Demographics of Lithuania
Encyclopedia
This article is about the demographic
features of the population
of Lithuania
, including population density
, ethnicity
, level of education, health, economic status, and religious affiliations.
dates back to 10,000 BC. Between 3000–2000 BC, the cord-ware culture people spread over a vast region of eastern Europe, between the Baltic Sea
and the Vistula River in the West and the Moscow
-Kursk
line in the East. Merging with the indigenous peoples
, they gave rise to the Balts
, a distinct Indo-European
ethnic group whose descendants are the present-day Lithuanian and Latvian nations and the former Old Prussians
.
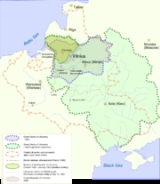
 The name of Lithuania
The name of Lithuania
– Lithuanians – was first mentioned in 1009. Among its etymologies there are a derivation from the word Lietava, for a small river, a possible derivation from a word leičiai
, but most probable is the name for union of Lithuanian ethnic tribes ('susilieti, lietis' means to unite and the word 'lietuva' means something which has been united).
The primary Lithuanian state, the Duchy of Lithuania, emerged in the territory of Lietuva
, the ethnic homeland of Lithuanians. At the birth of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania (GDL), ethnic Lithuanians made up about 70% of the population. With the acquisition of new Ruthenia
n territories, this proportion decreased to 50% and later to 30%. By the time of the largest expansion towards Kievan Rus'
lands, at the end of the 13th and during the 14th century, the territory of the GDL was about 800,000 km2, of which 10% was ethnically Lithuanian. The ethnic Lithuanian population is estimated to have been 420,000 out of 1.4 million in 1375 (the territory was about 700,000 km2), and 550,000 out of 3.8 million in 1490 (territory: 850,000 km2) Ruthenians were only nowadays Ukrainians and the whole Belarus including Smolensk and Mozhaisk Galindians were of Lithuanian ethnicity (belonging to the same family as Prussians or Latvians). In addition to the Ruthenians and Lithuanians, other significant ethnic groups throughout GDL were Jews
and Tatars
. The combined population of Poland and GDL in 1493 is estimated as 7.5 million, of whom 3.25 million were Poles, 3.75 million Ruthenians and 0.5 million Lithuanians. With the Union of Lublin
Lithuanian Grand Duchy lost large part of lands to the Polish Crown (see demographics of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth). An ethnic Lithuanian proportion being about 1/4 in GDL after the Union of Lublin was held till the partitions. There was much devastation and population loss throughout the GDL in the mid and late 17th century, including the ethnic Lithuanian population in Vilnius voivodeship
. Besides devastation, the Ruthenian population declined proportionally after the territorial losses to the Russian Empire
. In 1770 there were about 4.84 million inhabitants in GDL, of which the largest ethnic group were Ruthenians, about 1.39 million – Lithuanians. The voivodeship
s with a majority ethnic Lithuanian population were Vilnius
, Trakai
and Samogitian
voivodeships, and these three voivodeships comprised the political center of the state. In the southern angle of Trakai voivodeship and south-eastern part of Vilnius voivodeship there were also many Belarusians; in some of the south-eastern areas they were the major linguistic group.
The Ruthenian population formed a majority in GDL from the time of the GDL's expansion in the mid 14th century; and the adjective "Lithuanian", besides denoting ethnic Lithuanians, from early times denoted any inhabitant of GDL, including Slavs and Jews.
The Ruthenian
language, corresponding to today's Belarusian
and Ukrainian
, was then called Russian
, and was used as one of the chancellery languages by Lithuanian monarchs. However there are fewer extant documents written in this language than those written in Latin and German from the time of Vytautas. Later, Ruthenian became the main language of documentation and writing. In the years that followed,, it was the main language of government until the introduction of Polish
as the chancellery language of the Lithuanian-Polish Commonwealth in 1697; however there are also examples of documents written in Ruthenian from the second half of the 18th century. The Lithuanian language was used orally in Vilnius, Trakai and Samogitian voivodeships, and by small numbers of people elsewhere. At the court of Zygmunt August, the last king of the Duchy, both Polish and Lithuanian were spoken.
of Lithuania
in the late 18th century, it become a part of Russian empire
. After the abolition of serfdom
in 1861, the use of the Polish language noticeably increased in eastern Lithuania and western Belarus. Many Lithuanians, living further east, were unable to receive the Lithuanian printed books smuggled into Lithuania by knygnešiai
during the time of the ban on printing books
in the Latin alphabet, and they switched to Polish. Although this also used the Latin alphabet, it was much less affected by the ban, because Polish was still used by the politically important class of the nobility, and also used predominantly in the biggest towns of Lithuania, and supported by the church.
had begun to intensify by the end of the 19th century, and the number of Lithuanian speakers and people identifying themselves as ethnic Lithuanians started to increase; but at the same time many Polish speaking Lithuanians, especially former szlachta, cut themselves adrift from the Lithuanian nation. There were population losses due to several border changes, Soviet deportations, a massacre of the Lithuanian Jewish
population, and German and Polish repatriations during and after World War II
. After World War II, the ethnic Lithuanian population remained stable: 79.3% in 1959 to 83.5% in 2002. Lithuania's citizenship law and the Constitution
meet international and OSCE
standards, guaranteeing universal human and civil rights.
are neither Slavic
nor Germanic
, although the union with Poland
, German
and Russia
n colonization and settlement left cultural and religious influences.
, Lithuania has the most homogeneous population. According to the census conducted in 2001, 83.4% of the population identified themselves as Lithuanians, 6.7% as Poles
, 6.3% as Russians
, 1.2% as Belarusians
, and 2.3% as members of other ethnic groups.
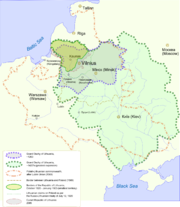
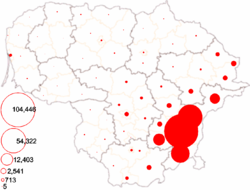 Poles are concentrated in the Vilnius Region
Poles are concentrated in the Vilnius Region
, the area controlled by Poland in the interwar period. There are especially large Polish communities in Vilnius district municipality
(61.3% of the population) and Šalčininkai district municipality
(79.5%). Such concentrations would allow Election Action of Lithuania's Poles, an ethnic minority-based political party, to exert political influence, but the 5% rule prevents it from entering the parliament of Lithuania. The party is more active in local politics and controls several municipal councils.
Russians, even though they are almost as numerous as Poles, are much more evenly scattered and lack a strong political party. The most prominent community lives in Visaginas
(52%). Most of them are scientists who moved with their families from the Russian SFSR
to work at the Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant
. Lithuania is noted for its success in limiting Russian immigration during the Soviet period (1945–1990), in comparison to Latvia
and Estonia
. A number of ethnic Russians (mostly military) left Lithuania after the declaration of independence in 1990.
