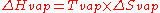Standard entropy change of vaporization
Encyclopedia
The entropy of vaporization is the increase in entropy
when vaporizing a substance. This is always positive since the degree of disorder increases in the transition
from an organized crystal
line solid
or a slightly less organized liquid
to the extremely disorganized structure of a gas
. It is denoted as ΔSovap and normally expressed in J
/mol
·K
.
A natural process such as a phase change will occur when the associated change in the Gibbs free energy
is negative. It follows that the standard entropy change of vaporization is related to the boiling point
and the standard enthalpy change of vaporization
:
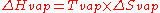
Entropy
Entropy is a thermodynamic property that can be used to determine the energy available for useful work in a thermodynamic process, such as in energy conversion devices, engines, or machines. Such devices can only be driven by convertible energy, and have a theoretical maximum efficiency when...
when vaporizing a substance. This is always positive since the degree of disorder increases in the transition
Phase transition
A phase transition is the transformation of a thermodynamic system from one phase or state of matter to another.A phase of a thermodynamic system and the states of matter have uniform physical properties....
from an organized crystal
Crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituent atoms, molecules, or ions are arranged in an orderly repeating pattern extending in all three spatial dimensions. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography...
line solid
Solid
Solid is one of the three classical states of matter . It is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to changes of shape or volume. Unlike a liquid, a solid object does not flow to take on the shape of its container, nor does it expand to fill the entire volume available to it like a...
or a slightly less organized liquid
Liquid
Liquid is one of the three classical states of matter . Like a gas, a liquid is able to flow and take the shape of a container. Some liquids resist compression, while others can be compressed. Unlike a gas, a liquid does not disperse to fill every space of a container, and maintains a fairly...
to the extremely disorganized structure of a gas
Gas
Gas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons...
. It is denoted as ΔS
Joule
The joule ; symbol J) is a derived unit of energy or work in the International System of Units. It is equal to the energy expended in applying a force of one newton through a distance of one metre , or in passing an electric current of one ampere through a resistance of one ohm for one second...
/mol
Mole (unit)
The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value...
·K
Kelvin
The kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
.
A natural process such as a phase change will occur when the associated change in the Gibbs free energy
Gibbs free energy
In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy is a thermodynamic potential that measures the "useful" or process-initiating work obtainable from a thermodynamic system at a constant temperature and pressure...
is negative. It follows that the standard entropy change of vaporization is related to the boiling point
Boiling point
The boiling point of an element or a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the environmental pressure surrounding the liquid....
and the standard enthalpy change of vaporization
Standard enthalpy change of vaporization
The enthalpy of vaporization, , also known as the heat of vaporization or heat of evaporation, is the energy required to transform a given quantity of a substance into a gas at a given pressure .It is often measured at the normal boiling point of a substance; although tabulated values are usually...
: