
Sunda megathrust
Encyclopedia
The Sunda megathrust is a fault that extends approximately 5,500 km (3300 mi) from Myanmar (Burma) in the north, running along the southwestern side of Sumatra
, to the south of Java
and Bali
before terminating near Australia
. It is a megathrust, located at a convergent plate boundary
where it forms the interface between the overriding Eurasian plate
and the subducting
Indo-Australian plate
. It is one of the most seismogenic structures on Earth, being responsible for many great and giant earthquake
s, including the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake
and tsunami
that killed over 230,000 people. The Sunda megathrust can be divided into the Andaman Megathrust, Sumatra(n) Megathrust and Java(n) Megathrust. The Bali
-Sumbawa
segment is much less active and therefore does not have the "megathrust" term associated with it.
and Burma
plates. The relative motion of the subducting and overriding plates varies slightly along strike due to these complexities but is always strongly oblique. The strike-slip component of the oblique convergence is accommodated by displacement on the Great Sumatran fault
, while the dip-slip component is taken up by the Sunda megathrust.
to about 30° below the coastline of Sumatra.
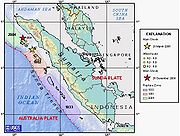 At this plate boundary, earthquakes occur along the Sunda megathrust and within both the subducting and overriding plates. The largest earthquakes are generated when the megathrust itself ruptures. Studies of both recent and historical earthquakes
At this plate boundary, earthquakes occur along the Sunda megathrust and within both the subducting and overriding plates. The largest earthquakes are generated when the megathrust itself ruptures. Studies of both recent and historical earthquakes
show that the megathrust is segmented. The largest earthquakes occur on separate 'patches' along the megathrust surface (1797
, 1833
, 1861
, 2004
, 2005
& 2007), with smaller events occurring at the boundaries between these patches (1935
, 1984
, 2000
& 2002). The rupture area of the 1861 event appears to be very similar to that for the 2005 event, suggesting that it can be regarded as a repeat event. The 2007 event is interpreted to be a partial failure of the rupture area of the 1833 event.
The 2004 earthquake ruptured an enormous segment of the megathrust surface. Research into evidence for previous events of this size suggests that they are rare, with two candidate earlier events occurring soon after AD 1290–1400 and AD 780–990.
The Java-Bali segment of the megathrust does not appear to be associated with great earthquakes, possibly due to mainly aseismic slip.
Sumatra
Sumatra is an island in western Indonesia, westernmost of the Sunda Islands. It is the largest island entirely in Indonesia , and the sixth largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 with a population of 50,365,538...
, to the south of Java
Java
Java is an island of Indonesia. With a population of 135 million , it is the world's most populous island, and one of the most densely populated regions in the world. It is home to 60% of Indonesia's population. The Indonesian capital city, Jakarta, is in west Java...
and Bali
Bali
Bali is an Indonesian island located in the westernmost end of the Lesser Sunda Islands, lying between Java to the west and Lombok to the east...
before terminating near Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
. It is a megathrust, located at a convergent plate boundary
Convergent boundary
In plate tectonics, a convergent boundary, also known as a destructive plate boundary , is an actively deforming region where two tectonic plates or fragments of lithosphere move toward one another and collide...
where it forms the interface between the overriding Eurasian plate
Eurasian Plate
The Eurasian Plate is a tectonic plate which includes most of the continent of Eurasia , with the notable exceptions of the Indian subcontinent, the Arabian subcontinent, and the area east of the Chersky Range in East Siberia...
and the subducting
Subduction
In geology, subduction is the process that takes place at convergent boundaries by which one tectonic plate moves under another tectonic plate, sinking into the Earth's mantle, as the plates converge. These 3D regions of mantle downwellings are known as "Subduction Zones"...
Indo-Australian plate
Indo-Australian Plate
The Indo-Australian Plate is a major tectonic plate that includes the continent of Australia and surrounding ocean, and extends northwest to include the Indian subcontinent and adjacent waters...