Another major change in the ethnic composition of Lithuania was the extermination of the Jewish population during the Holocaust
. Before World War II
about 7.5% of the population was Jewish; they were concentrated in cities and towns and had a significant influence on crafts and business. They were called Litvaks
and had a strong culture. The population of Vilnius, sometimes nicknamed Northern Jerusalem, was about 30% Jewish. Almost all of these Jews were killed during the Nazi German
occupation, or later emigrated to the United States
and Israel
. Now there are only about 4,000 Jews living in Lithuania.
has made Lithuanian citizenship all the more appealing. Lithuanian citizenship
is theoretically easier (see court ruling notes below) to obtain than that of many other European countries - only one great-grandparent is necessary to become a Lithuanian citizen. Persons who held citizenship in the Republic of Lithuania prior to June 15, 1940, and their children, grandchildren, and great-grandchildren (provided that these persons did not repatriate) are eligible for Lithuanian citizenship http://www.lithuanianembassy.ca/documents/Lithuanian%20citizenship%20information.pdf.
Lithuanian citizens are allowed to travel throughout the European Union
without a visa. As far as work is concerned, the United Kingdom
, Sweden
, Ireland
, Spain
, Portugal
, Finland
, and Greece
place no restrictions on Lithuanians working in their respective countries. The other older member nations of the European Union still place restrictions on work, but these are merely transitional arrangements.
The Lithuanian Parliament amended the Citizenship Law substantially as a result of this court ruling, allowing dual Citizenship for children of at least one Lithuanian parent that are born abroad, but preventing Lithuanians from keeping their Lithuanian citizenship after obtaining citizenship of another country.
There are some special cases still permitting dual citizenship. See Lithuanian nationality law
.
The Lithuanian language
, which uses a modified Latin alphabet
, is the country's official language. It is the first language of 82% of population and is also spoken by 356,000 out of 577,000 non-Lithuanians. The Soviet era had imposed the official use of Russian, so most adult Lithuanians speak Russian as a second language, while the original Polish population generally speaks Polish and Russians who immigrated after World War II speak Russian as their first language. The younger generation usually speaks English as their second language. According to census of 2001, 17% of population can speak English fluently (21% in urban areas, 9% in rural areas).
About 30,600 pupils started their 2003 school year in schools where the entire curriculum is conducted in Russian (down from 76,000 in 1991), and about 20,500 enrolled in Polish schools (up from 11,400 in 1991). There are also schools in the Belarusian language
(these enrolled about 160 students in 2003), as well as in German
.
There are perhaps 50 speakers of Karaim
, a Turkic language spoken by Karaite Jews, in Lithuania.

According to the 2005 Eurobarometer Poll
, 12% said that "they do not believe there is any sort of spirit
, god
, or life force", 36% answered that "they believe there is some sort of spirit
or life force" and 49% of Lithuanian citizens responded that "they believe there is a God
".
Age structure:
0–14 years: 14.2% (male 258,423/female 245,115)
15–64 years: 69.6% (male 1,214,743/female 1,261,413)
65 years and over: 16.2% (male 198,714/female 376,771) (2009 est.)
Population growth rate:
−0.28% (2009 est.)
Net migration rate:
-0.72 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2009 est.)
Sex ratio:
at birth:
1.06 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
0.96 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.53 male(s)/female
total population:
0.89 male(s)/female (2009 est.)
Infant mortality rate:
Total: 6.47 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 7.73 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 5.13 deaths/1,000 live births (2009 est.)
Life expectancy at birth:
total population: 74.9 years
male: 69.98 years
female: 80.1 years (2009 est.)
Total fertility rate:
1.55 children born/woman (2009) http://db1.stat.gov.lt/statbank/selectvarval/saveselections.asp?MainTable=M3010508&PLanguage=1&TableStyle=&Buttons=&PXSId=3213&IQY=&TC=&ST=ST&rvar0=&rvar1=&rvar2=&rvar3=&rvar4=&rvar5=&rvar6=&rvar7=&rvar8=&rvar9=&rvar10=&rvar11=&rvar12=&rvar13=&rvar14=
Suicide rate:
31.5 suicide
s per every 100,000 people (2009)
Divorce rate:
With 2.8 divorces per every 1000 people (2009), Lithuania in 2004 had one of the highest divorce rate in the European Union http://www.delfi.lt/news/daily/lithuania/article.php?id=9902334.
1 the figures of 1939 exclude the Klaipėda Region
is almost free. Depending on grades, a student might receive a stipend or make a payment of 520 litas
per semester. There are also small social stipends available for students with economic difficulties. In 2003 43,900 students were admitted to the 21 universities in Lithuania (11,100 of them to master programs). About 70% of high school graduates continue to study in universities or professional schools.
Demographics
Demographics are the most recent statistical characteristics of a population. These types of data are used widely in sociology , public policy, and marketing. Commonly examined demographics include gender, race, age, disabilities, mobility, home ownership, employment status, and even location...
features of the population
Population
A population is all the organisms that both belong to the same group or species and live in the same geographical area. The area that is used to define a sexual population is such that inter-breeding is possible between any pair within the area and more probable than cross-breeding with individuals...
of Lithuania
Lithuania
Lithuania , officially the Republic of Lithuania is a country in Northern Europe, the biggest of the three Baltic states. It is situated along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea, whereby to the west lie Sweden and Denmark...
, including population density
Population density
Population density is a measurement of population per unit area or unit volume. It is frequently applied to living organisms, and particularly to humans...
, ethnicity
Ethnic group
An ethnic group is a group of people whose members identify with each other, through a common heritage, often consisting of a common language, a common culture and/or an ideology that stresses common ancestry or endogamy...
, level of education, health, economic status, and religious affiliations.
Prehistory
The earliest evidence of inhabitants in present-day LithuaniaLithuania
Lithuania , officially the Republic of Lithuania is a country in Northern Europe, the biggest of the three Baltic states. It is situated along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea, whereby to the west lie Sweden and Denmark...
dates back to 10,000 BC. Between 3000–2000 BC, the cord-ware culture people spread over a vast region of eastern Europe, between the Baltic Sea
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
and the Vistula River in the West and the Moscow
Moscow
Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent...
-Kursk
Kursk
Kursk is a city and the administrative center of Kursk Oblast, Russia, located at the confluence of the Kur, Tuskar, and Seym Rivers. The area around Kursk was site of a turning point in the Russian-German struggle during World War II and the site of the largest tank battle in history...
line in the East. Merging with the indigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples are ethnic groups that are defined as indigenous according to one of the various definitions of the term, there is no universally accepted definition but most of which carry connotations of being the "original inhabitants" of a territory....
, they gave rise to the Balts
Balts
The Balts or Baltic peoples , defined as speakers of one of the Baltic languages, a branch of the Indo-European language family, are descended from a group of Indo-European tribes who settled the area between the Jutland peninsula in the west and Moscow, Oka and Volga rivers basins in the east...
, a distinct Indo-European
Proto-Indo-Europeans
The Proto-Indo-Europeans were the speakers of the Proto-Indo-European language , a reconstructed prehistoric language of Eurasia.Knowledge of them comes chiefly from the linguistic reconstruction, along with material evidence from archaeology and archaeogenetics...
ethnic group whose descendants are the present-day Lithuanian and Latvian nations and the former Old Prussians
Old Prussians
The Old Prussians or Baltic Prussians were an ethnic group, autochthonous Baltic tribes that inhabited Prussia, the lands of the southeastern Baltic Sea in the area around the Vistula and Curonian Lagoons...
