
Defining equation (physical chemistry)
Encyclopedia
In physical chemistry, there are numerous quantities associated with chemical compounds and reactions
; notably in terms of amounts of substance, activity or concentration of a substance, and the rate of reaction. This article uses SI units.
requires quantities
from core physics
, such as time
, volume
, temperature
, and pressure
. But the highly quantitative nature of physical chemistry, in a more specialized way than core physics; uses molar amounts of substance
rather than simply counting numbers, leads to the specialized definitions in this article. Core physics itself rarely uses the mole, except in areas overlapping thermodynamics
and chemistry
.
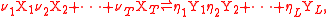
and the defining equation for the rate constant k applies to the simpler synthesis reaction (one product
only):

where:
i = dummy index labelling component i of reactant
mixture,
i = dummy index labelling component i of product
mixture,
Xi = component i of the reactant mixture,
Yj = reactant component j of the product mixture,
T = number of reactant components,
L = number of product components,
νi = stoichiometry
number for component i in product mixture,
ηj = stoichiometry number for component j in product mixture,
σi = order of reaction
for component i in reactant mixture.
The dummy indices on the substances X and Y label the components (arbitrary but fixed for calculation); they are not the numbers of each component molecules as in usual chemistry notation
.
The units for the chemical constants are unusual since they can vary depending on the stoichiometry of the reaction, and the number of reactant and product components. The general units for equilibrium constants can be determined by usual methods of dimensional analysis
. For the generality of the kinetics and equilibria units below, let the indices for the units be;
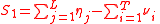
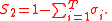
For the constant Kc;
Substitute the concentration units into the equation and simplify:,
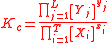
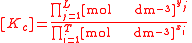
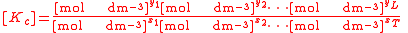
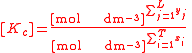
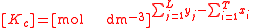 .
.
The procedure is exactly identical for Kp.
For the constant k
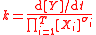
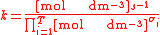
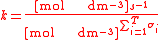
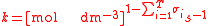
standard electrode potential
s is as follows. The redox reaction
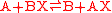
split into:
a reduction reaction
: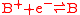
and an oxidation reaction
: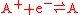
(written this way by convention) the electrode potential for the half reactions are written as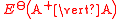 and
and 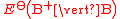 respectivley.
respectivley.
For the case of a metal-metal half electrode, letting M represent the metal
and z be its valency
, the half reaction takes the form of a reduction reaction:
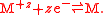
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
; notably in terms of amounts of substance, activity or concentration of a substance, and the rate of reaction. This article uses SI units.
Introduction
Theoretical chemistryTheoretical chemistry
Theoretical chemistry seeks to provide theories that explain chemical observations. Often, it uses mathematical and computational methods that, at times, require advanced knowledge. Quantum chemistry, the application of quantum mechanics to the understanding of valency, is a major component of...
requires quantities
Physical quantity
A physical quantity is a physical property of a phenomenon, body, or substance, that can be quantified by measurement.-Definition of a physical quantity:Formally, the International Vocabulary of Metrology, 3rd edition defines quantity as:...
from core physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, such as time
Time
Time is a part of the measuring system used to sequence events, to compare the durations of events and the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change such as the motions of objects....
, volume
Volume
Volume is the quantity of three-dimensional space enclosed by some closed boundary, for example, the space that a substance or shape occupies or contains....
, temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
, and pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
. But the highly quantitative nature of physical chemistry, in a more specialized way than core physics; uses molar amounts of substance
Amount of substance
Amount of substance is a standards-defined quantity that measures the size of an ensemble of elementary entities, such as atoms, molecules, electrons, and other particles. It is sometimes referred to as chemical amount. The International System of Units defines the amount of substance to be...
rather than simply counting numbers, leads to the specialized definitions in this article. Core physics itself rarely uses the mole, except in areas overlapping thermodynamics
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a physical science that studies the effects on material bodies, and on radiation in regions of space, of transfer of heat and of work done on or by the bodies or radiation...
and chemistry
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
.
