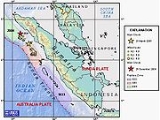
2005 Sumatra earthquake
Encyclopedia
The 2005 Sumatra earthquake, referred to as the Nias Earthquake by the scientific community, was a major earthquake on 28 March 2005, located off the west coast of northern Sumatra
, Indonesia
. Approximately 1300 people were killed by the earthquake, mostly on the island of Nias
. The event caused panic in the region, which had previously been devastated by the massive tsunami
triggered by the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake
, but this earthquake generated a relatively small tsunami that caused limited damage. It was the third most powerful earthquake since 1965 in Indonesia.
The earthquake occurred at 16:09:36 UTC (23:09:36 local time) on 28 March 2005. The hypocenter
was located at 2°04′35"N 97°00′58"E, 30 kilometres (18.6 mi) below the surface of the Indian Ocean
, where subduction
is forcing the Indo-Australian Plate
to the south-west under the Eurasian plate
's Sunda edge. The area is 200 kilometres (124.3 mi) west of Sibolga
, Sumatra
, or 1400 kilometres (869.9 mi) northwest of Jakarta
, approximately halfway between the islands of Nias
and Simeulue
. Seismic recordings give the earthquake
a moment magnitude
of about 8.7, and effects were felt as far away as Bangkok
, Thailand
; over 1000 kilometres (621.4 mi) away.
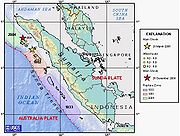 The earthquake lasted for about two minutes in total. In the twenty-four hours immediately after the event, there were eight major aftershocks, measuring between 5.5 and 6.0. Despite the proximity of the epicenter
The earthquake lasted for about two minutes in total. In the twenty-four hours immediately after the event, there were eight major aftershocks, measuring between 5.5 and 6.0. Despite the proximity of the epicenter
to that for the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake, it ruptured a separate segment of the Sunda megathrust
and was most likely triggered by stress changes associated with that earlier event.
On the Indonesian island of Nias
, off the coast of Sumatra, hundreds of buildings were destroyed by the earthquake. The death toll on Nias was at least one thousand, with 220 dying in Gunungsitoli, the island's largest town. Nearly half of Gunungsitoli's population (27000) fled the town.
The earthquake was strongly felt across the island of Sumatra
, and caused widespread power outage
s in the Indonesian city of Banda Aceh
, already devastated by the December 2004 tsunami, and prompted thousands to flee their homes and seek higher ground.
It was also strongly felt along the west coast of Thailand and Malaysia, and in Kuala Lumpur
high-rise buildings were evacuated. The earthquake was felt less strongly in the Maldives
, India
, and Sri Lanka
.
that it might trigger a tsunami similar to the massive one generated three months earlier by the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake
on 26 December 2004. Evacuations were carried out in coastal regions of Thailand
, Malaysia, and Sri Lanka
. This earthquake, however, produced a relatively tiny tsunami. A 3 metres (9.8 ft) tsunami caused moderate damage to port and airport facilities on Simeulue
, and a 2 metres (6.6 ft) tsunami was recorded on the west coast of Nias. Much smaller waves, most detectable only in tide gauge
recording systems, were recorded across the Indian Ocean; for example, a 25 centimetres (9.8 in) wave was recorded at Colombo, Sri Lanka.
Tsunami
warnings were issued by the Pacific Tsunami Warning Center
, operated by the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
(NOAA) , and by the government of Thailand
. There were initial concerns that a major tsunami could be generated, particularly travelling south from the event's hypocenter.
Portions of Thailand's southern coast were evacuated as a precaution, and NOAA advised an evacuation of 965 kilometres (599.6 mi) of coastline in Sumatra. Evacuations also occurred in the northern Malaysian states of Penang
and Kedah
, as well as the eastern coast of Sri Lanka
, where ten people were killed in the confusion of the evacuation. Many of the southern states of India
were also put on high alert; all of these areas had seen significant damage from December's tsunami. After the detection of a minor tsunami south of the epicenter, including a 30 cm tsunami on Australia's Cocos Islands, the island states of Mauritius
, Madagascar
, and the Seychelles
in the Indian Ocean issued warnings to their populations.
