.gif)
Water (data page)
Encyclopedia
This page provides supplementary data of the properties of water
.
Further comprehensive authoritative data can be found at the NIST Webbook page on thermophysical properties of fluids.
where P is equilibrium vapor pressure in kPa
, and T is temperature in kelvin
s.
for T = 273 K to 333 K: A = 7.2326; B = 1750.286; C = 38.1
for T = 333 K to 423 K: A = 7.0917; B = 1668.21; C = 45.1
Data in the table above is given for water-steam equilibria at various temperatures over the entire temperature range at which liquid water can exist. Pressure of the equilibrium is given in the second column in kPa
. The third column is the heat content of each gram of the liquid phase relative to water at 0 °C. The fourth column is the heat of vaporization of each gram of liquid that changes to vapor. The fifth column is the PV work done by each gram of liquid that changes to vapor. The sixth column is the density of the vapor.
‡Ice XI triple point is theoretical and has never been obtained
Note: ρ is density, n is refractive index at 589 nm and η is viscosity, all at 20 °C; Teq is the equilibrium temperature between two phases: ice/liquid solution for Teq < 0-0.1 and NaCl/liquid solution for Teq above 0.1 °C.

----
(equivalent to 1 bar). Up to 99.63 °C (the boiling point of water at 0.1 MPa), at this pressure water exists as a liquid. Above that, it exists as water vapor. Note that the boiling point of 100.0 °C is at a pressure of 0.101325 MPa (1 atm
), which is the average atmospheric pressure.
(equivalent to 0.006117 bar). Up to a temperature of 0.01 °C, the triple point
of water, water normally exists as ice, except for supercooled water, for which one data point is tabulated here. At the triple point, ice can exist together with both liquid water and vapor. At higher temperatures, the data are for water vapor only.
To use the values correctly, consider the following points:
.
Over liquid water
For temperature range: 173.15 K to 373.15 K or equivalently −100 °C to 100 °C
Over ice
For temperature range: 173.15 K to 273.15 K or equivalently −100 °C to 0 °C
At triple point
An important basic value, which is not registered in the table, is the saturated vapor pressure at the triple point
of water. The internationally accepted value according to measurements of Guildner, Johnson and Jones (1976) amounts to:
Water (properties)
Water is the most abundant compound on Earth's surface, covering about 70%. In nature, it exists in liquid, solid, and gaseous states. It is in dynamic equilibrium between the liquid and gas states at standard temperature and pressure. At room temperature, it is a tasteless and odorless liquid,...
.
Further comprehensive authoritative data can be found at the NIST Webbook page on thermophysical properties of fluids.
Structure and properties
| Structure and properties | |
|---|---|
| Index of refraction, nD | 1.333 at 20 °C |
| Dielectric constant Dielectric constant The relative permittivity of a material under given conditions reflects the extent to which it concentrates electrostatic lines of flux. In technical terms, it is the ratio of the amount of electrical energy stored in a material by an applied voltage, relative to that stored in a vacuum... |
88.00 ε0 at 0 °C 86.04 ε0 at 5 °C 84.11 ε0 at 10 °C 82.22 ε0 at 15 °C 80.36 ε0 at 20 °C 78.54 ε0 at 25 °C 76.75 ε0 at 30 °C 75.00 ε0 at 35 °C 73.28 ε0 at 40 °C 71.59 ε0 at 45 °C 69.94 ε0 at 50 °C 66.74 ε0 at 60 °C 63.68 ε0 at 70 °C 60.76 ε0 at 80 °C 57.98 ε0 at 90 °C 55.33 ε0 at 100 °C |
| Bond strength | 492.215 kJ/mol O–H bond dissociation energy |
| Bond length Bond length - Explanation :Bond length is related to bond order, when more electrons participate in bond formation the bond will get shorter. Bond length is also inversely related to bond strength and the bond dissociation energy, as a stronger bond will be shorter... |
95.87 pm (equilibrium) |
| Bond angle | 104.4776° (equilibrium) |
| Magnetic susceptibility Magnetic susceptibility In electromagnetism, the magnetic susceptibility \chi_m is a dimensionless proportionality constant that indicates the degree of magnetization of a material in response to an applied magnetic field... |
−9.04 × 10−6 volume SI Si Si, si, or SI may refer to :- Measurement, mathematics and science :* International System of Units , the modern international standard version of the metric system... units |
Thermodynamic properties
| Phase behavior | |
|---|---|
| Triple point Triple point In thermodynamics, the triple point of a substance is the temperature and pressure at which the three phases of that substance coexist in thermodynamic equilibrium... |
273.16 K (0.01 °C), 611.73 Pa |
| Critical point Critical point (thermodynamics) In physical chemistry, thermodynamics, chemistry and condensed matter physics, a critical point, also called a critical state, specifies the conditions at which a phase boundary ceases to exist... |
647 K (374 °C), 22.1 MPa |
| Std enthalpy change of fusion, ΔfusH |
6.01 kJ/mol |
| Std entropy change of fusion Standard entropy change of fusion The entropy of fusion is the increase in entropy when melting a substance. This is always positive since the degree of disorder increases in the transition from an organized crystalline solid to the disorganized structure of a liquid... , ΔfusS |
22.0 J/(mol·K) |
| Std enthalpy change of vaporization Standard enthalpy change of vaporization The enthalpy of vaporization, , also known as the heat of vaporization or heat of evaporation, is the energy required to transform a given quantity of a substance into a gas at a given pressure .It is often measured at the normal boiling point of a substance; although tabulated values are usually... , ΔvapH |
40.68 kJ/mol |
| Std entropy change of vaporization Standard entropy change of vaporization The entropy of vaporization is the increase in entropy when vaporizing a substance. This is always positive since the degree of disorder increases in the transition from an organized crystalline solid or a slightly less organized liquid to the extremely disorganized structure of a gas... , ΔvapS |
108.9 J/(mol·K) |
| Std enthalpy change of sublimation, ΔsubH |
46.70 kJ/mol |
| Std entropy change of sublimation, ΔsubS |
130.9 J/(mol·K) |
| Molal freezing point constant Freezing-point depression Freezing-point depression describes the phenomenon in which the freezing point of a liquid is depressed when another compound is added, meaning that a solution has a lower freezing point than a pure solvent. This happens whenever a non-volatile solute is added to a pure solvent, such as water... |
−1.858 °C kg/mol |
| Molal boiling point constant Boiling-point elevation Boiling-point elevation describes the phenomenon that the boiling point of a liquid will be higher when another compound is added, meaning that a solution has a higher boiling point than a pure solvent. This happens whenever a non-volatile solute, such as a salt, is added to a pure solvent, such... |
0.512 °C kg/mol |
| Solid properties | |
| Std enthalpy change of formation Standard enthalpy change of formation The standard enthalpy of formation or standard heat of formation of a compound is the change of enthalpy that accompanies the formation of 1 mole of a substance in its standard state from its constituent elements in their standard states... , ΔfH |
−291.83 kJ/mol |
