Industrial Revolution in China
Encyclopedia
In the 1960s, about 60% of the Chinese labor force were employed in agriculture. The figure remained more or less constant throughout the early phase of industrialization between the 1960s and 1990s, but in view of the rapid population growth this amounted to a rapid growth of the industrial sector in absolute terms, of up to 8% per year during the 1970s. By 1990, the fraction of the labor force employed in agriculture had fallen to about 30%, and by 2000 still further.
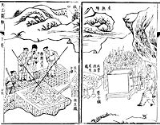
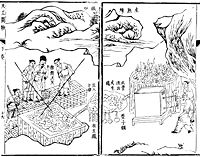
saw intensive industry in steel production, and coal mining.
 Western historians debate whether bloomin'-based ironworking ever spread to China from the Middle East. Around 500 BC, however, metalworkers in the southern state of Wu developed an iron smelting technology that would not be practiced in Europe until late medieval times. In Wu, iron smelters achieved a temperature of 1130°C, hot enough to be considered a blast furnace
Western historians debate whether bloomin'-based ironworking ever spread to China from the Middle East. Around 500 BC, however, metalworkers in the southern state of Wu developed an iron smelting technology that would not be practiced in Europe until late medieval times. In Wu, iron smelters achieved a temperature of 1130°C, hot enough to be considered a blast furnace
which could create cast iron. At this temperature, iron combines with 4.3% carbon and melts. As a liquid, iron can be cast
into molds
, a method far less laborious than individually forging each piece of iron from a bloom.
Cast iron is rather brittle and unsuitable for striking implements. It can, however, be decarburized to steel or wrought iron by heating it in air for several days. In China, these ironworking methods spread northward, and by 300 BC
, iron was the material of choice throughout China for most tools and weapons. A mass grave in Hebei
province, dated to the early third century BC, contains several soldiers buried with their weapons and other equipment. The artifacts recovered from this grave are variously made of wrought iron, cast iron, malleabilized cast iron, and quench-hardened steel, with only a few, probably ornamental, bronze weapons.
 During the Han Dynasty
During the Han Dynasty
(202 BC
–AD 220
), the government established ironworking as a state monopoly (yet repealed during the latter half of the dynasty, returned to private entrepreneurship) and built a series of large blast furnaces in Henan
province, each capable of producing several tons of iron per day. By this time, Chinese metallurgists had discovered how to puddle molten pig iron, stirring it in the open air until it lost its carbon and became wrought iron. (In Chinese
, the process was called chao, literally, stir frying
.) By the 1st century BC, Chinese metallurgists had found that wrought iron and cast iron could be melted together to yield an alloy of intermediate carbon content, that is, steel
. According to legend, the sword of Liu Bang, the first Han emperor, was made in this fashion. Some texts of the era mention "harmonizing the hard and the soft" in the context of ironworking; the phrase may refer to this process. Also, the ancient city of Wan (Nanyang
) from the Han period forward was a major center of the iron and steel industry. Along with their original methods of forging steel, the Chinese had also adopted the production methods of creating Wootz steel
, an idea imported from India
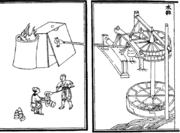
to China by the 5th century AD. The Chinese during the ancient Han Dynasty were also the first to apply hydraulic power (i.e. a waterwheel) in working the inflatable bellows of the blast furnace. This was recorded in the year 31 AD, an innovation of the engineer
Du Shi
, Prefect
of Nanyang
. Although Du Shi was the first to apply water power to bellows in metallurgy, the first drawn and printed illustration of its operation with water power came in 1313 AD, in the Yuan Dynasty
era text called the Nong Shu. In the 11th century, there is evidence of the production of steel in Song China
using two techniques: a "berganesque" method that produced inferior, heterogeneous steel and a precursor to the modern Bessemer process that utilized partial decarbonization via repeated forging under a cold blast. By the 11th century, there was also a large amount of deforestation in China due to the iron industry's demands for charcoal
. However, by this time the Chinese had figured out how to use bituminous coke
to replace the use of charcoal, and with this switch in resources many acres of prime timberland in China were spared. This switch in resources from charcoal to coal
was later used in Europe by the 17th century.
The economy of the Song Dynasty was one of the most prosperous and advanced economies in the medieval world. Song Chinese invested their funds in joint stock companies
and in multiple sailing vessels at a time when monetary gain was assured from the vigorous overseas trade and indigenous trade along the Grand Canal and Yangzi River. Prominent merchant families and private businesses were allowed to occupy industries that were not already government-operated monopolies
. Both private and government-controlled industries met the needs of a growing Chinese population in the Song. Both artisans and merchants formed guild
s which the state had to deal with when assessing taxes, requisitioning goods, and setting standard worker's wages and prices on goods.
The iron industry was pursued by both private entrepreneur
s who owned their own smelters as well as government-supervised smelting facilities. The Song economy was stable enough to produce over a hundred million kg (over two hundred million lb) of iron
product a year. Large scale deforestation
in China would have continued if not for the 11th century innovation of the use of coal
instead of charcoal
in blast furnace
s for smelting cast iron
. Much of this iron was reserved for military use in crafting weapons and armoring troops, but some was used to fashion the many iron products needed to fill the demands of the growing indigenous market. The iron trade within China was furthered by the building of new canal
s which aided the flow of iron products from production centers to the large market found in the capital city.