General basic quantities
| Quantity (Common Name/s) | (Common) Symbol/s | SI Units | Dimension |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of molecules | N | dimensionless | dimensionless |
| Mass | m | kg | [M] |
| Number of moles, amount of substance, amount | n | mol | [N] |
| Volume of mixture or solvent, unless otherwise stated | V | m3 | [L]3 |
General derived quantities
| Quantity (Common Name/s) | (Common) Symbol/s | Defining Equation | SI Units | Dimension |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relative atomic mass of an element | Ar, A, mram | 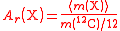 The average mass 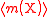 is the average of the T masses mi(X) corresponding the T isotopes of X (i is a dummy index labelling each isotope): is the average of the T masses mi(X) corresponding the T isotopes of X (i is a dummy index labelling each isotope):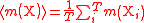 |
dimensionless | dimensionless |
| Relative formula mass of a compound, containing elements Xj | Mr, M, mrfm | 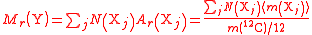 j = index labelling each element, N = number of atoms of each element Xi. |
dimensionless | dimensionless |
| Molar concentration, concentration, molarity of a component i in a mixture | ci, [Xi] | 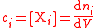 |
mol dm−3 = 10−3 mol m−3 | [N] [L]−3 |
| Molality of a component i in a mixture | mi, m(Xi) |  where solv = solvent (liquid solution). |
mol dm−3 kg = 10−3 mol m−3 | [N] [L]−3 |
| Mole fraction of a component i in a mixture | xi, x(Xi) | 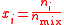 where Mix = mixture. |
dimensionless | dimensionless |
| Partial pressure Partial pressure In a mixture of ideal gases, each gas has a partial pressure which is the pressure which the gas would have if it alone occupied the volume. The total pressure of a gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of each individual gas in the mixture.... of a gaseous component i in a gas mixture |
pi, p(Xi) | 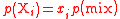 where mix = gaseous mixture. |
Pa = N m−2 | [M][T][L]−1 |
| Density Density The mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight... , mass concentration |
ρi, γi, ρ(Xi) | 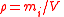 |
kg m−3 | [M] [L]3 |
| Number density Number density In physics, astronomy, and chemistry, number density is an intensive quantity used to describe the degree of concentration of countable objects in the three-dimensional physical space... , number concentration |
Ci, C(Xi) | 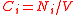 |
m- 3 | [L]- 3 |
| Volume fraction, volume concentration | ϕi, ϕ(Xi) | 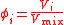 |
dimensionless | dimensionless |
| Mixing ratio Mixing ratio In chemistry and physics, the dimensionless mixing ratio is defined as the abundance of one component of a mixture relative to that of all other components... , mole ratio |
ri, r(Xi) | 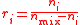 |
dimensionless | dimensionless |
| Mass fraction | wi, w(Xi) | 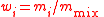 m(Xi) = mass of Xi |
dimensionless | dimensionless |
| Mixing ratio Mixing ratio In chemistry and physics, the dimensionless mixing ratio is defined as the abundance of one component of a mixture relative to that of all other components... , mass ratio |
ζi, ζ(Xi) | 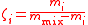 m(Xi) = mass of Xi |
dimensionless | dimensionless |
Kinetics and Equilibria
The defining formulae for the equilibrium constants Kc (all reactions) and Kp (gaseous reactions) apply to the general chemical reaction: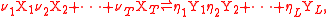
and the defining equation for the rate constant k applies to the simpler synthesis reaction (one product
Product (chemistry)
Product are formed during chemical reactions as reagents are consumed. Products have lower energy than the reagents and are produced during the reaction according to the second law of thermodynamics. The released energy comes from changes in chemical bonds between atoms in reagent molecules and...
only):

where:
i = dummy index labelling component i of reactant
Reagent
A reagent is a "substance or compound that is added to a system in order to bring about a chemical reaction, or added to see if a reaction occurs." Although the terms reactant and reagent are often used interchangeably, a reactant is less specifically a "substance that is consumed in the course of...
mixture,
i = dummy index labelling component i of product
Product (chemistry)
Product are formed during chemical reactions as reagents are consumed. Products have lower energy than the reagents and are produced during the reaction according to the second law of thermodynamics. The released energy comes from changes in chemical bonds between atoms in reagent molecules and...
mixture,
Xi = component i of the reactant mixture,
Yj = reactant component j of the product mixture,
T = number of reactant components,
L = number of product components,
νi = stoichiometry
Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry is a branch of chemistry that deals with the relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions. In a balanced chemical reaction, the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of whole numbers...
number for component i in product mixture,
ηj = stoichiometry number for component j in product mixture,
σi = order of reaction
Order of reaction
In chemical kinetics, the order of reaction with respect to certain reactant, is defined as the power to which its concentration term in the rate equation is raised .For example, given a chemical reaction 2A + B → C with a rate equation...
for component i in reactant mixture.
The dummy indices on the substances X and Y label the components (arbitrary but fixed for calculation); they are not the numbers of each component molecules as in usual chemistry notation
Chemical formula
A chemical formula or molecular formula is a way of expressing information about the atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound....