| Standard molar entropy Standard molar entropy In chemistry, the standard molar entropy is the entropy content of one mole of substance, under standard conditions .... , S |
41 J/(mol K) |
| Heat capacity Heat capacity Heat capacity , or thermal capacity, is the measurable physical quantity that characterizes the amount of heat required to change a substance's temperature by a given amount... , cp |
12.2 J/(mol K) at −200 °C 15.0 J/(mol K) at −180 °C 17.3 J/(mol K) at −160 °C 19.8 J/(mol K) at −140 °C 24.8 J/(mol K) at −100 °C 29.6 J/(mol K) at −60 °C 32.77 J/(mol K) at −38.3 °C 33.84 J/(mol K) at −30.6 °C 35.20 J/(mol K) at −20.8 °C 36.66 J/(mol K) at −11.0 °C 37.19 J/(mol K) at −4.9 °C 37.84 J/(mol K) at −2.2 °C |
| Liquid properties | |
| Std enthalpy change of formation Standard enthalpy change of formation The standard enthalpy of formation or standard heat of formation of a compound is the change of enthalpy that accompanies the formation of 1 mole of a substance in its standard state from its constituent elements in their standard states... , ΔfH |
−285.83 kJ/mol |
| Standard molar entropy Standard molar entropy In chemistry, the standard molar entropy is the entropy content of one mole of substance, under standard conditions .... , S |
69.95 J/(mol K) |
| Heat capacity Heat capacity Heat capacity , or thermal capacity, is the measurable physical quantity that characterizes the amount of heat required to change a substance's temperature by a given amount... , cp |
75.97 J/(mol K) at 0 °C 75.42 J/(mol K) at 10 °C 75.33 J/(mol K) at 20 °C 75.28 J/(mol K) at 25 °C 75.26 J/(mol K) at 30 °C 75.26 J/(mol K) at 40 °C 75.30 J/(mol K) at 50 °C 75.37 J/(mol K) at 60 °C 75.46 J/(mol K) at 70 °C 75.58 J/(mol K) at 80 °C 75.74 J/(mol K) at 90 °C 75.94 J/(mol K) at 100 °C |
| Gas properties | |
| Std enthalpy change of formation Standard enthalpy change of formation The standard enthalpy of formation or standard heat of formation of a compound is the change of enthalpy that accompanies the formation of 1 mole of a substance in its standard state from its constituent elements in their standard states... , ΔfH |
−241.83 kJ/mol |
| Standard molar entropy Standard molar entropy In chemistry, the standard molar entropy is the entropy content of one mole of substance, under standard conditions .... , S |
188.84 J/(mol K) |
| Heat capacity Heat capacity Heat capacity , or thermal capacity, is the measurable physical quantity that characterizes the amount of heat required to change a substance's temperature by a given amount... , cp |
36.5 J/(mol K) at 100 °C 36.1 J/(mol K) at 200 °C 36.2 J/(mol K) at 400 °C 37.9 J/(mol K) at 700 °C 41.4 J/(mol K) at 1000 °C |
| Heat capacity Heat capacity Heat capacity , or thermal capacity, is the measurable physical quantity that characterizes the amount of heat required to change a substance's temperature by a given amount... , cv |
27.5 J/(mol K) at 100 °C 27.6 J/(mol K) at 200 °C 27.8 J/(mol K) at 400 °C 29.5 J/(mol K) at 700 °C 33.1 J/(mol K) at 1000 °C |
| Heat capacity ratio Heat capacity ratio The heat capacity ratio or adiabatic index or ratio of specific heats, is the ratio of the heat capacity at constant pressure to heat capacity at constant volume . It is sometimes also known as the isentropic expansion factor and is denoted by \gamma or \kappa . The latter symbol kappa is... , γ = cp/cv |
1.324 at 100 °C 1.310 at 200 °C 1.301 at 400 °C 1.282 at 700 °C 1.252 at 1000 °C |
| van der Waals' constants Van der Waals equation The van der Waals equation is an equation of state for a fluid composed of particles that have a non-zero volume and a pairwise attractive inter-particle force It was derived by Johannes Diderik van der Waals in 1873, who received the Nobel prize in 1910 for "his work on the equation of state for... |
a = 553.6 L2 kPa/mol2 b = 0.03049 liter per mole |
Liquid physical properties

| Velocity of sound in water Velocity of Sound Velocity of Sound is an album by The Apples in Stereo. It was the group's fifth album, released in October 2002. The American release has an orange album cover, while the European version is green and the Japanese version is blue... |
|
|---|---|
| c in distilled water at 25 °C | 1498 m/s |
| c at other temperatures | 1403 m/s at 0 °C 1427 m/s at 5 °C 1447 m/s at 10 °C 1481 m/s at 20 °C 1507 m/s at 30 °C 1526 m/s at 40 °C 1541 m/s at 50 °C 1552 m/s at 60 °C 1555 m/s at 70 °C1555 m/s at 80 °C 1550 m/s at 90 °C 1543 m/s at 100 °C |
| Density Density The mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight... |
|
| 0.99984 g/cm3 at 0 °C | 0.98804 g/cm3 at 50 °C |
| 0.99997 g/cm3 at 4 °C | 0.98570 g/cm3 at 55 °C |
| 0.99996 g/cm3 at 5 °C | 0.98321 g/cm3 at 60 °C |
| 0.99970 g/cm3 at 10 °C | 0.98056 g/cm3 at 65 °C |
| 0.99910 g/cm3 at 15 °C | 0.97778 g/cm3 at 70 °C |
| 0.99820 g/cm3 at 20 °C | 0.97486 g/cm3 at 75 °C |
| 0.99704 g/cm3 at 25 °C | 0.97180 g/cm3 at 80 °C |
| 0.99564 g/cm3 at 30 °C | 0.96862 g/cm3 at 85 °C |
| 0.99403 g/cm3 at 35 °C | 0.96531 g/cm3 at 90 °C |
| 0.99221 g/cm3 at 40 °C | 0.96189 g/cm3 at 95 °C |
| 0.99022 g/cm3 at 45 °C | 0.95835 g/cm3 at 100 °C |
| Viscosity Viscosity Viscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid which is being deformed by either shear or tensile stress. In everyday terms , viscosity is "thickness" or "internal friction". Thus, water is "thin", having a lower viscosity, while honey is "thick", having a higher viscosity... |
|
| η = 1.7921 mPa·s (cP Poise The poise is the unit of dynamic viscosity in the centimetre gram second system of units. It is named after Jean Louis Marie Poiseuille .... ) at 0 °C |
η = 0.5494 mPa·s at 50 °C |
| η = 1.5188 mPa·s at 5 °C | η = 0.5064 mPa·s at 55 °C |
| η = 1.3077 mPa·s at 10 °C | η = 0.4688 mPa·s at 60 °C |
| η = 1.1404 mPa·s at 15 °C | η = 0.4355 mPa·s at 65 °C |
| η = 1.0050 mPa·s at 20 °C | η = 0.4061 mPa·s at 70 °C |
| η = 0.8937 mPa·s at 25 °C | η = 0.3799 mPa·s at 75 °C |
| η = 0.8007 mPa·s at 30 °C | η = 0.3635 mPa·s at 80 °C |
| η = 0.7225 mPa·s at 35 °C | η = 0.3355 mPa·s at 85 °C |
| η = 0.6560 mPa·s at 40 °C | η = 0.3165 mPa·s at 90 °C |
| η = 0.5988 mPa·s at 45 °C | η = 0.2994 mPa·s at 95 °C |
| η = 0.2838 mPa·s at 100 °C | |
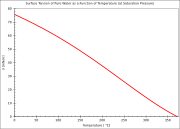
| Surface tension Surface tension Surface tension is a property of the surface of a liquid that allows it to resist an external force. It is revealed, for example, in floating of some objects on the surface of water, even though they are denser than water, and in the ability of some insects to run on the water surface... |
|
| 75.64 dyn Dyn Dyn or DYN may refer to:* DYN * Dyne, unit of force* DynDNS... /cm at 0 °C |
69.56 dyn/cm at 40 °C |
| 74.92 dyn/cm at 5 °C | 68.74 dyn/cm at 45 °C |
| 74.22 dyn/cm at 10 °C | 67.91 dyn/cm at 50 °C |
| 73.49 dyn/cm at 15 °C | 66.18 dyn/cm at 60 °C |
| 72.75 dyn/cm at 20 °C | 64.42 dyn/cm at 70 °C |
| 71.97 dyn/cm at 25 °C | 62.61 dyn/cm at 80 °C |
| 71.18 dyn/cm at 30 °C | 60.75 dyn/cm at 90 °C |
| 70.38 dyn/cm at 35 °C | 58.85 dyn/cm at 100 °C |
| Temperature, °C | Conductivity, μS/m |
|---|---|
| 0.01 | 1.15 |
| 25 | 5.50 |
| 100 | 76.5 |
| 200 | 299 |
| 300 | 241 |
Water/steam equilibrium properties
Vapor pressure formula for steam in equilibrium with liquid water:-
- log10(P) = A − B / (T – C)
where P is equilibrium vapor pressure in kPa
Pascal (unit)
The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre...