 The annual output of minted copper currency in 1085 alone reached roughly six billion coins. The most notable advancement in the Song economy was the establishment of the world's first government issued paper-printed money, known as Jiaozi
The annual output of minted copper currency in 1085 alone reached roughly six billion coins. The most notable advancement in the Song economy was the establishment of the world's first government issued paper-printed money, known as Jiaozi
(see also Huizi
). For the printing of paper money
alone, the Song court established several government-run factories in the cities of Huizhou
, Chengdu
, Hangzhou
, and Anqi. The size of the workforce employed in paper money factories was large; it was recorded in 1175 that the factory at Hangzhou employed more than a thousand workers a day.
The economic power of Song China heavily influenced foreign economies abroad. The Moroccan
geographer
al-Idrisi wrote in 1154 of the prowess of Chinese merchant ships in the Indian Ocean and of their annual voyages that brought iron, swords, silk, velvet, porcelain, and various textiles to places such as Aden
(Yemen
), the Indus River
, and the Euphrates
in modern-day Iraq. Foreigners, in turn, had an impact on the Chinese economy. For example, many West Asian and Central Asian Muslim
s went to China
to trade, becoming a preeminent force in the import and export industry, while some were even appointed as officers supervising economic affairs. Sea trade with the Southeast Pacific, the Hindu world, the Islamic world, and the East African world brought merchants great fortune and spurred an enormous growth in the shipbuilding
industry of Song-era Fujian
province. However, there was risk involved in such long overseas ventures. To reduce the risk of losing money on maritime trade missions abroad, the historians Ebrey, Walthall, and Palais write:
and Max Weber
credit the different belief systems in China and Europe with dictating where the revolution occurred. The religion and beliefs of Europe were largely products of Judaeo-Christianity, Socrates
, Plato
, and Aristotle
. Conversely, Chinese society was founded on men like Confucius
, Mencius
, Han Feizi (Legalism
), Lao Tzu (Taoism
), and Buddha
(Buddhism
). The key difference between these belief systems was that those from Europe focused on the individual, while Chinese beliefs centered around relationships between people. The family unit was more important than the individual for the large majority of Chinese history, and this may have played a role in why the Industrial Revolution
took much longer to occur in China. There was the additional difference as to whether people looked backwards to a reputedly glorious past for answers to their questions or looked hopefully to the future.
has dubbed the "English school" which argues that China was not essentially different from Europe, and that many of the assertions that it was are based on bad historical evidence.
Mark Elvin
argues that China was in a high level equilibrium trap
in which the non-industrial methods were efficient enough to prevent use of industrial methods with high initial capital. Kenneth Pomeranz
, in the Great Divergence, argues that Europe and China were remarkably similar in 1700, and that the crucial differences which created the Industrial Revolution in Europe were sources of coal
near manufacturing centers, and raw materials such as food and wood from the New World
, which allowed Europe to expand economically in a way that China could not.
Some have compared England directly to China, but the comparison between England and China has been viewed as a faulty one, since China is so much larger than England. A more relevant comparison would be between China's Yangtze Delta region, China's most advanced region, the location of Hangzhou
, Nanjing
and contemporary Shanghai
, and England. This region of China is said to have had similar labor costs to England. Moreover, an overall look at economic data from 1750 is somewhat staggering for a person used to Eurocentric conceptions. According to Andre Gunder Frank, "Particularly significant is the comparison of Asia's 66 percent share of world population, confirmed above all by estimates for 1750, with its 80 percent share of production in the world at the same time. So, two thirds of the world's people in Asia produced four-fifths of total world output, while one-fifth of world population in Europe produced only a part of the remaining one-fifth share of world production, to which Europeans and Americans also contributed." China was clearly Asia's most advanced economy at the time and was in the middle of its 18th century boom brought on by a long period of stability under the Qing Dynasty
.
. This was the plan used from 1958 to 1961 to transform the People's Republic of China
from a primarily agrarian economy by peasant farmers into a modern communist society through the process of agriculturalization and industrialization. Mao Zedong
based this program on the Theory of Productive Forces
. It ended in catastrophe as it triggered a widespread famine that resulted in millions of deaths.
As political stability was gradually restored following the Cultural Revolution
of the late 1960s, a renewed drive for coordinated, balanced development was set in motion under the leadership of Premier Zhou Enlai
. To revive efficiency in industry, Communist Party of China committees were returned to positions of leadership over the revolutionary committees, and a campaign was carried out to return skilled and highly educated personnel to the jobs from which they had been displaced during the Cultural Revolution. Universities began to reopen, and foreign contacts were expanded. Once again the economy suffered from imbalances in the capacities of different industrial sectors and an urgent need for increased supplies of modern inputs for agriculture. In response to these problems, there was a significant increase in investment, including the signing of contracts with foreign firms for the construction of major facilities for chemical fertilizer production, steel finishing, and oil extraction and refining. The most notable of these contracts was for thirteen of the world's largest and most modern chemical fertilizer plants. During this period, industrial output grew at an average rate of 8 percent a year.
At the milestone Third Plenum of the National Party Congress's 11th Central Committee which opened on December 22, 1978, the party leaders decided to undertake a program of gradual but fundamental reform of the economic system. They concluded that the Maoist version of the centrally planned economy had failed to produce efficient economic growth and had caused China to fall far behind not only the industrialized nations of the West but also the new industrial powers of Asia
: Japan
, the Republic of Korea, Singapore
, Taiwan
, and Hong Kong
. In the late 1970s, while Japan and Hong Kong rivaled European countries in modern technology, China's citizens had to make do with barely sufficient food supplies, rationed clothing, inadequate housing, and a service sector that was inadequate and inefficient. All of these shortcomings embarrassed China internationally.
