accumulating around it, and is found in the temperate zone and in the...
– growing on another organism but not parasitic. Not growing on the ground.- Epiphytic – having the nature of an epiphyte.
- Equinoctial – a plants that has flowers that open and close at definite times during the day.
- Erect – having an essentially upright vertical habit or position.
- Escape – plant originally under cultivation that has become wild, garden plant growing in natural areas.
- EvergreenEvergreenIn botany, an evergreen plant is a plant that has leaves in all seasons. This contrasts with deciduous plants, which completely lose their foliage during the winter or dry season.There are many different kinds of evergreen plants, both trees and shrubs...
– remaining green in the winter or during the normal dormancy period for other plants. - Eupotamous – living in rivers and streams.
- Euryhaline – normally living in salt water but tolerant of variable salinity rates.
- Eurythermous – tolerant of a wide range of temperature.
- Exclusive species – confined to specific location.
- ExoticIntroduced speciesAn introduced species — or neozoon, alien, exotic, non-indigenous, or non-native species, or simply an introduction, is a species living outside its indigenous or native distributional range, and has arrived in an ecosystem or plant community by human activity, either deliberate or accidental...
– not native to the area or region. - Exsiccatus – a dried plant, most often used for specimens in a herbarium.
- Indeterminate growthIndeterminate growthIn biology and especially botany, indeterminate growth refers to growth that is not terminated in contrast to determinate growth that stops once a genetically pre-determined structure has completely formed. Thus, a plant that grows and produces flowers and fruit until killed by frost or some other...
– Inflorescence and leaves growing for an indeterminate time, until stopped by other factors such as frost - Lax – non upright, growth not strictly upright or hangs down from the point of origin.
- ParasiticParasitismParasitism is a type of symbiotic relationship between organisms of different species where one organism, the parasite, benefits at the expense of the other, the host. Traditionally parasite referred to organisms with lifestages that needed more than one host . These are now called macroparasites...
– using another plant as a source of nourishment. - Precocious – flowering before the leaves emerge.
- Procumbent – growing prostrate or trailing but not rooting at the nodes.
- Prostrate – laying flat on the ground, stems or even flowers in some species.
- Repent – creeping.
- RosetteRosette (botany)In botany, a rosette is a circular arrangement of leaves, with all the leaves at a single height.Though rosettes usually sit near the soil, their structure is an example of a modified stem.-Function:...
– cluster of leaves with very short internodes that are crowded together, normally on the soil surface but sometimes higher on the stem.- Rostellate – like a rosette.
- Rosulate – arranged into a rosette.
- Runner – an elongated, slender branch that roots at the nodes or tip.
- StolonStolonIn biology, stolons are horizontal connections between organisms. They may be part of the organism, or of its skeleton; typically, animal stolons are external skeletons.-In botany:...
– A branch that forms near the base of the plant and grows horizontally and roots and produces new plants at the nodes or apex.- Stoloniferous – plants produce stolons.
- Semi-erect – Not growing perfectly straight.
- Suffrutescent – somewhat shrubby, or shrubby at the base.
- Upright – Growing upward.
- Virgate – wand-like, slender erect growing stem with many leaves or very short branches.
- WoodyWoody plantA woody plant is a plant that uses wood as its structural tissue. These are typically perennial plants whose stems and larger roots are reinforced with wood produced adjacent to the vascular tissues. The main stem, larger branches, and roots of these plants are usually covered by a layer of...
– forming secondary growth laterally around the plant so as to form woodWoodWood is a hard, fibrous tissue found in many trees. It has been used for hundreds of thousands of years for both fuel and as a construction material. It is an organic material, a natural composite of cellulose fibers embedded in a matrix of lignin which resists compression...
.
Duration
Duration of individual plant lives are described using these terms:- AnnualAnnual plantAn annual plant is a plant that usually germinates, flowers, and dies in a year or season. True annuals will only live longer than a year if they are prevented from setting seed...
– plants that live, reproduce and die in one growing season. - BiennialBiennial plantA biennial plant is a flowering plant that takes two years to complete its biological lifecycle. In the first year the plant grows leaves, stems, and roots , then it enters a period of dormancy over the colder months. Usually the stem remains very short and the leaves are low to the ground, forming...
– plants that need two growing seasons to complete their life cycle, normally vegetative growth the first year and flowering the second year. - Herbs – see herbaceous.
- HerbaceousHerbaceous plantA herbaceous plant is a plant that has leaves and stems that die down at the end of the growing season to the soil level. They have no persistent woody stem above ground...
– plants with shoot systems that die back to ground each year – both annual and non-woody perennial plants. - Herbaceous perennialPerennial plantA perennial plant or simply perennial is a plant that lives for more than two years. The term is often used to differentiate a plant from shorter lived annuals and biennials. The term is sometimes misused by commercial gardeners or horticulturalists to describe only herbaceous perennials...
– non-woody plants that live for more than two years and the shoot system dies back to the soil level each year. - Woody perennialWoody plantA woody plant is a plant that uses wood as its structural tissue. These are typically perennial plants whose stems and larger roots are reinforced with wood produced adjacent to the vascular tissues. The main stem, larger branches, and roots of these plants are usually covered by a layer of...
– true shrubs and trees or some vines with shoot systems that remain alive above the soil surface from one year to the next. - MonocarpicMonocarpicMonocarpic plants are those that flower, set seeds and then die. Other terms with the same meaning are hapaxanth and semelparous. The term was first used by Alphonse de Candolle....
– plants that live for a number of years then after flowering and seed set die.
Vegetative morphology
- Ptyxis - the way in which an individual leaf is folded within an unopened bud.
- VernationVernationVernation is the formation of new leaves or fronds. In plant anatomy, it is the arrangement of leaves in a bud....
