
Urban runoff
Encyclopedia

Surface runoff
Surface runoff is the water flow that occurs when soil is infiltrated to full capacity and excess water from rain, meltwater, or other sources flows over the land. This is a major component of the water cycle. Runoff that occurs on surfaces before reaching a channel is also called a nonpoint source...
of rainwater created by urbanization
Urbanization
Urbanization, urbanisation or urban drift is the physical growth of urban areas as a result of global change. The United Nations projected that half of the world's population would live in urban areas at the end of 2008....
. This runoff is a major source of water pollution
Water pollution
Water pollution is the contamination of water bodies . Water pollution occurs when pollutants are discharged directly or indirectly into water bodies without adequate treatment to remove harmful compounds....
in many parts of the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
and other urban communities worldwide.
Overview
Road
A road is a thoroughfare, route, or way on land between two places, which typically has been paved or otherwise improved to allow travel by some conveyance, including a horse, cart, or motor vehicle. Roads consist of one, or sometimes two, roadways each with one or more lanes and also any...
s, parking lot
Parking lot
A parking lot , also known as car lot, is a cleared area that is intended for parking vehicles. Usually, the term refers to a dedicated area that has been provided with a durable or semi-durable surface....
s and sidewalk
Sidewalk
A sidewalk, or pavement, footpath, footway, and sometimes platform, is a path along the side of a road. A sidewalk may accommodate moderate changes in grade and is normally separated from the vehicular section by a curb...
s) are constructed during land development
Land development
Land development refers to altering the landscape in any number of ways such as:* changing landforms from a natural or semi-natural state for a purpose such as agriculture or housing...
. During rain
Rain
Rain is liquid precipitation, as opposed to non-liquid kinds of precipitation such as snow, hail and sleet. Rain requires the presence of a thick layer of the atmosphere to have temperatures above the melting point of water near and above the Earth's surface...
storms and other precipitation
Precipitation (meteorology)
In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation (also known as one of the classes of hydrometeors, which are atmospheric water phenomena is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravity. The main forms of precipitation...
events, these surfaces (built from materials such as asphalt
Asphalt
Asphalt or , also known as bitumen, is a sticky, black and highly viscous liquid or semi-solid that is present in most crude petroleums and in some natural deposits, it is a substance classed as a pitch...
and concrete
Concrete
Concrete is a composite construction material, composed of cement and other cementitious materials such as fly ash and slag cement, aggregate , water and chemical admixtures.The word concrete comes from the Latin word...
), along with roof
Roof
A roof is the covering on the uppermost part of a building. A roof protects the building and its contents from the effects of weather. Structures that require roofs range from a letter box to a cathedral or stadium, dwellings being the most numerous....
tops, carry polluted stormwater
Stormwater
Stormwater is water that originates during precipitation events. It may also be used to apply to water that originates with snowmelt that enters the stormwater system...
to storm drains, instead of allowing the water to percolate
Infiltration (hydrology)
Infiltration is the process by which water on the ground surface enters the soil. Infiltration rate in soil science is a measure of the rate at which soil is able to absorb rainfall or irrigation. It is measured in inches per hour or millimeters per hour. The rate decreases as the soil becomes...
through soil
Soil
Soil is a natural body consisting of layers of mineral constituents of variable thicknesses, which differ from the parent materials in their morphological, physical, chemical, and mineralogical characteristics...
. This causes lowering of the water table
Water table
The water table is the level at which the submarine pressure is far from atmospheric pressure. It may be conveniently visualized as the 'surface' of the subsurface materials that are saturated with groundwater in a given vicinity. However, saturated conditions may extend above the water table as...
(because groundwater recharge is lessened) and flood
Flood
A flood is an overflow of an expanse of water that submerges land. The EU Floods directive defines a flood as a temporary covering by water of land not normally covered by water...
ing since the amount of water that remains on the surface is greater. Most municipal storm sewer systems discharge stormwater, untreated, to stream
Stream
A stream is a body of water with a current, confined within a bed and stream banks. Depending on its locale or certain characteristics, a stream may be referred to as a branch, brook, beck, burn, creek, "crick", gill , kill, lick, rill, river, syke, bayou, rivulet, streamage, wash, run or...
s, river
River
A river is a natural watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, a lake, a sea, or another river. In a few cases, a river simply flows into the ground or dries up completely before reaching another body of water. Small rivers may also be called by several other names, including...
s and bay
Bay
A bay is an area of water mostly surrounded by land. Bays generally have calmer waters than the surrounding sea, due to the surrounding land blocking some waves and often reducing winds. Bays also exist as an inlet in a lake or pond. A large bay may be called a gulf, a sea, a sound, or a bight...
s.