The purpose of the reform program was not to abandon communism
but to make it work better by substantially increasing the role of market mechanism
s in the system and by reducing—not eliminating—government planning and direct control. The process of reform was incremental. New measures were first introduced experimentally in a few localities and then were popularized and disseminated nationally if they proved successful. By 1987 the program had achieved remarkable results in increasing supplies of food and other consumer goods and had created a new climate of dynamism and opportunity in the economy. At the same time, however, the reforms also had created new problems and tensions, leading to intense questioning and political struggles over the program's future.
The first few years of the reform program were designated the "period of readjustment," during which key imbalances in the economy were to be corrected and a foundation was to be laid for a well-planned modernization drive. The schedule of Hua Guofeng's ten-year plan was discarded, although many of its elements were retained. The major goals of the readjustment process were to expand exports rapidly; overcome key deficiencies in transportation, communications, coal, iron, steel, building materials, and electric power; and redress the imbalance between light and heavy industry by increasing the growth rate of light industry and reducing investment in heavy industry.
In 1984, the fourteen largest coastal cities were designated as economic development zones, including Dalian
, Tianjin
, Shanghai
, and Guangzhou
, all of which were major commercial and industrial centers. These zones were to create productive exchanges between foreign firms with advanced technology and major Chinese economic networks.
Historical precursors of industrialization
In the State of Wu of China, steel was first made, preceding the Europeans by over 1,000 years. The Song dynastySong Dynasty
The Song Dynasty was a ruling dynasty in China between 960 and 1279; it succeeded the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period, and was followed by the Yuan Dynasty. It was the first government in world history to issue banknotes or paper money, and the first Chinese government to establish a...
saw intensive industry in steel production, and coal mining.

Blast furnace
A blast furnace is a type of metallurgical furnace used for smelting to produce industrial metals, generally iron.In a blast furnace, fuel and ore and flux are continuously supplied through the top of the furnace, while air is blown into the bottom of the chamber, so that the chemical reactions...
which could create cast iron. At this temperature, iron combines with 4.3% carbon and melts. As a liquid, iron can be cast
Casting
In metalworking, casting involves pouring liquid metal into a mold, which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape, and then allowing it to cool and solidify. The solidified part is also known as a casting, which is ejected or broken out of the mold to complete the process...
into molds
Molding (process)
Molding or moulding is the process of manufacturing by shaping pliable raw material using a rigid frame or model called a pattern....
, a method far less laborious than individually forging each piece of iron from a bloom.
Cast iron is rather brittle and unsuitable for striking implements. It can, however, be decarburized to steel or wrought iron by heating it in air for several days. In China, these ironworking methods spread northward, and by 300 BC
300 BC
Year 300 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Corvus and Pansa...
, iron was the material of choice throughout China for most tools and weapons. A mass grave in Hebei
Hebei
' is a province of the People's Republic of China in the North China region. Its one-character abbreviation is "" , named after Ji Province, a Han Dynasty province that included what is now southern Hebei...
province, dated to the early third century BC, contains several soldiers buried with their weapons and other equipment. The artifacts recovered from this grave are variously made of wrought iron, cast iron, malleabilized cast iron, and quench-hardened steel, with only a few, probably ornamental, bronze weapons.

Han Dynasty
The Han Dynasty was the second imperial dynasty of China, preceded by the Qin Dynasty and succeeded by the Three Kingdoms . It was founded by the rebel leader Liu Bang, known posthumously as Emperor Gaozu of Han. It was briefly interrupted by the Xin Dynasty of the former regent Wang Mang...
(202 BC
202 BC
Year 202 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Geminus and Nero...
–AD 220
220
Year 220 was a leap year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Antonius and Eutychianus...
), the government established ironworking as a state monopoly (yet repealed during the latter half of the dynasty, returned to private entrepreneurship) and built a series of large blast furnaces in Henan
Henan
Henan , is a province of the People's Republic of China, located in the central part of the country. Its one-character abbreviation is "豫" , named after Yuzhou , a Han Dynasty state that included parts of Henan...
province, each capable of producing several tons of iron per day. By this time, Chinese metallurgists had discovered how to puddle molten pig iron, stirring it in the open air until it lost its carbon and became wrought iron. (In Chinese
Chinese language
The Chinese language is a language or language family consisting of varieties which are mutually intelligible to varying degrees. Originally the indigenous languages spoken by the Han Chinese in China, it forms one of the branches of Sino-Tibetan family of languages...
, the process was called chao, literally, stir frying
Stir frying
Stir frying is an umbrella term used to describe two Chinese cooking techniques for preparing food in a wok: chǎo and bào . The term stir-fry was introduced into the English language by Buwei Yang Chao, in her book How to Cook and Eat in Chinese, to describe the chǎo technique...
.) By the 1st century BC, Chinese metallurgists had found that wrought iron and cast iron could be melted together to yield an alloy of intermediate carbon content, that is, steel
Steel
Steel is an alloy that consists mostly of iron and has a carbon content between 0.2% and 2.1% by weight, depending on the grade. Carbon is the most common alloying material for iron, but various other alloying elements are used, such as manganese, chromium, vanadium, and tungsten...
. According to legend, the sword of Liu Bang, the first Han emperor, was made in this fashion. Some texts of the era mention "harmonizing the hard and the soft" in the context of ironworking; the phrase may refer to this process. Also, the ancient city of Wan (Nanyang
Nanyang
Nanyang may refer to:* Nanyang is a Chinese term denoting the greater Nusantara region including Singapore, Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, but excluding other Southeast Asian nations, especially the other nations on the Indochinese peninsula-China:* Nanyang, Henan , prefecture-level...
