
Christian Brothers University
Encyclopedia
Christian Brothers University is the oldest collegiate degree-granting institution in the city of Memphis
. The university is run by the Christian Brothers
, a Roman Catholic religious order founded by St. John Baptist de la Salle
, the patron saint
of teachers. It is located in Midtown Memphis near Liberty Bowl Memorial Stadium
.
 Christian Brothers College was founded November 19, 1871, by members of the De La Salle Christian Brothers. The Brothers came to Memphis at the request of the people and clergy
Christian Brothers College was founded November 19, 1871, by members of the De La Salle Christian Brothers. The Brothers came to Memphis at the request of the people and clergy
of the city, after more than a decade of efforts to persuade the Brothers to open a college in Memphis.
Christian Brothers University traces its origins to priest and educational innovator, St. John Baptist de la Salle. De la Salle began a system of Christian
schools in which teachers assist parents in the educational, ethical, and religious formation of their children. To continue his spiritual
and pedagogical
vision, de la Salle founded the Institute of the Brothers of the Christian Schools, known today as the De La Salle Christian Brothers.
Today, the spirit and tradition of the Lasallian community thrives in 81 countries and in more than 1,000 educational institutions. Over 4,000 De La Salle Christian Brothers, along with 56,000 Lasallian lay
colleagues (such as Lasallian Volunteers), serve over 750,000 students and their families worldwide. In the United States, there are over 100 Lasallian educational institutions.
Christian Brothers College officially became Christian Brothers University in June 1990.
Brother Maurelian was appointed the first president. His two terms as president totalled 33 years. During his presidency, the Brothers purchased the 612 Adams Street building, which housed the college until 1940 when the college moved to its present location at Central Avenue and East Parkway South.
Functioning as a combined elementary school, high school (now Christian Brothers High School
), and college, Christian Brothers College granted high school diploma
s as well as Bachelor's
and Master's Degrees
until 1915, when the college division was suspended. Elementary classes were dropped in 1922, and the institution operated as only a high school for 18 years. Reopened in 1940 as a junior college
, the college began granting Associate's Degrees
in 1942.
) also claims a founding year of 1871, but it was an elementary and secondary school at the time. The city's largest university, The University of Memphis
, was not founded until 1912. Although Rhodes College
claims a founding date of 1848, it did not actually move to Memphis until 1925, some 54 years after the founding of Christian Brothers, making it the youngest of the major colleges in Memphis. Rhodes' original 1848 campus became Austin Peay State University
, and Rhodes became "Southwestern at Memphis."
. De la Salle began a system of Christian
schools in which teachers assist parents in the educational, ethical, and religious formation of their children. To continue his spiritual
and pedagogical
vision, de la Salle founded the Institute of the Brothers of the Christian Schools, known today as the De La Salle Christian Brothers.
Today, the spirit and tradition of the Lasallian community thrives in 81 countries and in more than 1,000 educational institutions. Over 4,000 De La Salle Christian Brothers, along with 56,000 Lasallian lay
colleagues, serve over 750,000 students and their families worldwide. In the United States, there are over 100 Lasallian educational institutions.
The university currently has a lay
interim president following the fatal car accident of former president Brother Vincent Malham in 2008.
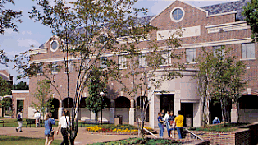 In 1953, the decision was made to expand the community college into a four-year institution to better serve the needs of the community. The four-year curriculum began with degrees in Business Administration and Electrical Engineering
In 1953, the decision was made to expand the community college into a four-year institution to better serve the needs of the community. The four-year curriculum began with degrees in Business Administration and Electrical Engineering
, with the first graduates in recent times receiving their degrees in 1955.
The curriculum was soon expanded to meet the needs for new programs in the fields of Mechanical Engineering
and Chemistry
. The following degree programs were later added: Biology
, Civil Engineering
, Mathematics
, English
, Physics
, Chemical Engineering
, History
, Psychology
, Natural Science
, Engineering Physics
, Computer Science
, and Religion and Philosophy. Teacher preparation programs in secondary education were added in 1969. An accelerated evening program offering a degree in Business Administration was added in 1978 to meet the needs of the adult student, and the Applied Psychology
degree was added in 1999. In Fall 2007, CBU introduced its Bachelor of Fine Arts
degree.
Programs at the graduate level were reinstated in 1987 with the Master's program in Telecommunication and Information Systems. The Master of Business Administration
and the Master in Engineering Management
were added in 1989. A Master of Education
was added in 1997, and the Master of Arts in Teaching
and Master of Science in Educational Leadership were offered beginning in 2001. The Master of Arts in Executive Leadership was added in 2005.
When another Catholic college in Memphis (the all-female Siena College
) closed, Christian Brothers University became coeducation
al in 1970. Currently, women comprise approximately 55% of the student body.
Christian Brothers College officially became Christian Brothers University in June 1990.
, Brazil
, China
, England
, France
, Ireland
, Italy
, Mexico
, South Africa
, and Spain
. Additionally, CBU offers study abroad courses during spring and fall vacations. Upcoming courses include travel in England, France, Italy, Mexico, and Uganda
. Medical missions to Haiti
are available but have been postponed for the present. Study abroad is optional for students but is required for completion of the global studies minor.
. 51% of students are White-American
(non-Hispanic), 33% are African-American
(non-Hispanic), 5% are Asian-American
or Pacific Islander-American
, 2% are Hispanic-American, and 2% are international student
s. 6% of students have an unknown ethnicity. Students hail from more than 28 states and 14 countries.
Although CBU is a Catholic
university, only 23% of students are Catholic. Religious observances are not required, and 32 different faiths are represented in the student body.
Notably, 99% of Christian Brothers University undergraduates receive financial aid, broken down as institutional grants (98%), state/local grants (68%), federal grants (29%), and student loans (58%).
There are 110 full-time faculty members. All of them hold at least master's degree
s, and 89% hold doctorate
s or terminal degree
s. No courses are taught by teaching assistant
s. The student to faculty ratio is 12 to 1. School of Sciences graduating classes from 2002 to 2006 boasted a 91% acceptance rate for medical school, and an 87% acceptance for pharmacy school.