Although tsunami warning systems for the region had been actively discussed before the December 2004 earthquake, none had yet been implemented in the Indian Ocean.
worked with the Indonesian government to take further actions to prevent a possible catastrophe after the strong earthquake, and the US State Department has announced that it will help countries affected by a possible tsunami. The government of India
announced aid of US$2 million for the earthquake victims.
Australia
announced it would provide A$1 million in emergency aid, and, at the request of the Indonesian Government, dispatched Australian Defence Force
medical teams and equipment to Nias. The Australian naval ship HMAS Kanimbla, having only recently left Aceh, was redeployed to the region from Singapore
. At about 09:30 (UTC) 2 April 2005, one of Kanimbla's two Sea King helicopters, Shark 02, crashed on the island of Nias while taking medical personnel to a village. Nine personnel were killed, and two others sustained injuries but were rescued from the site by the other helicopter. The crash occurred one day before a state visit
by President
Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono
to Australia, where he and Prime Minister of Australia
John Howard
expressed mutual sorrow for their countries' losses.
The US Navy also responded to this earthquake by deploying the USNS Mercy, a 100-bed hospital ship, off the coast of Nias.
Sumatra
Sumatra is an island in western Indonesia, westernmost of the Sunda Islands. It is the largest island entirely in Indonesia , and the sixth largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 with a population of 50,365,538...
, Indonesia
Indonesia
Indonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an...
. Approximately 1300 people were killed by the earthquake, mostly on the island of Nias
Nias
Nīas is an island off the western coast of Sumatra, Indonesia. Nias is also the name of the archipelago, containing the Hinako archipelago....
. The event caused panic in the region, which had previously been devastated by the massive tsunami
Tsunami
A tsunami is a series of water waves caused by the displacement of a large volume of a body of water, typically an ocean or a large lake...
triggered by the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake
2004 Indian Ocean earthquake
The 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake was an undersea megathrust earthquake that occurred at 00:58:53 UTC on Sunday, December 26, 2004, with an epicentre off the west coast of Sumatra, Indonesia. The quake itself is known by the scientific community as the Sumatra-Andaman earthquake...
, but this earthquake generated a relatively small tsunami that caused limited damage. It was the third most powerful earthquake since 1965 in Indonesia.
The earthquake occurred at 16:09:36 UTC (23:09:36 local time) on 28 March 2005. The hypocenter
Hypocenter
The hypocenter refers to the site of an earthquake or a nuclear explosion...
was located at 2°04′35"N 97°00′58"E, 30 kilometres (18.6 mi) below the surface of the Indian Ocean
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third largest of the world's oceanic divisions, covering approximately 20% of the water on the Earth's surface. It is bounded on the north by the Indian Subcontinent and Arabian Peninsula ; on the west by eastern Africa; on the east by Indochina, the Sunda Islands, and...
, where subduction
Subduction
In geology, subduction is the process that takes place at convergent boundaries by which one tectonic plate moves under another tectonic plate, sinking into the Earth's mantle, as the plates converge. These 3D regions of mantle downwellings are known as "Subduction Zones"...
is forcing the Indo-Australian Plate
Indo-Australian Plate
The Indo-Australian Plate is a major tectonic plate that includes the continent of Australia and surrounding ocean, and extends northwest to include the Indian subcontinent and adjacent waters...
to the south-west under the Eurasian plate
Eurasian Plate
The Eurasian Plate is a tectonic plate which includes most of the continent of Eurasia , with the notable exceptions of the Indian subcontinent, the Arabian subcontinent, and the area east of the Chersky Range in East Siberia...
's Sunda edge. The area is 200 kilometres (124.3 mi) west of Sibolga
Sibolga
Sibolga is a city and a port on the west coast of North Sumatra province, in Indonesia. It is located on the western side of North Sumatra, facing the Indian Ocean and is a transit harbour to Nias island. It was hard hit during the 2004 Indian Ocean Earthquake.- History :Poncan Ketek Island in...