) from the Han period forward was a major center of the iron and steel industry. Along with their original methods of forging steel, the Chinese had also adopted the production methods of creating Wootz steel
Wootz steel
Wootz steel is a steel characterized by a pattern of bands or sheets of micro carbides within a tempered martensite or pearlite matrix. It was developed in India around 300 BCE...
, an idea imported from India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
to China by the 5th century AD. The Chinese during the ancient Han Dynasty were also the first to apply hydraulic power (i.e. a waterwheel) in working the inflatable bellows of the blast furnace. This was recorded in the year 31 AD, an innovation of the engineer
Engineer
An engineer is a professional practitioner of engineering, concerned with applying scientific knowledge, mathematics and ingenuity to develop solutions for technical problems. Engineers design materials, structures, machines and systems while considering the limitations imposed by practicality,...
Du Shi
Du Shi
Du Shi was a Chinese governmental Prefect of Nanyang in 31 AD and a mechanical engineer of the Eastern Han Dynasty in ancient China. Du Shi is credited with being the first to apply hydraulic power to operate bellows in metallurgy...
, Prefect
Prefect
Prefect is a magisterial title of varying definition....
of Nanyang
Nanyang
Nanyang may refer to:* Nanyang is a Chinese term denoting the greater Nusantara region including Singapore, Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, but excluding other Southeast Asian nations, especially the other nations on the Indochinese peninsula-China:* Nanyang, Henan , prefecture-level...
. Although Du Shi was the first to apply water power to bellows in metallurgy, the first drawn and printed illustration of its operation with water power came in 1313 AD, in the Yuan Dynasty
Yuan Dynasty
The Yuan Dynasty , or Great Yuan Empire was a ruling dynasty founded by the Mongol leader Kublai Khan, who ruled most of present-day China, all of modern Mongolia and its surrounding areas, lasting officially from 1271 to 1368. It is considered both as a division of the Mongol Empire and as an...
era text called the Nong Shu. In the 11th century, there is evidence of the production of steel in Song China
Song Dynasty
The Song Dynasty was a ruling dynasty in China between 960 and 1279; it succeeded the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period, and was followed by the Yuan Dynasty. It was the first government in world history to issue banknotes or paper money, and the first Chinese government to establish a...
using two techniques: a "berganesque" method that produced inferior, heterogeneous steel and a precursor to the modern Bessemer process that utilized partial decarbonization via repeated forging under a cold blast. By the 11th century, there was also a large amount of deforestation in China due to the iron industry's demands for charcoal
Charcoal
Charcoal is the dark grey residue consisting of carbon, and any remaining ash, obtained by removing water and other volatile constituents from animal and vegetation substances. Charcoal is usually produced by slow pyrolysis, the heating of wood or other substances in the absence of oxygen...
. However, by this time the Chinese had figured out how to use bituminous coke
Coke (fuel)
Coke is the solid carbonaceous material derived from destructive distillation of low-ash, low-sulfur bituminous coal. Cokes from coal are grey, hard, and porous. While coke can be formed naturally, the commonly used form is man-made.- History :...
to replace the use of charcoal, and with this switch in resources many acres of prime timberland in China were spared. This switch in resources from charcoal to coal
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure...
was later used in Europe by the 17th century.
The economy of the Song Dynasty was one of the most prosperous and advanced economies in the medieval world. Song Chinese invested their funds in joint stock companies
Joint stock company
A joint-stock company is a type of corporation or partnership involving two or more individuals that own shares of stock in the company...
and in multiple sailing vessels at a time when monetary gain was assured from the vigorous overseas trade and indigenous trade along the Grand Canal and Yangzi River. Prominent merchant families and private businesses were allowed to occupy industries that were not already government-operated monopolies
Monopoly
A monopoly exists when a specific person or enterprise is the only supplier of a particular commodity...
. Both private and government-controlled industries met the needs of a growing Chinese population in the Song. Both artisans and merchants formed guild
Guild
A guild is an association of craftsmen in a particular trade. The earliest types of guild were formed as confraternities of workers. They were organized in a manner something between a trade union, a cartel, and a secret society...
s which the state had to deal with when assessing taxes, requisitioning goods, and setting standard worker's wages and prices on goods.
The iron industry was pursued by both private entrepreneur
Entrepreneur
An entrepreneur is an owner or manager of a business enterprise who makes money through risk and initiative.The term was originally a loanword from French and was first defined by the Irish-French economist Richard Cantillon. Entrepreneur in English is a term applied to a person who is willing to...
s who owned their own smelters as well as government-supervised smelting facilities. The Song economy was stable enough to produce over a hundred million kg (over two hundred million lb) of iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
product a year. Large scale deforestation
Deforestation
Deforestation is the removal of a forest or stand of trees where the land is thereafter converted to a nonforest use. Examples of deforestation include conversion of forestland to farms, ranches, or urban use....
in China would have continued if not for the 11th century innovation of the use of coal
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure...
instead of charcoal
Charcoal
Charcoal is the dark grey residue consisting of carbon, and any remaining ash, obtained by removing water and other volatile constituents from animal and vegetation substances. Charcoal is usually produced by slow pyrolysis, the heating of wood or other substances in the absence of oxygen...
in blast furnace
Blast furnace
A blast furnace is a type of metallurgical furnace used for smelting to produce industrial metals, generally iron.In a blast furnace, fuel and ore and flux are continuously supplied through the top of the furnace, while air is blown into the bottom of the chamber, so that the chemical reactions...
s for smelting cast iron
Cast iron
Cast iron is derived from pig iron, and while it usually refers to gray iron, it also identifies a large group of ferrous alloys which solidify with a eutectic. The color of a fractured surface can be used to identify an alloy. White cast iron is named after its white surface when fractured, due...