, four miles (6 km) east of Downtown
.
Kenrick Hall is the oldest building on campus, constructed in 1939 as the original Christian Brothers High School
.
The university's architecture follows the Georgian style
popular at the time of the campus' relocation to East Parkway. Arch-covered walkways traverse the main campus, allowing students and faculty to get to most buildings shaded from the weather. The campus is enclosed by an iron fence with brick accents with entrances on East Parkway South, Central Avenue, and Avery Avenue.
in the city of Memphis.
The arena was fully renovated in 2004 and has a capacity of 1,000.
. Buccaneer teams include baseball, basketball, cross country, golf, and soccer. Lady Buccaneer teams include basketball, cross country, golf, soccer, softball, and volleyball.
The Lady Buccaneers and Buccaneers have won multiple athletic competitions, including the 2002 Division II women's soccer championship
and the 2008 GSC men's basketball championship.
Campus Greek councils include the Interfraternity Council
(IFC), the Panhellenic Council
(NPC), and the National Pan-Hellenic Council
(NPHC).
exist at CBU to recognize excellence in academia and leadership. Active honor societies and their specialties include: Alpha Chi (general academic), Beta Beta Beta (biology), the Order of Omega
(fraternity and sorority members), Phi Alpha Theta
(history), Psi Chi
(psychology), Sigma Tau Delta
(English), Alpha Psi Omega
(theatre), and Tau Beta Pi
(engineering).
Professional organizations include: American Institute of Chemical Engineers
, American Society of Civil Engineers
, American Society of Mechanical Engineers
, Institute of Electrical Engineers, Society of Physics Students
, and the Student Affiliates of the American Chemical Society
.
s to compete at annual Deep South regional conferences for student chapters of the American Society of Civil Engineers
. These canoes must be able to float and support the weight of several students as they will be raced.
Competition organized by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
. The 2008 competition was held in Huntsville, Alabama
.
.

letters and symbols.
Painting The Rock has its own rules of etiquette. The Rock can only be painted between sunset and sunrise. Any group currently next to The Rock is guarding it, and it cannot be taken by another group at that time (although the occasional fight has happened in the past). The Rock can be painted several times in one night; however, it is a gentlemanly tradition among the fraternities not to paint over a sorority Rock for at least two to three days.
The term taking The Rock refers to adding a completely new coat of paint whereas tagging is just spray painting marks on top of someone else's paint, typically to add the names of the painters or insults to the current holder of The Rock.
Older Rock traditions (until the 1970s) include paint fights between upperclassmen and lowerclassmen the first few days of school, but these have been discontinued.
----

Memphis, Tennessee
Memphis is a city in the southwestern corner of the U.S. state of Tennessee, and the county seat of Shelby County. The city is located on the 4th Chickasaw Bluff, south of the confluence of the Wolf and Mississippi rivers....
. The university is run by the Christian Brothers
Institute of the Brothers of the Christian Schools
The Institute of the Brothers of the Christian Schools is a Roman Catholic religious teaching congregation, founded in France by Saint Jean-Baptiste de la Salle and now based in Rome...
, a Roman Catholic religious order founded by St. John Baptist de la Salle
Jean-Baptiste de La Salle
Saint Jean-Baptiste de La Salle or John Baptist de La Salle was a priest, educational reformer, and founder of Institute of the Brothers of the Christian Schools...
, the patron saint
Patron saint
A patron saint is a saint who is regarded as the intercessor and advocate in heaven of a nation, place, craft, activity, class, clan, family, or person...
of teachers. It is located in Midtown Memphis near Liberty Bowl Memorial Stadium
Liberty Bowl Memorial Stadium
Liberty Bowl Memorial Stadium is a football stadium, located at the Mid-South Fairgrounds, in Midtown Memphis, Tennessee, United States. The stadium is the site of the annual AutoZone Liberty Bowl, and is the home field of the University of Memphis Tigers football team...
.
History

Clergy
Clergy is the generic term used to describe the formal religious leadership within a given religion. A clergyman, churchman or cleric is a member of the clergy, especially one who is a priest, preacher, pastor, or other religious professional....
of the city, after more than a decade of efforts to persuade the Brothers to open a college in Memphis.
Christian Brothers University traces its origins to priest and educational innovator, St. John Baptist de la Salle. De la Salle began a system of Christian
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
schools in which teachers assist parents in the educational, ethical, and religious formation of their children. To continue his spiritual
Spirituality
Spirituality can refer to an ultimate or an alleged immaterial reality; an inner path enabling a person to discover the essence of his/her being; or the “deepest values and meanings by which people live.” Spiritual practices, including meditation, prayer and contemplation, are intended to develop...
and pedagogical
Pedagogy
Pedagogy is the study of being a teacher or the process of teaching. The term generally refers to strategies of instruction, or a style of instruction....
vision, de la Salle founded the Institute of the Brothers of the Christian Schools, known today as the De La Salle Christian Brothers.
Today, the spirit and tradition of the Lasallian community thrives in 81 countries and in more than 1,000 educational institutions. Over 4,000 De La Salle Christian Brothers, along with 56,000 Lasallian lay
Laity
In religious organizations, the laity comprises all people who are not in the clergy. A person who is a member of a religious order who is not ordained legitimate clergy is considered as a member of the laity, even though they are members of a religious order .In the past in Christian cultures, the...
colleagues (such as Lasallian Volunteers), serve over 750,000 students and their families worldwide. In the United States, there are over 100 Lasallian educational institutions.
Christian Brothers College officially became Christian Brothers University in June 1990.
Founding
After more than a decade of efforts to persuade the Brothers to open a college in Memphis, Christian Brothers College was founded in 1871.Brother Maurelian was appointed the first president. His two terms as president totalled 33 years. During his presidency, the Brothers purchased the 612 Adams Street building, which housed the college until 1940 when the college moved to its present location at Central Avenue and East Parkway South.