– the arrangement of leaves in an unopened bud.
RootRootIn vascular plants, the root is the organ of a plant that typically lies below the surface of the soil. This is not always the case, however, since a root can also be aerial or aerating . Furthermore, a stem normally occurring below ground is not exceptional either...
s
Roots generally do not offer many characters used in plant identification and classification but are important in determining plant duration though in some groups they very important for proper identification including the grasses.- Adventitious – roots that form from other than the hypocotyl or from other roots. Roots forming on the stem are adventitious.
- Aerial – roots growing in the air.
- CrownRoot crownA root crown is that part of a root system from which a stem arises. Since roots and stems have quite different vascular anatomies, major vascular changes take place at this point....
– the place where the roots and stem meet, which may or may not be clearly visible. - Fibrous – describes roots are thread-like and normally tough.
- Fleshy – describes roots are relatively thick and soft, normally made up of storage tissue. Roots are typically long and thick but not thickly rounded in shape.
- HaustorialHaustoriumIn botany, a haustorium is the appendage or portion of a parasitic fungus or of the root of a parasitic plant that penetrates the host's tissue and draws nutrients from it. Haustoria do not penetrate the host's cell membranes.Fungi in all major divisions form haustoria...
– specialized roots that invade other plants and absorb nutrients from those plants. - LignotuberLignotuberA lignotuber is a starchy swelling of the root crown possessed by some plants as a protection against destruction of the plant stem by fire. The crown contains buds from which new stems may sprout, and a sufficient store of nutrients to support a period of growth in the absence of...
– root tissue that allows plants to regenerate after fire or other damage. - Primary – roots that develops from the radicleRadicleIn botany, the radicle is the first part of a seedling to emerge from the seed during the process of germination. The radicle is the embryonic root of the plant, and grows downward in the soil...
of the embryo, normally the first root to emerge from the seed as it germinates. - Root Hairs – very small roots, often one cell wide, that do most of the water and nutrient absorption.
- Secondary – roots forming off of the primary root, often called branch roots.
- TaprootTaprootA taproot is an enlarged, somewhat straight to tapering plant root that grows vertically downward. It forms a center from which other roots sprout laterally.Plants with taproots are difficult to transplant...
– a primary root that more or less enlarges and grows downward into the soil. - TuberTuberTubers are various types of modified plant structures that are enlarged to store nutrients. They are used by plants to survive the winter or dry months and provide energy and nutrients for regrowth during the next growing season and they are a means of asexual reproduction...
ous – describes roots that are thick and soft, with storage tissue. Typically thick round in shape.
Stems
- Accessory buds – an embryonic shoot occurring above or to the side of an axillary bud;also known as supernumerary bud.
- Acrocarpous – produced at the end of a branch.
- Acutangular – a stem that has several longitudinally running ridges with sharp edges.
- Adventitious buds – a bud that arises at points on the plant other than at the stem apex or a leaf axil.
- Alternate – buds are staggered on opposite sides of the branch
- BarkBarkBark is the outermost layers of stems and roots of woody plants. Plants with bark include trees, woody vines and shrubs. Bark refers to all the tissues outside of the vascular cambium and is a nontechnical term. It overlays the wood and consists of the inner bark and the outer bark. The inner...
– the outer layers of woody plants; corkCork cambiumCork cambium is a tissue found in many vascular plants as part of the periderm. The cork cambium is a lateral meristem and is responsible for secondary growth that replaces the epidermis in roots and stems...
, phloemPhloemIn vascular plants, phloem is the living tissue that carries organic nutrients , in particular, glucose, a sugar, to all parts of the plant where needed. In trees, the phloem is the innermost layer of the bark, hence the name, derived from the Greek word "bark"...
, and vascular cambiumVascular cambiumThe vascular cambium is a part of the morphology of plants. It consists of cells that are partly specialized, for the tissues that transport water solutions, but have not reached any of the final forms that occur in their branch of the specialization graph...
.
- BranchBranchA branch or tree branch is a woody structural member connected to but not part of the central trunk of a tree...
es –
- Bud – an immature stem tip, typically an embryonic shoot, ether producing a stem, leaves or flowers.
- Bulb – an underground stem normally with a short basal surface and with thick fleshy leaves.
- Bundle scar —A small mark on a leaf scar indicating a point where a vein from the leaf was once connected with the stem.
- Caudex – the hard base produced by herbaceous perennials used to overwinter the plant.
- Caulescent – with a distinctive stem.
- Cladode —A flattened stem that performs the function of a leaf; an example is the pad of the opuntia cactus.
- Cladophyll – a flattened stem that is leaf-like and green – used for photosynthesis, normally plants have no or greatly reduced leaves.
- Climbing – typically long stems, that cling to other objects.
- Corm – a compact, upright orientated stem that is bulb-like with hard or fleshy texture and normally covered with papery, thin dry leaves. Most often produced under the soil surface.
- Cuticle – a waxy membrane covering some leaves and roots that is watertight.
- Decumbent – stems that lay on the ground but have the ends turning upward.
- Dormant – a state of no growth or reduced growth
- Earlywood —The portion of the annual ring that is formed during the early part of a tree's growing.
- EpidermisEpidermis (botany)The epidermis is a single-layered group of cells that covers plants' leaves, flowers, roots and stems. It forms a boundary between the plant and the external environment. The epidermis serves several functions, it protects against water loss, regulates gas exchange, secretes metabolic compounds,...
– a layer of cells that cover all primary tissue separating them from the outside environment. - Erect – growing upright.
- Flower bud —a bud from which only a flower or flowers develop
- Fruticose – woody stemmed with a shrub-like habit. Branching near the soil with woody based stems.
- Guard cell —One of the paired epidermal cells that control the opening and closing of a stoma in plant tissue.
- Herbaceous – non-woody and dying to the ground at the end of the growing season. Annual plants die, while perennials regrow from parts on the soil surface or below ground the next growing season.
- Heartwood —The older, nonliving central wood of a tree or woody plant, usually darker and harder than the younger sapwood. Also called duramen.
- Internode – spaces between the nodes.
- Latent buds – An axillary bud whose development is inhibited, sometimes for many years, due to the influence of apical and other buds. Also known as dormant bud
- Late wood – The portion of the annual ring that is formed after formation of earlywood has ceased.
- Lateral buds —A bud located on the side of the stem, usually in a leaf axil.
- Leaf – the photosynthetic organ of a plant that is attached to a stem, generally at specific intervals.
- Leaf axils – the space created between a leaf and its branch. This is especially pronounced on monocots like bromeliads.
- Leaf buds – A bud that produces a leafy shoot.
- Leaf scar – the mark left on a branch from the previous location of a bud or leaf.
- Lenticel – One of the small, corky pores or narrow lines on the surface of the stems of woody plants that allow the interchange of gases between the interior tissue and the surrounding air.
- Lenticels – lens-shaped or warty patches of parenchymatous tissue on the surface of the stem.
- Node – were leaves and buds are attached to the stem.
- Orthotropic growth – growth in a vertical direction.
- Pith – the spongy tissue at the center of a stem.
-
- Chambered pith – A form of pith in which the parenchyma collapses or is torn during development, leaving the sclerenchyma plates to alternate with hollow zones
-
- Continuous pith –
-
- Diaphragmed pith – Pith in which plates or nests of sclerenchyma may be interspersed with the parenchyma.
- Spine – an adapted leaf that is usually hard and sharp and is used for protection, and occasionally shading of the plant
- Plagiotropic growth – growth inclined away from the vertical, inclined towards the horizontal
- Prickle – an extension of the cortex and epidermis that ends with a sharp point.
- Prostrate – growing flat on the soil surface.
- Rhizome – A horizontally orientated, prostrate stem with reduced scale-like leaves, normally growing under ground but also at the soil surface. Also produced by some species that grow in trees or water.
- Rootstock – the underground part of a plant normally referring to a caudex or rhizome.
- Runner – an above ground stem usually rooting and producing new plants at the nodes.
- Scandent – a stem that climbs.
- StemPlant stemA stem is one of two main structural axes of a vascular plant. The stem is normally divided into nodes and internodes, the nodes hold buds which grow into one or more leaves, inflorescence , conifer cones, roots, other stems etc. The internodes distance one node from another...
– vascular tissue that provides support for the plant,
- StolonStolonIn biology, stolons are horizontal connections between organisms. They may be part of the organism, or of its skeleton; typically, animal stolons are external skeletons.-In botany:...
– a horizontally growing stem similar to a rhizome, produced near the base of the plant. They spread out above or along the soil surface, roots and new plants develop at the nodes or ends.
-
- stoloniferous – a plant that produces stolons.
- Suberose – Having a corky texture.
- Tendril – a thigmotropic organ which attached a climbing plant to a support, a portion of a stem or leaf modified to serve as a holdfast to other objects.
- Terminal –
- Terminal scale bud scar –
- Thorn –
- TillerTiller (botany)A tiller is a stem produced by grass plants, and refers to all shoots that grow after the initial parent shoot grows from a seed. Tillers are segmented, each segment possessing its own two-part leaf...
– a shoot of a grass plant.
- TuberTuberTubers are various types of modified plant structures that are enlarged to store nutrients. They are used by plants to survive the winter or dry months and provide energy and nutrients for regrowth during the next growing season and they are a means of asexual reproduction...
– an enlarged stem or root that stores nutrients.
- Turgid – swollen.
- Twigs –
- Opposite – buds are arranged in pairs on opposite sides of the branch
- Pith –
- Pore –
- RhizomeRhizomeIn botany and dendrology, a rhizome is a characteristically horizontal stem of a plant that is usually found underground, often sending out roots and shoots from its nodes...
– an underground stem, typically horizontal, that sends out roots and shoots.
- Sapwood –
- Stoma –
- Vascular bundles – a strand of woodWoodWood is a hard, fibrous tissue found in many trees. It has been used for hundreds of thousands of years for both fuel and as a construction material. It is an organic material, a natural composite of cellulose fibers embedded in a matrix of lignin which resists compression...
y fibers and associated tissues.
- Verticil – a whorl of leaves or flowers.
-
- Verticillate – arranged in whorls.
- Whorled – said of a collection of three or more leaves or flowers that arise from the same point.
BudBudIn botany, a bud is an undeveloped or embryonic shoot and normally occurs in the axil of a leaf or at the tip of the stem. Once formed, a bud may remain for some time in a dormant condition, or it may form a shoot immediately. Buds may be specialized to develop flowers or short shoots, or may have...
s
- Accessory bud – an embryonic shoot occurring above or to the side of an axillary bud;also known as supernumerary bud.
- Adventitious bud – a bud that arises at points on the plant other than at the stem apex or a leaf axil.
- Axillary –
- Dormant – see Latent bud
- Epicormic – vegetative buds that lie dormant beneath the bark, shooting after crown disturbance
- Flower bud –
- Lateral –
- Latent bud – An axillary bud whose development is inhibited, sometimes for many years, due to the influence of apical and other buds. Also known as dormant bud
- Leaf bud – A bud that produces a leafy shoot.
- Mixed – buds that have both embryonic flowers and leaves.
- Naked –
- Pseudoterminal –
- Reproductive – buds with embryonic flowers.
- Scaly –
- Terminal – bud at the tip or end of the stem.
- Vegetative – buds containing embryonic leaves.