. Much of this iron was reserved for military use in crafting weapons and armoring troops, but some was used to fashion the many iron products needed to fill the demands of the growing indigenous market. The iron trade within China was furthered by the building of new canal
Canal
Canals are man-made channels for water. There are two types of canal:#Waterways: navigable transportation canals used for carrying ships and boats shipping goods and conveying people, further subdivided into two kinds:...
s which aided the flow of iron products from production centers to the large market found in the capital city.

Jiaozi (currency)
Jiaozi is a form of banknote which appeared around 10th century in the Sichuan capital of Chengdu, China. Most numismatists generally regard it as the first paper money in history, a development of the Chinese Song Dynasty ....
(see also Huizi
Huizi (currency)
The Huizi , issued in the year 1160, was the official banknote of the Chinese Southern Song Dynasty. It has the highest amount of issuance among various banknote types during the Song Dynasty.-See also:* Economy of Song Dynasty...
). For the printing of paper money
Banknote
A banknote is a kind of negotiable instrument, a promissory note made by a bank payable to the bearer on demand, used as money, and in many jurisdictions is legal tender. In addition to coins, banknotes make up the cash or bearer forms of all modern fiat money...
alone, the Song court established several government-run factories in the cities of Huizhou
Huizhou
Huizhou , historically known as Waichow, is a city located in central Guangdong province of the People's Republic of China. Part of the Pearl River Delta, Huizhou borders the provincial capital of Guangzhou to the west, Shaoguan to the north, Heyuan to the northeast, Shanwei to the east, Shenzhen...
, Chengdu
Chengdu
Chengdu , formerly transliterated Chengtu, is the capital of Sichuan province in Southwest China. It holds sub-provincial administrative status...
, Hangzhou
Hangzhou
Hangzhou , formerly transliterated as Hangchow, is the capital and largest city of Zhejiang Province in Eastern China. Governed as a sub-provincial city, and as of 2010, its entire administrative division or prefecture had a registered population of 8.7 million people...
, and Anqi. The size of the workforce employed in paper money factories was large; it was recorded in 1175 that the factory at Hangzhou employed more than a thousand workers a day.
The economic power of Song China heavily influenced foreign economies abroad. The Moroccan
Morocco
Morocco , officially the Kingdom of Morocco , is a country located in North Africa. It has a population of more than 32 million and an area of 710,850 km², and also primarily administers the disputed region of the Western Sahara...
geographer
Geographer
A geographer is a scholar whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society.Although geographers are historically known as people who make maps, map making is actually the field of study of cartography, a subset of geography...
al-Idrisi wrote in 1154 of the prowess of Chinese merchant ships in the Indian Ocean and of their annual voyages that brought iron, swords, silk, velvet, porcelain, and various textiles to places such as Aden
Aden
Aden is a seaport city in Yemen, located by the eastern approach to the Red Sea , some 170 kilometres east of Bab-el-Mandeb. Its population is approximately 800,000. Aden's ancient, natural harbour lies in the crater of an extinct volcano which now forms a peninsula, joined to the mainland by a...
(Yemen
Yemen
The Republic of Yemen , commonly known as Yemen , is a country located in the Middle East, occupying the southwestern to southern end of the Arabian Peninsula. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the north, the Red Sea to the west, and Oman to the east....
), the Indus River
Indus River
The Indus River is a major river which flows through Pakistan. It also has courses through China and India.Originating in the Tibetan plateau of western China in the vicinity of Lake Mansarovar in Tibet Autonomous Region, the river runs a course through the Ladakh district of Jammu and Kashmir and...
, and the Euphrates
Euphrates
The Euphrates is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia...
in modern-day Iraq. Foreigners, in turn, had an impact on the Chinese economy. For example, many West Asian and Central Asian Muslim
Muslim
A Muslim, also spelled Moslem, is an adherent of Islam, a monotheistic, Abrahamic religion based on the Quran, which Muslims consider the verbatim word of God as revealed to prophet Muhammad. "Muslim" is the Arabic term for "submitter" .Muslims believe that God is one and incomparable...
s went to China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
to trade, becoming a preeminent force in the import and export industry, while some were even appointed as officers supervising economic affairs. Sea trade with the Southeast Pacific, the Hindu world, the Islamic world, and the East African world brought merchants great fortune and spurred an enormous growth in the shipbuilding
Shipbuilding
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to before recorded history.Shipbuilding and ship repairs, both...
industry of Song-era Fujian
Fujian
' , formerly romanised as Fukien or Huguing or Foukien, is a province on the southeast coast of mainland China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, and Guangdong to the south. Taiwan lies to the east, across the Taiwan Strait...
province. However, there was risk involved in such long overseas ventures. To reduce the risk of losing money on maritime trade missions abroad, the historians Ebrey, Walthall, and Palais write:
[Song era] investors usually divided their investment among many ships, and each ship had many investors behind it. One observer thought eagerness to invest in overseas trade was leading to an outflow of copper cash. He wrote, 'People along the coast are on intimate terms with the merchants who engage in overseas trade, either because they are fellow-countrymen or personal acquaintances...[They give the merchants] money to take with them on their ships for purchase and return conveyance of foreign goods. They invest from ten to a hundred strings of cash, and regularly make profits of several hundred percent'.