Pollutants in urban runoff
Water running off these impervious surfaces tends to pick up gasolineGasoline
Gasoline , or petrol , is a toxic, translucent, petroleum-derived liquid that is primarily used as a fuel in internal combustion engines. It consists mostly of organic compounds obtained by the fractional distillation of petroleum, enhanced with a variety of additives. Some gasolines also contain...
, motor oil
Motor oil
Motor oil or engine oil is an oil used for lubrication of various internal combustion engines. The main function is to lubricate moving parts; it also cleans, inhibits corrosion, improves sealing, and cools the engine by carrying heat away from moving parts.Motor oils are derived from...
, heavy metals
Heavy metals
A heavy metal is a member of a loosely-defined subset of elements that exhibit metallic properties. It mainly includes the transition metals, some metalloids, lanthanides, and actinides. Many different definitions have been proposed—some based on density, some on atomic number or atomic weight,...
, trash
Waste
Waste is unwanted or useless materials. In biology, waste is any of the many unwanted substances or toxins that are expelled from living organisms, metabolic waste; such as urea, sweat or feces. Litter is waste which has been disposed of improperly...
and other pollutants from roadways and parking lots, as well as fertilizers and pesticides from lawns. Roads and parking lots are major sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons , also known as poly-aromatic hydrocarbons or polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons, are potent atmospheric pollutants that consist of fused aromatic rings and do not contain heteroatoms or carry substituents. Naphthalene is the simplest example of a PAH...
s (PAHs), which are created as combustion
Combustion
Combustion or burning is the sequence of exothermic chemical reactions between a fuel and an oxidant accompanied by the production of heat and conversion of chemical species. The release of heat can result in the production of light in the form of either glowing or a flame...
byproducts of gasoline and other fossil fuel
Fossil fuel
Fossil fuels are fuels formed by natural processes such as anaerobic decomposition of buried dead organisms. The age of the organisms and their resulting fossil fuels is typically millions of years, and sometimes exceeds 650 million years...
s, as well as of the heavy metals nickel
Nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel belongs to the transition metals and is hard and ductile...
, copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
, zinc
Zinc
Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2...
, cadmium
Cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element with the symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, bluish-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Similar to zinc, it prefers oxidation state +2 in most of its compounds and similar to mercury it shows a low...
, and lead
Lead
Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed...
. Roof runoff contributes high levels of synthetic
Chemical synthesis
In chemistry, chemical synthesis is purposeful execution of chemical reactions to get a product, or several products. This happens by physical and chemical manipulations usually involving one or more reactions...
organic compound
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
s and zinc
Zinc
Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2...
(from galvanized
Galvanization
Galvanization is the process of applying a protective zinc coating to steel or iron, in order to prevent rusting. The term is derived from the name of Italian scientist Luigi Galvani....
gutters). Fertilizer use on residential lawns, parks and golf courses is a significant source of nitrates and phosphorus
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is the chemical element that has the symbol P and atomic number 15. A multivalent nonmetal of the nitrogen group, phosphorus as a mineral is almost always present in its maximally oxidized state, as inorganic phosphate rocks...
in urban runoff.
As stormwater is channeled into storm drains and surface waters, the natural sediment
Sediment
Sediment is naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of fluids such as wind, water, or ice, and/or by the force of gravity acting on the particle itself....
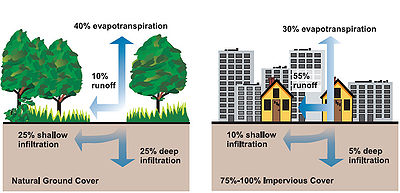
load discharged to receiving waters decreases, but the water flow and velocity increases. In fact, the impervious cover in a typical city creates five times the runoff of a typical woodland of the same size.
--National Research Council, Urban Stormwater Management in the United States
The runoff also increases temperatures in streams, harming fish
Fish
Fish are a paraphyletic group of organisms that consist of all gill-bearing aquatic vertebrate animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as various extinct related groups...
and other organisms. (A sudden burst of runoff from a rainstorm can cause a fish-killing shock of hot water.) Also, road salt used to melt snow on sidewalks and roadways can contaminate streams and groundwater aquifer
Aquifer
An aquifer is a wet underground layer of water-bearing permeable rock or unconsolidated materials from which groundwater can be usefully extracted using a water well. The study of water flow in aquifers and the characterization of aquifers is called hydrogeology...
s.
