
Leukopenia
Encyclopedia
Leukopenia is a decrease in the number of white blood cell
s (leukocytes) found in the blood
, which places individuals at increased risk of infection
.
Neutropenia
is a sub-type of leukopenia that refers to a decrease in the number of circulating neutrophil granulocyte
s, the most abundant white blood cells. The terms leukopenia and neutropenia may occasionally be used interchangeably, as the neutrophil count is the most important indicator of infection risk.
, radiation therapy
, myelofibrosis
and aplastic anemia
(failure of white and red cell creation, along with poor platelet production). In addition, many common medication
s can cause leukopenia (see below). HIV
and AIDS
are also a threat to white cells.
Other causes of low white blood cell count include: Influenza
, systemic lupus erythematosus
, Hodgkin's lymphoma
, some types of cancer
, typhoid, malaria
, tuberculosis
, dengue, Rickettsial infections
, enlargement of the spleen
, folate deficiencies, psittacosis
and sepsis
. Many other causes exist, such as a deficiency in certain minerals such as copper
and zinc
.
Pseudoleukopenia can develop upon the onset of infection. The leukocytes (predominately neutrophils, responding to injury first) are marginalized in the blood vessels so that they can scan for the site of infection. This means that even though there is increased WBC production, it will appear as though it is low from a blood sample, since the blood sample is of core blood and does not include the marginalized leukocytes.
, an antipsychotic
medication with a rare adverse effect leading to the total absence of all granulocytes (neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils). Other medications include immunosuppressive
drugs, such as sirolimus
, mycophenolate mofetil
, tacrolimus
, and cyclosporine. Interferons used to treat multiple sclerosis
, like Rebif, Avonex, and Betaseron, can also cause leukopenia. The antidepressant and smoking addiction treatment drug Wellbutrin (Bupropion HCL) can also cause leukopenia with long-term use. Minocycline, a commonly prescribed antibiotic, is another drug known to cause leukopenia.
There are also reports of leukopenia caused by Depakote (divalproex sodium or valproic acid), a drug used for epilepsy (seizures), mania (with bipolar disorder) and migraine. Decreased white blood cell count (leukopenia) may be present in cases of arsenic
toxicity.
The anticonvulsant
drug, Lamotrigine
, has been associated with a decrease in white blood cell count.
.
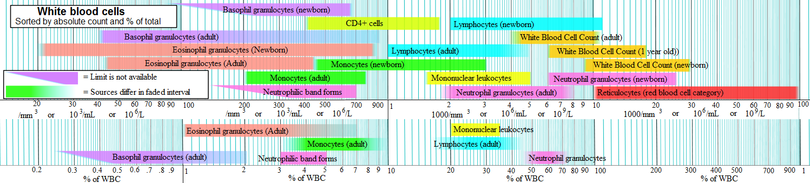
Below are blood reference ranges for various types leucocytes/WBCs. The 2.5 percentile (right limits in intervals in image, showing 95% prediction interval
s) is a common limit for defining leukocytosis
.
White blood cell
White blood cells, or leukocytes , are cells of the immune system involved in defending the body against both infectious disease and foreign materials. Five different and diverse types of leukocytes exist, but they are all produced and derived from a multipotent cell in the bone marrow known as a...
s (leukocytes) found in the blood
Blood
Blood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells....
, which places individuals at increased risk of infection
Infection
An infection is the colonization of a host organism by parasite species. Infecting parasites seek to use the host's resources to reproduce, often resulting in disease...
.
Neutropenia
Neutropenia
Neutropenia, from Latin prefix neutro- and Greek suffix -πενία , is a granulocyte disorder characterized by an abnormally low number of neutrophils, the most important type of white blood cell...
is a sub-type of leukopenia that refers to a decrease in the number of circulating neutrophil granulocyte
Neutrophil granulocyte
Neutrophil granulocytes are the most abundant type of white blood cells in mammals and form an essential part of the innate immune system. They are generally referred to as either neutrophils or polymorphonuclear neutrophils , and are subdivided into segmented neutrophils and banded neutrophils...
s, the most abundant white blood cells. The terms leukopenia and neutropenia may occasionally be used interchangeably, as the neutrophil count is the most important indicator of infection risk.