.
The units for the chemical constants are unusual since they can vary depending on the stoichiometry of the reaction, and the number of reactant and product components. The general units for equilibrium constants can be determined by usual methods of dimensional analysis
Dimensional analysis
In physics and all science, dimensional analysis is a tool to find or check relations among physical quantities by using their dimensions. The dimension of a physical quantity is the combination of the basic physical dimensions which describe it; for example, speed has the dimension length per...
. For the generality of the kinetics and equilibria units below, let the indices for the units be;
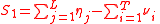
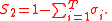
For the constant Kc;
Substitute the concentration units into the equation and simplify:,
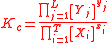
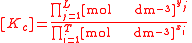
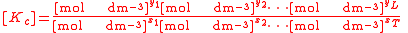
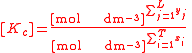
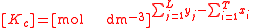 .
.The procedure is exactly identical for Kp.
For the constant k
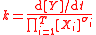
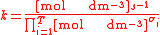
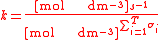
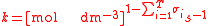
| Quantity (Common Name/s) | (Common) Symbol/s | Defining Equation | SI Units | Dimension |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reaction progress variable, extent of reaction Stoichiometry Stoichiometry is a branch of chemistry that deals with the relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions. In a balanced chemical reaction, the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of whole numbers... |
ξ | 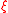 |
dimensionless | dimensionless |
| Stoichiometric coefficient Stoichiometry Stoichiometry is a branch of chemistry that deals with the relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions. In a balanced chemical reaction, the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of whole numbers... of a component i in a mixture, in reaction j (many reactions could occur at once) |
νi | 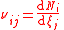 where Ni = number of molecules of component i. |
dimensionless | dimensionless |
| Chemical affinity Chemical affinity In chemical physics and physical chemistry, chemical affinity is the electronic property by which dissimilar chemical species are capable of forming chemical compounds... |
A | 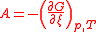 |
J | [M][L]2[T]−2 |
| Reaction rate Reaction rate The reaction rate or speed of reaction for a reactant or product in a particular reaction is intuitively defined as how fast or slow a reaction takes place... with respect to component i |
r, R | 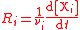 |
mol dm−3 s−1 = 10−3 mol m−3 s−1 | [N] [L]−3 [T]−1 |
| Activity Activity (chemistry) In chemical thermodynamics, activity is a measure of the “effective concentration” of a species in a mixture, meaning that the species' chemical potential depends on the activity of a real solution in the same way that it would depend on concentration for an ideal solution.By convention, activity... of a component i in a mixture |
ai | 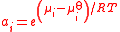 |
dimensionless | dimensionless |
| Mole fraction, molality, and molar concentration activity coefficient Activity coefficient An activity coefficient is a factor used in thermodynamics to account for deviations from ideal behaviour in a mixture of chemical substances. In an ideal mixture, the interactions between each pair of chemical species are the same and, as a result, properties of the mixtures can be expressed... s |
γxi for mole fraction, γmi for molality, γci for molar concentration. | Three coefficients are used; 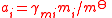 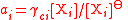 |
dimensionless | dimensionless |
| Rate constant | k | 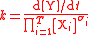 |
(mol dm−3)(S2) s−1 | ([N] [L]−3)(S2) [T]−1 |
| General equilibrium constant | Kc | 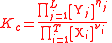 |
(mol dm−3)(S1) | ([N] [L]−3)(S1) |
| General thermodynamic activity constant | K0 | 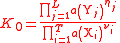 a(Xi) and a(Yj) are activities of Xi and Yj respectively. |
(mol dm−3)(S1) | ([N] [L]−3)(S1) |
| Equilibrium constant for gaseous reactions, using Partial pressures | Kp | 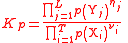 |
Pa(S1) | ([M] [L]−1 [T]−2)(S1) |
| Logarithm of any equilibrium constant | pKc | 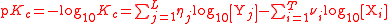 |
dimensionless | dimensionless |
| Logarithm of dissociation constant Dissociation constant In chemistry, biochemistry, and pharmacology, a dissociation constant is a specific type of equilibrium constant that measures the propensity of a larger object to separate reversibly into smaller components, as when a complex falls apart into its component molecules, or when a salt splits up into... |
pK | 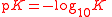 |
dimensionless | dimensionless |
| Logarithm of hydrogen ion (H+) activity, pH PH In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline... |
pH | 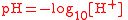 |
dimensionless | dimensionless |
| Logarithm of hydroxide ion (OH-) activity, pOH PH In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline... |
pOH | 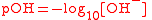 |
dimensionless | dimensionless |
General basic quantities