LeavesLeafA leaf is an organ of a vascular plant, as defined in botanical terms, and in particular in plant morphology. Foliage is a mass noun that refers to leaves as a feature of plants....

- Blade – the flat and laterally-expanded portion of a leaf
- Leaflet – a separate blade among others comprising a compound leaf
- Ligule – a projection from the top of the sheath on the adaxial side of the sheath-blade joint in grasses
- Midrib – the central vein of the leaf blade
- Midvein – the central vein of a leaflet
- Petiole – a leaf stalk supporting a blade and attaching to a stem at a node
- Petiolule -the leaf stalk of a leaflet
- Pulvinus – the swollen base of a petiole or petiolule usually involved in leaf movements and leaf orientatio
- Rachilla – a secondary axis of a multiply compound leaf
- Rachis – main axis of a pinnately compound leaf
- Sheath – the proximal portion of a grass leaf usually surrounding the stem
- Stipules – paired scales, spines, glands, or blade-like structures at the base of a petiole
- Stipels – paired scales, spines, glands, or blade-like structures at the base of a petiolule
- Stipuloid – resembling stipules.
Duration of leaves:
- DeciduousDeciduousDeciduous means "falling off at maturity" or "tending to fall off", and is typically used in reference to trees or shrubs that lose their leaves seasonally, and to the shedding of other plant structures such as petals after flowering or fruit when ripe...
– - EvergreenEvergreenIn botany, an evergreen plant is a plant that has leaves in all seasons. This contrasts with deciduous plants, which completely lose their foliage during the winter or dry season.There are many different kinds of evergreen plants, both trees and shrubs...
– - Fugacious – lasting for a short time: soon falling away from the parent plant.
- MarcescentMarcescenceMarcescence is the retention of dead plant organs that normally are shed. It is most obvious in deciduous trees that retain leaves through the winter. Several trees normally have marcescent leaves such as oak , beech and hornbeam . Marcescent leaves of pin oak complete development of their...
– - Persistent –
Venation:
- Acrodramous – when the veins run parallel to the leaf edge and fuse at the leaf tip.
- Actinodromous – when the main veins of a leaf radiate from the tip of the petiole.
- Macrophyllous – leaves with a branching vascular system.
- Furcate – forked, dividing into two divergent branches.
- Vein – the externally visible vascular bundles, found on leafs, petals and other parts.
- Veinlet – a small vein.
Leaf Arrangement or Phyllotaxy:
- Whorl – three or more leaves or branches or pedicels arising from the same node.
Leaf Type:
- Abruptly pinnate – a compound leaf without a terminal leaflet.
Leaf Blade Shape:
- Acicular (acicularis): Slender and pointed, needle-like
- Acuminate (acuminata): Tapering to a long point
- Aristate (aristata): Ending in a stiff, bristle-like point
- Bipinnate (bipinnata): Each leaflet also pinnate
- Cordate (cordata): Heart-shaped, stem attaches to cleft
- Cuneate (cuneata): Triangular, stem attaches to point
- Deltoid (deltoidea): Triangular, stem attaches to side
- Digitate (digitata): Divided into finger-like lobes
- Elliptic (elliptica): Oval, with a short or no point
- Falcate (falcata): sickle-shaped
- Flabellate (flabellata): Semi-circular, or fan-like
- Hastate (hastata): shaped like a spear point, with flaring pointed lobes at the base
- Lance-shaped, lanceolate (lanceolata): Long, wider in the middle
- Linear (linearis): Long and very narrow
- Lobed (lobata): With several points
- Obcordate (obcordata): Heart-shaped, stem attaches to tapering point
- Oblanceolate (oblanceolata): Top wider than bottom
- Oblong (oblongus): Having an elongated form with slightly parallel sides
- Obovate (obovata): Teardrop-shaped, stem attaches to tapering point
- Obtuse (obtusus): With a blunt tip
- Orbicular (orbicularis): Circular
- Ovate (ovata): Oval, egg-shaped, with a tapering point
- Palmate (palmata): Divided into many lobes
- Pedate (pedata): Palmate, with cleft lobes
- Peltate (peltata): Rounded, stem underneath
- Perfoliate (perfoliata): Stem through the leaves
- PinnatePinnatePinnate is a term used to describe feather-like or multi-divided features arising from both sides of a common axis in plant or animal structures, and comes from the Latin word pinna meaning "feather", "wing", or "fin". A similar term is pectinate, which refers to a comb-like arrangement of parts...
(pinnata): Two rows of leaflets- odd-pinnate : pinnate with a terminal leaflet
- paripinnate, even-pinnate : pinnate lacking a terminal leaflet
- Pinnatisect (pinnatifida): Cut, but not to the midrib (it would be pinnate then)
- Reniform (reniformis): Kidney-shaped
- Rhomboid (rhomboidalis): Diamond-shaped
- Round (rotundifolia): Circular
- Sagittate (sagittata): Arrowhead-shaped
- Spatulate, spathulate (spathulata): Spoon-shaped
- Spear-shaped (hastata): Pointed, with barbs
- Subulate (subulata): AwlScratch awlA scratch awl is a woodworking layout and point-making tool. It is used to scribe a line to be followed by a hand saw or chisel when making woodworking joints and other operations....
-shaped with a tapering point - Sword-shaped (ensiformis): Long, thin, pointed
- Trifoliate, ternate (or trifoliolate) (trifoliata): Divided into three leaflets
- Tripinnate (tripinnata): Pinnately compound in which each leaflet is itself bipinnate
- Truncate (truncata): With a squared off end
- Unifoliate (unifoliata): with a single leaf
Leaf Base Shape:
- Semiamplexicaul – the leaf base wraps around the stem, but not completely.
Leaf Blade Apex:
- Acuminate – narrowing to a point, used for other structures too.
- Acute – with a sharp rather abrupt ending point.