Functioning as a combined elementary school, high school (now Christian Brothers High School
Christian Brothers High School (Memphis, Tennessee)
Christian Brothers High School ' is located in Memphis, Tennessee, at 5900 Walnut Grove Rd. It is an all-male college preparatory school and Catholic school that has a strong Lasallian tradition that can be traced back to John Baptist de La Salle...
), and college, Christian Brothers College granted high school diploma
High school diploma
A high school diploma is a diploma awarded for the completion of high school. In the United States and Canada, it is considered the minimum education required for government jobs and higher education. An equivalent is the GED.-Past diploma styles:...
s as well as Bachelor's
Bachelor's degree
A bachelor's degree is usually an academic degree awarded for an undergraduate course or major that generally lasts for three or four years, but can range anywhere from two to six years depending on the region of the world...
and Master's Degrees
Master's degree
A master's is an academic degree granted to individuals who have undergone study demonstrating a mastery or high-order overview of a specific field of study or area of professional practice...
until 1915, when the college division was suspended. Elementary classes were dropped in 1922, and the institution operated as only a high school for 18 years. Reopened in 1940 as a junior college
Junior college
The term junior college refers to different educational institutions in different countries.-India:In India, most states provide schooling through 12th grade...
, the college began granting Associate's Degrees
Associate's degree
An associate degree is an undergraduate academic degree awarded by community colleges, junior colleges, technical colleges, and bachelor's degree-granting colleges and universities upon completion of a course of study usually lasting two years...
in 1942.
Oldest degree-granting institution in Memphis
Christian Brothers awarded the first post-secondary degree in the city in 1875. LeMoyne College (one of the two constituent parts of present-day LeMoyne-Owen CollegeLeMoyne-Owen College
-External links:*...
) also claims a founding year of 1871, but it was an elementary and secondary school at the time. The city's largest university, The University of Memphis
University of Memphis
The University of Memphis is an American public research university located in the Normal Station neighborhood of Memphis, Tennessee and is the flagship public research university of the Tennessee Board of Regents system....
, was not founded until 1912. Although Rhodes College
Rhodes College
Rhodes College is a private, predominantly undergraduate, liberal arts college located in Memphis, Tennessee, USA. Originally founded by freemasons in 1848, Rhodes became affiliated with the Presbyterian Church in 1855. Rhodes enrolls approximately 1,700 students pursuing bachelor's and master's...
claims a founding date of 1848, it did not actually move to Memphis until 1925, some 54 years after the founding of Christian Brothers, making it the youngest of the major colleges in Memphis. Rhodes' original 1848 campus became Austin Peay State University
Austin Peay State University
Austin Peay State University is a four-year public university located in Clarksville, Tennessee, and operated by the Tennessee Board of Regents. It is accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools .-History:...
, and Rhodes became "Southwestern at Memphis."
Lasallian tradition
Christian Brothers University traces its origins to priest and educational innovator, St. John Baptist de la SalleJean-Baptiste de La Salle
Saint Jean-Baptiste de La Salle or John Baptist de La Salle was a priest, educational reformer, and founder of Institute of the Brothers of the Christian Schools...
. De la Salle began a system of Christian
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
schools in which teachers assist parents in the educational, ethical, and religious formation of their children. To continue his spiritual
Spirituality
Spirituality can refer to an ultimate or an alleged immaterial reality; an inner path enabling a person to discover the essence of his/her being; or the “deepest values and meanings by which people live.” Spiritual practices, including meditation, prayer and contemplation, are intended to develop...
and pedagogical
Pedagogy
Pedagogy is the study of being a teacher or the process of teaching. The term generally refers to strategies of instruction, or a style of instruction....
vision, de la Salle founded the Institute of the Brothers of the Christian Schools, known today as the De La Salle Christian Brothers.
Today, the spirit and tradition of the Lasallian community thrives in 81 countries and in more than 1,000 educational institutions. Over 4,000 De La Salle Christian Brothers, along with 56,000 Lasallian lay
Laity
In religious organizations, the laity comprises all people who are not in the clergy. A person who is a member of a religious order who is not ordained legitimate clergy is considered as a member of the laity, even though they are members of a religious order .In the past in Christian cultures, the...
colleagues, serve over 750,000 students and their families worldwide. In the United States, there are over 100 Lasallian educational institutions.
The university currently has a lay
Laity
In religious organizations, the laity comprises all people who are not in the clergy. A person who is a member of a religious order who is not ordained legitimate clergy is considered as a member of the laity, even though they are members of a religious order .In the past in Christian cultures, the...
interim president following the fatal car accident of former president Brother Vincent Malham in 2008.
Higher education
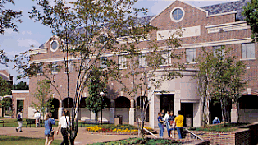
Electrical engineering
Electrical engineering is a field of engineering that generally deals with the study and application of electricity, electronics and electromagnetism. The field first became an identifiable occupation in the late nineteenth century after commercialization of the electric telegraph and electrical...
, with the first graduates in recent times receiving their degrees in 1955.
The curriculum was soon expanded to meet the needs for new programs in the fields of Mechanical Engineering
Mechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering is a discipline of engineering that applies the principles of physics and materials science for analysis, design, manufacturing, and maintenance of mechanical systems. It is the branch of engineering that involves the production and usage of heat and mechanical power for the...
and Chemistry
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
. The following degree programs were later added: Biology
Biology
Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Biology is a vast subject containing many subdivisions, topics, and disciplines...
, Civil Engineering
Civil engineering
Civil engineering is a professional engineering discipline that deals with the design, construction, and maintenance of the physical and naturally built environment, including works like roads, bridges, canals, dams, and buildings...
, Mathematics
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, English
English studies
English studies is an academic discipline that includes the study of literatures written in the English language , English linguistics English studies is an academic discipline that includes the study of literatures written in the English language (including literatures from the U.K., U.S.,...
, Physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, Chemical Engineering
Chemical engineering
Chemical engineering is the branch of engineering that deals with physical science , and life sciences with mathematics and economics, to the process of converting raw materials or chemicals into more useful or valuable forms...
, History
History
History is the discovery, collection, organization, and presentation of information about past events. History can also mean the period of time after writing was invented. Scholars who write about history are called historians...