| Quantity (Common Name/s) | (Common) Symbol/s | SI Units | Dimension |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of molecules | N | dimensionless | dimensionless |
| Number of moles | n | mol | [N] |
| Temperature Temperature Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot... |
T | K | [Θ] |
| Heat Energy Heat In physics and thermodynamics, heat is energy transferred from one body, region, or thermodynamic system to another due to thermal contact or thermal radiation when the systems are at different temperatures. It is often described as one of the fundamental processes of energy transfer between... |
Q, q | J | [M][L]2[T]−2 |
| Latent Heat Latent heat Latent heat is the heat released or absorbed by a chemical substance or a thermodynamic system during a process that occurs without a change in temperature. A typical example is a change of state of matter, meaning a phase transition such as the melting of ice or the boiling of water. The term was... |
QL | J | [M][L]2[T]−2 |
| Entropy Entropy Entropy is a thermodynamic property that can be used to determine the energy available for useful work in a thermodynamic process, such as in energy conversion devices, engines, or machines. Such devices can only be driven by convertible energy, and have a theoretical maximum efficiency when... |
S | J K−1 | [M][L]2[T]−2 [Θ]−1 |
| Negentropy Negentropy The negentropy, also negative entropy or syntropy, of a living system is the entropy that it exports to keep its own entropy low; it lies at the intersection of entropy and life... |
J | J K−1 | [M][L]2[T]−2 [Θ]−1 |
General derived quantities
| Quantity (Common Name/s) | (Common) Symbol/s | Defining Equation | SI Units | Dimension |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Internal Energy Sum of all total energies which constitute the system |
U | 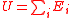 |
J | [M][L]2[T]−2 |
| Enthalpy Enthalpy Enthalpy is a measure of the total energy of a thermodynamic system. It includes the internal energy, which is the energy required to create a system, and the amount of energy required to make room for it by displacing its environment and establishing its volume and pressure.Enthalpy is a... |
H | 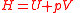 |
J | [M][L]2[T]−2 |
| Partition Function Partition function (statistical mechanics) Partition functions describe the statistical properties of a system in thermodynamic equilibrium. It is a function of temperature and other parameters, such as the volume enclosing a gas... |
Z | dimensionless | dimensionless | |
| Thermodynamic beta, Inverse temperature | β | 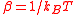 |
J−1 | [T]2[M]−1[L]−2 |
| Gibbs free energy Gibbs free energy In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy is a thermodynamic potential that measures the "useful" or process-initiating work obtainable from a thermodynamic system at a constant temperature and pressure... |
G | 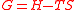 |
J | [M][L]2[T]−2 |
| Chemical potential Chemical potential Chemical potential, symbolized by μ, is a measure first described by the American engineer, chemist and mathematical physicist Josiah Willard Gibbs. It is the potential that a substance has to produce in order to alter a system... (of component i in a mixture) |
μi | 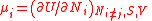 (Ni, S, V must all be constant) |
J | [M][L]2[T]−2 |
| Helmholtz free energy Helmholtz free energy In thermodynamics, the Helmholtz free energy is a thermodynamic potential that measures the “useful” work obtainable from a closed thermodynamic system at a constant temperature and volume... |
A, F | 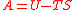 |
J | [M][L]2[T]−2 |
| Landau potential, Landau Free Energy |
Ω | 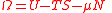 |
J | [M][L]2[T]−2 |
| Grand potential | ΦG | 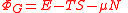 |
J | [M][L]2[T]−2 |
| Massieu Potential, Helmholtz free entropy Free entropy A thermodynamic free entropy is an entropic thermodynamic potential analogous to the free energy. Also known as a Massieu, Planck, or Massieu-Planck potentials , or free information. In statistical mechanics, free entropies frequently appear as the logarithm of a partition function... |
Φ | 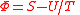 |
J K−1 | [M][L]2[T]−2 [Θ]−1 |
| Planck potential, Gibbs free entropy Free entropy A thermodynamic free entropy is an entropic thermodynamic potential analogous to the free energy. Also known as a Massieu, Planck, or Massieu-Planck potentials , or free information. In statistical mechanics, free entropies frequently appear as the logarithm of a partition function... |
Ξ | 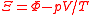 |
J K−1 | [M][L]2[T]−2 [Θ]−1 |
Electrochemistry
Notation for half-reactionHalf-reaction
A half reaction is either the oxidation or reduction reaction component of a redox reaction. A half reaction is obtained by considering the change in oxidation states of individual substances involved in the redox reaction.-Example:...
standard electrode potential
Standard electrode potential
In electrochemistry, the standard electrode potential, abbreviated E° or E , is the measure of individual potential of a reversible electrode at standard state, which is with solutes at an effective concentration of 1 mol dm−3, and gases at a pressure of 1 atm...
s is as follows. The redox reaction
Redox
Redox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed....