, Sumatra
Sumatra
Sumatra is an island in western Indonesia, westernmost of the Sunda Islands. It is the largest island entirely in Indonesia , and the sixth largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 with a population of 50,365,538...
, or 1400 kilometres (869.9 mi) northwest of Jakarta
Jakarta
Jakarta is the capital and largest city of Indonesia. Officially known as the Special Capital Territory of Jakarta, it is located on the northwest coast of Java, has an area of , and a population of 9,580,000. Jakarta is the country's economic, cultural and political centre...
, approximately halfway between the islands of Nias
Nias
Nīas is an island off the western coast of Sumatra, Indonesia. Nias is also the name of the archipelago, containing the Hinako archipelago....
and Simeulue
Simeulue
Simeulue Regency is a regency in the Aceh province of Indonesia. It occupies the whole island of Simeulue , 150 km off the west coast of Sumatra, with a population of 80,279 ....
. Seismic recordings give the earthquake
Earthquake
An earthquake is the result of a sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves. The seismicity, seismism or seismic activity of an area refers to the frequency, type and size of earthquakes experienced over a period of time...
a moment magnitude
Moment magnitude scale
The moment magnitude scale is used by seismologists to measure the size of earthquakes in terms of the energy released. The magnitude is based on the seismic moment of the earthquake, which is equal to the rigidity of the Earth multiplied by the average amount of slip on the fault and the size of...
of about 8.7, and effects were felt as far away as Bangkok
Bangkok
Bangkok is the capital and largest urban area city in Thailand. It is known in Thai as Krung Thep Maha Nakhon or simply Krung Thep , meaning "city of angels." The full name of Bangkok is Krung Thep Mahanakhon Amon Rattanakosin Mahintharayutthaya Mahadilok Phop Noppharat Ratchathani Burirom...
, Thailand
Thailand
Thailand , officially the Kingdom of Thailand , formerly known as Siam , is a country located at the centre of the Indochina peninsula and Southeast Asia. It is bordered to the north by Burma and Laos, to the east by Laos and Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the...
; over 1000 kilometres (621.4 mi) away.
Earthquake and damage

Epicenter
The epicenter or epicentre is the point on the Earth's surface that is directly above the hypocenter or focus, the point where an earthquake or underground explosion originates...
to that for the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake, it ruptured a separate segment of the Sunda megathrust
Sunda megathrust
The Sunda megathrust is a fault that extends approximately 5,500 km from Myanmar in the north, running along the southwestern side of Sumatra, to the south of Java and Bali before terminating near Australia...
and was most likely triggered by stress changes associated with that earlier event.
On the Indonesian island of Nias
Nias
Nīas is an island off the western coast of Sumatra, Indonesia. Nias is also the name of the archipelago, containing the Hinako archipelago....
, off the coast of Sumatra, hundreds of buildings were destroyed by the earthquake. The death toll on Nias was at least one thousand, with 220 dying in Gunungsitoli, the island's largest town. Nearly half of Gunungsitoli's population (27000) fled the town.
The earthquake was strongly felt across the island of Sumatra
Sumatra
Sumatra is an island in western Indonesia, westernmost of the Sunda Islands. It is the largest island entirely in Indonesia , and the sixth largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 with a population of 50,365,538...
, and caused widespread power outage
Power outage
A power outage is a short- or long-term loss of the electric power to an area.There are many causes of power failures in an electricity network...
s in the Indonesian city of Banda Aceh
Banda Aceh
Banda Aceh is the provincial capital and largest city in the province of Aceh, Indonesia, located on the island of Sumatra, with an elevation of 35 meters. The city regency covers an area of 64 square kilometres and according to the 2000 census had a population of 219,070 people...
, already devastated by the December 2004 tsunami, and prompted thousands to flee their homes and seek higher ground.