, Psychology
Psychology
Psychology is the study of the mind and behavior. Its immediate goal is to understand individuals and groups by both establishing general principles and researching specific cases. For many, the ultimate goal of psychology is to benefit society...
, Natural Science
Natural science
The natural sciences are branches of science that seek to elucidate the rules that govern the natural world by using empirical and scientific methods...
, Engineering Physics
Engineering physics
Engineering physics is the study of the combined disciplines of physics, engineering and mathematics in order to develop an understanding of the interrelationships of these three disciplines. Fundamental physics is combined with problem solving and engineering skills, which then has broad...
, Computer Science
Computer science
Computer science or computing science is the study of the theoretical foundations of information and computation and of practical techniques for their implementation and application in computer systems...
, and Religion and Philosophy. Teacher preparation programs in secondary education were added in 1969. An accelerated evening program offering a degree in Business Administration was added in 1978 to meet the needs of the adult student, and the Applied Psychology
Applied psychology
The basic premise of applied psychology is the use of psychological principles and theories to overcome problems in other areas, such as mental health, business management, education, health, product design, ergonomics, and law...
degree was added in 1999. In Fall 2007, CBU introduced its Bachelor of Fine Arts
Bachelor of Fine Arts
In the United States and Canada, the Bachelor of Fine Arts degree, usually abbreviated BFA, is the standard undergraduate degree for students seeking a professional education in the visual or performing arts. In some countries such a degree is called a Bachelor of Creative Arts or BCA...
degree.
Programs at the graduate level were reinstated in 1987 with the Master's program in Telecommunication and Information Systems. The Master of Business Administration
Master of Business Administration
The Master of Business Administration is a :master's degree in business administration, which attracts people from a wide range of academic disciplines. The MBA designation originated in the United States, emerging from the late 19th century as the country industrialized and companies sought out...
and the Master in Engineering Management
Engineering management
Engineering Management or Management Engineering is a specialized form of management and engineering that is concerned with the application of engineering principles to business practice...
were added in 1989. A Master of Education
Master of Education
The Master of Education is a postgraduate academic master's degree awarded by universities in a large number of countries. This degree in education often includes the following majors: curriculum and instruction, counseling, and administration. It is often conferred for educators advancing in...
was added in 1997, and the Master of Arts in Teaching
Master of Arts in Teaching
The Master of Arts in Teaching degree is generally a pre-service degree that usually requires a minimum of 30 semester hours beyond the Bachelor's degree. While the program often requires education classes in order to meet state licensure requirements, it emphasizes advanced course work in a...
and Master of Science in Educational Leadership were offered beginning in 2001. The Master of Arts in Executive Leadership was added in 2005.
When another Catholic college in Memphis (the all-female Siena College
Siena College (Memphis, Tennessee)
Siena College was a private, Catholic college located in Memphis, Tennessee. It was established by Dominican nuns in 1922 as St. Agnes College, the first Catholic women's college in the Diocese of Nashville and in the Memphis metro area. Initially, the campus housed a Kindergarten through twelfth...
) closed, Christian Brothers University became coeducation
Coeducation
Mixed-sex education, also known as coeducation or co-education, is the integrated education of male and female persons in the same institution. It is the opposite of single-sex education...
al in 1970. Currently, women comprise approximately 55% of the student body.
Christian Brothers College officially became Christian Brothers University in June 1990.
Schools, deans, and degrees
| School | Dean | Undergraduate Degrees | Master's Degrees |
|---|---|---|---|
| School of Arts Liberal arts The term liberal arts refers to those subjects which in classical antiquity were considered essential for a free citizen to study. Grammar, Rhetoric and Logic were the core liberal arts. In medieval times these subjects were extended to include mathematics, geometry, music and astronomy... |
Dr. Paul Haught | Applied Psychology Applied psychology The basic premise of applied psychology is the use of psychological principles and theories to overcome problems in other areas, such as mental health, business management, education, health, product design, ergonomics, and law... , Elementary Education Education in the United States Education in the United States is mainly provided by the public sector, with control and funding coming from three levels: federal, state, and local. Child education is compulsory.Public education is universally available... , English English studies English studies is an academic discipline that includes the study of literatures written in the English language , English linguistics English studies is an academic discipline that includes the study of literatures written in the English language (including literatures from the U.K., U.S.,... , English for Corporate Communications, Fine Arts Fine art Fine art or the fine arts encompass art forms developed primarily for aesthetics and/or concept rather than practical application. Art is often a synonym for fine art, as employed in the term "art gallery".... , History History History is the discovery, collection, organization, and presentation of information about past events. History can also mean the period of time after writing was invented. Scholars who write about history are called historians... , Psychology Psychology Psychology is the study of the mind and behavior. Its immediate goal is to understand individuals and groups by both establishing general principles and researching specific cases. For many, the ultimate goal of psychology is to benefit society... , Religion & Philosophy |
Catholic Studies Roman Catholic Church The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the world's largest Christian church, with over a billion members. Led by the Pope, it defines its mission as spreading the gospel of Jesus Christ, administering the sacraments and exercising charity... , Education Education in the United States Education in the United States is mainly provided by the public sector, with control and funding coming from three levels: federal, state, and local. Child education is compulsory.Public education is universally available... , Teaching Teacher A teacher or schoolteacher is a person who provides education for pupils and students . The role of teacher is often formal and ongoing, carried out at a school or other place of formal education. In many countries, a person who wishes to become a teacher must first obtain specified professional... |
| School of Business Business A business is an organization engaged in the trade of goods, services, or both to consumers. Businesses are predominant in capitalist economies, where most of them are privately owned and administered to earn profit to increase the wealth of their owners. Businesses may also be not-for-profit... |