.
Grand Duchy of Lithuania
- See also: Demographics and Languages of Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Demographics of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth

Name of Lithuania
The first known record of the name of Lithuania is in a 9 March 1009 story of Saint Bruno recorded in the Quedlinburg Chronicle . The Chronicle recorded a Latinized Slavic form of the name Lietuva: Litua pronounced [litvā]...
– Lithuanians – was first mentioned in 1009. Among its etymologies there are a derivation from the word Lietava, for a small river, a possible derivation from a word leičiai
Leičiai
Leičiai were a distinct social group of the Lithuanian society in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, subordinates to Lithuanian ruler or the state itself. The 15-16th centuries were the time of degradation of this social group and it disappeared with the execution of Wallach reform...
, but most probable is the name for union of Lithuanian ethnic tribes ('susilieti, lietis' means to unite and the word 'lietuva' means something which has been united).
The primary Lithuanian state, the Duchy of Lithuania, emerged in the territory of Lietuva
Duchy of Lithuania
Duchy of Lithuania was a state-territorial formation of ethnic Lithuanians, that existed from the 12th century until 1413. Most of the time it was a constituent part and a nucleus of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania...
, the ethnic homeland of Lithuanians. At the birth of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania (GDL), ethnic Lithuanians made up about 70% of the population. With the acquisition of new Ruthenia
Ruthenia
Ruthenia is the Latin word used onwards from the 13th century, describing lands of the Ancient Rus in European manuscripts. Its geographic and culturo-ethnic name at that time was applied to the parts of Eastern Europe. Essentially, the word is a false Latin rendering of the ancient place name Rus...
n territories, this proportion decreased to 50% and later to 30%. By the time of the largest expansion towards Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rus was a medieval polity in Eastern Europe, from the late 9th to the mid 13th century, when it disintegrated under the pressure of the Mongol invasion of 1237–1240....
lands, at the end of the 13th and during the 14th century, the territory of the GDL was about 800,000 km2, of which 10% was ethnically Lithuanian. The ethnic Lithuanian population is estimated to have been 420,000 out of 1.4 million in 1375 (the territory was about 700,000 km2), and 550,000 out of 3.8 million in 1490 (territory: 850,000 km2) Ruthenians were only nowadays Ukrainians and the whole Belarus including Smolensk and Mozhaisk Galindians were of Lithuanian ethnicity (belonging to the same family as Prussians or Latvians). In addition to the Ruthenians and Lithuanians, other significant ethnic groups throughout GDL were Jews
Lithuanian Jews
Lithuanian Jews or Litvaks are Jews with roots in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania:...
and Tatars
Tatars
Tatars are a Turkic speaking ethnic group , numbering roughly 7 million.The majority of Tatars live in the Russian Federation, with a population of around 5.5 million, about 2 million of which in the republic of Tatarstan.Significant minority populations are found in Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan,...
. The combined population of Poland and GDL in 1493 is estimated as 7.5 million, of whom 3.25 million were Poles, 3.75 million Ruthenians and 0.5 million Lithuanians. With the Union of Lublin
Union of Lublin
The Union of Lublin replaced the personal union of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania with a real union and an elective monarchy, since Sigismund II Augustus, the last of the Jagiellons, remained childless after three marriages. In addition, the autonomy of Royal Prussia was...
Lithuanian Grand Duchy lost large part of lands to the Polish Crown (see demographics of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth). An ethnic Lithuanian proportion being about 1/4 in GDL after the Union of Lublin was held till the partitions. There was much devastation and population loss throughout the GDL in the mid and late 17th century, including the ethnic Lithuanian population in Vilnius voivodeship
Vilnius Voivodeship
The Vilnius Voivodeship was one of voivodeships in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, created in 1413, from the Duchy of Lithuania and neighbouring lands.- Geography and administrative division :...
. Besides devastation, the Ruthenian population declined proportionally after the territorial losses to the Russian Empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
. In 1770 there were about 4.84 million inhabitants in GDL, of which the largest ethnic group were Ruthenians, about 1.39 million – Lithuanians. The voivodeship
Voivodeship
Voivodship is a term denoting the position of, or more commonly the area administered by, a voivod. Voivodeships have existed since medieval times in Poland, Romania, Hungary, Lithuania, Latvia, Russia and Serbia....
s with a majority ethnic Lithuanian population were Vilnius
Vilnius Voivodeship
The Vilnius Voivodeship was one of voivodeships in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, created in 1413, from the Duchy of Lithuania and neighbouring lands.- Geography and administrative division :...
, Trakai
Trakai Voivodeship
Trakai Voivodeship, Trakai Palatinate, or Troki Voivodeship , was a unit of administrative division and local government in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania from 1413 until 1795.-History:...
and Samogitian
Eldership of Samogitia
The Duchy of Samogitia had been the administrative unit of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania from 1422 . Between 1422 to 1441 it was known as the Eldership of Samogitia...
voivodeships, and these three voivodeships comprised the political center of the state. In the southern angle of Trakai voivodeship and south-eastern part of Vilnius voivodeship there were also many Belarusians; in some of the south-eastern areas they were the major linguistic group.
The Ruthenian population formed a majority in GDL from the time of the GDL's expansion in the mid 14th century; and the adjective "Lithuanian", besides denoting ethnic Lithuanians, from early times denoted any inhabitant of GDL, including Slavs and Jews.
The Ruthenian
Ruthenian language
Ruthenian, or Old Ruthenian , is a term used for the varieties of Eastern Slavonic spoken in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and later in the East Slavic territories of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth....
language, corresponding to today's Belarusian
Belarusian language
The Belarusian language , sometimes referred to as White Russian or White Ruthenian, is the language of the Belarusian people...
and Ukrainian
Ukrainian language
Ukrainian is a language of the East Slavic subgroup of the Slavic languages. It is the official state language of Ukraine. Written Ukrainian uses a variant of the Cyrillic alphabet....
, was then called Russian
Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rus was a medieval polity in Eastern Europe, from the late 9th to the mid 13th century, when it disintegrated under the pressure of the Mongol invasion of 1237–1240....
, and was used as one of the chancellery languages by Lithuanian monarchs. However there are fewer extant documents written in this language than those written in Latin and German from the time of Vytautas. Later, Ruthenian became the main language of documentation and writing. In the years that followed,, it was the main language of government until the introduction of Polish
Polish language
Polish is a language of the Lechitic subgroup of West Slavic languages, used throughout Poland and by Polish minorities in other countries...
as the chancellery language of the Lithuanian-Polish Commonwealth in 1697; however there are also examples of documents written in Ruthenian from the second half of the 18th century. The Lithuanian language was used orally in Vilnius, Trakai and Samogitian voivodeships, and by small numbers of people elsewhere. At the court of Zygmunt August, the last king of the Duchy, both Polish and Lithuanian were spoken.
