Human parasites
Encyclopedia
Human parasites include various protozoa
and worms which may infect
humans, causing parasitic diseases.
Human parasites are divided into endoparasites, which cause infection inside the body, and ectoparasites, which cause infection superficially within the skin.
The cysts and eggs of endoparasites may be found in feces
which aids in the detection of the parasite in the human host while also providing a means for the parasitic species to exit the current host and enter other hosts.- Although there are number of ways in which humans can contract parasitic infections, observing basic hygiene and cleanliness tips can reduce its probability.
and is estimated to be from around 5900BC. There are also claims of hookworm
eggs from around 5000BC in Brazil
and large roundworm eggs from around 2330BC in Peru. Tapeworm eggs have also been found present in Egyptian
mummies dating from around 2000BC, 1250BC, and 1000BC along with a well preserved and calcified female worm inside of a mummy .
records. They identify parasites such as roundworms, Guinea worms, threadworms, and some tapeworms of unknown varieties. In ancient Greece
, Hippocrates
and Aristotle
documented several parasites in his collection of works Corpus Hippocraticus. In this book, they documented the presence of worms and other parasites inside of fish, domesticated animals, and humans. The bladder worm is well documented in its presence in pigs along with the larval stages of a tapeworm (Taenia Solium). These tapeworms were mentioned in a play by Aristophanes as “hailstones” with Aristotle in the section about pig diseases in his book History of Animals. The cysts of the Echinococcus granulosus tapeworm were also well known in ancient cultures mainly because of their presence in slaughtered and sacrificed animals .
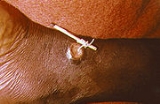
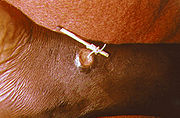
The major parasitic disease which has been documented in early records is dracunculiasis
. This disease is caused by the Guinea worm and is characterized by the female worm emerging from the leg. This symptom is so specific to the disease that it is mentioned in many texts and plays which predate 1000AD .
Another worm which was commonly written about in ancient Greek texts was the tapeworm Echinococccus granulosus. This worm was distinguished by the presence of “massive cysts” in the liver
of animals. This condition was documented so well mainly because of its presence in slaughtered and sacrificed animals
. It was documented by several different cultures of the time other than the Greeks including the Arabs, Romans
, and Babylonians .
Not many parasitic diseases were identified in ancient Greek and Roman texts mainly because the symptoms for parasitic diseases are shared with many other illnesses such as the flu, the common cold
, and dysentery
. However, several diseases such as Dracunculiasis (Guinea worm disease), Hookworm, Elephantiasis
, Schistosomiasis
, Malaria
, and Amebiasis cause unique and specific symptoms and are well documented because of this. The most documented by far was Guinea worm disease mainly because the grown female worm emerges from the skin which causes considerable irritation and which cannot really be ignored. This particular disease is widely accepted to also be the “fiery serpents” written about in the Old Testament of the Bible
. This disease was mentioned by Hippocrates in Greece along with Pliny the Elder
, Galen
, Aetius of Amida, and Paulus Aegineta of Alexandria in Rome. Strangely, this disease was never present in Greece even though it was documented .
records the presence of several parasites
in animal
s and in his patient
s including Guinea worm, threadworms, tapeworms, and the Ascaris worm. This followed a tradition of Arab
medical writings spanning over 1000 years in the area near the Red Sea
. However, the Arabs never made the connection between parasites and the disease
s they caused .
As with Greek
and Roman
texts, the Guinea worm is very well documented in Middle East
ern medical texts. Several Assyria
n document
s in the library
of King Ashurbanipal
refer to an affliction which has been interpreted as Guinea Worm disease .
In Egypt
, the Ebers Papyrus
contains one of the few references to hookworm
disease
in ancient texts. This disease does not have very specific symptom
s and was vaguely mentioned. However vague the reference, it is one of the few that connects the disease to the hookworm parasite . Another documented disease is elephantiasis
. Symptoms of this disease are highly visible, since it causes extreme swelling in the limbs, breasts, and genitals. A number of surviving statue
s indicate that Pharaoh
Mentuhotep II
is likely to have suffered from elephantiasis. This disease was well known to Arab
physician
s including Avicenna
, who noted specific differences between elephantiasis and leprosy
.