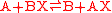
split into:
a reduction reaction
Redox
Redox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed....
:
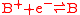
and an oxidation reaction
Redox
Redox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed....
:
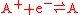
(written this way by convention) the electrode potential for the half reactions are written as
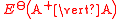 and
and 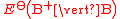 respectivley.
respectivley.For the case of a metal-metal half electrode, letting M represent the metal
Metal
A metal , is an element, compound, or alloy that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat. Metals are usually malleable and shiny, that is they reflect most of incident light...
and z be its valency
Valence (chemistry)
In chemistry, valence, also known as valency or valence number, is a measure of the number of bonds formed by an atom of a given element. "Valence" can be defined as the number of valence bonds...
, the half reaction takes the form of a reduction reaction:
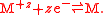
| Quantity (Common Name/s) | (Common) Symbol/s | Defining Equation | SI Units | Dimension |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard EMF of an electrode Standard electrode potential In electrochemistry, the standard electrode potential, abbreviated E° or E , is the measure of individual potential of a reversible electrode at standard state, which is with solutes at an effective concentration of 1 mol dm−3, and gases at a pressure of 1 atm... |
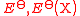 |
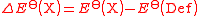 where Def is the standard electrode of definition, defined to have zero potential. The chosen one Standard hydrogen electrode The standard hydrogen electrode , is a redox electrode which forms the basis of the thermodynamic scale of oxidation-reduction potentials... is hydrogen Hydrogen Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly... :  |
V | [M][L]2[I][T]−1 |
| Standard EMF of an electrochemical cell Electrochemical cell An electrochemical cell is a device capable of either deriving electrical energy from chemical reactions, or facilitating chemical reactions through the introduction of electrical energy. A common example of an electrochemical cell is a standard 1.5-volt "battery"... |
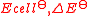 |
 where Cat is the cathode Cathode A cathode is an electrode through which electric current flows out of a polarized electrical device. Mnemonic: CCD .Cathode polarity is not always negative... substance and An is the anode Anode An anode is an electrode through which electric current flows into a polarized electrical device. Mnemonic: ACID .... substance. |
V | [M][L]2[I][T]−1 |
| Ionic strength Ionic strength The ionic strength of a solution is a measure of the concentration of ions in that solution. Ionic compounds, when dissolved in water, dissociate into ions. The total electrolyte concentration in solution will affect important properties such as the dissociation or the solubility of different salts... |
I | Two definitions are used, one using molarity concentration,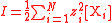 and one using molality, 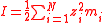 The sum is taken over all ions in the solution Solution In chemistry, a solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of only one phase. In such a mixture, a solute is dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent. The solvent does the dissolving.- Types of solutions :... . |
mol dm−3 or mol dm−3 kg−1 | [N] [L]−3 [M]−1 |
| Electrochemical potential (of component i in a mixture) | 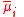 |
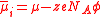 φ = local electrostatic potential Electric potential In classical electromagnetism, the electric potential at a point within a defined space is equal to the electric potential energy at that location divided by the charge there... (see below also) zi = valency (charge) of the ion i |
J | [M][L]2[T]−2 |
Quantum chemistry
| Quantity (Common Name/s) | (Common) Symbol/s | Defining Equation | SI Units | Dimension |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electronegativity Electronegativity Electronegativity, symbol χ , is a chemical property that describes the tendency of an atom or a functional group to attract electrons towards itself. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance that its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus... |
χ | Pauling (difference between atoms A and B):  Mulliken (absolute):  Energies (in eV Electronvolt In physics, the electron volt is a unit of energy equal to approximately joule . By definition, it is equal to the amount of kinetic energy gained by a single unbound electron when it accelerates through an electric potential difference of one volt... ) Ed = Bond dissociation EI = Ionization EEA = Electron affinity |
dimensionless | dimensionless |
Sources
- Physical chemistry, P.W. Atkins, Oxford University Press, 1978, ISBN 0 19 855148 7
- Chemistry, Matter and the Universe, R.E. Dickerson, I. Geis, W.A. Benjamin Inc. (USA), 1976, ISBN 0 8053 2369 4
- http://goldbook.iupac.org/index.html
- Chemical thermodynamics, D.J.G. Ives, University Cchemistry Series, Macdonald Technical and Scientific co. ISBN 0356 03736 3.