Russian empire
After partitionPartitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland or Partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth took place in the second half of the 18th century and ended the existence of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland for 123 years...
of Lithuania
Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state from the 12th /13th century until 1569 and then as a constituent part of Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth until 1791 when Constitution of May 3, 1791 abolished it in favor of unitary state. It was founded by the Lithuanians, one of the polytheistic...
in the late 18th century, it become a part of Russian empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
. After the abolition of serfdom
Emancipation reform of 1861
The Emancipation Reform of 1861 in Russia was the first and most important of liberal reforms effected during the reign of Alexander II of Russia. The reform, together with a related reform in 1861, amounted to the liquidation of serf dependence previously suffered by peasants of the Russian Empire...
in 1861, the use of the Polish language noticeably increased in eastern Lithuania and western Belarus. Many Lithuanians, living further east, were unable to receive the Lithuanian printed books smuggled into Lithuania by knygnešiai
Knygnešiai
Book smugglers were people who transported Lithuanian language books printed in the Latin alphabet into Lithuanian-speaking areas of the Russian Empire, defying a ban on such materials in force from 1866 to 1904...
during the time of the ban on printing books
Lithuanian press ban
The Lithuanian press ban was a ban on all Lithuanian language publications printed in the Latin alphabet within the Russian Empire, which controlled Lithuania at the time. Lithuanian-language publications that used the Cyrillic alphabet were allowed and even encouraged...
in the Latin alphabet, and they switched to Polish. Although this also used the Latin alphabet, it was much less affected by the ban, because Polish was still used by the politically important class of the nobility, and also used predominantly in the biggest towns of Lithuania, and supported by the church.
National revival
The Lithuanian National RevivalLithuanian National Revival
Lithuanian National Revival, alternatively Lithuanian National Awakening , was a period of the history of Lithuania in the 19th century at the time when a major part of Lithuanian inhabited areas belonged to the Russian Empire...
had begun to intensify by the end of the 19th century, and the number of Lithuanian speakers and people identifying themselves as ethnic Lithuanians started to increase; but at the same time many Polish speaking Lithuanians, especially former szlachta, cut themselves adrift from the Lithuanian nation. There were population losses due to several border changes, Soviet deportations, a massacre of the Lithuanian Jewish
Lithuanian Jews
Lithuanian Jews or Litvaks are Jews with roots in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania:...
population, and German and Polish repatriations during and after World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
. After World War II, the ethnic Lithuanian population remained stable: 79.3% in 1959 to 83.5% in 2002. Lithuania's citizenship law and the Constitution
Constitution of Lithuania
The Constitution of the Republic of Lithuania defines the legal foundation for all laws passed in the Republic of Lithuania. It was approved in a referendum on October 25, 1992.-History:...
meet international and OSCE
Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe
The Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe is the world's largest security-oriented intergovernmental organization. Its mandate includes issues such as arms control, human rights, freedom of the press and fair elections...
standards, guaranteeing universal human and civil rights.
Ethnic composition
LithuaniansLithuanians
Lithuanians are the Baltic ethnic group native to Lithuania, where they number around 2,765,600 people. Another million or more make up the Lithuanian diaspora, largely found in countries such as the United States, Brazil, Canada, Colombia, Russia, United Kingdom and Ireland. Their native language...
are neither Slavic
Slavic peoples
The Slavic people are an Indo-European panethnicity living in Eastern Europe, Southeast Europe, North Asia and Central Asia. The term Slavic represents a broad ethno-linguistic group of people, who speak languages belonging to the Slavic language family and share, to varying degrees, certain...
nor Germanic
Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples are an Indo-European ethno-linguistic group of Northern European origin, identified by their use of the Indo-European Germanic languages which diversified out of Proto-Germanic during the Pre-Roman Iron Age.Originating about 1800 BCE from the Corded Ware Culture on the North...
, although the union with Poland
Poland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
, German
Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples are an Indo-European ethno-linguistic group of Northern European origin, identified by their use of the Indo-European Germanic languages which diversified out of Proto-Germanic during the Pre-Roman Iron Age.Originating about 1800 BCE from the Corded Ware Culture on the North...
and Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
n colonization and settlement left cultural and religious influences.
Before WW II
| Ethnic group |
census 1923 of Lithuania | census 1925 of the Klaipėda Region Klaipėda Region The Klaipėda Region or Memel Territory was defined by the Treaty of Versailles in 1920 when it was put under the administration of the Council of Ambassadors... |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | |
| Lithuanians Lithuanians Lithuanians are the Baltic ethnic group native to Lithuania, where they number around 2,765,600 people. Another million or more make up the Lithuanian diaspora, largely found in countries such as the United States, Brazil, Canada, Colombia, Russia, United Kingdom and Ireland. Their native language... |
1,701,863 | 89.3 | 37,626 | 26.6 |
| Memels | 34,227 | 24.2 | ||
| Jews Jews The Jews , also known as the Jewish people, are a nation and ethnoreligious group originating in the Israelites or Hebrews of the Ancient Near East. The Jewish ethnicity, nationality, and religion are strongly interrelated, as Judaism is the traditional faith of the Jewish nation... |
153,743 | 7.6 | 578 | 0.4 |
| Germans Germans The Germans are a Germanic ethnic group native to Central Europe. The English term Germans has referred to the German-speaking population of the Holy Roman Empire since the Late Middle Ages.... |
29,231 | 1.4 | 59,337 | 41.9 |
| Poles Poles thumb|right|180px|The state flag of [[Poland]] as used by Polish government and diplomatic authoritiesThe Polish people, or Poles , are a nation indigenous to Poland. They are united by the Polish language, which belongs to the historical Lechitic subgroup of West Slavic languages of Central Europe... |
65,599 | 3.2 | 29 | 0.0 |
| Russians Russians The Russian people are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Russia, speaking the Russian language and primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries.... |
50,460 | 2.5 | 267 | 0.2 |
| Latvians Latvians Latvians or Letts are the indigenous Baltic people of Latvia.-History:Latvians occasionally refer to themselves by the ancient name of Latvji, which may have originated from the word Latve which is a name of the river that presumably flowed through what is now eastern Latvia... |
14,883 | 0.7 | 47 | 0.0 |
| Belarusians Belarusians Belarusians ; are an East Slavic ethnic group who populate the majority of the Republic of Belarus. Introduced to the world as a new state in the early 1990s, the Republic of Belarus brought with it the notion of a re-emerging Belarusian ethnicity, drawn upon the lines of the Old Belarusian... |
4,421 | 0.2 | - | - |
| Tatars Tatars Tatars are a Turkic speaking ethnic group , numbering roughly 7 million.The majority of Tatars live in the Russian Federation, with a population of around 5.5 million, about 2 million of which in the republic of Tatarstan.Significant minority populations are found in Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan,... |
973 | 0.0 | ||
| Romani | 284 | 0.0 | ||
| Karaites | 141 | 0.0 | ||
| Estonians Estonians Estonians are a Finnic people closely related to the Finns and inhabiting, primarily, the country of Estonia. They speak a Finnic language known as Estonian... |
46 | 0.0 | ||
| Ukrainians Ukrainians Ukrainians are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine, which is the sixth-largest nation in Europe. The Constitution of Ukraine applies the term 'Ukrainians' to all its citizens... |
43 | 0.0 | ||
| Others | 7,284 | 0.2 | 9,424 | 6.7 |
| Total | 2,028,971 | 141,645 | ||
| 1 Source: http://www.stat.gov.lt/uploads/leidiniai/Lietuvos_gyv_sur.pdf. The Klaipėda Region was annexed from Germany in 1923, but was not included in the 1923 census. A separate census in the Klaipėda region was held in 1925. | ||||
After WW II
Among the Baltic statesBaltic states
The term Baltic states refers to the Baltic territories which gained independence from the Russian Empire in the wake of World War I: primarily the contiguous trio of Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania ; Finland also fell within the scope of the term after initially gaining independence in the 1920s.The...