That the disease schistosomiasis
was extremely common in Ancient Egypt
is suggested by mummified evidence, but it is not specifically documented in surviving texts. Other names for this disease include bilharzia, Katayama disease, Red Water fever, snail fever, and big belly. The only really defining symptom is bloody urine
, but this can easily be overlooked as several other diseases exhibit the same symptom. However, the main reason it was not documented is probably because it was simply so common. In the same way, the Greeks
and Romans
did not acknowledge the existence of colds and coughs because of how common they were .
mostly documented diseases rather than the parasites associated with them. Chinese texts contain one of the few references to Hookworm disease found in ancient records, but no connection to hookworm is made . The Emperor Huang Ti recorded the earliest mentioning (2700BC) of malaria in his text Nei Ching. He lists chills, headaches, and fevers as the main symptoms and distinguished between the different kinds of fevers.
, the Charaka Samhita
and Sushruta Samhita
document Malaria. These documents list the main symptoms as fever and enlarged spleens.
The Brigu-Samhita from 1000BC makes the earliest reference to Amebiasis. The symptoms were given as bloody and mucosal diarrhea.
Protozoa
Protozoa are a diverse group of single-cells eukaryotic organisms, many of which are motile. Throughout history, protozoa have been defined as single-cell protists with animal-like behavior, e.g., movement...
and worms which may infect
Infectious disease
Infectious diseases, also known as communicable diseases, contagious diseases or transmissible diseases comprise clinically evident illness resulting from the infection, presence and growth of pathogenic biological agents in an individual host organism...
humans, causing parasitic diseases.
Human parasites are divided into endoparasites, which cause infection inside the body, and ectoparasites, which cause infection superficially within the skin.
The cysts and eggs of endoparasites may be found in feces
Feces
Feces, faeces, or fæces is a waste product from an animal's digestive tract expelled through the anus or cloaca during defecation.-Etymology:...
which aids in the detection of the parasite in the human host while also providing a means for the parasitic species to exit the current host and enter other hosts.- Although there are number of ways in which humans can contract parasitic infections, observing basic hygiene and cleanliness tips can reduce its probability.
Archaeological evidence
It is assumed that early human ancestors generally had parasites, but until recently there was no evidence to support this claim. Generally, the discovery of parasites in ancient humans relies on the study of feces and other fossilized material. The earliest known parasite in a human was eggs of the lung fluke found in fossilized feces in northern ChileChile
Chile ,officially the Republic of Chile , is a country in South America occupying a long, narrow coastal strip between the Andes mountains to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. It borders Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far...
and is estimated to be from around 5900BC. There are also claims of hookworm
Hookworm
The hookworm is a parasitic nematode that lives in the small intestine of its host, which may be a mammal such as a dog, cat, or human. Two species of hookworms commonly infect humans, Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus. A. duodenale predominates in the Middle East, North Africa, India...
eggs from around 5000BC in Brazil
Brazil
Brazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
and large roundworm eggs from around 2330BC in Peru. Tapeworm eggs have also been found present in Egyptian
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt was an ancient civilization of Northeastern Africa, concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in what is now the modern country of Egypt. Egyptian civilization coalesced around 3150 BC with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the first pharaoh...
mummies dating from around 2000BC, 1250BC, and 1000BC along with a well preserved and calcified female worm inside of a mummy .
Written Evidence
The first written records of parasites date from 3000 to 400BC in Egyptian papyrusPapyrus
Papyrus is a thick paper-like material produced from the pith of the papyrus plant, Cyperus papyrus, a wetland sedge that was once abundant in the Nile Delta of Egypt....
records. They identify parasites such as roundworms, Guinea worms, threadworms, and some tapeworms of unknown varieties. In ancient Greece
Greece
Greece , officially the Hellenic Republic , and historically Hellas or the Republic of Greece in English, is a country in southeastern Europe....
, Hippocrates
Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Cos or Hippokrates of Kos was an ancient Greek physician of the Age of Pericles , and is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of medicine...
and Aristotle
Aristotle
Aristotle was a Greek philosopher and polymath, a student of Plato and teacher of Alexander the Great. His writings cover many subjects, including physics, metaphysics, poetry, theater, music, logic, rhetoric, linguistics, politics, government, ethics, biology, and zoology...
documented several parasites in his collection of works Corpus Hippocraticus. In this book, they documented the presence of worms and other parasites inside of fish, domesticated animals, and humans. The bladder worm is well documented in its presence in pigs along with the larval stages of a tapeworm (Taenia Solium). These tapeworms were mentioned in a play by Aristophanes as “hailstones” with Aristotle in the section about pig diseases in his book History of Animals. The cysts of the Echinococcus granulosus tapeworm were also well known in ancient cultures mainly because of their presence in slaughtered and sacrificed animals .