Dr. Jack Hargett | Accounting, Finance Finance "Finance" is often defined simply as the management of money or “funds” management Modern finance, however, is a family of business activity that includes the origination, marketing, and management of cash and money surrogates through a variety of capital accounts, instruments, and markets created... , Human Resources Management, International Business International Business International business is a term used to collectively describe all commercial transactions that take place between two or more regions, countries and nations beyond their political boundary... , Management Management Management in all business and organizational activities is the act of getting people together to accomplish desired goals and objectives using available resources efficiently and effectively... , Marketing Marketing Marketing is the process used to determine what products or services may be of interest to customers, and the strategy to use in sales, communications and business development. It generates the strategy that underlies sales techniques, business communication, and business developments... , Sport Management Sport management Sport management is a field of education and vocation concerning the business aspect of sport. Some examples of sport managers include the front office system in professional sports, college sports managers, recreational sport managers, sports marketing, event management, facility management,... |
Business Administration |
| School of Engineering Engineering Engineering is the discipline, art, skill and profession of acquiring and applying scientific, mathematical, economic, social, and practical knowledge, in order to design and build structures, machines, devices, systems, materials and processes that safely realize improvements to the lives of... |
Dr. Eric B. Welch | Biochemical Engineering Biochemical engineering Biochemical engineering is a branch of chemical engineering or biological engineering that mainly deals with the design and construction of unit processes that involve biological organisms or molecules, such as bioreactors... , Chemical Engineering Chemical engineering Chemical engineering is the branch of engineering that deals with physical science , and life sciences with mathematics and economics, to the process of converting raw materials or chemicals into more useful or valuable forms... , Civil Engineering Civil engineering Civil engineering is a professional engineering discipline that deals with the design, construction, and maintenance of the physical and naturally built environment, including works like roads, bridges, canals, dams, and buildings... , Computer Engineering Computer engineering Computer engineering, also called computer systems engineering, is a discipline that integrates several fields of electrical engineering and computer science required to develop computer systems. Computer engineers usually have training in electronic engineering, software design, and... , Electrical Engineering Electrical engineering Electrical engineering is a field of engineering that generally deals with the study and application of electricity, electronics and electromagnetism. The field first became an identifiable occupation in the late nineteenth century after commercialization of the electric telegraph and electrical... , Mechanical Engineering Mechanical engineering Mechanical engineering is a discipline of engineering that applies the principles of physics and materials science for analysis, design, manufacturing, and maintenance of mechanical systems. It is the branch of engineering that involves the production and usage of heat and mechanical power for the... |
Engineering Management Engineering management Engineering Management or Management Engineering is a specialized form of management and engineering that is concerned with the application of engineering principles to business practice... |
| School of Sciences Science Science is a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe... |
Dr. Johnny Holmes | Biochemistry Biochemistry Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes in living organisms, including, but not limited to, living matter. Biochemistry governs all living organisms and living processes... , Biology Biology Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Biology is a vast subject containing many subdivisions, topics, and disciplines... , Biomedical Science, Chemistry Chemistry Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds.... , Computer Science Computer science Computer science or computing science is the study of the theoretical foundations of information and computation and of practical techniques for their implementation and application in computer systems... , Mathematics Mathematics Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity... , Mathematics & Computer Science, Natural Science Natural science The natural sciences are branches of science that seek to elucidate the rules that govern the natural world by using empirical and scientific methods... , Physics Physics Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic... |
N/A |
Recognition
- Named one of the Best Southeastern Colleges by The Princeton ReviewThe Princeton ReviewThe Princeton Review is an American-based standardized test preparation and admissions consulting company. The Princeton Review operates in 41 states and 22 countries across the globe. It offers test preparation for standardized aptitude tests such as the SAT and advice regarding college...
, 2010 - Ranked 19th for Master's Universities (South) by U.S. NewsU.S. News & World ReportU.S. News & World Report is an American news magazine published from Washington, D.C. Along with Time and Newsweek it was for many years a leading news weekly, focusing more than its counterparts on political, economic, health and education stories...
, 2010 - Ranked 3rd for Economic Diversity Among Top-Ranked Schools: Master's Universities (South) by U.S. News, 2010
- Ranked 7th for Racial Diversity: Master's Universities (South) by U.S. News, 2010
- Received "Best in Memphis" award from the Memphis City Beautiful Commission, 2006
Study abroad
As a member of the Lasallian Consortium, i.e. the seven Lasallian universities in the United States, CBU offers study abroad semesters in AustraliaAustralia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
, Brazil
Brazil
Brazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
, China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
, England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
, France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, Ireland
Ireland
Ireland is an island to the northwest of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth...
, Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
, Mexico
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
, South Africa
South Africa
The Republic of South Africa is a country in southern Africa. Located at the southern tip of Africa, it is divided into nine provinces, with of coastline on the Atlantic and Indian oceans...
, and Spain
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
. Additionally, CBU offers study abroad courses during spring and fall vacations. Upcoming courses include travel in England, France, Italy, Mexico, and Uganda
Uganda
Uganda , officially the Republic of Uganda, is a landlocked country in East Africa. Uganda is also known as the "Pearl of Africa". It is bordered on the east by Kenya, on the north by South Sudan, on the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, on the southwest by Rwanda, and on the south by...
. Medical missions to Haiti
Haiti
Haiti , officially the Republic of Haiti , is a Caribbean country. It occupies the western, smaller portion of the island of Hispaniola, in the Greater Antillean archipelago, which it shares with the Dominican Republic. Ayiti was the indigenous Taíno or Amerindian name for the island...
are available but have been postponed for the present. Study abroad is optional for students but is required for completion of the global studies minor.
Demographics
CBU has one of the most diverse student bodies in the SouthSouthern United States
The Southern United States—commonly referred to as the American South, Dixie, or simply the South—constitutes a large distinctive area in the southeastern and south-central United States...
. 51% of students are White-American
White American
White Americans are people of the United States who are considered or consider themselves White. The United States Census Bureau defines White people as those "having origins in any of the original peoples of Europe, the Middle East, or North Africa...
(non-Hispanic), 33% are African-American
African American
African Americans are citizens or residents of the United States who have at least partial ancestry from any of the native populations of Sub-Saharan Africa and are the direct descendants of enslaved Africans within the boundaries of the present United States...
(non-Hispanic), 5% are Asian-American
Asian American
Asian Americans are Americans of Asian descent. The U.S. Census Bureau definition of Asians as "Asian” refers to a person having origins in any of the original peoples of the Far East, Southeast Asia, or the Indian subcontinent, including, for example, Cambodia, China, India, Indonesia, Japan,...
or Pacific Islander-American
Pacific Islander American
Pacific Islander Americans, also known as Oceanian Americans, are residents of the United States with original ancestry from Oceania. They represent the smallest racial group counted in the United States census of 2000. They numbered 874,000 people or 0.3 percent of the United States population...
, 2% are Hispanic-American, and 2% are international student
International student
According to Organization of Economic Cooperation and Development , international students are those who travel to a country different from their own for the purpose of tertiary study. Despite that, the definition of international students varies in each country in accordance to their own national...
s. 6% of students have an unknown ethnicity. Students hail from more than 28 states and 14 countries.
Although CBU is a Catholic
Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the world's largest Christian church, with over a billion members. Led by the Pope, it defines its mission as spreading the gospel of Jesus Christ, administering the sacraments and exercising charity...
university, only 23% of students are Catholic. Religious observances are not required, and 32 different faiths are represented in the student body.
Notably, 99% of Christian Brothers University undergraduates receive financial aid, broken down as institutional grants (98%), state/local grants (68%), federal grants (29%), and student loans (58%).
There are 110 full-time faculty members. All of them hold at least master's degree
Master's degree
A master's is an academic degree granted to individuals who have undergone study demonstrating a mastery or high-order overview of a specific field of study or area of professional practice...
s, and 89% hold doctorate
Doctorate
A doctorate is an academic degree or professional degree that in most countries refers to a class of degrees which qualify the holder to teach in a specific field, A doctorate is an academic degree or professional degree that in most countries refers to a class of degrees which qualify the holder...
s or terminal degree
Terminal degree
A terminal degree is, in some countries, the highest academic degree in a given field of study. This phrase is in common use in the United States, but is not universal in an international context: the concept is not in general use in the United Kingdom, for example, and the exact definition varies...
s. No courses are taught by teaching assistant
Teaching assistant
A teaching assistant is an individual who assists a professor or teacher with instructional responsibilities. TAs include graduate teaching assistants , who are graduate students; undergraduate teaching assistants , who are undergraduate students; secondary school TAs, who are either high school...
s. The student to faculty ratio is 12 to 1. School of Sciences graduating classes from 2002 to 2006 boasted a 91% acceptance rate for medical school, and an 87% acceptance for pharmacy school.
Notable alumni
- Richard T. Gadomski, Founder & former CEO of PSI Group of Companies, now Lurgi PSI
Campus
Christian Brothers University is located on a 75 acres (303,514.5 m²) wooded campus in the heart of Midtown, MemphisMidtown, Memphis
- Overview :Architecturally, Midtown Memphis, Tennessee is marked with residential vintage housing, specialty stores, and high-rise buildings, often all located on the same avenue...
, four miles (6 km) east of Downtown
Downtown Memphis, Tennessee
Downtown Memphis, Tennessee is the central business district of Memphis, Tennessee and is located along the Mississippi River between Interstate 40 to the north, Interstate 55 to the south and I-240 to the east, where it abuts Midtown Memphis....
.
Kenrick Hall is the oldest building on campus, constructed in 1939 as the original Christian Brothers High School
Christian Brothers High School (Memphis, Tennessee)
Christian Brothers High School ' is located in Memphis, Tennessee, at 5900 Walnut Grove Rd. It is an all-male college preparatory school and Catholic school that has a strong Lasallian tradition that can be traced back to John Baptist de La Salle...
.
The university's architecture follows the Georgian style
Georgian architecture
Georgian architecture is the name given in most English-speaking countries to the set of architectural styles current between 1720 and 1840. It is eponymous for the first four British monarchs of the House of Hanover—George I of Great Britain, George II of Great Britain, George III of the United...
popular at the time of the campus' relocation to East Parkway. Arch-covered walkways traverse the main campus, allowing students and faculty to get to most buildings shaded from the weather. The campus is enclosed by an iron fence with brick accents with entrances on East Parkway South, Central Avenue, and Avery Avenue.
Outside organizations housed on campus
- Barret School of Banking
- Facing History and Ourselves
Canale Arena
Canale Arena, originally called De La Salle Gymnasium, was completed in 1950. At that time, it was the largest indoor arenaArena
An arena is an enclosed area, often circular or oval-shaped, designed to showcase theater, musical performances, or sporting events. It is composed of a large open space surrounded on most or all sides by tiered seating for spectators. The key feature of an arena is that the event space is the...
in the city of Memphis.
The arena was fully renovated in 2004 and has a capacity of 1,000.
Athletics
CBU is a Division II team and a member of the Gulf South ConferenceGulf South Conference
The Gulf South Conference is a College Athletic Conference which operates in the southeastern United States. It participates in the NCAA's Division II.-History:...
. Buccaneer teams include baseball, basketball, cross country, golf, and soccer. Lady Buccaneer teams include basketball, cross country, golf, soccer, softball, and volleyball.
The Lady Buccaneers and Buccaneers have won multiple athletic competitions, including the 2002 Division II women's soccer championship
NCAA Women's Soccer Championship
NCAA Women's Soccer Championships are divided into three divisions. This article lists NCAA Women's soccer championships.-Division I:The NCAA began conducting a Women's Division I Soccer Championship tournament in 1982 with a 12-team tournament...
and the 2008 GSC men's basketball championship.
Greek life
21% of male students and 24% of female students are members of fraternities and sororitiesFraternities and sororities
Fraternities and sororities are fraternal social organizations for undergraduate students. In Latin, the term refers mainly to such organizations at colleges and universities in the United States, although it is also applied to analogous European groups also known as corporations...
Campus Greek councils include the Interfraternity Council
North-American Interfraternity Conference
The North-American Interfraternity Conference , is an association of collegiate men's fraternities that was formally organized in 1910, although it began on November 27, 1909. The power of the organization rests in a House of Delegates where each member fraternity is represented by a single delegate...
(IFC), the Panhellenic Council
National Panhellenic Conference
The National Panhellenic Conference , founded in 1902, is an umbrella organization for 26 national women's sororities.Each member group is autonomous as a social, Greek-letter society of college women and alumnae...
