Elephantiasis
Overview
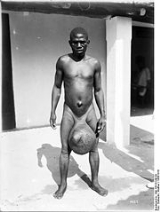
Elephantiasis (ˌɛlɨfənˈtaɪ.əsɨs ) is a disease that is characterized by the thickening of the skin and underlying tissues, especially in the legs and male genitals. In some cases the disease can cause certain body parts, such as the scrotum
, to swell to the size of a softball
or basketball
. It is caused by filariasis
or podoconiosis.
The proper medical term for the disease is elephantiasis. It is commonly misheard as "Elephantitis", which substitutes for the ending -iasis (meaning process or resulting condition) the more commonly heard -itis (irritation or inflammation), resulting in "Elephantitis" meaning "inflammation of the elephant".
Elephantiasis occurs in the presence of microscopic, thread-like parasitic worms such as Wuchereria bancrofti
, Brugia malayi
, and B. timori
, all of which are transmitted by mosquito
es.
Scrotum
In some male mammals the scrotum is a dual-chambered protuberance of skin and muscle containing the testicles and divided by a septum. It is an extension of the perineum, and is located between the penis and anus. In humans and some other mammals, the base of the scrotum becomes covered with curly...
, to swell to the size of a softball
Softball
Softball is a bat-and-ball sport played between two teams of 10 to 14 players. It is a direct descendant of baseball although there are some key differences: softballs are larger than baseballs, and the pitches are thrown underhand rather than overhand...
or basketball
Basketball (ball)
A basketball is a spherical inflated ball used in the game of basketball. Basketballs typically range in size from very small promotional items only a few inches in diameter to extra large balls nearly a foot in diameter used in training exercises to increase the skill of players...
. It is caused by filariasis
Filariasis
Filariasis is a parasitic disease and is considered an infectious tropical disease, that is caused by thread-like nematodes belonging to the superfamily Filarioidea, also known as "filariae"....
or podoconiosis.
The proper medical term for the disease is elephantiasis. It is commonly misheard as "Elephantitis", which substitutes for the ending -iasis (meaning process or resulting condition) the more commonly heard -itis (irritation or inflammation), resulting in "Elephantitis" meaning "inflammation of the elephant".
Elephantiasis occurs in the presence of microscopic, thread-like parasitic worms such as Wuchereria bancrofti
Wuchereria bancrofti
Filaria, is a parasitic filarial nematode spread by a mosquito vector. It is one of the three parasites that cause lymphatic filariasis, an infection of the lymphatic system by filarial worms. It affects over 120 million people, primarily in Africa, South America, and other tropical and...
, Brugia malayi
Brugia malayi
Brugia malayi is a nematode , one of the three causative agents of lymphatic filariasis in humans. Lymphatic filariasis, also known as elephantiasis, is a condition characterized by swelling of the lower limbs. The two other filarial causes of lymphatic filariasis are Wuchereria bancrofti and...
, and B. timori
Brugia timori
Brugia timori is a human filarial parasitic nematode which causes the disease "Timor filariasis." While this disease was first described in 1965, the identity of Brugia timori as the causative agent was not known until 1977...
, all of which are transmitted by mosquito
Mosquito
Mosquitoes are members of a family of nematocerid flies: the Culicidae . The word Mosquito is from the Spanish and Portuguese for little fly...
es.
Discussions