Reasons for the delay in industrialization
Some historians such as David LandesDavid Landes
David S. Landes is a professor emeritus of economics at Harvard University and retired professor of history at George Washington University. He is the author of Revolution in Time, The Unbound Prometheus, The Wealth and Poverty of Nations, and Dynasties...
and Max Weber
Max Weber
Karl Emil Maximilian "Max" Weber was a German sociologist and political economist who profoundly influenced social theory, social research, and the discipline of sociology itself...
credit the different belief systems in China and Europe with dictating where the revolution occurred. The religion and beliefs of Europe were largely products of Judaeo-Christianity, Socrates
Socrates
Socrates was a classical Greek Athenian philosopher. Credited as one of the founders of Western philosophy, he is an enigmatic figure known chiefly through the accounts of later classical writers, especially the writings of his students Plato and Xenophon, and the plays of his contemporary ...
, Plato
Plato
Plato , was a Classical Greek philosopher, mathematician, student of Socrates, writer of philosophical dialogues, and founder of the Academy in Athens, the first institution of higher learning in the Western world. Along with his mentor, Socrates, and his student, Aristotle, Plato helped to lay the...
, and Aristotle
Aristotle
Aristotle was a Greek philosopher and polymath, a student of Plato and teacher of Alexander the Great. His writings cover many subjects, including physics, metaphysics, poetry, theater, music, logic, rhetoric, linguistics, politics, government, ethics, biology, and zoology...
. Conversely, Chinese society was founded on men like Confucius
Confucius
Confucius , literally "Master Kong", was a Chinese thinker and social philosopher of the Spring and Autumn Period....
, Mencius
Mencius
Mencius was a Chinese philosopher who was arguably the most famous Confucian after Confucius himself.-Life:Mencius, also known by his birth name Meng Ke or Ko, was born in the State of Zou, now forming the territory of the county-level city of Zoucheng , Shandong province, only thirty kilometres ...
, Han Feizi (Legalism
Legalism (Chinese philosophy)
In Chinese history, Legalism was one of the main philosophic currents during the Warring States Period, although the term itself was invented in the Han Dynasty and thus does not refer to an organized 'school' of thought....
), Lao Tzu (Taoism
Taoism
Taoism refers to a philosophical or religious tradition in which the basic concept is to establish harmony with the Tao , which is the mechanism of everything that exists...
), and Buddha
Gautama Buddha
Siddhārtha Gautama was a spiritual teacher from the Indian subcontinent, on whose teachings Buddhism was founded. In most Buddhist traditions, he is regarded as the Supreme Buddha Siddhārtha Gautama (Sanskrit: सिद्धार्थ गौतम; Pali: Siddhattha Gotama) was a spiritual teacher from the Indian...
(Buddhism
Buddhism
Buddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th...
). The key difference between these belief systems was that those from Europe focused on the individual, while Chinese beliefs centered around relationships between people. The family unit was more important than the individual for the large majority of Chinese history, and this may have played a role in why the Industrial Revolution
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was a period from the 18th to the 19th century where major changes in agriculture, manufacturing, mining, transportation, and technology had a profound effect on the social, economic and cultural conditions of the times...
took much longer to occur in China. There was the additional difference as to whether people looked backwards to a reputedly glorious past for answers to their questions or looked hopefully to the future.
The English school
By contrast, there is a historical school which Jack GoldstoneJack Goldstone
Jack A. Goldstone is an American sociologist and political scientist, specializing in studies of social movements, revolutions, and international politics. According to Peter Turchin , he made a significant contribution to the development of cliodynamics...
has dubbed the "English school" which argues that China was not essentially different from Europe, and that many of the assertions that it was are based on bad historical evidence.
Mark Elvin
Mark Elvin
Mark Elvin is a professor emeritus of Chinese history at Australian National University, specializing in the late imperial period.He is famous for his high level equilibrium trap theory to explain why an industrial revolution happened in Europe but not in China, despite the fact that the state of...
argues that China was in a high level equilibrium trap
High level equilibrium trap
The high level equilibrium trap is a concept developed by Mark Elvin to explain why China never underwent an indigenous Industrial Revolution, despite its wealth, stability, and high level of scientific achievement...
in which the non-industrial methods were efficient enough to prevent use of industrial methods with high initial capital. Kenneth Pomeranz
Kenneth Pomeranz
Kenneth Pomeranz is the of History at the University of California, Irvine in the US. He received his B.A. from Cornell University in 1980 and his Ph.D. from Yale University in 1988, where he was a student of Jonathan Spence.-Research:...
, in the Great Divergence, argues that Europe and China were remarkably similar in 1700, and that the crucial differences which created the Industrial Revolution in Europe were sources of coal
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure...
near manufacturing centers, and raw materials such as food and wood from the New World
New World
The New World is one of the names used for the Western Hemisphere, specifically America and sometimes Oceania . The term originated in the late 15th century, when America had been recently discovered by European explorers, expanding the geographical horizon of the people of the European middle...
, which allowed Europe to expand economically in a way that China could not.
Some have compared England directly to China, but the comparison between England and China has been viewed as a faulty one, since China is so much larger than England. A more relevant comparison would be between China's Yangtze Delta region, China's most advanced region, the location of Hangzhou
Hangzhou
Hangzhou , formerly transliterated as Hangchow, is the capital and largest city of Zhejiang Province in Eastern China. Governed as a sub-provincial city, and as of 2010, its entire administrative division or prefecture had a registered population of 8.7 million people...