It was also strongly felt along the west coast of Thailand and Malaysia, and in Kuala Lumpur
Kuala Lumpur
Kuala Lumpur is the capital and the second largest city in Malaysia by population. The city proper, making up an area of , has a population of 1.4 million as of 2010. Greater Kuala Lumpur, also known as the Klang Valley, is an urban agglomeration of 7.2 million...
high-rise buildings were evacuated. The earthquake was felt less strongly in the Maldives
Maldives
The Maldives , , officially Republic of Maldives , also referred to as the Maldive Islands, is an island nation in the Indian Ocean formed by a double chain of twenty-six atolls oriented north-south off India's Lakshadweep islands, between Minicoy Island and...
, India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
, and Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka is a country off the southern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Known until 1972 as Ceylon , Sri Lanka is an island surrounded by the Indian Ocean, the Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait, and lies in the vicinity of India and the...
.
Tsunami
The earthquake caused great concern around the Indian OceanIndian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third largest of the world's oceanic divisions, covering approximately 20% of the water on the Earth's surface. It is bounded on the north by the Indian Subcontinent and Arabian Peninsula ; on the west by eastern Africa; on the east by Indochina, the Sunda Islands, and...
that it might trigger a tsunami similar to the massive one generated three months earlier by the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake
2004 Indian Ocean earthquake
The 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake was an undersea megathrust earthquake that occurred at 00:58:53 UTC on Sunday, December 26, 2004, with an epicentre off the west coast of Sumatra, Indonesia. The quake itself is known by the scientific community as the Sumatra-Andaman earthquake...
on 26 December 2004. Evacuations were carried out in coastal regions of Thailand
Thailand
Thailand , officially the Kingdom of Thailand , formerly known as Siam , is a country located at the centre of the Indochina peninsula and Southeast Asia. It is bordered to the north by Burma and Laos, to the east by Laos and Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the...
, Malaysia, and Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka is a country off the southern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Known until 1972 as Ceylon , Sri Lanka is an island surrounded by the Indian Ocean, the Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait, and lies in the vicinity of India and the...
. This earthquake, however, produced a relatively tiny tsunami. A 3 metres (9.8 ft) tsunami caused moderate damage to port and airport facilities on Simeulue
Simeulue
Simeulue Regency is a regency in the Aceh province of Indonesia. It occupies the whole island of Simeulue , 150 km off the west coast of Sumatra, with a population of 80,279 ....
, and a 2 metres (6.6 ft) tsunami was recorded on the west coast of Nias. Much smaller waves, most detectable only in tide gauge
Tide gauge
A tide gauge is a device for measuring sea level and detecting tsunamis.Sensors continuously record the height of the water level with respect to a height reference surface close to the geoid...
recording systems, were recorded across the Indian Ocean; for example, a 25 centimetres (9.8 in) wave was recorded at Colombo, Sri Lanka.
Tsunami
Tsunami
A tsunami is a series of water waves caused by the displacement of a large volume of a body of water, typically an ocean or a large lake...
warnings were issued by the Pacific Tsunami Warning Center
Pacific Tsunami Warning Center
The Pacific Tsunami Warning Center is one of two tsunami warning centers that are operated by NOAA in the United States. Headquartered in Ewa Beach, Hawaii, the PTWC is part of an international tsunami warning system program and serves as the operational center for TWS of the Pacific issuing...
, operated by the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration , pronounced , like "noah", is a scientific agency within the United States Department of Commerce focused on the conditions of the oceans and the atmosphere...
(NOAA) , and by the government of Thailand
Thailand
Thailand , officially the Kingdom of Thailand , formerly known as Siam , is a country located at the centre of the Indochina peninsula and Southeast Asia. It is bordered to the north by Burma and Laos, to the east by Laos and Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the...
. There were initial concerns that a major tsunami could be generated, particularly travelling south from the event's hypocenter.
Portions of Thailand's southern coast were evacuated as a precaution, and NOAA advised an evacuation of 965 kilometres (599.6 mi) of coastline in Sumatra. Evacuations also occurred in the northern Malaysian states of Penang
Penang
Penang is a state in Malaysia and the name of its constituent island, located on the northwest coast of Peninsular Malaysia by the Strait of Malacca. It is bordered by Kedah in the north and east, and Perak in the south. Penang is the second smallest Malaysian state in area after Perlis, and the...
and Kedah
Kedah
Kedah is a state of Malaysia, located in the northwestern part of Peninsular Malaysia. The state covers a total area of over 9,000 km², and it consists of the mainland and Langkawi. The mainland has a relatively flat terrain, which is used to grow rice...