Causes
Low white cell counts may be due to a recent infection such as a cold/flu. It can also be associated with chemotherapyChemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the treatment of cancer with an antineoplastic drug or with a combination of such drugs into a standardized treatment regimen....
, radiation therapy
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy , radiation oncology, or radiotherapy , sometimes abbreviated to XRT or DXT, is the medical use of ionizing radiation, generally as part of cancer treatment to control malignant cells.Radiation therapy is commonly applied to the cancerous tumor because of its ability to control...
, myelofibrosis
Myelofibrosis
Myelofibrosis, also known as myeloid metaplasia, chronic idiopathic myelofibrosis, osteomyelofibrosis and primary myelofibrosis is a disorder of the bone marrow...
and aplastic anemia
Aplastic anemia
Aplastic anemia is a condition where bone marrow does not produce sufficient new cells to replenish blood cells. The condition, per its name, involves both aplasia and anemia...
(failure of white and red cell creation, along with poor platelet production). In addition, many common medication
Medication
A pharmaceutical drug, also referred to as medicine, medication or medicament, can be loosely defined as any chemical substance intended for use in the medical diagnosis, cure, treatment, or prevention of disease.- Classification :...
s can cause leukopenia (see below). HIV
HIV
Human immunodeficiency virus is a lentivirus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome , a condition in humans in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive...
and AIDS
AIDS
Acquired immune deficiency syndrome or acquired immunodeficiency syndrome is a disease of the human immune system caused by the human immunodeficiency virus...
are also a threat to white cells.
Other causes of low white blood cell count include: Influenza
Influenza
Influenza, commonly referred to as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by RNA viruses of the family Orthomyxoviridae , that affects birds and mammals...
, systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus , often abbreviated to SLE or lupus, is a systemic autoimmune disease that can affect any part of the body. As occurs in other autoimmune diseases, the immune system attacks the body's cells and tissue, resulting in inflammation and tissue damage...
, Hodgkin's lymphoma
Hodgkin's lymphoma
Hodgkin's lymphoma, previously known as Hodgkin's disease, is a type of lymphoma, which is a cancer originating from white blood cells called lymphocytes...
, some types of cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
, typhoid, malaria
Malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease of humans and other animals caused by eukaryotic protists of the genus Plasmodium. The disease results from the multiplication of Plasmodium parasites within red blood cells, causing symptoms that typically include fever and headache, in severe cases...
, tuberculosis
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis, MTB, or TB is a common, and in many cases lethal, infectious disease caused by various strains of mycobacteria, usually Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis usually attacks the lungs but can also affect other parts of the body...
, dengue, Rickettsial infections
Rickettsia
Rickettsia is a genus of non-motile, Gram-negative, non-sporeforming, highly pleomorphic bacteria that can present as cocci , rods or thread-like . Being obligate intracellular parasites, the Rickettsia survival depends on entry, growth, and replication within the cytoplasm of eukaryotic host cells...
, enlargement of the spleen
Spleen
The spleen is an organ found in virtually all vertebrate animals with important roles in regard to red blood cells and the immune system. In humans, it is located in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen. It removes old red blood cells and holds a reserve of blood in case of hemorrhagic shock...
, folate deficiencies, psittacosis
Psittacosis
In medicine , psittacosis — also known as parrot disease, parrot fever, and ornithosis — is a zoonotic infectious disease caused by a bacterium called Chlamydophila psittaci and contracted from parrots, such as macaws, cockatiels and budgerigars, and pigeons, sparrows, ducks, hens, gulls and many...
and sepsis
Sepsis
Sepsis is a potentially deadly medical condition that is characterized by a whole-body inflammatory state and the presence of a known or suspected infection. The body may develop this inflammatory response by the immune system to microbes in the blood, urine, lungs, skin, or other tissues...
. Many other causes exist, such as a deficiency in certain minerals such as copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
and zinc
Zinc
Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2...
.
Pseudoleukopenia can develop upon the onset of infection. The leukocytes (predominately neutrophils, responding to injury first) are marginalized in the blood vessels so that they can scan for the site of infection. This means that even though there is increased WBC production, it will appear as though it is low from a blood sample, since the blood sample is of core blood and does not include the marginalized leukocytes.
Medications causing leukopenia
Some medications can have an impact on the number and function of white blood cells. Medications which can cause leukopenia include clozapineClozapine
Clozapine is an antipsychotic medication used in the treatment of schizophrenia, and is also used off-label in the treatment of bipolar disorder. Wyatt. R and Chew...
, an antipsychotic
Antipsychotic
An antipsychotic is a tranquilizing psychiatric medication primarily used to manage psychosis , particularly in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. A first generation of antipsychotics, known as typical antipsychotics, was discovered in the 1950s...
medication with a rare adverse effect leading to the total absence of all granulocytes (neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils). Other medications include immunosuppressive
Immunosuppression
Immunosuppression involves an act that reduces the activation or efficacy of the immune system. Some portions of the immune system itself have immuno-suppressive effects on other parts of the immune system, and immunosuppression may occur as an adverse reaction to treatment of other...
drugs, such as sirolimus
Sirolimus
Sirolimus , also known as rapamycin, is an immunosuppressant drug used to prevent rejection in organ transplantation; it is especially useful in kidney transplants. A macrolide, sirolimus was first discovered as a product of the bacterium Streptomyces hygroscopicus in a soil sample from Easter...
, mycophenolate mofetil
Mycophenolate mofetil
Mycophenolate mofetil is an immunosuppressant and prodrug of mycophenolic acid, used extensively in transplant medicine. It is a reversible inhibitor of inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase in purine biosynthesis, which is necessary for the growth of T cells and B cells...
, tacrolimus
Tacrolimus
Tacrolimus is an immunosuppressive drug that is mainly used after allogeneic organ transplant to reduce the activity of the patient's immune system and so lower the risk of organ rejection...
, and cyclosporine. Interferons used to treat multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis is an inflammatory disease in which the fatty myelin sheaths around the axons of the brain and spinal cord are damaged, leading to demyelination and scarring as well as a broad spectrum of signs and symptoms...
, like Rebif, Avonex, and Betaseron, can also cause leukopenia. The antidepressant and smoking addiction treatment drug Wellbutrin (Bupropion HCL) can also cause leukopenia with long-term use. Minocycline, a commonly prescribed antibiotic, is another drug known to cause leukopenia.
There are also reports of leukopenia caused by Depakote (divalproex sodium or valproic acid), a drug used for epilepsy (seizures), mania (with bipolar disorder) and migraine. Decreased white blood cell count (leukopenia) may be present in cases of arsenic
Arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As, atomic number 33 and relative atomic mass 74.92. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in conjunction with sulfur and metals, and also as a pure elemental crystal. It was first documented by Albertus Magnus in 1250.Arsenic is a metalloid...
toxicity.
The anticonvulsant
Anticonvulsant
The anticonvulsants are a diverse group of pharmaceuticals used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of bipolar disorder, since many seem to act as mood stabilizers, and in the treatment of neuropathic pain. The goal of an...
drug, Lamotrigine
Lamotrigine
Lamotrigine, marketed in the US and most of Europe as Lamictal by GlaxoSmithKline, is an anticonvulsant drug used in the treatment of epilepsy and bipolar disorder. It is also used as an adjunct in treating depression, though this is considered off-label usage...
, has been associated with a decrease in white blood cell count.
Diagnosis
Leukopenia can be identified with a complete blood countComplete blood count
A complete blood count , also known as full blood count or full blood exam or blood panel, is a test panel requested by a doctor or other medical professional that gives information about the cells in a patient's blood...
.
Below are blood reference ranges for various types leucocytes/WBCs. The 2.5 percentile (right limits in intervals in image, showing 95% prediction interval
Prediction interval
In statistical inference, specifically predictive inference, a prediction interval is an estimate of an interval in which future observations will fall, with a certain probability, given what has already been observed...
s) is a common limit for defining leukocytosis
Leukocytosis
Leukocytosis is a raised white blood cell count above the normal range in the blood. It is frequently a sign of an inflammatory response, most commonly the result of infection, and is observed in certain parasitic infections...
.

External links
- http://doublecheckmd.com/EffectsDetail.do?dname=buPROPion&sid=12112&eid=2237#relse