. It is one of the most seismogenic structures on Earth, being responsible for many great and giant earthquake
Earthquake
An earthquake is the result of a sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves. The seismicity, seismism or seismic activity of an area refers to the frequency, type and size of earthquakes experienced over a period of time...
s, including the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake
2004 Indian Ocean earthquake
The 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake was an undersea megathrust earthquake that occurred at 00:58:53 UTC on Sunday, December 26, 2004, with an epicentre off the west coast of Sumatra, Indonesia. The quake itself is known by the scientific community as the Sumatra-Andaman earthquake...
and tsunami
Tsunami
A tsunami is a series of water waves caused by the displacement of a large volume of a body of water, typically an ocean or a large lake...
that killed over 230,000 people. The Sunda megathrust can be divided into the Andaman Megathrust, Sumatra(n) Megathrust and Java(n) Megathrust. The Bali
Bali
Bali is an Indonesian island located in the westernmost end of the Lesser Sunda Islands, lying between Java to the west and Lombok to the east...
-Sumbawa
Sumbawa
Sumbawa is an Indonesian island, located in the middle of the Lesser Sunda Islands chain, with Lombok to the west, Flores to the east, and Sumba further to the southeast. It is in the province of West Nusa Tenggara....
segment is much less active and therefore does not have the "megathrust" term associated with it.
Tectonic setting
The subducting plate consists of two protoplates, the Indian and Australian plates. Similarly the overriding plate consists of two microplates, the SundaSunda Plate
The Sunda Plate is the tectonic plate on which the majority of Southeast Asia is located. It was formerly considered a part of the Eurasian Plate, but GPS measurements have confirmed its independent movement at 10 mm/yr eastward relative to Eurasia...
and Burma
Burma Plate
The Burma Plate is a small tectonic plate or microplate located in Southeast Asia, often considered a part of the larger Eurasian Plate. The Andaman Islands, Nicobar Islands, and northwestern Sumatra are located on the plate...
plates. The relative motion of the subducting and overriding plates varies slightly along strike due to these complexities but is always strongly oblique. The strike-slip component of the oblique convergence is accommodated by displacement on the Great Sumatran fault
Great Sumatran fault
The Indonesian island of Sumatra is located in a highly seismic area of the world. In addition to the subduction zone and the associated Sunda Arc off the west coast of the island, Sumatra also has a large strike-slip fault, the so-called Great Sumatran Fault, running the entire length of the island...
, while the dip-slip component is taken up by the Sunda megathrust.
Megathrust geometry
The Sunda megathrust is curviplanar, forming an arc in map view and, at least in Sumatra, increasing in dip from 5°-7° near the trench, then increasing gradually from 15°-20° beneath the Mentawai IslandsMentawai Islands
The Mentawai Islands are a chain of about seventy islands and islets off the western coast of Sumatra in Indonesia. Siberut is the largest of the islands. The other major islands are Sipura, North Pagai and South Pagai . The islands lie approximately 150 km off the Sumatran coast, across the...
to about 30° below the coastline of Sumatra.
Earthquakes

Historical earthquakes
Historical earthquakes is a list of significant earthquakes from before the 20th century. As the events listed here occurred before routine instrumental recordings, they rely mainly on the analysis of written sources. There is often significant uncertainty in location and magnitude and sometimes...
show that the megathrust is segmented. The largest earthquakes occur on separate 'patches' along the megathrust surface (1797
1797 Sumatra earthquake
The 1797 Sumatra earthquake was the first in a series of great earthquakes that ruptured part of the Sumatran segment of the Sunda megathrust. It caused a damaging tsunami that was particularly severe near Padang, where a 150-200 ton English ship was driven 1 km inland up the Arau...
, 1833
1833 Sumatra earthquake
The 1833 Sumatra earthquake occurred on November 25, 1833, about 22:00 local time, with an estimated magnitude in the range Mw= 8.8–9.2. It caused a large tsunami that flooded the southwestern coast of the island. There are no reliable records of the loss of life, with the casualties being...
, 1861
1861 Sumatra earthquake
The 1861 Sumatra earthquake occurred on February 16, 1861. It was the last in a sequences of earthquakes that ruptured adjacent parts of the Sumatran segment of the Sunda megathrust. It caused a devastating tsunami which led to several thousand fatalities. The earthquake was felt as far away as the...
, 2004
2004 Indian Ocean earthquake
The 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake was an undersea megathrust earthquake that occurred at 00:58:53 UTC on Sunday, December 26, 2004, with an epicentre off the west coast of Sumatra, Indonesia. The quake itself is known by the scientific community as the Sumatra-Andaman earthquake...