, and T is temperature in kelvin
Kelvin
The kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
s.
for T = 273 K to 333 K: A = 7.2326; B = 1750.286; C = 38.1
for T = 333 K to 423 K: A = 7.0917; B = 1668.21; C = 45.1
| Steam table | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temp. | Pressure | H of liquid | ΔvapH | ΔvapW | ρ of vapor |
| 0 °C | 0.612 kPa | 0.00 J/g | 2496.5 J/g | 126.0 J/g | 0.004845 kg/m3 |
| 10 °C | 1.227 kPa | 42.0 J/g | 2473.5 J/g | 130.5 J/g | 0.009398 kg/m3 |
| 20 °C | 2.536 kPa | 83.8 J/g | 2450.9 J/g | 135.1 J/g | 0.01728 kg/m3 |
| 30 °C | 4.242 kPa | 125.6 J/g | 2427.9 J/g | 139.7 J/g | 0.03036 kg/m3 |
| 40 °C | 7.370 kPa | 167.2 J/g | 2404.9 J/g | 144.2 J/g | 0.05107 kg/m3 |
| 50 °C | 12.33 kPa | 209.0 J/g | 2381.4 J/g | 148.7 J/g | 0.08285 kg/m3 |
| 60 °C | 19.90 kPa | 250.8 J/g | 2357.6 J/g | 153.0 J/g | 0.1300 kg/m3 |
| 70 °C | 31.15 kPa | 292.7 J/g | 2332.9 J/g | 157.3 J/g | 0.1979 kg/m3 |
| 80 °C | 46.12 kPa | 334.6 J/g | 2307.7 J/g | 161.5 J/g | 0.2931 kg/m3 |
| 90 °C | 70.10 kPa | 376.6 J/g | 2282.6 J/g | 165.5 J/g | 0.4232 kg/m3 |
| 100 °C | 101.32 kPa | 419.0 J/g | 2256.3 J/g | 169.4 J/g | 0.5974 kg/m3 |
| 110 °C | 143.27 kPa | 460.8 J/g | 2229.5 J/g | 173.1 J/g | 0.8264 kg/m3 |
| 120 °C | 198.50 kPa | 503.2 J/g | 2201.4 J/g | 176.7 J/g | 1.121 kg/m3 |
| 130 °C | 270.13 kPa | 545.8 J/g | 2172.5 J/g | 180.2 J/g | 1.497 kg/m3 |
| 140 °C | 361.4 kPa | 588.5 J/g | 2142.8 J/g | 183.2 J/g | 1.967 kg/m3 |
| 150 °C | 476.0 kPa | 631.5 J/g | 2111.8 J/g | 186.1 J/g | 2.548 kg/m3 |
| 160 °C | 618.1 kPa | 674.7 J/g | 2080.0 J/g | 188.7 J/g | 3.263 kg/m3 |
| 170 °C | 792.0 kPa | 718.5 J/g | 2047.0 J/g | 190.6 J/g | 4.023 kg/m3 |
| 180 °C | 1002.7 kPa | 762.5 J/g | 2012.2 J/g | 192.8 J/g | 5.165 kg/m3 |
| 190 °C | 1254.9 kPa | 807.0 J/g | 1975.8 J/g | 194.5 J/g | 6.402 kg/m3 |
| 200 °C | 1554.3 kPa | 851.9 J/g | 1937.3 J/g | 195.6 J/g | 7.868 kg/m3 |
| 210 °C | 1907.9 kPa | 897.5 J/g | 1897.5 J/g | 196.3 J/g | 9.606 kg/m3 |
| 221.1 °C | 2369.8 kPa | 948.5 J/g | 1850.2 J/g | 196.6 J/g | 11.88 kg/m3 |
| 229.4 °C | 2769.6 kPa | 987.9 J/g | 1812.5 J/g | 196.2 J/g | 13.87 kg/m3 |
| 240.6 °C | 3381.1 kPa | 1040.6 J/g | 1759.4 J/g | 195.1 J/g | 16.96 kg/m3 |
| 248.9 °C | 3904.1 kPa | 1080.3 J/g | 1715.8 J/g | 193.7 J/g | 19.66 kg/m3 |
| 260.0 °C | 4695.9 kPa | 1134.8 J/g | 1653.9 J/g | 190.8 J/g | 23.84 kg/m3 |
| 271.1 °C | 5603.4 kPa | 1195.9 J/g | 1586.5 J/g | 186.9 J/g | 28.83 kg/m3 |
| 279.4 °C | 6366.5 kPa | 1240.7 J/g | 1532.5 J/g | 183.3 J/g | 33.18 kg/m3 |
| 290.6 °C | 7506.2 kPa | 1302.3 J/g | 1456.3 J/g | 177.4 J/g | 39.95 kg/m3 |
| 298.9 °C | 8463.9 kPa | 1350.0 J/g | 1394.8 J/g | 172.2 J/g | 45.93 kg/m3 |
| 310.0 °C | 9878.0 kPa | 1415.7 J/g | 1307.7 J/g | 164.2 J/g | 55.25 kg/m3 |
| 321.1 °C | 11461 kPa | 1483.9 J/g | 1212.7 J/g | 154.5 J/g | 66.58 kg/m3 |
| 329.4 °C | 12785 kPa | 1537.9 J/g | 1133.2 J/g | 145.6 J/g | 76.92 kg/m3 |
| 340.6 °C | 14727 kPa | 1617.9 J/g | 1007.6 J/g | 130.9 J/g | 94.25 kg/m3 |
| 348.9 °C | 16331 kPa | 1687.0 J/g | 892.0 J/g | 117.0 J/g | 111.5 kg/m3 |
| 360.0 °C | 18682 kPa | 1797.0 J/g | 694.0 J/g | 91.0 J/g | 145.3 kg/m3 |
| 371.1 °C | 21349 kPa | 1968.3 J/g | 365.0 J/g | 47.0 J/g | 214.5 kg/m3 |
| 374.4 °C | 22242 kPa | 2151.2 J/g | 0 J/g | 0 J/g | 306.8 kg/m3 |
| Temp. | Pressure | H of liquid | ΔvapH | ΔvapW | ρ of vapor |
Data in the table above is given for water-steam equilibria at various temperatures over the entire temperature range at which liquid water can exist. Pressure of the equilibrium is given in the second column in kPa
Pascal (unit)
The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre...
. The third column is the heat content of each gram of the liquid phase relative to water at 0 °C. The fourth column is the heat of vaporization of each gram of liquid that changes to vapor. The fifth column is the PV work done by each gram of liquid that changes to vapor. The sixth column is the density of the vapor.
Melting point of ice at various pressures
Data obtained from CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics 44th ed., p. 2390| Pressure kPa KPA KPA may refer to:* Kenya Ports Authority* Kiln phosphoric acid, a dry process to produce phosphoric acid at high temperature in a kiln* Kilopascal , a unit of pressure* Known-plaintext attack, a method of cryptanalysis* Korean People's Army... |
Temp. °C |
| 101.325 | 0.0 |
| 32950 | −2.5 |
| 60311 | −5.0 |
| 87279 | −7.5 |
| 113267 | −10.0 |
| 138274 | −12.5 |
| 159358 | −15.0 |
| 179952 | −17.5 |
| 200251 | −20.0 |
| 215746 | −22.1 |
Table of various forms of ice
| Properties of various forms of ice Ice Ice is water frozen into the solid state. Usually ice is the phase known as ice Ih, which is the most abundant of the varying solid phases on the Earth's surface. It can appear transparent or opaque bluish-white color, depending on the presence of impurities or air inclusions... |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ice form | Density g/cm3 | Crystal structure | Triple points | TP temp °C | TP pressure MPa |
| Ih Ice Ih thumb|Photograph showing details of an ice cube under magnification. Ice Ih is the form of ice commonly seen on earth.Ice Ih is the hexagonal crystal form of ordinary ice, or frozen water. Virtually all ice in the biosphere is ice Ih, with the exception only of a small amount of ice Ic which is... |
0.92 | hexagonal Hexagonal crystal system In crystallography, the hexagonal crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems, the hexagonal lattice system is one of the 7 lattice systems, and the hexagonal crystal family is one of the 6 crystal families... |
Lq, Vap, Ih | 0.01 | 0.000612 |
| Lq, Ih, III | −22.0 | 207.5 | |||
| Ih, II, III | −34.7 | 212.9 | |||
| Ic Ice Ic Ice Ic is a metastable cubic crystalline variant of ice. The oxygen atoms are arranged in a diamond structure. It is produced at temperatures between 130 and 220 K , and can exist up to 240 K, when it transforms into ice Ih. It may occasionally be present in the upper atmosphere.Ordinary water ice... |
0.92 | cubic Cubic crystal system In crystallography, the cubic crystal system is a crystal system where the unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals.... |
|||
| II Ice II Ice II is a rhombohedral crystalline form of ice with highly ordered structure. It is formed from ice Ih by compressing it at temperature of 198 K at 300 MPa or by decompressing ice V. When heated it undergoes transformation to ice III.... |
1.17 | rhombohedral Rhombohedral crystal system In crystallography, the trigonal crystal system is one of the seven crystal systems, and the rhombohedral lattice system is one of the seven lattice systems... |
Ih, II, III | −34.7 | 212.9 |
| II, III, V | −24.3 | 344.3 | |||
| II, V, VI | −55 (est) | 620 | |||
| III Ice III Ice III is a form of solid matter which consists of tetragonal crystalline ice, formed by cooling water down to at . It is the least dense of the high-pressure water phases, with a density of . The proton-ordered form of is ice IX.... |
1.14 | tetragonal Tetragonal crystal system In crystallography, the tetragonal crystal system is one of the 7 lattice point groups. Tetragonal crystal lattices result from stretching a cubic lattice along one of its lattice vectors, so that the cube becomes a rectangular prism with a square base and height .There are two tetragonal Bravais... |
Lq, Ih, III | −22.0 | 207.5 |
| Lq, III, V | −17 | 346.3 | |||
| Ih, II, III | −34.7 | 212.9 | |||
| II, III, V | −24.3 | 344.3 | |||
| IV | 1.27 | rhombohedral | |||
| V | 1.23 | monoclinic Monoclinic crystal system In crystallography, the monoclinic crystal system is one of the 7 lattice point groups. A crystal system is described by three vectors. In the monoclinic system, the crystal is described by vectors of unequal length, as in the orthorhombic system. They form a rectangular prism with a... |
Lq, III, V | −17 | 346.3 |
| Lq, V, VI | 0.16 | 625.9 | |||
| II, III, V | −24.3 | 344.3 | |||
| II, V, VI | −55 (est) | 620 | |||
| VI | 1.31 | tetragonal | Lq, V, VI | 0.16 | 625.9 |
| Lq, VI, VII | 81.6 | 2200 | |||
| II, V, VI | −55 (est) | 620 | |||
| VI, VII, VIII | ≈5 | 2100 | |||
| VII Ice VII Ice VII is a cubic crystalline form of ice. It has a triple point with liquid water and Ice VI at 355 K and 2.216 GPa, with the melt line extending to at least 715 K and 10 GPa. It can also be reached in the solid state by increasing the pressure on ice VI at ambient temperature. Like the majority... |
1.50 | cubic | Lq, VI, VII | 81.6 | 2200 |
| VI, VII, VIII | ≈5 | 2100 | |||
| VII, VIII, X | −173 | 62000 | |||
| VIII Ice VIII Ice VIII is a tetragonal crystalline form of ice formed from ice VII by cooling it below 5 °C. It is more ordered than ice VII, since the hydrogen atoms assume fixed positions.... |
1.46 | tetragonal | VI, VII, VIII | ≈5 | 2100 |
| VII, VIII, X | −173 | 62000 | |||
| IX Ice IX Ice IX is a form of solid water stable at temperatures below 140 K and pressures between 200 and 400 MPa. It has a tetragonal crystal lattice and a density of 1.16 g/cm³, 26% higher than ordinary ice. It is formed by cooling ice III from 208 K to 165 K... |
1.16 | tetragonal | |||
| X | 2.46 | cubic | VII, VIII, X | −173 | 62000 |
| XI‡ | 0.92 | orthorhombic Orthorhombic crystal system In crystallography, the orthorhombic crystal system is one of the seven lattice point groups. Orthorhombic lattices result from stretching a cubic lattice along two of its orthogonal pairs by two different factors, resulting in a rectangular prism with a rectangular base and height , such that a,... |
Vap, Ih, XI | −201.5 | 0 (expected) |
| XII Ice XII Ice XII is a metastable, dense, crystalline phase of solid water, a type of ice. Ice XII was first reported in 1996 by C. Lobban, J.L. Finney and W.F. Kuhs and, after initial caution, was properly identified in 1998.... |
1.29 | tetragonal | |||
| XIII | 1.23 | monoclinic | |||
| XIV | 1.29 | orthorhombic | |||
‡Ice XI triple point is theoretical and has never been obtained
Phase diagram
Water with dissolved NaCl
| NaCl, wt% | Teq, °C | ρ, g/cm3 | n | η, mPa·s |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0.99984 | 1.333 | 1.002 |
| 0.5 | −0.3 | 1.0018 | 1.3339 | 1.011 |
| 1 | −0.59 | 1.0053 | 1.3347 | 1.02 |
| 2 | −1.19 | 1.0125 | 1.3365 | 1.036 |
| 3 | −1.79 | 1.0196 | 1.3383 | 1.052 |
| 4 | −2.41 | 1.0268 | 1.34 | 1.068 |
| 5 | −3.05 | 1.034 | 1.3418 | 1.085 |
| 6 | −3.7 | 1.0413 | 1.3435 | 1.104 |
| 7 | −4.38 | 1.0486 | 1.3453 | 1.124 |
| 8 | −5.08 | 1.0559 | 1.347 | 1.145 |
| 9 | −5.81 | 1.0633 | 1.3488 | 1.168 |
| 10 | −6.56 | 1.0707 | 1.3505 | 1.193 |
| 12 | −8.18 | 1.0857 | 1.3541 | 1.25 |
| 14 | −9.94 | 1.1008 | 1.3576 | 1.317 |
| 16 | −11.89 | 1.1162 | 1.3612 | 1.388 |
| 18 | −14.04 | 1.1319 | 1.3648 | 1.463 |
| 20 | −16.46 | 1.1478 | 1.3684 | 1.557 |
| 22 | −19.18 | 1.164 | 1.3721 | 1.676 |
| 23.3 | −21.1 | |||
| 23.7 | −17.3 | |||
| 24.9 | −11.1 | |||
| 26.1 | −2.7 | |||
| 26.28 | 0 | |||
| 26.32 | 10 | |||
| 26.41 | 20 | |||
| 26.45 | 25 | |||
| 26.52 | 30 | |||
| 26.67 | 40 | |||
| 26.84 | 50 | |||
| 27.03 | 60 | |||
| 27.25 | 70 | |||
| 27.5 | 80 | |||
| 27.78 | 90 | |||
| 28.05 | 100 |
Note: ρ is density, n is refractive index at 589 nm and η is viscosity, all at 20 °C; Teq is the equilibrium temperature between two phases: ice/liquid solution for Teq < 0-0.1 and NaCl/liquid solution for Teq above 0.1 °C.