- Acutifolius – with acute leaves.
- Attenuate – tapering gradually to a narrow end.
Leaf Blade Margins:
- Crenulate – with shallow, small rounded teeth.
Leaf Modifications:
Epidermis and periderm texture
- Acanceous – being prickly.
- Acantha – a prickle or spine.
- Acanthocarpus – fruits are spiny.
- Acanthocladous – the branches are spiny.
- Aculeate – having a covering of prickles or needle-like growth.
- Aculeolate – having spine-like processes.
- Aden – a gland.
- Adenoid – gland like.
- Adenophore – a stalk that supports a gland.
- Adenophyllous – leaves with glands.
- Arachnoid – having a cobwebby appearance with entangled hairs.
- Bloom – the waxy coating that covers some plants.
- Canescent – with gray pubescence.
- Ciliate – with a fringe of marginal hairs.
- Coriaceouse – with a tough or leathery texture.
- Fimbriate – finely cut into fringes, the edge of a frilly petal or leaf.
- Floccose –
- Glabrate –
- Glabrous – smooth without any pubescences at all.
- Glandular –
- Glandular-punctate – covered across the surface with glands.
- Hirsute – with long shaggy hairs, often stiff or bristly to the touch.
- Lanate – with woolly hairs. Thick wool like hairs.
- Verrucose – with a wart surface, with low rounded bumps.
- Villose – covered with fine long hairs that are not matted.
- Villosity – villous indument.
Floral morphology
- Accrescent – Growing larger after anthesis, normally used for the calyx.
- Anthesis – the period when the flower is fully open and functional, ends when the stigma or stamens wither.
Basic flowerFlowerA flower, sometimes known as a bloom or blossom, is the reproductive structure found in flowering plants . The biological function of a flower is to effect reproduction, usually by providing a mechanism for the union of sperm with eggs...
parts
- Acephalous – without a head, used for flower styles without a well-developed stigma.
- Androecium – the stamens collectively.
- Basifixed – attached by the base.
- Connective – the part of the stamen joining the anther cells.
- Diadelphous –
- Didynamous –
- Epipetalous – born on the corolla, often used in reference to stamens attached to the corolla.
- Exserted – sticking out past the corolla, the stamens protrude past the margin of the corolla lip.
- Extrose – opening towards the outside of the flower.
- Gynandrium – combined male & female structure
- Gynostregium –
- Included –
- Introrse – opening on the inside of the corolla, the stamens are contained within the margins of the petals.
- Monodelphous – stamen filaments united into a tube.
- Poricidal – anthers opening by terminal pores.
- Staminode – a sterile stamen.
- Staminodial – (1) concerning a sterile stamen (2) flowers with sterile stamens.
- Synandrous – the anthers are connected (AraceaeAraceaeAraceae are a family of monocotyledonous flowering plants in which flowers are borne on a type of inflorescence called a spadix. The spadix is usually accompanied by, and sometimes partially enclosed in, a spathe or leaf-like bract. Also known as the Arum family, members are often colloquially...
) - Syngenesious – the anthers are united into a tube, the filaments are free (AsteraceaeAsteraceaeThe Asteraceae or Compositae , is an exceedingly large and widespread family of vascular plants. The group has more than 22,750 currently accepted species, spread across 1620 genera and 12 subfamilies...
). - Tetradynamous –
- Translator – a structure uniting the pollinia in AsclepiadaceaeAsclepiadaceaeAccording to APG II, the Asclepiadaceae is a former plant family now treated as a subfamily in the Apocynaceae...
and OrchidaceaeOrchidaceaeThe Orchidaceae, commonly referred to as the orchid family, is a morphologically diverse and widespread family of monocots in the order Asparagales. Along with the Asteraceae, it is one of the two largest families of flowering plants, with between 21,950 and 26,049 currently accepted species,...
. - Trinucleate – pollen containing three nuclei when shed.
- Valvular – anthers opening by valves or small flaps, e.g. BerberisBerberisBerberis , the barberries or pepperidge bushes, is a genus of about 450-500 species of deciduous and evergreen shrubs from 1-5 m tall with thorny shoots, native to the temperate and subtropical regions of Europe, Asia, Africa, North America and South America. They are closely related to the genus...
. - Versatile – anthers pivoting freely on the filament.
- Anther – the distal end of the stamen where pollenPollenPollen is a fine to coarse powder containing the microgametophytes of seed plants, which produce the male gametes . Pollen grains have a hard coat that protects the sperm cells during the process of their movement from the stamens to the pistil of flowering plants or from the male cone to the...
is produced, normally composed of two parts called anther-sacs and pollen-sacs (thecae). - Bract – the leaf-like or scale-like leafy appendages that are located just below a flower, a flower stalk, or an inflorescence; they usually are reduced in size and sometimes showy or brightly colored.

- Calyx – the whorl of sepals at the base of a flower, the outer whorl of the perianth.
- Carpel – the ovule-producing reproductive organ of a flower, consisting of the stigma, style and ovary.
- Claw – a noticeably narrowed and attenuate organ base, typically a petal. ViolaViolaThe viola is a bowed string instrument. It is the middle voice of the violin family, between the violin and the cello.- Form :The viola is similar in material and construction to the violin. A full-size viola's body is between and longer than the body of a full-size violin , with an average...
. - Connate – when the same parts of a flower are fused to each other, petals in a gamopetalous flower. PetuniaPetuniaPetunia is a widely cultivated genus of flowering plants of South American origin, closely related with tobacco, cape gooseberries, tomatoes, deadly nightshades, potatoes and chili peppers; in the family Solanaceae. The popular flower derived its name from French, which took the word petun, meaning...
. - Corolla – the whorl of petals of a flower.
- Corona – an additional structure between the petals and the stamens.Disk – an enlargement or outgrowth from the receptacle of the flower, located at the center of the flower of various plants. The term is also use as the central area of the head in composites were the tubular flowers are attached.
- Filament – the stalk of a stamen
- Floral axis –
- Floral envelope –
- Flower –
- Fruit – a structure contain all the seeds produced by a single flower.
- Gynoecium – the whorl of carpels. May comprise one (syncarpous) or more (apocarpous) pistils. Each pistil consists of an ovary, style and stigma (female reproductive organs of the flower).
- Apocarpus – the gynoecium comprises more than one pistil.
- Cell –
- Compound pistil –
- Funicle – the stalk that connects the ovule to the placenta.
- Funiculus –
- Loculus – the cavities located with in a carpel, ovary or anther.
- Locule –
- multicarpellate –
- Placentra –
- Placentation –
- Axile –
- Basal –
- Free-central –
- Pariental –
- Septum –
- Simple pistil –
- Syncarpous – the gynoecium comprises one pistil.
- Unicarpellate –
- Hypanthium –
- Nectar – a fluid produce by nectaries high in sugar content, used to attract pollinators.
- Nectary – a gland that secrets nectar, most often found in flowers but also produced on other parts of plants too.
- Nectar disk – when the floral disk contains nectar secreting glands, often modified as its main function in some flowers.
- OvaryOvary (plants)In the flowering plants, an ovary is a part of the female reproductive organ of the flower or gynoecium. Specifically, it is the part of the pistil which holds the ovule and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals...
– - Ovules –
- Pedicel – the stem or stalk that holds a single flower in an inflorescence.
- Peduncle – the part of a stem that bears the entire inflorescence, normally having no leaves or the leaves are reduce to bracts. When the flower is solitary, it is the stem or stalk holding the flower.
- Peduncular – referring to or having a peduncle.
- Pedunculate – having a peduncle.
- Perianth –
- Achlamydeous – without a perianth.
- Petal –
- Pistil –
- Pollen –
- Rachis –
- Receptacle – the end of the pedicel that joins to the flower were the different parts of the flower are joined together, also called the torus. In AsteraceaeAsteraceaeThe Asteraceae or Compositae , is an exceedingly large and widespread family of vascular plants. The group has more than 22,750 currently accepted species, spread across 1620 genera and 12 subfamilies...
the top of the pedicel upon which the flowers are joined. - Seed –
- Sepal –
- Stamen –
- Antipetalous – when the stamens are the same number as the corolla segments and oppositely arranged the corolla segments. PrimulaPrimulaPrimula is a genus of 400–500 species of low-growing herbs in the family Primulaceae. They include primrose, auricula, cowslip and oxlip. Many species are grown for their ornamental flowers...
. - Antisepalouse – when the stamens are the same number as the calyx segments and oppositely arranged the calyx segments.
- Connective – the part of the stamen joining the anther cells.
- Antipetalous – when the stamens are the same number as the corolla segments and oppositely arranged the corolla segments. Primula
- Staminode –
- Stigma –
- Style –
- Tepal –
Inflorescences
- Capitulum – the flowers are arranged into a head composed of many separate unstalked flowers, the single flowers are called florets and are packed close together. The typical arrangement of flowers in the AsteraceaeAsteraceaeThe Asteraceae or Compositae , is an exceedingly large and widespread family of vascular plants. The group has more than 22,750 currently accepted species, spread across 1620 genera and 12 subfamilies...
. - Compound Umbel – is an umbel where each stalk of the main umbel produces another smaller umbel of flowers.
- Corymb – a grouping of flowers where all the flowers are at the same level, the flower stalks of different lengths forming a flat-topped flower cluster.
- Cyme – is a cluster of flowers were the end of each growing point produces a flower. New growth comes from side shoots and the oldest and first flowers to bloom are at the top.
- Single – one flower per stem or the flowers are greatly spread-apart as to appear they do not arise from the same branch.
- Spike – when flowers arising from the main stem are without individual flower stalks. The flowers attach directly to the stem.
- Solitary – same as single, with one flower per stem.
- Raceme – is a flower spike with flowers that have stalks of equal length. The stem tip continues to grow and produce more flowers with the bottom flowers open first and blooming progresses up the stem.
- Panicle – is a raceme with branches and each branch having a smaller raceme of flowers. The terminal bud of each branch continues to grow, producing more side shoots and flowers.
- PedicelPedicel (botany)A pedicel is a stem that attaches single flowers to the main stem of the inflorescence. It is the branches or stalks that hold each flower in an inflorescence that contains more than one flower....
– stem holding a one flower in an inflorescences. - Peduncle – stem holding an inflorescences, or a single flower.
- Umbel – were the flower head has all the flower stalks rising from the same point of the same length, the flower head is rounded like an umbrella or almost circular.
- Verticillaster – a whorled collection of flowers around the stem, the flowers produced in rings at intervals up the stem. As the stem tip continues to grow more whorls of flowers are produced. Typical in LamiaceaeLamiaceaeThe mints, taxonomically known as Lamiaceae or Labiatae, are a family of flowering plants. They have traditionally been considered closely related to Verbenaceae, but in the 1990s, phylogenetic studies suggested that many genera classified in Verbenaceae belong instead in Lamiaceae...
.
-
- Verticil – flowers arranged in whorls at the nodes.
Insertion of floral parts
- Epigynous –
- Half-inferior –
- Hypogynous –
- Inferior –
- Insertion –
- Stamens –
- Ovary –
- Perigynous –
- Superior –
Specialized terms
- Wing – term used for the lateral petals of the flowers on species in FabaceaeFabaceaeThe Fabaceae or Leguminosae, commonly known as the legume, pea, or bean family, is a large and economically important family of flowering plants. The group is the third largest land plant family, behind only the Orchidaceae and Asteraceae, with 730 genera and over 19,400 species...
and PolygalaceaePolygalaceaeThe Polygalaceae or Milkwort family is a family of flowering plants in the order Fabales. They have a near-cosmopolitan range, with about 17 genera and 900–1,000 species of herbs, shrubs and trees...
. - Valvate – meeting along the margins but not overlapping.
Union of flower parts
- Adelphous – the androecium with the stamen filaments partly or completely fused together.
Flower sexuality and presence of floral parts
- Achlamydeous – flower without a perianth.
- Apetalous – a flower without petals.
- Accrescent – said of the calyx when it is persistent and enlarges as the fruit grows and ripens, applied to other structure sometimes.
- Androgynous – used for the inflorescence of CarexCarexCarex is a genus of plants in the family Cyperaceae, commonly known as sedges. Other members of the Cyperaceae family are also called sedges, however those of genus Carex may be called "true" sedges, and it is the most species-rich genus in the family. The study of Carex is known as...
when a spike has both staminate and pistillate flowers – the pistillate flowers are normally at the base of the spike. - Bisexual –
- Complete –
- Gynodioecy – describes a plant species or population that has some plants that are female and some plants that are hermaphrodites.
- Homogamous – when the flower anthers and the stigma are ripe at the same time.
- Imperfect –
- Naked –
- Perfect – possessing both stamens and ovary (male and female parts)
Flower symmetry
- Actinomorphic – having a radial symmetry, as in regular flowers.
- Actinomorphy – when the flower parts are arranged with radial symmetry.
- Dialypetalae –
- Incomplete –
- Radial – Symmetric when bisected from any angle (circular)
- Unisexual –
- Zygomorphic – one axis of symmetry running down the middle of the flower so the right and left halves reflect each other.
- Zygomorphy – the type of symmetry that most irregular flowers have with the upper half of the flower unlike the lower half. the left and right halves tend to be mirror images of each other.
PollinationPollinationPollination is the process by which pollen is transferred in plants, thereby enabling fertilisation and sexual reproduction. Pollen grains transport the male gametes to where the female gamete are contained within the carpel; in gymnosperms the pollen is directly applied to the ovule itself...
and fertilization
- AllogamyAllogamyAllogamy is a term used in the field of biological reproduction describing the fertilization of an ovum from one individual with the spermatozoa of another. By contrast, autogamy is the term used for self-fertilization. In humans, the fertilization event is an instance of allogamy...
– cross pollination, when one plant pollinates another plant - Anemophilous – wind pollinated.
- Autogamy – self-pollination, when the flowers of the same plant pollinate flowers on the same plant or themselves.
- Cantharophilous – beetle pollinated
- Chiropterophilous – bat pollinated.
- Cleistogamous – self-pollination of a flower that does not open.
- Dichogamy – Flowers that cannot pollinate themselves because pollen is produced at a time when the stigmas are not receptive of pollen.
- Entomophilous – insect pollinated.
- Hydrophilous – Water pollinated, pollen is moved in water from one flower to the next.
- Malacophilous – pollinated by snails and slugs.
- Ornithophilous – pollinated by birds.
- Pollination – the movement of pollen from the anther to the stigma.
- Protandrous – when pollen is produced and shed before the carpels are mature.
- Progynous – when the carpels mature before the stamens produce pollen.
Embryo development
- Antipodal cell –
- Chalazal –
- Coleoptile – protective sheathe on SAM
- Coleorhiza – protecting layer of a seed
- Cotyledon – 'Seed leaves' (First leaves sprouted – in a dicotDicotyledonThe dicotyledons, also known as dicots, are a group of flowering plants whose seed typically has two embryonic leaves or cotyledons. There are around 199,350 species within this group...
, there are two cotyledons in a seedling) - Diploid
- Double ferilization –
- Embryo –
- Embryo sac –
- Endosperm –
- Filiform apparatus –
- Germination –
- Plumule —the part of an embryo that give rise to the shoot system of a plant
- Polar nuclei –
- Radicle – Initial root-determined cells (Root apical meristem)
- Scutellum –
- Synergid –
- Tegmen –
- Testa –
- Triploid –
- Xenia –
- Zygote –
Fruits and seeds
Fruits are the matured ovary of seed bearing plants and they include the contents of the ovary, which can be floral parts like the receptacle, involucre, calyx and others that are fused to it. Fruits are often used to identify plant taxa and help to place the species in the correct family or differentiate different groups with in the same family.Terms for fruits
- Accessory structures – parts of fruits that do not form from the ovary.
- Beak – normally the slender elongated end of a fruit, typically a persistent style-base.
- Circumscissile – a type of fruit dehiscences were the top of the fruit falls away like a lid or covering.
- Dehiscent – the way a fruit openings and releases its contents, normally in a regular and distinctive fashion.
- Endocarp – includes the wall of the seed chamber, the inner part of the pericarp.
- Exocarp – the pericarp's outer part.
- Fleshy – soft and juicy.
- Indehiscent – fruits that do not have specialized structures for opening and releasing the seeds, they remain closed after the seeds ripen and are opened by animals, weathering, fire or other external means.
- Mesocarp – the middle layer of the pericarp.
- Pericarp – the body of the fruit from its outside surface to the chamber were the seeds are, including the outside skin of the fruit and the inside lining of the seed chamber.
- Suture – the seam along which the fruit opens, normally in most fruits it is were the carpel or carpels are fused together.
- Valve – one of the segments of the capsule.
Fruit types


- Achaenocarp – see achene.
- AcheneAcheneAn achene is a type of simple dry fruit produced by many species of flowering plants. Achenes are monocarpellate and indehiscent...