, 2005
2005 Sumatra earthquake
The 2005 Sumatra earthquake, referred to as the Nias Earthquake by the scientific community, was a major earthquake on 28 March 2005, located off the west coast of northern Sumatra, Indonesia. Approximately 1300 people were killed by the earthquake, mostly on the island of Nias...
& 2007), with smaller events occurring at the boundaries between these patches (1935
1935 Sumatra earthquake
The 1935 Sumatra earthquake occurred at 02:35 UTC on 28 December 1935. It had a magnitude of Mw = 7.7 and a maximum felt intensity of VIII on the mercalli intensity scale. It triggered a minor tsunami.-Tectonic setting:...
, 1984
1984 Northern Sumatra earthquake
The 1984 Northern Sumatra earthquake occurred on November 17, 1984 at 06:49 UTC. The epicenter was located off the coast of Sumatra, near the island of Nias. It was an Mw 7.2 earthquake. Building damage was reported in Nias island. This earthquake could be strongly felt in parts of Northern...
, 2000
2000 Sumatra earthquake
The 2000 Sumatra earthquake struck at 23:30 local time on June 4, 2000 off the coast of southern Sumatra, Indonesia with a magnitude of 7.9 Mw. The United States Geological Survey reported 103 fatalities, in addition to 2,174 injured people...
& 2002). The rupture area of the 1861 event appears to be very similar to that for the 2005 event, suggesting that it can be regarded as a repeat event. The 2007 event is interpreted to be a partial failure of the rupture area of the 1833 event.
The 2004 earthquake ruptured an enormous segment of the megathrust surface. Research into evidence for previous events of this size suggests that they are rare, with two candidate earlier events occurring soon after AD 1290–1400 and AD 780–990.
The Java-Bali segment of the megathrust does not appear to be associated with great earthquakes, possibly due to mainly aseismic slip.
List of Sunda megathrust earthquakes
| Date/Time‡ | Location | Coordinates | Fatalities | Magnitude Moment magnitude scale The moment magnitude scale is used by seismologists to measure the size of earthquakes in terms of the energy released. The magnitude is based on the seismic moment of the earthquake, which is equal to the rigidity of the Earth multiplied by the average amount of slip on the fault and the size of... |
Comments | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1797-02-10 | just north of Siberut Siberut Siberut is the largest and northernmost of the Mentawai Islands, lying 150 kilometres west of Sumatra in the Indian Ocean. A part of Indonesia, the island is the most important home for the Mentawai people. The western half of the island was set aside as the Siberut National Park in 1993... , Mentawai islands Mentawai Islands The Mentawai Islands are a chain of about seventy islands and islets off the western coast of Sumatra in Indonesia. Siberut is the largest of the islands. The other major islands are Sipura, North Pagai and South Pagai . The islands lie approximately 150 km off the Sumatran coast, across the... |
1.0°N 99.0°W | 300 | 8.4 | See 1797 Sumatra earthquake 1797 Sumatra earthquake The 1797 Sumatra earthquake was the first in a series of great earthquakes that ruptured part of the Sumatran segment of the Sunda megathrust. It caused a damaging tsunami that was particularly severe near Padang, where a 150-200 ton English ship was driven 1 km inland up the Arau... |
|
| 1833-11-25 | 50 km NE of North Pagai North Pagai North Pagai is one of the Mentawai Islands off the west coast of Sumatra in Indonesia. It is south of Sipura and north of South Pagai Island.... , Mentawai islands Mentawai Islands The Mentawai Islands are a chain of about seventy islands and islets off the western coast of Sumatra in Indonesia. Siberut is the largest of the islands. The other major islands are Sipura, North Pagai and South Pagai . The islands lie approximately 150 km off the Sumatran coast, across the... |
2.5°N 100.5°W | "numerous victims" | 8.8–9.2 Mw | See 1833 Sumatra earthquake 1833 Sumatra earthquake The 1833 Sumatra earthquake occurred on November 25, 1833, about 22:00 local time, with an estimated magnitude in the range Mw= 8.8–9.2. It caused a large tsunami that flooded the southwestern coast of the island. There are no reliable records of the loss of life, with the casualties being... |
