
Leukocytosis
Encyclopedia
Leukocytosis is a raised white blood cell count (the leukocyte count) above the normal range in the blood. It is frequently a sign of an inflammatory response, most commonly the result of infection, and is observed in certain parasitic infections. It may also occur after strenuous exercise, convulsions such as epilepsy, emotional stress, pregnancy and labour, anesthesia, and epiniephrine administration.
There are five principle types of leukocytosis:
Acute exercise is one of the healthiest ways to create leukocytosis within hours. This increase in leukocytes (primarily neutrophils) is usually accompanied by a "left shift" in the ratio of immature to mature neutrophils. The increase in immature leukocytes increases due to proliferation and release of granulocyte and monocyte precursors in the bone marrow which is stimulated by several products of inflammation including C3a and G-CSF.
Although it may indicate illness, leukocytosis is considered a laboratory finding instead of a separate disease
. This classification is similar to that of fever
, which is also a test result instead of a disease.
"Right shift" in the ratio of immature to mature neutrophils is considered with reduced count or lack of "young neutrophils" (metamyelocytes, and band
neutrophils) in blood smear, associated with the presence of "giant neutrophils". This fact shows suppression of bone marrow activity, as a hematological sign specific for pernicious anemia
and radiation sickness
.
A leukocyte count above 25 to 30 x 109/L
is termed a leukemoid reaction
, which is the reaction of a healthy bone marrow to extreme stress, trauma, or infection. It is different from leukemia
and from leukoerythroblastosis, in which either immature white blood cells (acute leukemia) or mature, yet non-functional, white blood cells (chronic leukemia) are present in peripheral blood.
s) is a common limit for defining leukocytosis.
; leukocytosis in which lymphocyte
count is elevated is lymphocytosis
; leukocytosis in which monocyte
count is elevated is monocytosis
; and leukocytosis in which eosinophil count is elevated is eosinophilia
.
Leukocytosis is very common in acutely ill patients. It occurs in response to a wide variety of conditions, including viral, bacterial, fungal, or parasitic infection, cancer, hemorrhage, and exposure to certain medications or chemicals including steroids.
For lung diseases such as pneumonia and tuberculosis, WBC count is very important for the diagnosis of the disease, as leukocytosis is usually present.
The mechanism that causes leukocytosis can be of several forms: an increased release of leukocytes from bone marrow
storage pools, decreased margination of leukocytes onto vessel walls, decreased extravasation
of leukocytes from the vessels into tissues, or an increase in number of precursor cells in the marrow.
Certain medications, including corticosteroid
s, lithium
and beta agonists, may cause leukocytosis.
There are five principle types of leukocytosis:
- NeutrophiliaNeutrophiliaNeutrophilia is a condition where a person has a high number of neutrophil granulocytes in their blood.-Causes:...
(the most common form) - LymphocytosisLymphocytosisLymphocytosis is an increase in the number or proportion of lymphocytes in the blood, usually detected when a complete blood count is routinely obtained. Lymphocytes normally represent 20 to 40% of circulating white blood cells...
- MonocytosisMonocytosisMonocytosis is an increase in the number of monocytes circulating in the blood. Monocytes are white blood cells that give rise to macrophages and dendritic cells in the immune system....
- BasophiliaBasophiliaBasophilia is a condition where the basophil quantity is abnormally elevated .-Causes:Basophilia as an isolated finding is uncommon. However it is a common feature of myeloproliferative disorders and particularly prominent in chronic myelogenous leukemia....
- EosinophiliaEosinophiliaEosinophilia is a condition in which the eosinophil count in the peripheral blood exceeds 0.45×109/L . A marked increase in non-blood tissue eosinophil count noticed upon histopathologic examination is diagnostic for tissue eosinophilia. Several causes are known, with the most common being...
Acute exercise is one of the healthiest ways to create leukocytosis within hours. This increase in leukocytes (primarily neutrophils) is usually accompanied by a "left shift" in the ratio of immature to mature neutrophils. The increase in immature leukocytes increases due to proliferation and release of granulocyte and monocyte precursors in the bone marrow which is stimulated by several products of inflammation including C3a and G-CSF.
Although it may indicate illness, leukocytosis is considered a laboratory finding instead of a separate disease
Disease
A disease is an abnormal condition affecting the body of an organism. It is often construed to be a medical condition associated with specific symptoms and signs. It may be caused by external factors, such as infectious disease, or it may be caused by internal dysfunctions, such as autoimmune...
. This classification is similar to that of fever
Fever
Fever is a common medical sign characterized by an elevation of temperature above the normal range of due to an increase in the body temperature regulatory set-point. This increase in set-point triggers increased muscle tone and shivering.As a person's temperature increases, there is, in...
, which is also a test result instead of a disease.
"Right shift" in the ratio of immature to mature neutrophils is considered with reduced count or lack of "young neutrophils" (metamyelocytes, and band
Band
- Clothing, jewelry, and accessories :* Bands , two pieces of cloth fitted around the neck as part of formal clothing for clergy, academics and lawyers* Bandolier or bandoleer, an ammunition belt* Belt * Wedding ring or wedding band...
neutrophils) in blood smear, associated with the presence of "giant neutrophils". This fact shows suppression of bone marrow activity, as a hematological sign specific for pernicious anemia
Pernicious anemia
Pernicious anemia is one of many types of the larger family of megaloblastic anemias...
and radiation sickness
Radiation Sickness
Radiation Sickness is a VHS by the thrash metal band Nuclear Assault. The video is a recording of a concert at the Hammersmith Odeon, London in 1988. It was released in 1991...
.
A leukocyte count above 25 to 30 x 109/L
Litre
pic|200px|right|thumb|One litre is equivalent to this cubeEach side is 10 cm1 litre water = 1 kilogram water The litre is a metric system unit of volume equal to 1 cubic decimetre , to 1,000 cubic centimetres , and to 1/1,000 cubic metre...
is termed a leukemoid reaction
Leukemoid reaction
The term leukemoid reaction describes an elevated white blood cell count, or leukocytosis, that is a physiological response to stress or infection .It may be lymphoid or myeloid....
, which is the reaction of a healthy bone marrow to extreme stress, trauma, or infection. It is different from leukemia
Leukemia
Leukemia or leukaemia is a type of cancer of the blood or bone marrow characterized by an abnormal increase of immature white blood cells called "blasts". Leukemia is a broad term covering a spectrum of diseases...
and from leukoerythroblastosis, in which either immature white blood cells (acute leukemia) or mature, yet non-functional, white blood cells (chronic leukemia) are present in peripheral blood.
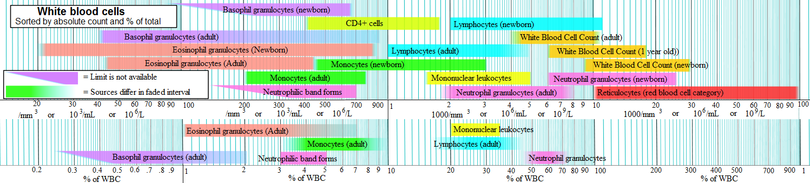
Leukocyte counts
Below are blood reference ranges for various types leucocytes/WBCs. The 97.5 percentile (right limits in intervals in image, showing 95% prediction intervalPrediction interval
In statistical inference, specifically predictive inference, a prediction interval is an estimate of an interval in which future observations will fall, with a certain probability, given what has already been observed...
s) is a common limit for defining leukocytosis.

Classification
Leukocytosis can be subcategorized by the type of white blood cell that is increased in number. Leukocytosis in which neutrophils are elevated is neutrophiliaNeutrophilia
Neutrophilia is a condition where a person has a high number of neutrophil granulocytes in their blood.-Causes:...
; leukocytosis in which lymphocyte
Lymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell in the vertebrate immune system.Under the microscope, lymphocytes can be divided into large lymphocytes and small lymphocytes. Large granular lymphocytes include natural killer cells...
count is elevated is lymphocytosis
Lymphocytosis
Lymphocytosis is an increase in the number or proportion of lymphocytes in the blood, usually detected when a complete blood count is routinely obtained. Lymphocytes normally represent 20 to 40% of circulating white blood cells...
; leukocytosis in which monocyte
Monocyte
Monocytes are a type of white blood cell and are part of the innate immune system of vertebrates including all mammals , birds, reptiles, and fish. Monocytes play multiple roles in immune function...
count is elevated is monocytosis
Monocytosis
Monocytosis is an increase in the number of monocytes circulating in the blood. Monocytes are white blood cells that give rise to macrophages and dendritic cells in the immune system....
; and leukocytosis in which eosinophil count is elevated is eosinophilia
Eosinophilia
Eosinophilia is a condition in which the eosinophil count in the peripheral blood exceeds 0.45×109/L . A marked increase in non-blood tissue eosinophil count noticed upon histopathologic examination is diagnostic for tissue eosinophilia. Several causes are known, with the most common being...
.