(NPC), and the National Pan-Hellenic Council
National Pan-Hellenic Council
The National Pan-Hellenic Council is a collaborative organization of nine historically African American, international Greek lettered fraternities and sororities. The nine NPHC organizations are sometimes collectively referred to as the "Divine Nine"...
(NPHC).
| IFC Fraternities | Panhellenic Sororities |
|---|---|
| Kappa Sigma Kappa Sigma Kappa Sigma , commonly nicknamed Kappa Sig, is an international fraternity with currently 282 active chapters and colonies in North America. Kappa Sigma has initiated more than 240,000 men on college campuses throughout the United States and Canada. Today, the Fraternity has over 175,000 living... (ΚΣ): 1996–present |
Alpha Sigma Alpha Alpha Sigma Alpha Alpha Sigma Alpha is a US national sorority founded on November 15, 1901 at the Virginia State Female Normal School in Farmville, Virginia... (ΑΣΑ): 1986-1992 |
| Pi Kappa Phi Pi Kappa Phi Pi Kappa Phi is an American social fraternity. It was founded by Andrew Alexander Kroeg, Jr., Lawrence Harry Mixson, and Simon Fogarty, Jr. on December 10, 1904 at the College of Charleston in Charleston, South Carolina... (ΠΚΦ): 1983-2001 |
Alpha Sigma Tau Alpha Sigma Tau Alpha Sigma Tau is a national Panhellenic sorority founded on November 4, 1899, at Michigan State Normal College... (ΑΣΤ): 2005–present |
| Sigma Alpha Epsilon Sigma Alpha Epsilon Sigma Alpha Epsilon is a North American Greek-letter social college fraternity founded at the University of Alabama on March 9, 1856. Of all existing national social fraternities today, Sigma Alpha Epsilon is the only one founded in the Antebellum South... (ΣΑΕ): 1989–present |
Alpha Xi Delta Alpha Xi Delta Alpha Xi Delta is a women's fraternity founded on April 17, 1893 at Lombard College, Galesburg, Illinois. Alpha Xi Delta is one of the oldest women's fraternities as well as one of the ten founding fraternities of the National Panhellenic Conference... (ΑΞΔ): 1994–present |
| Tau Kappa Epsilon Tau Kappa Epsilon Tau Kappa Epsilon is a college fraternity founded on January 10, 1899 at Illinois Wesleyan University with chapters in the United States, and Canada, and affiliation with a German fraternity system known as the Corps of the Weinheimer Senioren Convent... (ΤΚΕ): 1979–present |
Zeta Tau Alpha Zeta Tau Alpha Zeta Tau Alpha is a women's fraternity, founded October 15, 1898 at the State Female Normal School in Farmville, Virginia. The Executive office is located in Indianapolis, Indiana... (ΖΤΑ): 1985–present |
| NPHC Fraternities | NPHC Sororities |
|---|---|
| Kappa Alpha Psi Kappa Alpha Psi Kappa Alpha Psi is a collegiate Greek-letter fraternity with a predominantly African American membership. Since the fraternity's founding on January 5, 1911 at Indiana University Bloomington, the fraternity has never limited membership based on color, creed or national origin... (ΚΑΨ): 1999–present |
Alpha Kappa Alpha Alpha Kappa Alpha Alpha Kappa Alpha is the first Greek-lettered sorority established and incorporated by African American college women. The sorority was founded on January 15, 1908, at Howard University in Washington, D.C., by a group of nine students, led by Ethel Hedgeman Lyle... (ΑΚΑ): 1978–present |
| Phi Beta Sigma Phi Beta Sigma Phi Beta Sigma is a predominantly African-American fraternity which was founded at Howard University in Washington, D.C. on January 9, 1914, by three young African-American male students. The founders A. Langston Taylor, Leonard F. Morse, and Charles I... (ΦΒΣ): 1996–present |
Delta Sigma Theta Delta Sigma Theta Delta Sigma Theta is a non-profit Greek-lettered sorority of college-educated women who perform public service and place emphasis on the African American community. Delta Sigma Theta Sorority was founded on January 13, 1913 by twenty-two collegiate women at Howard University... (ΔΣΘ): 1998–present |
| Sigma Gamma Rho Sigma Gamma Rho Sigma Gamma Rho Sorority, Inc. was founded on the campus of Butler University on November 12, 1922, by seven school teachers in Indianapolis, Indiana... (ΣΓΡ): 2001–present |
| Professional Fraternity |
|---|
| Delta Sigma Pi Delta Sigma Pi ΔΣΠ ' is one of the largest co-ed professional business fraternities. Delta Sigma Pi was founded on November 7, 1907 at the School of Commerce, Accounts and Finance, New York University, New York, New York and is currently headquartered in Oxford, Ohio... (ΔΣΠ): 1964–present |
| Local & Non-Traditional Fraternities & Sororities |
|---|
| Gamma Theta Phi Gamma Theta Phi Gamma Theta Phi was a fraternity founded in 1964, primarily at Catholic colleges. Unlike traditional fraternities, Gamma was organized by the student services departments at each school since several colleges did not want national fraternities coming on their campus... (ΓΘΦ / Gamma): 1964-1997 |
| Knights of Columbus Knights of Columbus The Knights of Columbus is the world's largest Catholic fraternal service organization. Founded in the United States in 1882, it is named in honor of Christopher Columbus.... (K of C): 1972-1988 |
| Association to Motivate Spirit (WAMS): 1978-1995 |
Honor societies and professional organizations
Chapters of a number of honor societiesHonor society
In the United States, an honor society is a rank organization that recognizes excellence among peers. Numerous societies recognize various fields and circumstances. The Order of the Arrow, for example, is the national honor society of the Boy Scouts of America...
exist at CBU to recognize excellence in academia and leadership. Active honor societies and their specialties include: Alpha Chi (general academic), Beta Beta Beta (biology), the Order of Omega
Order of Omega
The Order of Omega is an undergraduate Greek society recognizing "fraternity men and women who have attained a high standard of leadership in inter-fraternity activities." It functions as an adjunct to traditional fraternal organizations, rather than a social or professional group in se...
