Van der Waals equation
Overview
Equation of state
In physics and thermodynamics, an equation of state is a relation between state variables. More specifically, an equation of state is a thermodynamic equation describing the state of matter under a given set of physical conditions...
for a fluid
Fluid
In physics, a fluid is a substance that continually deforms under an applied shear stress. Fluids are a subset of the phases of matter and include liquids, gases, plasmas and, to some extent, plastic solids....
composed of particles that have a non-zero volume and a pairwise attractive inter-particle force
Force
In physics, a force is any influence that causes an object to undergo a change in speed, a change in direction, or a change in shape. In other words, a force is that which can cause an object with mass to change its velocity , i.e., to accelerate, or which can cause a flexible object to deform...
(such as the van der Waals force
Van der Waals force
In physical chemistry, the van der Waals force , named after Dutch scientist Johannes Diderik van der Waals, is the sum of the attractive or repulsive forces between molecules other than those due to covalent bonds or to the electrostatic interaction of ions with one another or with neutral...
.) It was derived by Johannes Diderik van der Waals
Johannes Diderik van der Waals
Johannes Diderik van der Waals was a Dutch theoretical physicist and thermodynamicist famous for his work on an equation of state for gases and liquids....
in 1873, who received the Nobel prize in 1910 for "his work on the equation of state for gases and liquids". The equation is based on a modification of the ideal gas law
Ideal gas law
The ideal gas law is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. It is a good approximation to the behavior of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations. It was first stated by Émile Clapeyron in 1834 as a combination of Boyle's law and Charles's law...
and approximates the behavior of real fluids, taking into account the nonzero size of molecules and the attraction between them.
The first form of this equation is
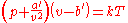
where
- p is the pressurePressurePressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
of the fluid - v is the volume of the container holding the particles divided by the total number of particles
- k is Boltzmann's constant
- T is the absolute temperatureTemperatureTemperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
- a is a measure for the attraction between the particles
- b is the average volume excluded from v by a particle
Upon introduction of the Avogadro constant NA, the number of moles
Mole (unit)
The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value...
n, and the total number of particles nNA, the equation can be cast into the second (better known) form
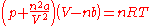
where
- p is the pressurePressurePressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
of the fluid - V is the total volume of the container containing the fluid
- a is a measure of the attraction between the particles
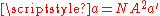
- b is the volume excluded by a mole of particles

- n is the number of moles
- R is the universal gas constantGas constantThe gas constant is a physical constant which is featured in many fundamental equations in the physical sciences, such as the ideal gas law and the Nernst equation. It is equivalent to the Boltzmann constant, but expressed in units of energy The gas constant (also known as the molar, universal,...
,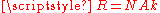
- T is the absolute temperatureTemperatureTemperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
A careful distinction must be drawn between the volume available to a particle and the volume of a particle.
Unanswered Questions