, Lithuania has the most homogeneous population. According to the census conducted in 2001, 83.4% of the population identified themselves as Lithuanians, 6.7% as Poles
Poles
thumb|right|180px|The state flag of [[Poland]] as used by Polish government and diplomatic authoritiesThe Polish people, or Poles , are a nation indigenous to Poland. They are united by the Polish language, which belongs to the historical Lechitic subgroup of West Slavic languages of Central Europe...
, 6.3% as Russians
Russians
The Russian people are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Russia, speaking the Russian language and primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries....
, 1.2% as Belarusians
Belarusians
Belarusians ; are an East Slavic ethnic group who populate the majority of the Republic of Belarus. Introduced to the world as a new state in the early 1990s, the Republic of Belarus brought with it the notion of a re-emerging Belarusian ethnicity, drawn upon the lines of the Old Belarusian...
, and 2.3% as members of other ethnic groups.

Vilnius region
Vilnius Region , refers to the territory in the present day Lithuania, that was originally inhabited by ethnic Baltic tribes and was a part of Lithuania proper, but came under East Slavic and Polish cultural influences over time,...
, the area controlled by Poland in the interwar period. There are especially large Polish communities in Vilnius district municipality
Vilnius district municipality
Vilnius district municipality is one of 60 municipalities in Lithuania. It surrounds the capital on 3 sides, and the Trakai district municipality touches it on one....
(61.3% of the population) and Šalčininkai district municipality
Šalcininkai district municipality
Šalčininkai district municipality is one of 60 municipalities in Lithuania.It has one of biggest Polish minority populations in Lithuania, with 31,223 or over 80% of the population claiming Polish ethnicity. Šalčininkai is the largest town in and the center of the region.-References:...
(79.5%). Such concentrations would allow Election Action of Lithuania's Poles, an ethnic minority-based political party, to exert political influence, but the 5% rule prevents it from entering the parliament of Lithuania. The party is more active in local politics and controls several municipal councils.
| Ethnic group |
census 19591 | census 19702 | census 19793 | census 19894 | census 20015 | 2011 estimate5 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | |
| Lithuanians Lithuanians Lithuanians are the Baltic ethnic group native to Lithuania, where they number around 2,765,600 people. Another million or more make up the Lithuanian diaspora, largely found in countries such as the United States, Brazil, Canada, Colombia, Russia, United Kingdom and Ireland. Their native language... |
2,150,7671 | 79.3 | 2,506,751 | 80.1 | 2,712,233 | 80.0 | 2,924,251 | 79.6 | 2,907,293 | 83.4 | 2,721,500 | 83.9 |
| Poles Poles thumb|right|180px|The state flag of [[Poland]] as used by Polish government and diplomatic authoritiesThe Polish people, or Poles , are a nation indigenous to Poland. They are united by the Polish language, which belongs to the historical Lechitic subgroup of West Slavic languages of Central Europe... |
230,107 | 8.5 | 240,203 | 7.7 | 247,022 | 7.3 | 257,994 | 7.0 | 234,989 | 6.7 | 212,800 | 6.6 |
| Russians Russians The Russian people are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Russia, speaking the Russian language and primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries.... |
231,014 | 8.5 | 267,989 | 8.6 | 303,493 | 8.9 | 344,455 | 9.4 | 219,789 | 6.3 | 174,900 | 5.4 |
| Belarusians Belarusians Belarusians ; are an East Slavic ethnic group who populate the majority of the Republic of Belarus. Introduced to the world as a new state in the early 1990s, the Republic of Belarus brought with it the notion of a re-emerging Belarusian ethnicity, drawn upon the lines of the Old Belarusian... |
30,256 | 1.1 | 45,412 | 1.5 | 57,584 | 1.7 | 63,169 | 1.7 | 42,866 | 1.2 | 41,100 | 1.3 |
| Ukrainians Ukrainians Ukrainians are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine, which is the sixth-largest nation in Europe. The Constitution of Ukraine applies the term 'Ukrainians' to all its citizens... |
17,692 | 0.7 | 25,099 | 0.8 | 31,982 | 0.9 | 44,789 | 1.2 | 22,488 | 0.6 | 21,100 | 0.6 |
| Jews Jews The Jews , also known as the Jewish people, are a nation and ethnoreligious group originating in the Israelites or Hebrews of the Ancient Near East. The Jewish ethnicity, nationality, and religion are strongly interrelated, as Judaism is the traditional faith of the Jewish nation... |
24,667 | 0.9 | 23,538 | 0.8 | 14,691 | 0.4 | 12,390 | 0.3 | 4,007 | 0.1 | 3,400 | 0.1 |
| Germans Germans The Germans are a Germanic ethnic group native to Central Europe. The English term Germans has referred to the German-speaking population of the Holy Roman Empire since the Late Middle Ages.... |
11,166 | 0.4 | 1,904 | 0.1 | 2,616 | 0.1 | 2,058 | 0.1 | 3,243 | 0.1 | 3,000 | 0.1 |
| Tatars Tatars Tatars are a Turkic speaking ethnic group , numbering roughly 7 million.The majority of Tatars live in the Russian Federation, with a population of around 5.5 million, about 2 million of which in the republic of Tatarstan.Significant minority populations are found in Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan,... |
3,020 | 0.1 | 3,454 | 0.1 | 3,984 | 0.1 | 5,135 | 0.1 | 3,235 | 0.1 | 3,100 | 0.1 |
| Latvians Latvians Latvians or Letts are the indigenous Baltic people of Latvia.-History:Latvians occasionally refer to themselves by the ancient name of Latvji, which may have originated from the word Latve which is a name of the river that presumably flowed through what is now eastern Latvia... |
6,318 | 0.2 | 5,063 | 0.2 | 4,354 | 0.1 | 4,229 | 0.1 | 2,955 | 0.1 | 2,400 | 0.1 |
| Romani | 1,238 | 0.1 | 1,880 | 0.1 | 2,306 | 0.1 | 2,718 | 0.1 | 2,571 | 0.1 | 2,900 | 0.1 |
| Estonians Estonians Estonians are a Finnic people closely related to the Finns and inhabiting, primarily, the country of Estonia. They speak a Finnic language known as Estonian... |
352 | 0.0 | 551 | 0.0 | 546 | 0.0 | 598 | 0.0 | 400 | 0.0 | ||
| Karaites | 423 | 0.0 | 388 | 0.0 | 352 | 0.0 | 289 | 0.0 | ||||
| Others or unspecified | 4,425 | 0.2 | 6,004 | 0.2 | 10,327 | 0.3 | 12,727 | 0.3 | 40,136 | 1.2 | 58,400 | 1.7 |
| Total | 2,711,445 | 3,128,236 | 3,391,490 | 3,674,802 | 3,483,972 | 3,244,600 | ||||||
| 1 Source: http://demoscope.ru/weekly/ssp/sng_nac_59.php. 2 Source: http://demoscope.ru/weekly/ssp/sng_nac_70.php. 3 Source: http://demoscope.ru/weekly/ssp/sng_nac_79.php. 4 Source: http://demoscope.ru/weekly/ssp/sng_nac_89.php. 5 Source: http://db1.stat.gov.lt/statbank/default.asp?w=1920. | ||||||||||||
Russians, even though they are almost as numerous as Poles, are much more evenly scattered and lack a strong political party. The most prominent community lives in Visaginas
Visaginas
Visaginas is a city with municipal rights in eastern Lithuania, situated near the country's biggest lake, Drūkšiai. Its administrative boundaries are in the process of being defined. The Vilnius–Daugavpils railway runs alongside the town, providing convenient communication with Vilnius and...