Self ionization

| °C | −35 | 0 | 25 | 60 | 300 (~50 MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pKw | 17 | 14.9 | 14.0 | 13.0 | 12 |
Spectral data
| UV-Vis | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| λmax | ? nm Nanometre A nanometre is a unit of length in the metric system, equal to one billionth of a metre. The name combines the SI prefix nano- with the parent unit name metre .The nanometre is often used to express dimensions on the atomic scale: the diameter... |
|||||||||||||||
| Extinction coefficient Molar absorptivity The molar absorption coefficient, molar extinction coefficient, or molar absorptivity, is a measurement of how strongly a chemical species absorbs light at a given wavelength... , ε |
? | |||||||||||||||
| IR Infrared Infrared light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of visible light, measured from the nominal edge of visible red light at 0.74 micrometres , and extending conventionally to 300 µm... |
||||||||||||||||
| Major absorption bands |
|
|||||||||||||||
| NMR NMR spectroscopy Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, most commonly known as NMR spectroscopy, is a research technique that exploits the magnetic properties of certain atomic nuclei to determine physical and chemical properties of atoms or the molecules in which they are contained... |
||||||||||||||||
| Proton NMR Proton NMR Proton NMR is the application of nuclear magnetic resonance in NMR spectroscopy with respect to hydrogen-1 nuclei within the molecules of a substance, in order to determine the structure of its molecules. In samples where natural hydrogen is used, practically all of the hydrogen consists of the... |
4.79 ppm in D2O ; 1.56 ppm in CDCl3 ; 0.40 ppm in C6D6 ; 4.87 in CD3OD | |||||||||||||||
| Carbon-13 NMR Carbon-13 NMR Carbon-13 NMR is the application of nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy to carbon. It is analogous to proton NMR and allows the identification of carbon atoms in an organic molecule just as proton NMR identifies hydrogen atoms... |
N/A | |||||||||||||||
| Other NMR data | ||||||||||||||||
| MS Mass spectrometry Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique that measures the mass-to-charge ratio of charged particles.It is used for determining masses of particles, for determining the elemental composition of a sample or molecule, and for elucidating the chemical structures of molecules, such as peptides and... |
||||||||||||||||
| Masses of main fragments |
||||||||||||||||
----
Additional data translated from German "Wasser (Stoffdaten)" page
The data that follows was copied and translated from the German language Wikipedia version of this page (which has moved to here). It provides supplementary physical, thermodynamic, and vapor pressure data, some of which is redundant with data in the tables above, and some of which is additional.Physical and thermodynamic tables
In the following tables, values are temperature dependent and to a lesser degree pressure dependent, and are arranged by state of aggregation (s=solid, lq=liquid, g=gas), which are clearly a function of temperature and pressure. All of the data were computed from data given in "Formulation of the Thermodynamic Properties of Ordinary Water Substance for Scientific and General Use" (1984). This applies to:- T – temperature in degrees CelsiusCelsiusCelsius is a scale and unit of measurement for temperature. It is named after the Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius , who developed a similar temperature scale two years before his death...
- V – specific volumeSpecific volumeIn thermodynamics, the specific volume of a substance is the ratio of the substance's volume to its mass. It is the reciprocal of density:In thermodynamics, the specific volume of a substance is the ratio of the substance's volume to its mass...
in decimeter3 per kilogram (1 dm3 is equivalent to 1 liter) - H – specific enthalpy in kJJouleThe joule ; symbol J) is a derived unit of energy or work in the International System of Units. It is equal to the energy expended in applying a force of one newton through a distance of one metre , or in passing an electric current of one ampere through a resistance of one ohm for one second...
per kilogram - U – specific internal energy in kJ per kilogram
- S – specific entropyEntropyEntropy is a thermodynamic property that can be used to determine the energy available for useful work in a thermodynamic process, such as in energy conversion devices, engines, or machines. Such devices can only be driven by convertible energy, and have a theoretical maximum efficiency when...
in kJ per kilogram-kelvin - cp – specific heat capacity at constant pressure in kJ per kilogram-kelvin
- γ – Thermal expansion coefficient as 10−3 per kelvin
- λ – Heat conductivity in milliwatt per meter-kelvin
- η – ViscosityViscosityViscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid which is being deformed by either shear or tensile stress. In everyday terms , viscosity is "thickness" or "internal friction". Thus, water is "thin", having a lower viscosity, while honey is "thick", having a higher viscosity...
in micropascalPascal (unit)The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre...
-seconds (1 cPPoiseThe poise is the unit of dynamic viscosity in the centimetre gram second system of units. It is named after Jean Louis Marie Poiseuille ....
= 1000 µPa·s) - σ – surface tensionSurface tensionSurface tension is a property of the surface of a liquid that allows it to resist an external force. It is revealed, for example, in floating of some objects on the surface of water, even though they are denser than water, and in the ability of some insects to run on the water surface...
in millinewtons per meter (equivalent to dyn/cm)
Standard conditions
In the following table, material data are given for standard pressure of 0.1 MPaPascal (unit)
The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre...
(equivalent to 1 bar). Up to 99.63 °C (the boiling point of water at 0.1 MPa), at this pressure water exists as a liquid. Above that, it exists as water vapor. Note that the boiling point of 100.0 °C is at a pressure of 0.101325 MPa (1 atm
Atmosphere (unit)
The standard atmosphere is an international reference pressure defined as 101325 Pa and formerly used as unit of pressure. For practical purposes it has been replaced by the bar which is 105 Pa...
), which is the average atmospheric pressure.
| Water/steam data table at standard pressure (0.1 MPa Pascal (unit) The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre... ) |
||||||||||
| T °C | V dm3/kg |
H kJ/kg |
U kJ/kg |
S kJ/(kg·K) |
cp kJ/(kg·K) |
γ 10−3/K |
λ mW / (m·K) |
η µPa·s |
σ ‡ mN/m |
|
| 0 | lq | 1.0002 | 0.06 | −0.04 | −0.0001 | 4.228 | −0.080 | 561.0 | 1792 | 75.65 |
| 5 | 1.0000 | 21.1 | 21.0 | 0.076 | 4.200 | 0.011 | 570.6 | 1518 | 74.95 | |
| 10 | 1.0003 | 42.1 | 42.0 | 0.151 | 4.188 | 0.087 | 580.0 | 1306 | 74.22 | |
| 15 | 1.0009 | 63.0 | 62.9 | 0.224 | 4.184 | 0.152 | 589.4 | 1137 | 73.49 | |
| 20 | 1.0018 | 83.9 | 83.8 | 0.296 | 4.183 | 0.209 | 598.4 | 1001 | 72.74 | |
| 25 | 1.0029 | 104.8 | 104.7 | 0.367 | 4.183 | 0.259 | 607.2 | 890.4 | 71.98 | |
| 30 | 1.0044 | 125.8 | 125.7 | 0.437 | 4.183 | 0.305 | 615.5 | 797.7 | 71.20 | |
| 35 | 1.0060 | 146.7 | 146.6 | 0.505 | 4.183 | 0.347 | 623.3 | 719.6 | 70.41 | |
| 40 | 1.0079 | 167.6 | 167.5 | 0.572 | 4.182 | 0.386 | 630.6 | 653.3 | 69.60 | |
| 45 | 1.0099 | 188.5 | 188.4 | 0.638 | 4.182 | 0.423 | 637.3 | 596.3 | 68.78 | |
| 50 | 1.0121 | 209.4 | 209.3 | 0.704 | 4.181 | 0.457 | 643.6 | 547.1 | 67.95 | |
| 60 | 1.0171 | 251.2 | 251.1 | 0.831 | 4.183 | 0.522 | 654.4 | 466.6 | 66.24 | |
| 70 | 1.0227 | 293.1 | 293.0 | 0.955 | 4.187 | 0.583 | 663.1 | 404.1 | 64.49 | |
| 80 | 1.0290 | 335.0 | 334.9 | 1.075 | 4.194 | 0.640 | 670.0 | 354.5 | 62.68 | |
| 90 | 1.0359 | 377.0 | 376.9 | 1.193 | 4.204 | 0.696 | 675.3 | 314.6 | 60.82 | |
| 99.63 | lq | 1.0431 | 417.5 | 417.4 | 1.303 | 4.217 | 0.748 | 679.0 | 283.0 | 58.99 |
| g | 1694.3 | 2675 | 2505 | 7.359 | 2.043 | 2.885 | 25.05 | 12.26 | – | |
| 100 | g | 1696.1 | 2675 | 2506 | 7.361 | 2.042 | 2.881 | 25.08 | 12.27 | 58.92 |
| 200 | 2172.3 | 2874 | 2657 | 7.833 | 1.975 | 2.100 | 33.28 | 16.18 | 37.68 | |
| 300 | 2638.8 | 3073 | 2810 | 8.215 | 2.013 | 1.761 | 43.42 | 20.29 | 14.37 | |
| 500 | 3565.5 | 3488 | 3131 | 8.834 | 2.135 | 1.297 | 66.970 | 28.57 | – | |
| 750 | 4721.0 | 4043 | 3571 | 9.455 | 2.308 | 0.978 | 100.30 | 38.48 | – | |
| 1000 | 5875.5 | 4642 | 4054 | 9.978 | 2.478 | 0.786 | 136.3 | 47.66 | – | |
| ‡ The values for surface tension for the liquid section of the table are for a liquid/air interface. Values for the gas section of the table are for a liquid/saturated steam interface. | ||||||||||
Triple point
In the following table, material data are given with a pressure of 611.7 PaPascal (unit)
The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre...
(equivalent to 0.006117 bar). Up to a temperature of 0.01 °C, the triple point
Triple point
In thermodynamics, the triple point of a substance is the temperature and pressure at which the three phases of that substance coexist in thermodynamic equilibrium...
of water, water normally exists as ice, except for supercooled water, for which one data point is tabulated here. At the triple point, ice can exist together with both liquid water and vapor. At higher temperatures, the data are for water vapor only.
| Water/steam data table at triple point pressure (0.0006117 MPa Pascal (unit) The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre... ) |
|||||||||
| T °C | V dm3/kg |
H kJ/kg |
U kJ/kg |
S kJ/(kg·K) |
cp kJ/(kg·K) |
γ 10−3/K |
λ mW / (m·K) |
η µPa·s |
|
| 0 | lq | 1.0002 | −0.04 | −0.04 | −0.0002 | 4.339 | −0.081 | 561.0 | 1792 |
| 0.01 | s | 1.0908 | −333.4 | −333.4 | −1.221 | 1.93 | 0.1 | 2.2 | – |
| lq | 1.0002 | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | 4.229 | −0.080 | 561.0 | 1791 | |
| g | 205986 | 2500 | 2374 | 9.154 | 1.868 | 3.672 | 17.07 | 9.22 | |
| 5 | g | 209913 | 2509 | 2381 | 9.188 | 1.867 | 3.605 | 17.33 | 9.34 |
| 10 | 213695 | 2519 | 2388 | 9.222 | 1.867 | 3.540 | 17.60 | 9.46 | |
| 15 | 217477 | 2528 | 2395 | 9.254 | 1.868 | 3.478 | 17.88 | 9.59 | |
| 20 | 221258 | 2537 | 2402 | 9.286 | 1.868 | 3.417 | 18.17 | 9.73 | |
| 25 | 225039 | 2547 | 2409 | 9.318 | 1.869 | 3.359 | 18.47 | 9.87 | |
| 30 | 228819 | 2556 | 2416 | 9.349 | 1.869 | 3.304 | 18.78 | 10.02 | |
| 35 | 232598 | 2565 | 2423 | 9.380 | 1.870 | 3.249 | 19.10 | 10.17 | |
| 40 | 236377 | 2575 | 2430 | 9.410 | 1.871 | 3.197 | 19.43 | 10.32 | |
| 45 | 240155 | 2584 | 2437 | 9.439 | 1.872 | 3.147 | 19.77 | 10.47 | |
| 50 | 243933 | 2593 | 2444 | 9.469 | 1.874 | 3.098 | 20.11 | 10.63 | |
| 60 | 251489 | 2612 | 2459 | 9.526 | 1.876 | 3.004 | 20.82 | 10.96 | |
| 70 | 259043 | 2631 | 2473 | 9.581 | 1.880 | 2.916 | 21.56 | 11.29 | |
| 80 | 266597 | 2650 | 2487 | 9.635 | 1.883 | 2.833 | 22.31 | 11.64 | |
| 90 | 274150 | 2669 | 2501 | 9.688 | 1.887 | 2.755 | 23.10 | 11.99 | |
| 100 | 281703 | 2688 | 2515 | 9.739 | 1.891 | 2.681 | 23.90 | 12.53 | |
| 200 | 357216 | 2879 | 2661 | 10.194 | 1.940 | 2.114 | 32.89 | 16.21 | |
| 300 | 432721 | 3076 | 2811 | 10.571 | 2.000 | 1.745 | 43.26 | 20.30 | |
| 500 | 583725 | 3489 | 3132 | 11.188 | 2.131 | 1.293 | 66.90 | 28.57 | |
| 750 | 772477 | 4043 | 3571 | 11.808 | 2.307 | 0.977 | 100.20 | 38.47 | |
| 1000 | 961227 | 4642 | 4054 | 12.331 | 2.478 | 0.785 | 136.30 | 47.66 | |
Saturated vapor pressure
The following table is based on different, complementary sources and approximation formulas, whose values are of various quality and accuracy. The values in the temperature range of −100 °C to 100 °C were inferred from D. Sunday (1982) and are quite uniform and exact. The values in the temperature range of the boiling point of the water up to the critical point (100 °C to 374 °C), are drawn from different sources and are substantially less accurate, hence they should be understood and used also only as approximate values.To use the values correctly, consider the following points:
- The values apply only to smooth interfaces and in the absence other gases or gas mixtures such as air. Hence they apply only to pure phases and need a correction factor for systems in which air is present.
- The values were not computed according formulas widely used in the US, but using somewhat more exact formulas (see below), which can also be used to compute further values in the appropriate temperature ranges.
- The saturated vapor pressure over water in the temperature range of −100 °C to −50 °C is only extrapolated [Translator's note: Supercooled liquid water is not known to exist below −42 °C].
- The values have various units (Pa, hPa or bar), which must be considered when reading them.
Formulas
The table values for −100 °C to 100 °C were computed by the following formulas, where T is in kelvins and vapor pressures, Pw and Pi, are in pascalsPascal (unit)
The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre...
.
Over liquid water
- loge(Pw) = –6094.4642 T−1 + 21.1249952 – 2.724552×10−2 T + 1.6853396×10−5 T2 + 2.4575506 loge(T)
For temperature range: 173.15 K to 373.15 K or equivalently −100 °C to 100 °C
Over ice
- loge(Pi) = –5504.4088 T−1 – 3.5704628 – 1.7337458×10−2 T + 6.5204209×10−6 T2 + 6.1295027 loge(T)
For temperature range: 173.15 K to 273.15 K or equivalently −100 °C to 0 °C
At triple point
An important basic value, which is not registered in the table, is the saturated vapor pressure at the triple point
Triple point
In thermodynamics, the triple point of a substance is the temperature and pressure at which the three phases of that substance coexist in thermodynamic equilibrium...
of water. The internationally accepted value according to measurements of Guildner, Johnson and Jones (1976) amounts to:
- Pw(ttp = 0.01 °C) = 611.657 PaPascal (unit)The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre...
± 0.010 PaPascal (unit)The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre...