The major parasitic disease which has been documented in early records is dracunculiasis
Dracunculiasis
Dracunculiasis , also called guinea worm disease , is a parasitic infection caused by Dracunculus medinensis, a long and very thin nematode . The infection begins when a person drinks stagnant water contaminated with copepods infested by the larvae of the guinea worm...
. This disease is caused by the Guinea worm and is characterized by the female worm emerging from the leg. This symptom is so specific to the disease that it is mentioned in many texts and plays which predate 1000AD .
Greece and Rome
In Greece, Hippocrates and Aristotle created considerable medical documentation about parasites in the Corpus Hippocraticus. In this work, they documented the presence of parasitic worms in many animals ranging from fish to domesticated animals and humans. Among the most extensively documented was the Bladder Worm (Taenia solium). This condition was called “measly pork” when present in pigs and was characterized by the presence of the larval stages of the Bladder Worm in muscle tissue. This disease was also mentioned by the playwright Aristophanes when he referred to “hailstones” in one of his plays. This naming convention is also reflected by Aristotle when he refers to “bladders that are like hailstones.”Another worm which was commonly written about in ancient Greek texts was the tapeworm Echinococccus granulosus. This worm was distinguished by the presence of “massive cysts” in the liver
Liver
The liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
of animals. This condition was documented so well mainly because of its presence in slaughtered and sacrificed animals
Animal sacrifice
Animal sacrifice is the ritual killing of an animal as part of a religion. It is practised by many religions as a means of appeasing a god or gods or changing the course of nature...
. It was documented by several different cultures of the time other than the Greeks including the Arabs, Romans
Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome was a thriving civilization that grew on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to one of the largest empires in the ancient world....
, and Babylonians .
Not many parasitic diseases were identified in ancient Greek and Roman texts mainly because the symptoms for parasitic diseases are shared with many other illnesses such as the flu, the common cold
Common cold
The common cold is a viral infectious disease of the upper respiratory system, caused primarily by rhinoviruses and coronaviruses. Common symptoms include a cough, sore throat, runny nose, and fever...
, and dysentery
Dysentery
Dysentery is an inflammatory disorder of the intestine, especially of the colon, that results in severe diarrhea containing mucus and/or blood in the faeces with fever and abdominal pain. If left untreated, dysentery can be fatal.There are differences between dysentery and normal bloody diarrhoea...
. However, several diseases such as Dracunculiasis (Guinea worm disease), Hookworm, Elephantiasis
Elephantiasis
Elephantiasis is a disease that is characterized by the thickening of the skin and underlying tissues, especially in the legs and male genitals. In some cases the disease can cause certain body parts, such as the scrotum, to swell to the size of a softball or basketball. It is caused by...
, Schistosomiasis
Schistosomiasis
Schistosomiasis is a parasitic disease caused by several species of trematodes , a parasitic worm of the genus Schistosoma. Snails often act as an intermediary agent for the infectious diseases until a new human host is found...
, Malaria
Malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease of humans and other animals caused by eukaryotic protists of the genus Plasmodium. The disease results from the multiplication of Plasmodium parasites within red blood cells, causing symptoms that typically include fever and headache, in severe cases...
, and Amebiasis cause unique and specific symptoms and are well documented because of this. The most documented by far was Guinea worm disease mainly because the grown female worm emerges from the skin which causes considerable irritation and which cannot really be ignored. This particular disease is widely accepted to also be the “fiery serpents” written about in the Old Testament of the Bible
Bible
The Bible refers to any one of the collections of the primary religious texts of Judaism and Christianity. There is no common version of the Bible, as the individual books , their contents and their order vary among denominations...
. This disease was mentioned by Hippocrates in Greece along with Pliny the Elder
Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus , better known as Pliny the Elder, was a Roman author, naturalist, and natural philosopher, as well as naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and personal friend of the emperor Vespasian...
, Galen
Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus , better known as Galen of Pergamon , was a prominent Roman physician, surgeon and philosopher...
, Aetius of Amida, and Paulus Aegineta of Alexandria in Rome. Strangely, this disease was never present in Greece even though it was documented .