(52%). Most of them are scientists who moved with their families from the Russian SFSR
Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic , commonly referred to as Soviet Russia, Bolshevik Russia, or simply Russia, was the largest, most populous and economically developed republic in the former Soviet Union....
to work at the Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant
Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant
The Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant is a closed two-unit RBMK-1500 nuclear power station in Visaginas, Lithuania. It was named after the nearby city of Ignalina...
. Lithuania is noted for its success in limiting Russian immigration during the Soviet period (1945–1990), in comparison to Latvia
Latvia
Latvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
and Estonia
Estonia
Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies...
. A number of ethnic Russians (mostly military) left Lithuania after the declaration of independence in 1990.
Another major change in the ethnic composition of Lithuania was the extermination of the Jewish population during the Holocaust
The Holocaust
The Holocaust , also known as the Shoah , was the genocide of approximately six million European Jews and millions of others during World War II, a programme of systematic state-sponsored murder by Nazi...
. Before World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
about 7.5% of the population was Jewish; they were concentrated in cities and towns and had a significant influence on crafts and business. They were called Litvaks
Lithuanian Jews
Lithuanian Jews or Litvaks are Jews with roots in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania:...
and had a strong culture. The population of Vilnius, sometimes nicknamed Northern Jerusalem, was about 30% Jewish. Almost all of these Jews were killed during the Nazi German
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany , also known as the Third Reich , but officially called German Reich from 1933 to 1943 and Greater German Reich from 26 June 1943 onward, is the name commonly used to refer to the state of Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a totalitarian dictatorship ruled by...
occupation, or later emigrated to the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
and Israel
Israel
The State of Israel is a parliamentary republic located in the Middle East, along the eastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea...
. Now there are only about 4,000 Jews living in Lithuania.
Citizenship
Lithuania's membership of the European UnionEuropean Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
has made Lithuanian citizenship all the more appealing. Lithuanian citizenship
Citizenship
Citizenship is the state of being a citizen of a particular social, political, national, or human resource community. Citizenship status, under social contract theory, carries with it both rights and responsibilities...
is theoretically easier (see court ruling notes below) to obtain than that of many other European countries - only one great-grandparent is necessary to become a Lithuanian citizen. Persons who held citizenship in the Republic of Lithuania prior to June 15, 1940, and their children, grandchildren, and great-grandchildren (provided that these persons did not repatriate) are eligible for Lithuanian citizenship http://www.lithuanianembassy.ca/documents/Lithuanian%20citizenship%20information.pdf.
Lithuanian citizens are allowed to travel throughout the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
without a visa. As far as work is concerned, the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
, Sweden
Sweden
Sweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
, Ireland
Ireland
Ireland is an island to the northwest of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth...
, Spain
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
, Portugal
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
, Finland
Finland
Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside...
, and Greece
Greece
Greece , officially the Hellenic Republic , and historically Hellas or the Republic of Greece in English, is a country in southeastern Europe....
place no restrictions on Lithuanians working in their respective countries. The other older member nations of the European Union still place restrictions on work, but these are merely transitional arrangements.
Dual citizenship ruled unconstitutional
The Lithuanian Constitutional Court ruled in November 2006 that a number of provisions of the Law of the Republic of Lithuania on citizenship are in conflict with the Lithuanian Constitution. In particular, the court ruled that a number of current provisions of the Citizenship Law implicitly or explicitly allowing dual citizenship are in conflict with the Constitution; such provisions amounted to the unconstitutional practice of making dual citizenship a common phenomenon rather than a rare exception. The provisions of the Citizenship Law announced unconstitutional are no longer valid and applicable to the extent stated by the Constitutional Court.The Lithuanian Parliament amended the Citizenship Law substantially as a result of this court ruling, allowing dual Citizenship for children of at least one Lithuanian parent that are born abroad, but preventing Lithuanians from keeping their Lithuanian citizenship after obtaining citizenship of another country.
There are some special cases still permitting dual citizenship. See Lithuanian nationality law
Lithuanian nationality law
right|150pxLithuanian nationality law automatically grants citizenship to persons born within the current borders of Lithuania. Citizenship may also be granted by naturalization...
.
Languages
Languages by mother tongue (census 2001)::- LithuanianLithuanian languageLithuanian is the official state language of Lithuania and is recognized as one of the official languages of the European Union. There are about 2.96 million native Lithuanian speakers in Lithuania and about 170,000 abroad. Lithuanian is a Baltic language, closely related to Latvian, although they...
- 82% - RussianRussian languageRussian is a Slavic language used primarily in Russia, Belarus, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan. It is an unofficial but widely spoken language in Ukraine, Moldova, Latvia, Turkmenistan and Estonia and, to a lesser extent, the other countries that were once constituent republics...
- 8% - PolishPolish languagePolish is a language of the Lechitic subgroup of West Slavic languages, used throughout Poland and by Polish minorities in other countries...
- 5.6% - Belorussian - 0.46%
- UkrainianUkrainian languageUkrainian is a language of the East Slavic subgroup of the Slavic languages. It is the official state language of Ukraine. Written Ukrainian uses a variant of the Cyrillic alphabet....
- 0.235% - Other - 0.28%
- Did not specify - 3.5%
The Lithuanian language
Lithuanian language
Lithuanian is the official state language of Lithuania and is recognized as one of the official languages of the European Union. There are about 2.96 million native Lithuanian speakers in Lithuania and about 170,000 abroad. Lithuanian is a Baltic language, closely related to Latvian, although they...
, which uses a modified Latin alphabet
Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most recognized alphabet used in the world today. It evolved from a western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, which was adopted and modified by the Etruscans who ruled early Rome...
, is the country's official language. It is the first language of 82% of population and is also spoken by 356,000 out of 577,000 non-Lithuanians. The Soviet era had imposed the official use of Russian, so most adult Lithuanians speak Russian as a second language, while the original Polish population generally speaks Polish and Russians who immigrated after World War II speak Russian as their first language. The younger generation usually speaks English as their second language. According to census of 2001, 17% of population can speak English fluently (21% in urban areas, 9% in rural areas).
