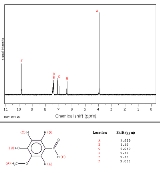
Proton NMR
Overview
Nuclear magnetic resonance
Nuclear magnetic resonance is a physical phenomenon in which magnetic nuclei in a magnetic field absorb and re-emit electromagnetic radiation...
in NMR spectroscopy
NMR spectroscopy
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, most commonly known as NMR spectroscopy, is a research technique that exploits the magnetic properties of certain atomic nuclei to determine physical and chemical properties of atoms or the molecules in which they are contained...
with respect to hydrogen-1 nuclei
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the very dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. It was discovered in 1911, as a result of Ernest Rutherford's interpretation of the famous 1909 Rutherford experiment performed by Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden, under the direction of Rutherford. The...
within the molecules of a substance, in order to determine the structure of its molecules. In samples where natural hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
(H) is used, practically all of the hydrogen consists of the isotope
Isotope
Isotopes are variants of atoms of a particular chemical element, which have differing numbers of neutrons. Atoms of a particular element by definition must contain the same number of protons but may have a distinct number of neutrons which differs from atom to atom, without changing the designation...
1H (hydrogen-1; i.e. having a proton
Proton
The proton is a subatomic particle with the symbol or and a positive electric charge of 1 elementary charge. One or more protons are present in the nucleus of each atom, along with neutrons. The number of protons in each atom is its atomic number....
for a nucleus).
Simple NMR spectra are recorded in solution
Solution
In chemistry, a solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of only one phase. In such a mixture, a solute is dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent. The solvent does the dissolving.- Types of solutions :...
, and solvent
Solvent
A solvent is a liquid, solid, or gas that dissolves another solid, liquid, or gaseous solute, resulting in a solution that is soluble in a certain volume of solvent at a specified temperature...
protons must not be allowed to interfere.