Northern Africa, The Middle East, and Mesopotamia
The ancient Persian doctor AvicennaAvicenna
Abū ʿAlī al-Ḥusayn ibn ʿAbd Allāh ibn Sīnā , commonly known as Ibn Sīnā or by his Latinized name Avicenna, was a Persian polymath, who wrote almost 450 treatises on a wide range of subjects, of which around 240 have survived...
records the presence of several parasites
Parasitism
Parasitism is a type of symbiotic relationship between organisms of different species where one organism, the parasite, benefits at the expense of the other, the host. Traditionally parasite referred to organisms with lifestages that needed more than one host . These are now called macroparasites...
in animal
Animal
Animals are a major group of multicellular, eukaryotic organisms of the kingdom Animalia or Metazoa. Their body plan eventually becomes fixed as they develop, although some undergo a process of metamorphosis later on in their life. Most animals are motile, meaning they can move spontaneously and...
s and in his patient
Patient
A patient is any recipient of healthcare services. The patient is most often ill or injured and in need of treatment by a physician, advanced practice registered nurse, veterinarian, or other health care provider....
s including Guinea worm, threadworms, tapeworms, and the Ascaris worm. This followed a tradition of Arab
Arab
Arab people, also known as Arabs , are a panethnicity primarily living in the Arab world, which is located in Western Asia and North Africa. They are identified as such on one or more of genealogical, linguistic, or cultural grounds, with tribal affiliations, and intra-tribal relationships playing...
medical writings spanning over 1000 years in the area near the Red Sea
Red Sea
The Red Sea is a seawater inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. The connection to the ocean is in the south through the Bab el Mandeb strait and the Gulf of Aden. In the north, there is the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez...
. However, the Arabs never made the connection between parasites and the disease
Disease
A disease is an abnormal condition affecting the body of an organism. It is often construed to be a medical condition associated with specific symptoms and signs. It may be caused by external factors, such as infectious disease, or it may be caused by internal dysfunctions, such as autoimmune...
s they caused .
As with Greek
Greek language
Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. Native to the southern Balkans, it has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history;...
and Roman
Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome was a thriving civilization that grew on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to one of the largest empires in the ancient world....
texts, the Guinea worm is very well documented in Middle East
Middle East
The Middle East is a region that encompasses Western Asia and Northern Africa. It is often used as a synonym for Near East, in opposition to Far East...
ern medical texts. Several Assyria
Assyria
Assyria was a Semitic Akkadian kingdom, extant as a nation state from the mid–23rd century BC to 608 BC centred on the Upper Tigris river, in northern Mesopotamia , that came to rule regional empires a number of times through history. It was named for its original capital, the ancient city of Assur...
n document
Document
The term document has multiple meanings in ordinary language and in scholarship. WordNet 3.1. lists four meanings :* document, written document, papers...
s in the library
Library
In a traditional sense, a library is a large collection of books, and can refer to the place in which the collection is housed. Today, the term can refer to any collection, including digital sources, resources, and services...
of King Ashurbanipal
Ashurbanipal
Ashurbanipal |Ashur]] is creator of an heir"; 685 BC – c. 627 BC), also spelled Assurbanipal or Ashshurbanipal, was an Assyrian king, the son of Esarhaddon and the last great king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire...
refer to an affliction which has been interpreted as Guinea Worm disease .
In Egypt
Egypt
Egypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world...
, the Ebers Papyrus
Ebers papyrus
The Ebers Papyrus, also known as Papyrus Ebers, is an Egyptian medical papyrus dating to circa 1550 BC. Among the oldest and most important medical papyri of ancient Egypt, it was purchased at Luxor, in the winter of 1873–74 by Georg Ebers...
contains one of the few references to hookworm
Hookworm
The hookworm is a parasitic nematode that lives in the small intestine of its host, which may be a mammal such as a dog, cat, or human. Two species of hookworms commonly infect humans, Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus. A. duodenale predominates in the Middle East, North Africa, India...
disease
Disease
A disease is an abnormal condition affecting the body of an organism. It is often construed to be a medical condition associated with specific symptoms and signs. It may be caused by external factors, such as infectious disease, or it may be caused by internal dysfunctions, such as autoimmune...
in ancient texts. This disease does not have very specific symptom
Symptom
A symptom is a departure from normal function or feeling which is noticed by a patient, indicating the presence of disease or abnormality...
s and was vaguely mentioned. However vague the reference, it is one of the few that connects the disease to the hookworm parasite . Another documented disease is elephantiasis
Elephantiasis
Elephantiasis is a disease that is characterized by the thickening of the skin and underlying tissues, especially in the legs and male genitals. In some cases the disease can cause certain body parts, such as the scrotum, to swell to the size of a softball or basketball. It is caused by...