– dry indehiscent fruit, they have one seed and form from a single carpel, the seed is distinct from the fruit wall. - DrupeDrupeIn botany, a drupe is a fruit in which an outer fleshy part surrounds a shell of hardened endocarp with a seed inside. These fruits develop from a single carpel, and mostly from flowers with superior ovaries...
– outer fleshy part surrounds a shell with a seed inside. - PomePomeIn botany, a pome is a type of fruit produced by flowering plants in the subfamily Maloideae of the family Rosaceae.A pome is an accessory fruit composed of one or more carpels surrounded by accessory tissue...
– accessory fruitAccessory fruitAn accessory fruit is a fruit in which some of the flesh is derived not from the ovary but from some adjacent tissue exterior to the carpel. Examples of accessory tissue are the receptacle of strawberries, figs, or mulberries, and the calyx of Gaultheria procumbens or Syzygium jambos...
from one or more carpels in the family MaloideaeMaloideaeThe Maloideae C.Weber are the apple subfamily, a grouping used by some taxonomists within the rose family, Rosaceae. Recent molecular phylogenetic evidence has shown that the traditional Spiraeoideae and Amygdaloideae form part of the same clade as the traditional Maloideae, and the correct name... - Utricle – a small inflated fruit with one seed that has thin walls,
Pteridophyte sporangiumSporangiumA sporangium is an enclosure in which spores are formed. It can be composed of a single cell or can be multicellular. All plants, fungi, and many other lineages form sporangia at some point in their life cycle...
terms
- Acrostichoid sorus – having several fused sori.
- Annulus – outer part of sporangium
- Elater –
- Indusium –
- Marginal –
- Peltate –
- Reniform –
- Sporophyll –
- Sorus / Sori –
- Strobilus –
- Submarginal –
Bryophyte gametangium terms
- Acrandrous – used for moss species that have antheridia at the top of the stem.
- Acrocarpous – In mosses, bearing the sporophyte at the axix of the main shoot
- Acrogynous – In liverworts, the female sex organs terminate the main shoot
- Anacrogynous – In liverworts, female sex organs are produced by a lateral cell, thus the growth of the main shoot is indeterminate
- Androcyte –
- Androecium –
- Androgynous – Monoicous, and producing both types of sex organs together.
- Antheridiophore – A specialised branch that bears the antheridia in the Marchantiales
- Antherozoid –
- Archegoniophore – A specialised branch that bears the archaegonia in the Marchantiales
- Autoicous – Produces male and female sex organs on the same plant but on separate inflorescences
- Bract –
- Cladautoicous – Male and female inflorescences on separate branches of the same plant
- Dioicous – Having two forms of gametophyte, one form bearing antheridia and one form bearing archegonia.
- Gonioautoicous – Male is bud-like in the axil of a female branch
- Inflorescence –
- Involucre – A tube of thallus tissue that protects the archegonia
- Monoicous – Having a single form of gametophyte bearing both antheridia and archegonia, either together or on separate branches.
- Paraphyses – Sterile hairs surrounding the archegonia and antheridia
- Perianth – A protective tube that surrounds the archegonia, characterises the Jungermannialean liverworts
- Perichaetium – The cluster of leaves with the enclosed female sex organs
- Perigonium – The cluster of leaves with the enclosed male sex organs
- Pseudautoicous – Dwarf male plants growing on living leaves of female plants
- Pseudomonoicous –
- Pseudoperianth – An involucre that resembles a perianth, but is made of thallus tissue, and usually forms after the sporophyte develops
- Rhizautoicous – Male inflorescence attached to the female stem by rhizoids
- Synoicous – Male and female sex organs on the same gametophyte but are not clustered
Bryophyte sporangiumSporangiumA sporangium is an enclosure in which spores are formed. It can be composed of a single cell or can be multicellular. All plants, fungi, and many other lineages form sporangia at some point in their life cycle...
terms
- Amphithecium – The external cell layers of the developing sporangium of a bryophyte. (Note: this term is also used in the mycology of lichens.)
- Anisosporous – Anisospore production is a rare condition in dioecious bryophytes; meiosis produces two small spores that develop into male gametophytes and two larger spores that develop into female gametophytes; contrast Isosporous.
- Annulus – in mosses, cells with thick walls along the rim of the sporangium and were the peristome teeth are attached.
- Apophysis –
- Archesporium –
- Arthrodontous –
- Articulate –
- Astomous –
- Basal membrane –
- Calyptra –
- Capsule –
- Cleistocarpous –
- Columella –
- Dehisce –
- Diplolepidous –
- Divisural line –
- Elater – structures derived from the sporangium of liverwortLiverwortLiverwort may refer to either*Marchantiophyta, a division of non-vascular plants*Hepatica, a genus of spring flowersliverworts are part of the bryophytes group and the bryophytes of the PlantaeIn the bryophytres group their are mosses too....
s that aid in spore dispersal - Endostome –
- Endothecium –
- Epiphragm –
- Exostome –
- Exothecium –
- Foot –
- Gymnostomous –
- Haplolepidous –
- Haustorium –
- Hypophysis –
- Immersed –
- Indehiscent –
- Inoperculate –
- Isosporous – unlike anisosporous species, whether monoecious or dioecious, all spores are the same size.
- Nematodontous –
- Nurse cells –
- Operculate –
- Operculum –
- Oral –
- Peristome –
- Pseudoelater – structures derived from the sporangium of hornwortHornwortHornworts are a group of bryophytes, or non-vascular plants, comprising the division Anthocerotophyta. The common name refers to the elongated horn-like structure, which is the sporophyte. The flattened, green plant body of a hornwort is the gametophyte plant.Hornworts may be found worldwide,...
s that aid in spore dispersal - Seta –
- Stegocarpous –
- Stoma –
- Suboral –
- Tapetum –
- Trabecula –
- Valve –