|
| 1861-02-16 | Nias Nias Nīas is an island off the western coast of Sumatra, Indonesia. Nias is also the name of the archipelago, containing the Hinako archipelago.... |
1.0°N 97.5°W | 905 | 8.5 | Caused major tsunami. See 1861 Sumatra earthquake 1861 Sumatra earthquake The 1861 Sumatra earthquake occurred on February 16, 1861. It was the last in a sequences of earthquakes that ruptured adjacent parts of the Sumatran segment of the Sunda megathrust. It caused a devastating tsunami which led to several thousand fatalities. The earthquake was felt as far away as the... . |
|
| 1935-12-28 02:35 | just west of the Batu Islands Batu Islands The Batu Islands are an archipelago of Indonesia located in the Indian Ocean off the west coast of Sumatra, between Nias and Siberut. The three primary islands, of approximately equal size, are Pini, Tanahmasa, and Tanahbala. There are forty-eight smaller islands, of which less than half are... |
0.0°N 98.2°W | 7.7 | See 1935 Sumatra earthquake 1935 Sumatra earthquake The 1935 Sumatra earthquake occurred at 02:35 UTC on 28 December 1935. It had a magnitude of Mw = 7.7 and a maximum felt intensity of VIII on the mercalli intensity scale. It triggered a minor tsunami.-Tectonic setting:... |
||
| 1984-11-17 06:49 | Between Nias and the Batu Islands | 0.20°N 98.03°W | 7.2 | See 1984 Northern Sumatra earthquake 1984 Northern Sumatra earthquake The 1984 Northern Sumatra earthquake occurred on November 17, 1984 at 06:49 UTC. The epicenter was located off the coast of Sumatra, near the island of Nias. It was an Mw 7.2 earthquake. Building damage was reported in Nias island. This earthquake could be strongly felt in parts of Northern... |
||
| 2000-06-04 16:28 | 70 km NNW of Enggano Island Enggano Island Enggano Island is about 100 km south west of Sumatra, Indonesia. It is about 35 km long from east to west and about 16 km wide from north to south. Its area is 402.6 km², the average elevation is about 100 m and the highest point is 281 m. Politically it is a... |
4.72°N 102.09°W | 46 | 7.9 | See 2000 Sumatra earthquake 2000 Sumatra earthquake The 2000 Sumatra earthquake struck at 23:30 local time on June 4, 2000 off the coast of southern Sumatra, Indonesia with a magnitude of 7.9 Mw. The United States Geological Survey reported 103 fatalities, in addition to 2,174 injured people... |
|
| 2002-11-02 01:26 | 8 km north of Simeulue Regency | 2.82°N 96.09°W | 3 | 7.3 | See 2002 Sumatra earthquake 2002 Sumatra earthquake The 2002 Sumatra earthquake occurred at 01:26 UTC on 2 November. It had a magnitude of 7.3 on the moment magnitude scale with an epicenter just north of Simeulue island and caused three deaths... |
|
| 2004-12-26 00:58 | 50 km north of Simeulue Regency | 3.30°N 95.87°W | 229,000 | 9.3 Mw (USGS) | See 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake The 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake was an undersea megathrust earthquake that occurred at 00:58:53 UTC on Sunday, December 26, 2004, with an epicentre off the west coast of Sumatra, Indonesia. The quake itself is known by the scientific community as the Sumatra-Andaman earthquake... |
|
| 2005-03-28 16:09 | Bangkaru, Banyak Islands Banyak Islands The Banyak Islands are a group of mostly uninhabited islands located between Simeulue and Nias off the western coast of Sumatra in Indonesia's Aceh Province, consisting of 99 small land masses. The largest island in the group is Tuangku , with the principal town of Alaban... |
2.08°N 97.11°W | 1,303 | 8.6 Mw (HRV) | See 2005 Sumatra earthquake 2005 Sumatra earthquake The 2005 Sumatra earthquake, referred to as the Nias Earthquake by the scientific community, was a major earthquake on 28 March 2005, located off the west coast of northern Sumatra, Indonesia. Approximately 1300 people were killed by the earthquake, mostly on the island of Nias... |
|
| 2007-09-12 11:10 | 125 km SW of Bengkulu Bengkulu Bengkulu is a province of Indonesia. It is on the southwest coast of the island of Sumatra, and borders the provinces of West Sumatra, Jambi, South Sumatra and Lampung. The capital and largest city is Bengkulu city. It was formerly the site of a British garrison, which they called Bencoolen... |
4.517°N 101.382°W | 25 | 8.4 Mw (HRV) | See September 2007 Sumatra earthquake |