. Symptoms of this disease are highly visible, since it causes extreme swelling in the limbs, breasts, and genitals. A number of surviving statue
Statue
A statue is a sculpture in the round representing a person or persons, an animal, an idea or an event, normally full-length, as opposed to a bust, and at least close to life-size, or larger...
s indicate that Pharaoh
Pharaoh
Pharaoh is a title used in many modern discussions of the ancient Egyptian rulers of all periods. The title originates in the term "pr-aa" which means "great house" and describes the royal palace...
Mentuhotep II
Mentuhotep II
Nebhepetre Mentuhotep II was a Pharaoh of the 11th dynasty, the son of Intef III of Egypt and a minor queen called Iah. His own wife was the 'king's mother' Tem. Other wives were Neferu and several secondary wives, one or more who it has been suggested were possibly Nubian, buried in his...
is likely to have suffered from elephantiasis. This disease was well known to Arab
Arab
Arab people, also known as Arabs , are a panethnicity primarily living in the Arab world, which is located in Western Asia and North Africa. They are identified as such on one or more of genealogical, linguistic, or cultural grounds, with tribal affiliations, and intra-tribal relationships playing...
physician
Physician
A physician is a health care provider who practices the profession of medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring human health through the study, diagnosis, and treatment of disease, injury and other physical and mental impairments...
s including Avicenna
Avicenna
Abū ʿAlī al-Ḥusayn ibn ʿAbd Allāh ibn Sīnā , commonly known as Ibn Sīnā or by his Latinized name Avicenna, was a Persian polymath, who wrote almost 450 treatises on a wide range of subjects, of which around 240 have survived...
, who noted specific differences between elephantiasis and leprosy
Leprosy
Leprosy or Hansen's disease is a chronic disease caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium leprae and Mycobacterium lepromatosis. Named after physician Gerhard Armauer Hansen, leprosy is primarily a granulomatous disease of the peripheral nerves and mucosa of the upper respiratory tract; skin lesions...
.
That the disease schistosomiasis
Schistosomiasis
Schistosomiasis is a parasitic disease caused by several species of trematodes , a parasitic worm of the genus Schistosoma. Snails often act as an intermediary agent for the infectious diseases until a new human host is found...
was extremely common in Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt was an ancient civilization of Northeastern Africa, concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in what is now the modern country of Egypt. Egyptian civilization coalesced around 3150 BC with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the first pharaoh...
is suggested by mummified evidence, but it is not specifically documented in surviving texts. Other names for this disease include bilharzia, Katayama disease, Red Water fever, snail fever, and big belly. The only really defining symptom is bloody urine
Urine
Urine is a typically sterile liquid by-product of the body that is secreted by the kidneys through a process called urination and excreted through the urethra. Cellular metabolism generates numerous by-products, many rich in nitrogen, that require elimination from the bloodstream...
, but this can easily be overlooked as several other diseases exhibit the same symptom. However, the main reason it was not documented is probably because it was simply so common. In the same way, the Greeks
Greeks
The Greeks, also known as the Hellenes , are a nation and ethnic group native to Greece, Cyprus and neighboring regions. They also form a significant diaspora, with Greek communities established around the world....
and Romans
Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome was a thriving civilization that grew on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to one of the largest empires in the ancient world....
did not acknowledge the existence of colds and coughs because of how common they were .
China
The ChineseChina
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
mostly documented diseases rather than the parasites associated with them. Chinese texts contain one of the few references to Hookworm disease found in ancient records, but no connection to hookworm is made . The Emperor Huang Ti recorded the earliest mentioning (2700BC) of malaria in his text Nei Ching. He lists chills, headaches, and fevers as the main symptoms and distinguished between the different kinds of fevers.
India
In IndiaIndia
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
, the Charaka Samhita
Charaka Samhita
The ' is an early Ayurvedic text on internal medicine. It is believed to be the oldest of the three ancient treatises of Ayurveda...
and Sushruta Samhita
Sushruta Samhita
The Sushruta Samhita is a Sanskrit text, attributed to one Sushruta, foundational to Ayurvedic medicine , with innovative chapters on surgery....
document Malaria. These documents list the main symptoms as fever and enlarged spleens.
The Brigu-Samhita from 1000BC makes the earliest reference to Amebiasis. The symptoms were given as bloody and mucosal diarrhea.