at (1-α) = 99%
| Values of saturated vapor pressure of water | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temp. T in °C |
Pi(T) over ice in Pa Pascal (unit) The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre... |
Pw(T) over water in Pa Pascal (unit) The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre... |
Temp. T in °C |
Pw(T) over water in hPa Pascal (unit) The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre... |
Temp. T in °C |
P(T) in bar Bar (unit) The bar is a unit of pressure equal to 100 kilopascals, and roughly equal to the atmospheric pressure on Earth at sea level. Other units derived from the bar are the megabar , kilobar , decibar , centibar , and millibar... |
Temp. T in °C |
P(T) in bar Bar (unit) The bar is a unit of pressure equal to 100 kilopascals, and roughly equal to the atmospheric pressure on Earth at sea level. Other units derived from the bar are the megabar , kilobar , decibar , centibar , and millibar... |
Temp. T in °C |
P(T) in bar Bar (unit) The bar is a unit of pressure equal to 100 kilopascals, and roughly equal to the atmospheric pressure on Earth at sea level. Other units derived from the bar are the megabar , kilobar , decibar , centibar , and millibar... |
||||
| −100 | 0.0013957 | 0.0036309 | 0 | 6.11213 | 100 | 1.01 | 200 | 15.55 | 300 | 85.88 | ||||
| −99 | 0.0017094 | 0.0044121 | 1 | 6.57069 | 101 | 1.05 | 201 | 15.88 | 301 | 87.09 | ||||
| −98 | 0.0020889 | 0.0053487 | 2 | 7.05949 | 102 | 1.09 | 202 | 16.21 | 302 | 88.32 | ||||
| −97 | 0.0025470 | 0.0064692 | 3 | 7.58023 | 103 | 1.13 | 203 | 16.55 | 303 | 89.57 | ||||
| −96 | 0.0030987 | 0.0078067 | 4 | 8.13467 | 104 | 1.17 | 204 | 16.89 | 304 | 90.82 | ||||
| −95 | 0.0037617 | 0.0093996 | 5 | 8.72469 | 105 | 1.21 | 205 | 17.24 | 305 | 92.09 | ||||
| −94 | 0.0045569 | 0.011293 | 6 | 9.35222 | 106 | 1.25 | 206 | 17.60 | 306 | 93.38 | ||||
| −93 | 0.0055087 | 0.013538 | 7 | 10.0193 | 107 | 1.30 | 207 | 17.96 | 307 | 94.67 | ||||
| −92 | 0.0066455 | 0.016195 | 8 | 10.7280 | 108 | 1.34 | 208 | 18.32 | 308 | 95.98 | ||||
| −91 | 0.0080008 | 0.019333 | 9 | 11.4806 | 109 | 1.39 | 209 | 18.70 | 309 | 97.31 | ||||
| −90 | 0.0096132 | 0.023031 | 10 | 12.2794 | 110 | 1.43 | 210 | 19.07 | 310 | 98.65 | ||||
| −89 | 0.011528 | 0.027381 | 11 | 13.1267 | 111 | 1.48 | 211 | 19.46 | 311 | 100.00 | ||||
| −88 | 0.013797 | 0.032489 | 12 | 14.0251 | 112 | 1.53 | 212 | 19.85 | 312 | 101.37 | ||||
| −87 | 0.016482 | 0.038474 | 13 | 14.9772 | 113 | 1.58 | 213 | 20.25 | 313 | 102.75 | ||||
| −86 | 0.019653 | 0.045473 | 14 | 15.9856 | 114 | 1.64 | 214 | 20.65 | 314 | 104.15 | ||||
| −85 | 0.02339 | 0.053645 | 15 | 17.0532 | 115 | 1.69 | 215 | 21.06 | 315 | 105.56 | ||||
| −84 | 0.027788 | 0.063166 | 16 | 18.1829 | 116 | 1.75 | 216 | 21.47 | 316 | 106.98 | ||||
| −83 | 0.032954 | 0.074241 | 17 | 19.3778 | 117 | 1.81 | 217 | 21.89 | 317 | 108.43 | ||||
| −82 | 0.039011 | 0.087101 | 18 | 20.6409 | 118 | 1.86 | 218 | 22.32 | 318 | 109.88 | ||||
| −81 | 0.046102 | 0.10201 | 19 | 21.9757 | 119 | 1.93 | 219 | 22.75 | 319 | 111.35 | ||||
| −80 | 0.054388 | 0.11925 | 20 | 23.3854 | 120 | 1.99 | 220 | 23.19 | 320 | 112.84 | ||||
| −79 | 0.064057 | 0.13918 | 21 | 24.8737 | 121 | 2.05 | 221 | 23.64 | 321 | 114.34 | ||||
| −78 | 0.075320 | 0.16215 | 22 | 26.4442 | 122 | 2.12 | 222 | 24.09 | 322 | 115.86 | ||||
| −77 | 0.088419 | 0.18860 | 23 | 28.1006 | 123 | 2.18 | 223 | 24.55 | 323 | 117.39 | ||||
| −76 | 0.10363 | 0.21901 | 24 | 29.8470 | 124 | 2.25 | 224 | 25.02 | 324 | 118.94 | ||||
| −75 | 0.12127 | 0.25391 | 25 | 31.6874 | 125 | 2.32 | 225 | 25.49 | 325 | 120.51 | ||||
| −74 | 0.14168 | 0.29390 | 26 | 33.6260 | 126 | 2.40 | 226 | 25.98 | 326 | 122.09 | ||||
| −73 | 0.16528 | 0.33966 | 27 | 35.6671 | 127 | 2.47 | 227 | 26.46 | 327 | 123.68 | ||||
| −72 | 0.19252 | 0.39193 | 28 | 37.8154 | 128 | 2.55 | 228 | 26.96 | 328 | 125.30 | ||||
| −71 | 0.22391 | 0.45156 | 29 | 40.0754 | 129 | 2.62 | 229 | 27.46 | 329 | 126.93 | ||||
| −70 | 0.26004 | 0.51948 | 30 | 42.4520 | 130 | 2.70 | 230 | 27.97 | 330 | 128.58 | ||||
| −69 | 0.30156 | 0.59672 | 31 | 44.9502 | 131 | 2.78 | 231 | 28.48 | 331 | 130.24 | ||||
| −68 | 0.34921 | 0.68446 | 32 | 47.5752 | 132 | 2.87 | 232 | 29.01 | 332 | 131.92 | ||||
| −67 | 0.40383 | 0.78397 | 33 | 50.3322 | 133 | 2.95 | 233 | 29.54 | 333 | 133.62 | ||||
| −66 | 0.46633 | 0.89668 | 34 | 53.2267 | 134 | 3.04 | 234 | 30.08 | 334 | 135.33 | ||||
| −65 | 0.53778 | 1.0242 | 35 | 56.2645 | 135 | 3.13 | 235 | 30.62 | 335 | 137.07 | ||||
| −64 | 0.61933 | 1.1682 | 36 | 59.4513 | 136 | 3.22 | 236 | 31.18 | 336 | 138.82 | ||||
| −63 | 0.71231 | 1.3306 | 37 | 62.7933 | 137 | 3.32 | 237 | 31.74 | 337 | 140.59 | ||||
| −62 | 0.81817 | 1.5136 | 38 | 66.2956 | 138 | 3.42 | 238 | 32.31 | 338 | 142.37 | ||||
| −61 | 0.93854 | 1.7195 | 39 | 69.9675 | 139 | 3.51 | 239 | 32.88 | 339 | 144.18 | ||||
| −60 | 1.0753 | 1.9509 | 40 | 73.8127 | 140 | 3.62 | 240 | 33.47 | 340 | 146.00 | ||||
| −59 | 1.2303 | 2.2106 | 41 | 77.8319 | 141 | 3.72 | 241 | 34.06 | 341 | 147.84 | ||||
| −58 | 1.4060 | 2.5018 | 42 | 82.0536 | 142 | 3.82 | 242 | 34.66 | 342 | 149.71 | ||||
| −57 | 1.6049 | 2.8277 | 43 | 86.4633 | 143 | 3.93 | 243 | 35.27 | 343 | 151.58 | ||||
| −56 | 1.8296 | 3.1922 | 44 | 91.0757 | 144 | 4.04 | 244 | 35.88 | 344 | 153.48 | ||||
| −55 | 2.0833 | 3.5993 | 45 | 95.8984 | 145 | 4.16 | 245 | 36.51 | 345 | 155.40 | ||||
| −54 | 2.3694 | 4.0535 | 46 | 100.939 | 146 | 4.27 | 246 | 37.14 | 346 | 157.34 | ||||
| −53 | 2.6917 | 4.5597 | 47 | 106.206 | 147 | 4.39 | 247 | 37.78 | 347 | 159.30 | ||||
| −52 | 3.0542 | 5.1231 | 48 | 111.708 | 148 | 4.51 | 248 | 38.43 | 348 | 161.28 | ||||