Causes
| Causes of leukocytosis | |
|---|---|
| Neutrophilic leukocytosis (neutrophilia Neutrophilia Neutrophilia is a condition where a person has a high number of neutrophil granulocytes in their blood.-Causes:... ) |
|
| Eosinophilic leukocytosis (eosinophilia Eosinophilia Eosinophilia is a condition in which the eosinophil count in the peripheral blood exceeds 0.45×109/L . A marked increase in non-blood tissue eosinophil count noticed upon histopathologic examination is diagnostic for tissue eosinophilia. Several causes are known, with the most common being... ) |
Allergy An Allergy is a hypersensitivity disorder of the immune system. Allergic reactions occur when a person's immune system reacts to normally harmless substances in the environment. A substance that causes a reaction is called an allergen. These reactions are acquired, predictable, and rapid... disorders
Systemic lupus erythematosus Systemic lupus erythematosus , often abbreviated to SLE or lupus, is a systemic autoimmune disease that can affect any part of the body. As occurs in other autoimmune diseases, the immune system attacks the body's cells and tissue, resulting in inflammation and tissue damage... ) Vasculitis Vasculitis refers to a heterogeneous group of disorders that are characterized by inflammatory destruction of blood vessels. Both arteries and veins are affected. Lymphangitis is sometimes considered a type of vasculitis... Cholesterol embolism Cholesterol embolism occurs when cholesterol is released, usually from an atherosclerotic plaque, and travels along with the bloodsteam to other places in the body, where it obstructs blood vessels... (transiently) |
| Basophilic leukocytosis Basophilia Basophilia Basophilia is a condition where the basophil quantity is abnormally elevated .-Causes:Basophilia as an isolated finding is uncommon. However it is a common feature of myeloproliferative disorders and particularly prominent in chronic myelogenous leukemia.... |
(rare)
Myeloproliferative disease The myeloproliferative diseases are a group of diseases of the bone marrow in which excess cells are produced. They are related to, and may evolve into, myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia, although the myeloproliferative diseases on the whole have a much better prognosis than... , e.g. Chronic myelogenous leukemia Chronic myelogenous leukemia Chronic myelogenous leukemia , also known as chronic granulocytic leukemia , is a cancer of the white blood cells. It is a form of leukemia characterized by the increased and unregulated growth of predominantly myeloid cells in the bone marrow and the accumulation of these cells in the blood... |
| Monocytosis Monocytosis Monocytosis is an increase in the number of monocytes circulating in the blood. Monocytes are white blood cells that give rise to macrophages and dendritic cells in the immune system.... |
Systemic lupus erythematosus Systemic lupus erythematosus , often abbreviated to SLE or lupus, is a systemic autoimmune disease that can affect any part of the body. As occurs in other autoimmune diseases, the immune system attacks the body's cells and tissue, resulting in inflammation and tissue damage... Inflammatory bowel disease In medicine, inflammatory bowel disease is a group of inflammatory conditions of the colon and small intestine. The major types of IBD are Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.-Classification:... s, e.g. ulcerative colitis Ulcerative colitis Ulcerative colitis is a form of inflammatory bowel disease . Ulcerative colitis is a form of colitis, a disease of the colon , that includes characteristic ulcers, or open sores. The main symptom of active disease is usually constant diarrhea mixed with blood, of gradual onset... |
| Lymphocytosis Lymphocytosis Lymphocytosis is an increase in the number or proportion of lymphocytes in the blood, usually detected when a complete blood count is routinely obtained. Lymphocytes normally represent 20 to 40% of circulating white blood cells... |
Pertussis Pertussis, also known as whooping cough , is a highly contagious bacterial disease caused by Bordetella pertussis. Symptoms are initially mild, and then develop into severe coughing fits, which produce the namesake high-pitched "whoop" sound in infected babies and children when they inhale air... |
Leukocytosis is very common in acutely ill patients. It occurs in response to a wide variety of conditions, including viral, bacterial, fungal, or parasitic infection, cancer, hemorrhage, and exposure to certain medications or chemicals including steroids.
For lung diseases such as pneumonia and tuberculosis, WBC count is very important for the diagnosis of the disease, as leukocytosis is usually present.
The mechanism that causes leukocytosis can be of several forms: an increased release of leukocytes from bone marrow
Bone marrow
Bone marrow is the flexible tissue found in the interior of bones. In humans, bone marrow in large bones produces new blood cells. On average, bone marrow constitutes 4% of the total body mass of humans; in adults weighing 65 kg , bone marrow accounts for approximately 2.6 kg...
storage pools, decreased margination of leukocytes onto vessel walls, decreased extravasation
Leukocyte extravasation
Leukocyte extravasation is the movement of leukocytes out of the circulatory system, towards the site of tissue damage or infection. This process forms part of the innate immune response, involving the recruitment of non-specific leukocytes...
of leukocytes from the vessels into tissues, or an increase in number of precursor cells in the marrow.
Certain medications, including corticosteroid
Corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex. Corticosteroids are involved in a wide range of physiologic systems such as stress response, immune response and regulation of inflammation, carbohydrate metabolism, protein catabolism, blood electrolyte...
s, lithium
Lithium pharmacology
Lithium pharmacology refers to use of the lithium ion, Li+, as a drug. A number of chemical salts of lithium are used medically as a mood stabilizing drug, primarily in the treatment of bipolar disorder, where they have a role in the treatment of depression and particularly of mania, both acutely...
and beta agonists, may cause leukocytosis.
See also
- Bacterial infection
- Complete blood countComplete blood countA complete blood count , also known as full blood count or full blood exam or blood panel, is a test panel requested by a doctor or other medical professional that gives information about the cells in a patient's blood...
- Leukocytosis in head traumaLeukocytosis in head traumaPatients who sustained head injury of different degree may have leukocytosis which is predictive of the severity of injury. Several researchers demonstrated that degree of leukocytosis correlates with severity of head trauma, and WBC of 22 correlates with severe head injury, 17- moderate and 12-...
- White blood cellWhite blood cellWhite blood cells, or leukocytes , are cells of the immune system involved in defending the body against both infectious disease and foreign materials. Five different and diverse types of leukocytes exist, but they are all produced and derived from a multipotent cell in the bone marrow known as a...