About 30,600 pupils started their 2003 school year in schools where the entire curriculum is conducted in Russian (down from 76,000 in 1991), and about 20,500 enrolled in Polish schools (up from 11,400 in 1991). There are also schools in the Belarusian language
Belarusian language
The Belarusian language , sometimes referred to as White Russian or White Ruthenian, is the language of the Belarusian people...
(these enrolled about 160 students in 2003), as well as in German
German language
German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
.
There are perhaps 50 speakers of Karaim
Karaim language
The Karaim language is a Turkic language with Hebrew influences, in a similar manner to Yiddish or Ladino. It is spoken by Crimean Karaites – ethnic Turkic adherents of Karaite Judaism in Crimea, Lithuania, Poland and western Ukraine...
, a Turkic language spoken by Karaite Jews, in Lithuania.
Religion
Population by Religious Confession (2001 census):
- Roman Catholics - 79% (2,752,447 people)
- Orthodox Believers - 4.05% (141,821)
- Old BelieversOld BelieversIn the context of Russian Orthodox church history, the Old Believers separated after 1666 from the official Russian Orthodox Church as a protest against church reforms introduced by Patriarch Nikon between 1652–66...
- 0.77% (27,073) - Evangelical Lutherans - 0.56% (19,637)
- Evangelical ReformistsReformed churchesThe Reformed churches are a group of Protestant denominations characterized by Calvinist doctrines. They are descended from the Swiss Reformation inaugurated by Huldrych Zwingli but developed more coherently by Martin Bucer, Heinrich Bullinger and especially John Calvin...
- 0.2% (7,082) - Jehovah's WitnessesJehovah's WitnessesJehovah's Witnesses is a millenarian restorationist Christian denomination with nontrinitarian beliefs distinct from mainstream Christianity. The religion reports worldwide membership of over 7 million adherents involved in evangelism, convention attendance of over 12 million, and annual...
- 0.1% (3,512) - Sunni Muslims - 0.08% (2,860)
- All Gospel Churches - 0.06% (2,207)
- Pentecostal Church - 0.04% (1,307)
- Judaists - 0.04% (1,272)
- Balts Believers - 0.04% (1,270)
- Baptists (and other independent churches) - 0.04% (1,249)
- Other believers - 0.135% (4,701)
- Not any - 9.5% (331,087)
- Not indicated - 5.35% (186,447)
According to the 2005 Eurobarometer Poll
Eurobarometer
Eurobarometer is a series of surveys regularly performed on behalf of the European Commission since 1973. It produces reports of public opinion of certain issues relating to the European Union across the member states...
, 12% said that "they do not believe there is any sort of spirit
Spirit
The English word spirit has many differing meanings and connotations, most of them relating to a non-corporeal substance contrasted with the material body.The spirit of a living thing usually refers to or explains its consciousness.The notions of a person's "spirit" and "soul" often also overlap,...
, god
God
God is the English name given to a singular being in theistic and deistic religions who is either the sole deity in monotheism, or a single deity in polytheism....
, or life force", 36% answered that "they believe there is some sort of spirit
Spirit
The English word spirit has many differing meanings and connotations, most of them relating to a non-corporeal substance contrasted with the material body.The spirit of a living thing usually refers to or explains its consciousness.The notions of a person's "spirit" and "soul" often also overlap,...
or life force" and 49% of Lithuanian citizens responded that "they believe there is a God
God
God is the English name given to a singular being in theistic and deistic religions who is either the sole deity in monotheism, or a single deity in polytheism....
".
CIA World Factbook demographic statistics
The following demographic statistics are from the CIA World Factbook, unless otherwise indicated.Age structure:
0–14 years: 14.2% (male 258,423/female 245,115)
15–64 years: 69.6% (male 1,214,743/female 1,261,413)
65 years and over: 16.2% (male 198,714/female 376,771) (2009 est.)
Population growth rate:
−0.28% (2009 est.)
Net migration rate:
-0.72 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2009 est.)
Sex ratio:
at birth:
1.06 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
0.96 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.53 male(s)/female
total population:
0.89 male(s)/female (2009 est.)
Infant mortality rate:
Total: 6.47 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 7.73 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 5.13 deaths/1,000 live births (2009 est.)
Life expectancy at birth:
total population: 74.9 years
male: 69.98 years
female: 80.1 years (2009 est.)
Total fertility rate:
1.55 children born/woman (2009) http://db1.stat.gov.lt/statbank/selectvarval/saveselections.asp?MainTable=M3010508&PLanguage=1&TableStyle=&Buttons=&PXSId=3213&IQY=&TC=&ST=ST&rvar0=&rvar1=&rvar2=&rvar3=&rvar4=&rvar5=&rvar6=&rvar7=&rvar8=&rvar9=&rvar10=&rvar11=&rvar12=&rvar13=&rvar14=
Suicide rate:
31.5 suicide
Suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Suicide is often committed out of despair or attributed to some underlying mental disorder, such as depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, alcoholism, or drug abuse...
s per every 100,000 people (2009)
Divorce rate:
With 2.8 divorces per every 1000 people (2009), Lithuania in 2004 had one of the highest divorce rate in the European Union http://www.delfi.lt/news/daily/lithuania/article.php?id=9902334.
Before WW II
- Source: Statistical yearbooks of Lithuania
Average population (x 1000) Live births Deaths Natural change Crude birth rate (per 1000) Crude death rate (per 1000) Natural change (per 1000) 1915 2 137 38 722 43 596 -4 874 18.1 20.4 -2.3 1916 2 137 35 565 31 512 4 053 16.6 14.7 1.9 1917 2 134 32 266 43 047 -10 781 15.1 20.2 -5.1 1918 2 121 33 176 47 522 -14 346 15.6 22.4 -6.8 1919 2 108 41 095 51 930 -10 835 19.5 24.6 -5.1 1920 2 104 47 642 44 487 3 155 22.6 21.1 1.5 1921 2 116 51 864 31 915 19 949 24.5 15.1 9.4 1922 2 136 58 064 37 598 20 466 27.2 17.6 9.6 1923 2 161 60 869 32 432 28 437 28.2 15.0 13.2 1924 2 189 63 864 35 493 28 371 29.2 16.2 13.0 1925 2 217 63 743 37 179 26 564 28.8 16.8 12.0 1926 2 245 63 655 34 380 29 275 28.4 15.3 13.0 1927 2 273 66 114 38 897 27 217 29.1 17.1 12.0 1928 2 301 65 945 35 698 27 116 28.7 15.5 11.8 1929 2 328 63 083 39 669 23 414 27.1 17.0 10.1 1930 2 354 64 164 37 151 27 013 27.3 15.8 11.5 1931 2 380 63 419 37 478 25 941 26.6 15.7 10.9 1932 2 407 65 371 36 577 28 794 27.2 15.2 12.0 1933 2 436 62 145 32 749 29 396 25.5 13.4 12.1 1934 2 464 60 770 35 789 24 981 24.7 14.5 10.1 1935 2 488 57 970 34 595 23 375 23.3 13.9 9.4 1936 2 513 60 446 33 440 25 939 24.1 13.3 10.3 1937 2 538 56 393 33 260 22 433 22.2 13.1 8.8 1938 2 563 57 951 32 256 24 562 22.6 12.6 9.6 19391 2 432 54 184 32 983 21 201 22.3 13.6 8.7
1 the figures of 1939 exclude the Klaipėda Region
Klaipėda Region
The Klaipėda Region or Memel Territory was defined by the Treaty of Versailles in 1920 when it was put under the administration of the Council of Ambassadors...