, Nanjing
Nanjing
' is the capital of Jiangsu province in China and has a prominent place in Chinese history and culture, having been the capital of China on several occasions...
and contemporary Shanghai
Shanghai
Shanghai is the largest city by population in China and the largest city proper in the world. It is one of the four province-level municipalities in the People's Republic of China, with a total population of over 23 million as of 2010...
, and England. This region of China is said to have had similar labor costs to England. Moreover, an overall look at economic data from 1750 is somewhat staggering for a person used to Eurocentric conceptions. According to Andre Gunder Frank, "Particularly significant is the comparison of Asia's 66 percent share of world population, confirmed above all by estimates for 1750, with its 80 percent share of production in the world at the same time. So, two thirds of the world's people in Asia produced four-fifths of total world output, while one-fifth of world population in Europe produced only a part of the remaining one-fifth share of world production, to which Europeans and Americans also contributed." China was clearly Asia's most advanced economy at the time and was in the middle of its 18th century boom brought on by a long period of stability under the Qing Dynasty
Qing Dynasty
The Qing Dynasty was the last dynasty of China, ruling from 1644 to 1912 with a brief, abortive restoration in 1917. It was preceded by the Ming Dynasty and followed by the Republic of China....
.
Industrialization of the People's Republic of China
Industrialization of China did occur on a significant scale only from the 1950s, in the Maoist Great Leap ForwardGreat Leap Forward
The Great Leap Forward of the People's Republic of China was an economic and social campaign of the Communist Party of China , reflected in planning decisions from 1958 to 1961, which aimed to use China's vast population to rapidly transform the country from an agrarian economy into a modern...
. This was the plan used from 1958 to 1961 to transform the People's Republic of China
People's Republic of China
China , officially the People's Republic of China , is the most populous country in the world, with over 1.3 billion citizens. Located in East Asia, the country covers approximately 9.6 million square kilometres...
from a primarily agrarian economy by peasant farmers into a modern communist society through the process of agriculturalization and industrialization. Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong, also transliterated as Mao Tse-tung , and commonly referred to as Chairman Mao , was a Chinese Communist revolutionary, guerrilla warfare strategist, Marxist political philosopher, and leader of the Chinese Revolution...
based this program on the Theory of Productive Forces
Theory of Productive Forces
The Theory of Productive Forces is a widely-used concept in communism and Marxism placing primary emphasis on technical advances and strong productive forces in a nominally socialist economy before real communism, or even real socialism, can have a hope of being achieved.The most influential...
. It ended in catastrophe as it triggered a widespread famine that resulted in millions of deaths.
As political stability was gradually restored following the Cultural Revolution
Cultural Revolution
The Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution, commonly known as the Cultural Revolution , was a socio-political movement that took place in the People's Republic of China from 1966 through 1976...
of the late 1960s, a renewed drive for coordinated, balanced development was set in motion under the leadership of Premier Zhou Enlai
Zhou Enlai
Zhou Enlai was the first Premier of the People's Republic of China, serving from October 1949 until his death in January 1976...
. To revive efficiency in industry, Communist Party of China committees were returned to positions of leadership over the revolutionary committees, and a campaign was carried out to return skilled and highly educated personnel to the jobs from which they had been displaced during the Cultural Revolution. Universities began to reopen, and foreign contacts were expanded. Once again the economy suffered from imbalances in the capacities of different industrial sectors and an urgent need for increased supplies of modern inputs for agriculture. In response to these problems, there was a significant increase in investment, including the signing of contracts with foreign firms for the construction of major facilities for chemical fertilizer production, steel finishing, and oil extraction and refining. The most notable of these contracts was for thirteen of the world's largest and most modern chemical fertilizer plants. During this period, industrial output grew at an average rate of 8 percent a year.
At the milestone Third Plenum of the National Party Congress's 11th Central Committee which opened on December 22, 1978, the party leaders decided to undertake a program of gradual but fundamental reform of the economic system. They concluded that the Maoist version of the centrally planned economy had failed to produce efficient economic growth and had caused China to fall far behind not only the industrialized nations of the West but also the new industrial powers of Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
: Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
, the Republic of Korea, Singapore
Singapore
Singapore , officially the Republic of Singapore, is a Southeast Asian city-state off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, north of the equator. An island country made up of 63 islands, it is separated from Malaysia by the Straits of Johor to its north and from Indonesia's Riau Islands by the...
, Taiwan
Taiwan
Taiwan , also known, especially in the past, as Formosa , is the largest island of the same-named island group of East Asia in the western Pacific Ocean and located off the southeastern coast of mainland China. The island forms over 99% of the current territory of the Republic of China following...
, and Hong Kong
Hong Kong
Hong Kong is one of two Special Administrative Regions of the People's Republic of China , the other being Macau. A city-state situated on China's south coast and enclosed by the Pearl River Delta and South China Sea, it is renowned for its expansive skyline and deep natural harbour...
. In the late 1970s, while Japan and Hong Kong rivaled European countries in modern technology, China's citizens had to make do with barely sufficient food supplies, rationed clothing, inadequate housing, and a service sector that was inadequate and inefficient. All of these shortcomings embarrassed China internationally.
