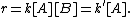Order of reaction
Encyclopedia
In chemical kinetics
, the order of reaction with respect to certain reactant, is defined as the power
to which its concentration
term in the rate equation
is raised .
For example, given a chemical reaction 2A + B → C with a rate equation
the reaction order with respect to A would be 2 and with respect to B would be 1, the total reaction order would be 2 + 1 = 3. It is not necessary that the order of a reaction be a whole number – zero and fractional values of order are possible – but they tend to be integers. Reaction orders can be determined only by experiment
. Their knowledge allows conclusions about the reaction mechanism
.
The reaction order is not necessarily related to the stoichiometry
of the reaction, unless the reaction is elementary
. Complex reactions may or may not have reaction orders equal to their stoichiometric coefficients
For example :
Reactions can also have an undefined reaction order with respect to a reactant, for example one can not talk about reaction order in the rate equation found when dealing with a bimolecular reaction between adsorbed molecules
:
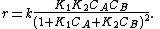
If the concentration of one of the reactants remains constant (because it is a catalyst or it is in great excess with respect to the other reactants) its concentration can be included in the rate constant, obtaining a pseudo constant: if B is the reactant whose concentration is constant then
The second-order rate equation has been reduced to a pseudo-first-order rate equation. This makes the treatment to obtain an integrated rate equation much easier.
Zero-order reactions are often seen for thermal chemical decomposition
s where the reaction rate
is independent of the concentration of the reactant (changing the concentration has no effect on the speed of the reaction):
In broken-order reactions the order is a non-integer typical of reactions with a complex reaction mechanism
. For example the chemical decomposition
of ethanal into methane
and carbon monoxide
proceeds with an order of 1.5 with respect to ethanal. The decomposition of phosgene
to carbon monoxide and chlorine
has order 1 with respect to phosgene itself and order 0.5 with respect to chlorine.
In a mixed-order reaction the order of a reaction changes in the course of a reaction as a result of changing variables such as pH
. An example is the oxidation of an alcohol
to a ketone
by a ruthenate (RuO42−) and a hexacyanoferrate, the latter serving as the sacrificial catalyst converting Ru(IV) back to Ru(VI) : the disappearing-rate of the ferrate is zero-order with respect to the ferrate at the onset of the reaction (when its concentration is high and the ruthenium catalyst is quickly regenerated) but changes to first-order when its concentration decreases.
Negative-order reactions are rare, for example the conversion of ozone
(order 2) to oxygen
(order −1).
Chemical kinetics
Chemical kinetics, also known as reaction kinetics, is the study of rates of chemical processes. Chemical kinetics includes investigations of how different experimental conditions can influence the speed of a chemical reaction and yield information about the reaction's mechanism and transition...
, the order of reaction with respect to certain reactant, is defined as the power
Exponentiation
Exponentiation is a mathematical operation, written as an, involving two numbers, the base a and the exponent n...
to which its concentration
Concentration
In chemistry, concentration is defined as the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Four types can be distinguished: mass concentration, molar concentration, number concentration, and volume concentration...
term in the rate equation
Rate equation
The rate law or rate equation for a chemical reaction is an equation that links the reaction rate with concentrations or pressures of reactants and constant parameters . To determine the rate equation for a particular system one combines the reaction rate with a mass balance for the system...
is raised .
For example, given a chemical reaction 2A + B → C with a rate equation
- r = k[A]2[B]1
the reaction order with respect to A would be 2 and with respect to B would be 1, the total reaction order would be 2 + 1 = 3. It is not necessary that the order of a reaction be a whole number – zero and fractional values of order are possible – but they tend to be integers. Reaction orders can be determined only by experiment
Experiment
An experiment is a methodical procedure carried out with the goal of verifying, falsifying, or establishing the validity of a hypothesis. Experiments vary greatly in their goal and scale, but always rely on repeatable procedure and logical analysis of the results...
. Their knowledge allows conclusions about the reaction mechanism
Reaction mechanism
In chemistry, a reaction mechanism is the step by step sequence of elementary reactions by which overall chemical change occurs.Although only the net chemical change is directly observable for most chemical reactions, experiments can often be designed that suggest the possible sequence of steps in...
.
The reaction order is not necessarily related to the stoichiometry
Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry is a branch of chemistry that deals with the relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions. In a balanced chemical reaction, the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of whole numbers...
of the reaction, unless the reaction is elementary
Elementary reaction
An elementary reaction is a chemical reaction in which one or more of the chemical species react directly to form products in a single reaction step and with a single transition state....
. Complex reactions may or may not have reaction orders equal to their stoichiometric coefficients
For example :
- The alkaline hydrolysisHydrolysisHydrolysis is a chemical reaction during which molecules of water are split into hydrogen cations and hydroxide anions in the process of a chemical mechanism. It is the type of reaction that is used to break down certain polymers, especially those made by condensation polymerization...
of ethyl acetateEthyl acetateEthyl acetate is the organic compound with the formula CH3COOCH2CH3. This colorless liquid has a characteristic sweet smell and is used in glues, nail polish removers, and cigarettes...
is a complex reaction:
-
- CH3COOC2H5 + OH− → CH3COO− + C2H5OH.