after WW II
- Source: Statistics Lithuania
Average population (x 1000) Live births Deaths Natural change Crude birth rate (per 1000) Crude death rate (per 1000) Natural change (per 1000) 1945 2 520 60 392 35 201 25 191 24.0 14.0 10.0 1946 2 530 58 399 37 688 20 711 23.1 14.9 8.2 1947 2 540 59 680 39 716 19 964 23.5 15.6 7.9 1948 2 550 58 780 35 137 23 643 23.1 13.8 9.3 1949 2 560 63 034 32 049 30 985 24.6 12.5 12.1 1950 2 567 60 719 30 870 29 849 23.7 12.0 11.6 1951 2 569 58 504 29 693 28 811 22.8 11.6 11.2 1952 2 576 56 944 28 166 28 778 22.1 10.9 11.2 1953 2 590 52 610 27 118 25 492 20.3 10.5 9.8 1954 2 607 54 229 25 559 28 670 20.8 9.8 11.0 1955 2 629 55 525 24 138 31 387 21.1 9.2 11.9 1956 2 653 53 741 21 869 31 872 20.3 8.2 12.0 1957 2 681 56 223 23 361 32 862 21.0 8.7 12.3 1958 2 711 61 190 22 103 39 087 22.6 8.2 14.4 1959 2 744 62 241 24 688 37 553 22.7 9.0 13.7 1960 2 782 62 485 21 611 40 874 22.5 7.8 14.7 1961 2 828 62 775 23 365 39 410 22.2 8.3 13.9 1962 2 865 59 728 24 925 34 803 20.8 8.7 12.1 1963 2 893 57 024 23 112 33 912 19.7 8.0 11.7 1964 2 928 55 856 21 830 34 026 19.1 7.5 11.6 1965 2 967 53 818 23 467 30 351 18.1 7.9 10.2 1966 3 006 54 275 23 799 30 476 18.1 7.9 10.1 1967 3 045 53 806 24 571 29 235 17.7 8.1 9.6 1968 3 083 54 258 25 725 28 533 17.6 8.3 9.3 1969 3 115 54 263 27 156 27 107 17.4 8.7 8.7 1970 3 144 55 519 28 048 27 471 17.7 8.9 8.7 1971 3 179 56 044 26 972 29 072 17.6 8.5 9.1 1972 3 214 54 616 29 252 25 364 17.0 9.1 7.9 1973 3 244 51 944 29 160 22 784 16.0 9.0 7.0 1974 3 274 51 941 29 612 22 329 15.9 9.0 6.8 1975 3 302 51 766 31 265 20 501 15.7 9.5 6.2 1976 3 329 52 296 31 972 20 324 15.7 9.6 6.1 1977 3 355 52 166 32 932 19 234 15.5 9.8 5.7 1978 3 379 51 821 34 008 17 813 15.3 10.1 5.3 1979 3 398 51 937 34 897 17 040 15.3 10.3 5.0 1980 3 413 51 765 35 871 15 894 15.2 10.5 4.7 1981 3 433 52 249 35 579 16 670 15.2 10.4 4.9 1982 3 457 53 141 35 040 18 101 15.4 10.1 5.2 1983 3 485 57 589 36 451 21 138 16.5 10.5 6.1 1984 3 514 57 576 38 666 18 910 16.4 11.0 5.4 1985 3 545 58 454 39 169 19 285 16.5 11.0 5.4 1986 3 579 59 705 35 788 23 917 16.7 10.0 6.7 1987 3 616 59 360 36 917 22 443 16.4 10.2 6.2 1988 3 655 56 727 37 649 19 078 15.5 10.3 5.2 1989 3 684 55 782 38 150 17 632 15.1 10.3 4.8 1990 3 698 56 868 39 760 17 108 15.3 10.7 4.6 1991 3 704 56 219 41 013 15 206 15.2 11.1 4.1 1992 3 700 53 617 41 455 12 162 14.5 11.2 3.3 1993 3 683 47 464 46 107 1 357 12.9 12.5 0.4 1994 3 657 42 376 46 486 -4 110 11.6 12.7 -1.1 1995 3 629 41 195 45 306 -4 111 11.4 12.5 -1.1 1996 3 602 39 066 42 896 -3 830 10.8 11.9 -1.1 1997 3 575 37 812 41 143 -3 331 10.6 11.5 -0.9 1998 3 549 37 508 40 793 -3 285 10.6 11.5 -0.9 1999 3 524 36 415 40 003 -3 588 10.3 11.4 -1.0 2000 3 500 34 149 38 919 -4 770 9.8 11.1 -1.4 2001 3 481 31 546 40 399 -8 853 9.1 11.6 -2.5 2002 3 469 30 014 41 072 -11 058 8.7 11.8 -3.2 2003 3 455 30 598 40 990 -10 392 8.9 11.9 -3.0 2004 3 436 30 419 41 340 -10 921 8.9 12.0 -3.2 2005 3 414 30 541 43 799 -13 258 8.9 12.8 -3.9 2006 3 394 31 265 44 813 -13 548 9.2 13.2 -4.0 2007 3 376 32 154 45 589 -13 435 9.5 13.5 -4.0 2008 3 358 35 272 43 820 -8 548 10.5 13.0 -2.5 2009 3 339 36 682 42 032 -5 350 11.0 12.6 -1.6 2010 3 287 35 948 42 114 -6 166 10.9 12.8 -1.9
Literacy
Lithuania is one of the most literate countries in the world. The proportion of people aged 15 and over who can read and write is 99.6% according to the 2001 census. The proportion is the same for males and females. Primary, secondary, and high school education is free to all residents. Ten years of schooling is required. Tertiary educationTertiary education
Tertiary education, also referred to as third stage, third level, and post-secondary education, is the educational level following the completion of a school providing a secondary education, such as a high school, secondary school, university-preparatory school...
is almost free. Depending on grades, a student might receive a stipend or make a payment of 520 litas
Lithuanian litas
The Lithuanian litas is the currency of Lithuania. It is divided into 100 centų...
per semester. There are also small social stipends available for students with economic difficulties. In 2003 43,900 students were admitted to the 21 universities in Lithuania (11,100 of them to master programs). About 70% of high school graduates continue to study in universities or professional schools.
See also
- LithuaniaLithuaniaLithuania , officially the Republic of Lithuania is a country in Northern Europe, the biggest of the three Baltic states. It is situated along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea, whereby to the west lie Sweden and Denmark...
- Lithuanians in BrazilLithuanians in BrazilLithuanian-Brazilian, is a Brazilian person of full, partial, or predominantly Lithuanian ancestry, or a Lithuanian-born person residing in Brazil....
- Ethnic history of the Vilnius region
- Russians in Lithuania
- Aging of EuropeAging of EuropeThe Ageing of Europe, also known as the greying of Europe, is a demographic phenomenon in Europe characterized by a decrease in fertility, a decrease in mortality rate, and a higher life expectancy among Europeans.-Overall trends:...