Protozoa
- PlasmodiumPlasmodiumPlasmodium is a genus of parasitic protists. Infection by these organisms is known as malaria. The genus Plasmodium was described in 1885 by Ettore Marchiafava and Angelo Celli. Currently over 200 species of this genus are recognized and new species continue to be described.Of the over 200 known...
spp. - causes MalariaMalariaMalaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease of humans and other animals caused by eukaryotic protists of the genus Plasmodium. The disease results from the multiplication of Plasmodium parasites within red blood cells, causing symptoms that typically include fever and headache, in severe cases... - EntamoebaEntamoebaEntamoeba is a genus of Amoebozoa found as internal parasites or commensals of animals.In 1875, Fedor Lösch described the first proven case of amoebic dysentery in St Petersburg, Russia. He referred to the amoeba he observed microscopically as 'Amoeba coli'; however it is not clear whether he was...
- causes amoebiasisAmoebiasisEntamebiasis is a term for the infection more commonly known as amoebiasis.It became the preferred term in MeSH in 1991, but the term amoebiasis is used by the World Health Organization and by those working in the field of amoebiasis research....
, amoebic dysentery - GiardiaGiardiaGiardia is a genus of anaerobic flagellated protozoan parasites of the phylum Metamonada in the supergroup "Excavata" that colonise and reproduce in the small intestines of several vertebrates, causing giardiasis, commonly known as Beaver fever...
- Toxoplasma gondiiToxoplasma gondiiToxoplasma gondii is a species of parasitic protozoa in the genus Toxoplasma. The definitive host of T. gondii is the cat, but the parasite can be carried by many warm-blooded animals . Toxoplasmosis, the disease of which T...
- causes ToxoplasmosisToxoplasmosisToxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease caused by the protozoan Toxoplasma gondii. The parasite infects most genera of warm-blooded animals, including humans, but the primary host is the felid family. Animals are infected by eating infected meat, by ingestion of feces of a cat that has itself...
Parasitic worms and flukes

- PinwormPinwormThe pinworm , also known as threadworm or seatworm, is a nematode and a common human intestinal parasite, especially in children...
- causes EnterobiasisEnterobiasisA pinworm infection or enterobiasis is a human parasitic disease and one of the most common childhood parasitic worm infections in the developed world. It is caused by infestation with the parasitic roundworm Enterobius vermicularis, commonly called the human pinworm... - SchistosomaSchistosomaA genus of trematodes, Schistosoma, commonly known as blood-flukes and bilharzia, includes flatworms which are responsible for a highly significant parasitic infection of humans by causing the disease schistosomiasis, and are considered by the World Health Organization as the second most...
- causes SchistosomiasisSchistosomiasisSchistosomiasis is a parasitic disease caused by several species of trematodes , a parasitic worm of the genus Schistosoma. Snails often act as an intermediary agent for the infectious diseases until a new human host is found... - Strongyloides stercoralisStrongyloides stercoralisStrongyloides stercoralis, also known as the threadworm, is the scientific name of a human parasitic roundworm causing the disease of strongyloidiasis....
- causes StrongyloidiasisStrongyloidiasisStrongyloidiasis is a human parasitic disease caused by the nematode Strongyloides stercoralis, or sometimes S. fülleborni. It can cause a number of symptoms in people, principally skin symptoms, abdominal pain, diarrhea and weight loss... - Guinea Worm - also known as Dracunculiasis.
- HookwormHookwormThe hookworm is a parasitic nematode that lives in the small intestine of its host, which may be a mammal such as a dog, cat, or human. Two species of hookworms commonly infect humans, Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus. A. duodenale predominates in the Middle East, North Africa, India...
- Tapeworm
Ectoparasites
- Sarcoptes scabieiSarcoptes scabieiSarcoptes scabiei or the itch mite is a parasitic arthropod that burrows into skin and causes scabies. Animals affected include not only human but also wild and domesticated dogs and cats in which it is one cause of mange...
- causes scabiesScabiesScabies , known colloquially as the seven-year itch, is a contagious skin infection that occurs among humans and other animals. It is caused by a tiny and usually not directly visible parasite, the mite Sarcoptes scabiei, which burrows under the host's skin, causing intense allergic itching... - Pediculus humanus capitis - causes headlice
- Phthirus pubis - causes pubic lice
- TickTickTicks are small arachnids in the order Ixodida, along with mites, constitute the subclass Acarina. Ticks are ectoparasites , living by hematophagy on the blood of mammals, birds, and sometimes reptiles and amphibians...
s (Ixodoidea)