, as well as the eastern coast of Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka is a country off the southern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Known until 1972 as Ceylon , Sri Lanka is an island surrounded by the Indian Ocean, the Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait, and lies in the vicinity of India and the...
, where ten people were killed in the confusion of the evacuation. Many of the southern states of India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
were also put on high alert; all of these areas had seen significant damage from December's tsunami. After the detection of a minor tsunami south of the epicenter, including a 30 cm tsunami on Australia's Cocos Islands, the island states of Mauritius
Mauritius
Mauritius , officially the Republic of Mauritius is an island nation off the southeast coast of the African continent in the southwest Indian Ocean, about east of Madagascar...
, Madagascar
Madagascar
The Republic of Madagascar is an island country located in the Indian Ocean off the southeastern coast of Africa...
, and the Seychelles
Seychelles
Seychelles , officially the Republic of Seychelles , is an island country spanning an archipelago of 115 islands in the Indian Ocean, some east of mainland Africa, northeast of the island of Madagascar....
in the Indian Ocean issued warnings to their populations.
Although tsunami warning systems for the region had been actively discussed before the December 2004 earthquake, none had yet been implemented in the Indian Ocean.
Humanitarian response
The United NationsUnited Nations
The United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
worked with the Indonesian government to take further actions to prevent a possible catastrophe after the strong earthquake, and the US State Department has announced that it will help countries affected by a possible tsunami. The government of India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
announced aid of US$2 million for the earthquake victims.
Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
announced it would provide A$1 million in emergency aid, and, at the request of the Indonesian Government, dispatched Australian Defence Force
Australian Defence Force
The Australian Defence Force is the military organisation responsible for the defence of Australia. It consists of the Royal Australian Navy , Australian Army, Royal Australian Air Force and a number of 'tri-service' units...
medical teams and equipment to Nias. The Australian naval ship HMAS Kanimbla, having only recently left Aceh, was redeployed to the region from Singapore
Singapore
Singapore , officially the Republic of Singapore, is a Southeast Asian city-state off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, north of the equator. An island country made up of 63 islands, it is separated from Malaysia by the Straits of Johor to its north and from Indonesia's Riau Islands by the...
. At about 09:30 (UTC) 2 April 2005, one of Kanimbla's two Sea King helicopters, Shark 02, crashed on the island of Nias while taking medical personnel to a village. Nine personnel were killed, and two others sustained injuries but were rescued from the site by the other helicopter. The crash occurred one day before a state visit
State visit
A state visit is a formal visit by a foreign head of state to another nation, at the invitation of that nation's head of state. State visits are the highest form of diplomatic contact between two nations, and are marked by ceremonial pomp and diplomatic protocol. In parliamentary democracies, heads...
by President
President of Indonesia
The President of the Republic of Indonesia is the head of state and the head of government of the Republic of Indonesia.The first president was Sukarno and the current president is Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono.- Sukarno era :...
Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono
Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono
Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono AC , is an Indonesian politician and retired Army general officer who has been President of Indonesia since 2004....
to Australia, where he and Prime Minister of Australia
Prime Minister of Australia
The Prime Minister of the Commonwealth of Australia is the highest minister of the Crown, leader of the Cabinet and Head of Her Majesty's Australian Government, holding office on commission from the Governor-General of Australia. The office of Prime Minister is, in practice, the most powerful...
John Howard
John Howard
John Winston Howard AC, SSI, was the 25th Prime Minister of Australia, from 11 March 1996 to 3 December 2007. He was the second-longest serving Australian Prime Minister after Sir Robert Menzies....
expressed mutual sorrow for their countries' losses.
The US Navy also responded to this earthquake by deploying the USNS Mercy, a 100-bed hospital ship, off the coast of Nias.
External links
- Special Event Page, Amateur Seismic Centre, India
- Royal Australian Navy assistance to earthquake relief