- It has the following rate equation: r = k[CH3COOC2H5][OH−]
- The rate equation for imidazoleImidazoleImidazole is an organic compound with the formula C3H4N2. This aromatic heterocyclic is a diazole and is classified as an alkaloid. Imidazole refers to the parent compound, whereas imidazoles are a class of heterocycles with similar ring structure, but varying substituents...
catalyzed hydrolysis is
- r = k[imidazole][CH3COOC2H5]
- The rate equation for imidazole
- although no imidazole is present in the stoichiometric chemical equationChemical equationA chemical equation is the symbolic representation of a chemical reaction where the reactant entities are given on the left hand side and the product entities on the right hand side. The coefficients next to the symbols and formulae of entities are the absolute values of the stoichiometric numbers...
- In the reaction of aryldiazonium ions with nucleophiles in aqueous solution ArN2+ + X− → ArX + N2 the rate equation is
- r = k[ArN2+]
Reactions can also have an undefined reaction order with respect to a reactant, for example one can not talk about reaction order in the rate equation found when dealing with a bimolecular reaction between adsorbed molecules
Reactions on surfaces
By reactions on surfaces it is understood reactions in which at least one of the steps of the reaction mechanism is the adsorption of one or more reactants...
:
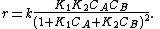
If the concentration of one of the reactants remains constant (because it is a catalyst or it is in great excess with respect to the other reactants) its concentration can be included in the rate constant, obtaining a pseudo constant: if B is the reactant whose concentration is constant then
The second-order rate equation has been reduced to a pseudo-first-order rate equation. This makes the treatment to obtain an integrated rate equation much easier.
Zero-order reactions are often seen for thermal chemical decomposition
Chemical decomposition
Chemical decomposition, analysis or breakdown is the separation of a chemical compound into elements or simpler compounds. It is sometimes defined as the exact opposite of a chemical synthesis. Chemical decomposition is often an undesired chemical reaction...
s where the reaction rate
Reaction rate
The reaction rate or speed of reaction for a reactant or product in a particular reaction is intuitively defined as how fast or slow a reaction takes place...
is independent of the concentration of the reactant (changing the concentration has no effect on the speed of the reaction):
In broken-order reactions the order is a non-integer typical of reactions with a complex reaction mechanism
Reaction mechanism
In chemistry, a reaction mechanism is the step by step sequence of elementary reactions by which overall chemical change occurs.Although only the net chemical change is directly observable for most chemical reactions, experiments can often be designed that suggest the possible sequence of steps in...
. For example the chemical decomposition
Chemical decomposition
Chemical decomposition, analysis or breakdown is the separation of a chemical compound into elements or simpler compounds. It is sometimes defined as the exact opposite of a chemical synthesis. Chemical decomposition is often an undesired chemical reaction...
of ethanal into methane
Methane
Methane is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is the simplest alkane, the principal component of natural gas, and probably the most abundant organic compound on earth. The relative abundance of methane makes it an attractive fuel...
and carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide , also called carbonous oxide, is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that is slightly lighter than air. It is highly toxic to humans and animals in higher quantities, although it is also produced in normal animal metabolism in low quantities, and is thought to have some normal...
proceeds with an order of 1.5 with respect to ethanal. The decomposition of phosgene
Phosgene
Phosgene is the chemical compound with the formula COCl2. This colorless gas gained infamy as a chemical weapon during World War I. It is also a valued industrial reagent and building block in synthesis of pharmaceuticals and other organic compounds. In low concentrations, its odor resembles...
to carbon monoxide and chlorine
Chlorine
Chlorine is the chemical element with atomic number 17 and symbol Cl. It is the second lightest halogen, found in the periodic table in group 17. The element forms diatomic molecules under standard conditions, called dichlorine...
has order 1 with respect to phosgene itself and order 0.5 with respect to chlorine.
In a mixed-order reaction the order of a reaction changes in the course of a reaction as a result of changing variables such as pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
. An example is the oxidation of an alcohol
Alcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
to a ketone
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure RCR', where R and R' can be a variety of atoms and groups of atoms. It features a carbonyl group bonded to two other carbon atoms. Many ketones are known and many are of great importance in industry and in biology...
by a ruthenate (RuO42−) and a hexacyanoferrate, the latter serving as the sacrificial catalyst converting Ru(IV) back to Ru(VI) : the disappearing-rate of the ferrate is zero-order with respect to the ferrate at the onset of the reaction (when its concentration is high and the ruthenium catalyst is quickly regenerated) but changes to first-order when its concentration decreases.
Negative-order reactions are rare, for example the conversion of ozone
Ozone
Ozone , or trioxygen, is a triatomic molecule, consisting of three oxygen atoms. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope...
(order 2) to oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
(order −1).
External links
- Chemical kinetics, reaction rate, and order (needs flash player)
- Reaction kinetics, examples of important rate laws (lecture with audio).
- Rates of Reaction