The purpose of the reform program was not to abandon communism
Communism
Communism is a social, political and economic ideology that aims at the establishment of a classless, moneyless, revolutionary and stateless socialist society structured upon common ownership of the means of production...
but to make it work better by substantially increasing the role of market mechanism
Market mechanism
Market mechanism is a term from economics referring to the use of money exchanged by buyers and sellers with an open and understood system of value and time trade offs to produce the best distribution of goods and services...
s in the system and by reducing—not eliminating—government planning and direct control. The process of reform was incremental. New measures were first introduced experimentally in a few localities and then were popularized and disseminated nationally if they proved successful. By 1987 the program had achieved remarkable results in increasing supplies of food and other consumer goods and had created a new climate of dynamism and opportunity in the economy. At the same time, however, the reforms also had created new problems and tensions, leading to intense questioning and political struggles over the program's future.
The first few years of the reform program were designated the "period of readjustment," during which key imbalances in the economy were to be corrected and a foundation was to be laid for a well-planned modernization drive. The schedule of Hua Guofeng's ten-year plan was discarded, although many of its elements were retained. The major goals of the readjustment process were to expand exports rapidly; overcome key deficiencies in transportation, communications, coal, iron, steel, building materials, and electric power; and redress the imbalance between light and heavy industry by increasing the growth rate of light industry and reducing investment in heavy industry.
In 1984, the fourteen largest coastal cities were designated as economic development zones, including Dalian
Dalian
Dalian is a major city and seaport in the south of Liaoning province, Northeast China. It faces Shandong to the south, the Yellow Sea to the east and the Bohai Sea to the west and south. Holding sub-provincial administrative status, Dalian is the southernmost city of Northeast China and China's...
, Tianjin
Tianjin
' is a metropolis in northern China and one of the five national central cities of the People's Republic of China. It is governed as a direct-controlled municipality, one of four such designations, and is, thus, under direct administration of the central government...
, Shanghai
Shanghai
Shanghai is the largest city by population in China and the largest city proper in the world. It is one of the four province-level municipalities in the People's Republic of China, with a total population of over 23 million as of 2010...
, and Guangzhou
Guangzhou
Guangzhou , known historically as Canton or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of the Guangdong province in the People's Republic of China. Located in southern China on the Pearl River, about north-northwest of Hong Kong, Guangzhou is a key national transportation hub and trading port...
, all of which were major commercial and industrial centers. These zones were to create productive exchanges between foreign firms with advanced technology and major Chinese economic networks.
See also
- Agriculture in ChinaAgriculture in ChinaAgriculture is an important economic sector of China, employing over 300 million farmers. China ranks first in worldwide farm output, primarily producing rice, wheat, potatoes, sorghum, peanuts, tea, millet, barley, cotton, oilseed, pork, and fish.-History:...
- Dependency theoryDependency theoryDependency theory or dependencia theory is a body of social science theories predicated on the notion that resources flow from a "periphery" of poor and underdeveloped states to a "core" of wealthy states, enriching the latter at the expense of the former...
- Economy of the People's Republic of ChinaEconomy of the People's Republic of ChinaThe People's Republic of China ranks since 2010 as the world's second largest economy after the United States. It has been the world's fastest-growing major economy, with consistent growth rates of around 10% over the past 30 years. China is also the largest exporter and second largest importer of...
- Economic history of China (Pre-1911)
- Economic history of Modern ChinaEconomic history of modern ChinaThe economic history of modern China began with the fall of the Qing Dynasty in 1911. Following the Qing, China underwent a period of instability and disrupted economic activity. Under the Nanjing decade , China advanced several industries, in particular those related to the military, in an effort...
- Great DivergenceGreat divergenceThe Great Divergence, a term coined by Samuel Huntington , refers to the process by which the Western world The Great Divergence, a term coined by Samuel Huntington (also known as the European miracle, a term coined by Eric Jones in 1981), refers to the process by which the Western world The Great...
- Industry of ChinaIndustry of ChinaIndustry produced 53.7 percent of the People's Republic of China’s gross domestic product in 2005. Industry contributed 46.8 percent of GDP in 2010 and occupied 27 percent of the workforce in 2007. The manufacturing sector produced 44.1 percent of GDP in 2004 and accounted for 11.3 percent of...
- Industrial history of China
- Industrial RevolutionIndustrial RevolutionThe Industrial Revolution was a period from the 18th to the 19th century where major changes in agriculture, manufacturing, mining, transportation, and technology had a profound effect on the social, economic and cultural conditions of the times...
- Industrialization
- International inequalityInternational inequalityInternational inequality is inequality between countries . Economic differences between rich and poor countries are considerable...
- ModernizationModernizationIn the social sciences, modernization or modernisation refers to a model of an evolutionary transition from a 'pre-modern' or 'traditional' to a 'modern' society. The teleology of modernization is described in social evolutionism theories, existing as a template that has been generally followed by...
- Science and technology in China
- Self-Strengthening MovementSelf-Strengthening MovementThe Self-Strengthening Movement , c 1861–1895, was a period of institutional reforms initiated during the late Qing Dynasty following a series of military defeats and concessions to foreign powers....
1861–1895 - Sino-German cooperation (1911–1941)
External links
- China in midway of industrialization gov.cn (Oct 2007)
- President: China to follow path of new type of industrialization gov.cn (Sept 2007)
- CASS: China to realize full industrialization by 2021 gov.cn (Aug 2007)
- Research on China's New Industrialization
- China Hi-Tech Industrialization Association
- China Net for Modernization Research
- China and Europe, 1500-2000 and beyond: What is modern? with Ken Pomeranz and Bin Wong
- http://www.hartford-hwp.com/archives/10/114.html, The Rise of the West or Not
- Needham Puzzle, Weber Question, and China's Miracle: Long Term Performance since the Sung Dynasty (pdf file)
- http://www.historycooperative.org/journals/whc/2.2/duchesne.html