(fraternity and sorority members), Phi Alpha Theta
Phi Alpha Theta
Phi Alpha Theta is an American honor society for undergraduate and graduate students and professors of history.The society is a charter member of the Association of College Honor Societies and has over 350,000 members, with about 9,500 new members joining each year through 860 local chapters.-...
(history), Psi Chi
Psi Chi
Psi Chi is the International Honor Society in Psychology, founded in 1929 for the purposes of encouraging, stimulating, and maintaining excellence in scholarship, and advancing the science of psychology. With over 1,050 chapters, Psi Chi is one of the largest honor societies in the United States...
(psychology), Sigma Tau Delta
Sigma Tau Delta
Sigma Tau Delta is an international collegiate honor society for students of English. It presently has over 800 active chapters located in Europe, the Caribbean, the United States, and 1 chapter in the Middle East , with more than 1,000 faculty sponsors...
(English), Alpha Psi Omega
Alpha Psi Omega
Alpha Psi Omega National Theatre Honor Society is an American recognition honor society recognizing participants in collegiate theatre. The Alpha Cast was founded at Fairmont State College on August 12, 1925 by professor Paul F...
(theatre), and Tau Beta Pi
Tau Beta Pi
The Tau Beta Pi Association is the oldest engineering honor society in the United States and the second oldest collegiate honor society in America. It honors engineering students who have shown a history of academic achievement as well as a commitment to personal and professional integrity...
(engineering).
Professional organizations include: American Institute of Chemical Engineers
American Institute of Chemical Engineers
The American Institute of Chemical Engineers is a professional organization for chemical engineers.AIChE was established in 1908 with the purpose of establishing chemical engineers as a profession independent from chemists and mechanical engineers.As of 2010, AIChE had over 40,000 members,...
, American Society of Civil Engineers
American Society of Civil Engineers
The American Society of Civil Engineers is a professional body founded in 1852 to represent members of the civil engineering profession worldwide. It is the oldest national engineering society in the United States. ASCE's vision is to have engineers positioned as global leaders who strive toward...
, American Society of Mechanical Engineers
American Society of Mechanical Engineers
The American Society of Mechanical Engineers is a professional body, specifically an engineering society, focused on mechanical engineering....
, Institute of Electrical Engineers, Society of Physics Students
Society of Physics Students
The Society of Physics Students is a professional association with international participation, granting membership through college chapters with the only requirement that the student member be interested in physics. All college majors are welcome to join SPS, but the highest representation tends...
, and the Student Affiliates of the American Chemical Society
American Chemical Society
The American Chemical Society is a scientific society based in the United States that supports scientific inquiry in the field of chemistry. Founded in 1876 at New York University, the ACS currently has more than 161,000 members at all degree-levels and in all fields of chemistry, chemical...
.
ASCE / AISC Student Steel Bridge Competition
Civil engineering students also compete in the annual Student Steel Bridge Competition, sponsored by the American Society of Civil Engineers and the American Institute of Steel Construction, Inc. Scale bridges are constructed; judging is based on speed of construction, strength and durability of the bridge, and more.ASCE National Concrete Canoe Competition
Civil engineering students construct concrete canoeConcrete canoe
A concrete canoe is a canoe made of concrete, typically created for an engineering competition.In spirit, the event is similar to that of a cardboard boat race—make the seemingly unfloatable float...
s to compete at annual Deep South regional conferences for student chapters of the American Society of Civil Engineers
American Society of Civil Engineers
The American Society of Civil Engineers is a professional body founded in 1852 to represent members of the civil engineering profession worldwide. It is the oldest national engineering society in the United States. ASCE's vision is to have engineers positioned as global leaders who strive toward...
. These canoes must be able to float and support the weight of several students as they will be raced.
IEEE Robotics Competition
Electrical and computer engineering students annually participate in a roboticsRobotics
Robotics is the branch of technology that deals with the design, construction, operation, structural disposition, manufacture and application of robots...
Competition organized by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers is a non-profit professional association headquartered in New York City that is dedicated to advancing technological innovation and excellence...
. The 2008 competition was held in Huntsville, Alabama
Huntsville, Alabama
Huntsville is a city located primarily in Madison County in the central part of the far northern region of the U.S. state of Alabama. Huntsville is the county seat of Madison County. The city extends west into neighboring Limestone County. Huntsville's population was 180,105 as of the 2010 Census....
.
NASA Great Moonbuggy Race
Mechanical engineering students gear up against competitors from schools across the country to build and race vehicles that can travel over simulated lunar terrain. The competition is held annually at the United States Space & Rocket CenterUnited States Space & Rocket Center
The U.S. Space & Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama is a museum showcasing rockets, achievements, and artifacts of the U.S. space program. The facility is also home to United States Space Camp and Aviation Challenge...
.
Student traditions

Painting The Rock
Students traditionally "paint The Rock". Painting The Rock is spray painting an on-campus boulder, usually to show off one's GreekFraternities and sororities
Fraternities and sororities are fraternal social organizations for undergraduate students. In Latin, the term refers mainly to such organizations at colleges and universities in the United States, although it is also applied to analogous European groups also known as corporations...
letters and symbols.
Painting The Rock has its own rules of etiquette. The Rock can only be painted between sunset and sunrise. Any group currently next to The Rock is guarding it, and it cannot be taken by another group at that time (although the occasional fight has happened in the past). The Rock can be painted several times in one night; however, it is a gentlemanly tradition among the fraternities not to paint over a sorority Rock for at least two to three days.
The term taking The Rock refers to adding a completely new coat of paint whereas tagging is just spray painting marks on top of someone else's paint, typically to add the names of the painters or insults to the current holder of The Rock.
Older Rock traditions (until the 1970s) include paint fights between upperclassmen and lowerclassmen the first few days of school, but these have been discontinued.
External links
- Christian Brothers University
- Go Bucs Go: university athletics
- Student organizations
- Campus map
- Study abroad
- The Brothers of the Christian Schools
- Lasallian Volunteers
----