| −51 | 3.4618 | 5.7496 | 49 | 117.452 | 149 | 4.64 | 249 | 39.09 | 349 | 163.27 | ||||
| −50 | 3.9193 | 6.4454 | 50 | 123.4478 | 150 | 4.76 | 250 | 39.76 | 350 | 165.29 | ||||
| −49 | 4.4324 | 7.2174 | 51 | 129.7042 | 151 | 4.89 | 251 | 40.44 | 351 | 167.33 | ||||
| −48 | 5.0073 | 8.0729 | 52 | 136.2304 | 152 | 5.02 | 252 | 41.12 | 352 | 169.39 | ||||
| −47 | 5.6506 | 9.0201 | 53 | 143.0357 | 153 | 5.16 | 253 | 41.81 | 353 | 171.47 | ||||
| −46 | 6.3699 | 10.068 | 54 | 150.1298 | 154 | 5.29 | 254 | 42.52 | 354 | 173.58 | ||||
| −45 | 7.1732 | 11.225 | 55 | 157.5226 | 155 | 5.43 | 255 | 43.23 | 355 | 175.70 | ||||
| −44 | 8.0695 | 12.503 | 56 | 165.2243 | 156 | 5.58 | 256 | 43.95 | 356 | 177.85 | ||||
| −43 | 9.0685 | 13.911 | 57 | 173.2451 | 157 | 5.72 | 257 | 44.68 | 357 | 180.02 | ||||
| −42 | 10.181 | 15.463 | 58 | 181.5959 | 158 | 5.87 | 258 | 45.42 | 358 | 182.21 | ||||
| −41 | 11.419 | 17.170 | 59 | 190.2874 | 159 | 6.03 | 259 | 46.16 | 359 | 184.43 | ||||
| −40 | 12.794 | 19.048 | 60 | 199.3309 | 160 | 6.18 | 260 | 46.92 | 360 | 186.66 | ||||
| −39 | 14.321 | 21.110 | 61 | 208.7378 | 161 | 6.34 | 261 | 47.69 | 361 | 188.93 | ||||
| −38 | 16.016 | 23.372 | 62 | 218.5198 | 162 | 6.50 | 262 | 48.46 | 362 | 191.21 | ||||
| −37 | 17.893 | 25.853 | 63 | 228.6888 | 163 | 6.67 | 263 | 49.25 | 363 | 193.52 | ||||
| −36 | 19.973 | 28.570 | 64 | 239.2572 | 164 | 6.84 | 264 | 50.05 | 364 | 195.86 | ||||
| −35 | 22.273 | 31.544 | 65 | 250.2373 | 165 | 7.01 | 265 | 50.85 | 365 | 198.22 | ||||
| −34 | 24.816 | 34.795 | 66 | 261.6421 | 166 | 7.18 | 266 | 51.67 | 366 | 200.61 | ||||
| −33 | 27.624 | 38.347 | 67 | 273.4845 | 167 | 7.36 | 267 | 52.49 | 367 | 203.02 | ||||
| −32 | 30.723 | 42.225 | 68 | 285.7781 | 168 | 7.55 | 268 | 53.33 | 368 | 205.47 | ||||
| −31 | 34.140 | 46.453 | 69 | 298.5363 | 169 | 7.73 | 269 | 54.17 | 369 | 207.93 | ||||
| −30 | 37.903 | 51.060 | 70 | 311.7731 | 170 | 7.92 | 270 | 55.03 | 370 | 210.43 | ||||
| −29 | 42.046 | 56.077 | 71 | 325.5029 | 171 | 8.11 | 271 | 55.89 | 371 | 212.96 | ||||
| −28 | 46.601 | 61.534 | 72 | 339.7401 | 172 | 8.31 | 272 | 56.77 | 372 | 215.53 | ||||
| −27 | 51.607 | 67.466 | 73 | 354.4995 | 173 | 8.51 | 273 | 57.66 | 373 | 218.13 | ||||
| −26 | 57.104 | 73.909 | 74 | 369.7963 | 174 | 8.72 | 274 | 58.56 | 374 | 220.64 | ||||
| −25 | 63.134 | 80.902 | 75 | 385.6459 | 175 | 8.92 | 275 | 59.46 | 374.15 | 221.20 | ||||
| −24 | 69.745 | 88.485 | 76 | 402.0641 | 176 | 9.14 | 276 | 60.38 | ||||||
| −23 | 76.987 | 96.701 | 77 | 419.0669 | 177 | 9.35 | 277 | 61.31 | ||||||
| −22 | 84.914 | 105.60 | 78 | 436.6708 | 178 | 9.57 | 278 | 62.25 | ||||||
| −21 | 93.584 | 115.22 | 79 | 454.8923 | 179 | 9.80 | 279 | 63.20 | ||||||
| −20 | 103.06 | 125.63 | 80 | 473.7485 | 180 | 10.03 | 280 | 64.17 | ||||||
| −19 | 113.41 | 136.88 | 81 | 493.2567 | 181 | 10.26 | 281 | 65.14 | ||||||
| −18 | 124.70 | 149.01 | 82 | 513.4345 | 182 | 10.50 | 282 | 66.12 | ||||||
| −17 | 137.02 | 162.11 | 83 | 534.3000 | 183 | 10.74 | 283 | 67.12 | ||||||
| −16 | 150.44 | 176.23 | 84 | 555.8714 | 184 | 10.98 | 284 | 68.13 | ||||||
| −15 | 165.06 | 191.44 | 85 | 578.1673 | 185 | 11.23 | 285 | 69.15 | ||||||
| −14 | 180.97 | 207.81 | 86 | 601.2068 | 186 | 11.49 | 286 | 70.18 | ||||||
| −13 | 198.27 | 225.43 | 87 | 625.0090 | 187 | 11.75 | 287 | 71.22 | ||||||
| −12 | 217.07 | 244.37 | 88 | 649.5936 | 188 | 12.01 | 288 | 72.27 | ||||||
| −11 | 237.49 | 264.72 | 89 | 674.9806 | 189 | 12.28 | 289 | 73.34 | ||||||
| −10 | 259.66 | 286.57 | 90 | 701.1904 | 190 | 12.55 | 290 | 74.42 | ||||||
| −9 | 283.69 | 310.02 | 91 | 728.2434 | 191 | 12.83 | 291 | 75.51 | ||||||
| −8 | 309.75 | 335.16 | 92 | 756.1608 | 192 | 13.11 | 292 | 76.61 | ||||||
| −7 | 337.97 | 362.10 | 93 | 784.9639 | 193 | 13.40 | 293 | 77.72 | ||||||
| −6 | 368.52 | 390.95 | 94 | 814.6743 | 194 | 13.69 | 294 | 78.85 | ||||||
| −5 | 401.58 | 421.84 | 95 | 845.3141 | 195 | 13.99 | 295 | 79.99 | ||||||
| −4 | 437.31 | 454.88 | 96 | 876.9057 | 196 | 14.29 | 296 | 81.14 | ||||||
| −3 | 475.92 | 490.19 | 97 | 909.4718 | 197 | 14.60 | 297 | 82.31 | ||||||
| −2 | 517.62 | 527.93 | 98 | 943.0355 | 198 | 14.91 | 298 | 83.48 | ||||||
| −1 | 562.62 | 568.22 | 99 | 977.6203 | 199 | 15.22 | 299 | 84.67 | ||||||
| 0 | 611.153 | 611.213 | 100 | 1013.25 | 200 | 15.55 | 300 | 85.88 | ||||||
| Temp. T in °C |
Pi(T) over ice in Pa Pascal (unit) The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre... |
Pw(T) over water in Pa Pascal (unit) The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre... |
Temp. T in °C |
Pw(T) over water in hPa Pascal (unit) The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre... |
Temp. T in °C |
P(T) in bar Bar (unit) The bar is a unit of pressure equal to 100 kilopascals, and roughly equal to the atmospheric pressure on Earth at sea level. Other units derived from the bar are the megabar , kilobar , decibar , centibar , and millibar... |
Temp. T in °C |
P(T) in bar Bar (unit) The bar is a unit of pressure equal to 100 kilopascals, and roughly equal to the atmospheric pressure on Earth at sea level. Other units derived from the bar are the megabar , kilobar , decibar , centibar , and millibar... |
Temp. T in °C |
P(T) in bar Bar (unit) The bar is a unit of pressure equal to 100 kilopascals, and roughly equal to the atmospheric pressure on Earth at sea level. Other units derived from the bar are the megabar , kilobar , decibar , centibar , and millibar... |
||||
External links
- Microwave Spectrum (by NIST)
- Compilation of properties, with citations by Martin Chaplin, London South Bank University.