One of the most pronounced effects of urban runoff is on watercourses that historically contained little or no water during dry weather periods (often called ephemeral streams). When an area around such a stream is urbanized
Urbanization
Urbanization, urbanisation or urban drift is the physical growth of urban areas as a result of global change. The United Nations projected that half of the world's population would live in urban areas at the end of 2008....
, the resultant runoff creates an unnatural year-round streamflow
Streamflow
Streamflow, or channel runoff, is the flow of water in streams, rivers, and other channels, and is a major element of the water cycle. It is one component of the runoff of water from the land to waterbodies, the other component being surface runoff...
that hurts the vegetation, wildlife
Wildlife
Wildlife includes all non-domesticated plants, animals and other organisms. Domesticating wild plant and animal species for human benefit has occurred many times all over the planet, and has a major impact on the environment, both positive and negative....
and stream bed
Stream bed
A stream bed is the channel bottom of a stream, river or creek; the physical confine of the normal water flow. The lateral confines or channel margins, during all but flood stage, are known as the stream banks or river banks. In fact, a flood occurs when a stream overflows its banks and flows onto...
of the waterway. Containing little or no sediment relative to the historic ratio of sediment to water, urban runoff rushes down the stream channel, ruining natural features such as meander
Meander
A meander in general is a bend in a sinuous watercourse. A meander is formed when the moving water in a stream erodes the outer banks and widens its valley. A stream of any volume may assume a meandering course, alternately eroding sediments from the outside of a bend and depositing them on the...
s and sandbars, and creates severe erosion—increasing sediment loads at the mouth while severely incising the stream bed
Stream bed
A stream bed is the channel bottom of a stream, river or creek; the physical confine of the normal water flow. The lateral confines or channel margins, during all but flood stage, are known as the stream banks or river banks. In fact, a flood occurs when a stream overflows its banks and flows onto...
upstream. As an example, on many Southern California
Southern California
Southern California is a megaregion, or megapolitan area, in the southern area of the U.S. state of California. Large urban areas include Greater Los Angeles and Greater San Diego. The urban area stretches along the coast from Ventura through the Southland and Inland Empire to San Diego...
beaches at the mouth of a waterway, urban runoff carries trash, pollutants, excessive silt, and other wastes, and can pose moderate to severe health hazards.
Because of fertilizer and organic waste that urban runoff often carries, eutrophication
Eutrophication
Eutrophication or more precisely hypertrophication, is the movement of a body of water′s trophic status in the direction of increasing plant biomass, by the addition of artificial or natural substances, such as nitrates and phosphates, through fertilizers or sewage, to an aquatic system...
often occurs in waterways affected by this type of runoff. After heavy rains, organic matter in the waterway is relatively high compared with natural levels, spurring growth of algae
Algae
Algae are a large and diverse group of simple, typically autotrophic organisms, ranging from unicellular to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelps that grow to 65 meters in length. They are photosynthetic like plants, and "simple" because their tissues are not organized into the many...
blooms that soon use up most of the oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
. Once the naturally occurring oxygen in the water is depleted, the algae blooms die, and in their decomposing process, cause further eutrophication. Algae blooms mostly occur in areas with still water, such as stream pool
Stream pool
A stream pool, in hydrology, is a stretch of a river or stream in which the water depth is above average and the water velocity is quite below average.-Formation:...
s and the pools behind dam
Dam
A dam is a barrier that impounds water or underground streams. Dams generally serve the primary purpose of retaining water, while other structures such as floodgates or levees are used to manage or prevent water flow into specific land regions. Hydropower and pumped-storage hydroelectricity are...
s, weir
Weir
A weir is a small overflow dam used to alter the flow characteristics of a river or stream. In most cases weirs take the form of a barrier across the river that causes water to pool behind the structure , but allows water to flow over the top...
s, and some drop structure
Drop structure
A drop structure, also known as a grade control, sill, or weir, is a manmade structure, typically small and built on minor streams, or as part of a dam's spillway, to pass water to a lower elevation while controlling the energy and velocity of the water as it passes over...
s. Eutrophication usually comes with deadly consequences for fish and other aquatic organisms.
Excessive stream bank erosion may cause flooding and property damage. For many years governments have often responded to urban stream erosion problems by modifying the streams through construction of hardened embankments
Levee
A levee, levée, dike , embankment, floodbank or stopbank is an elongated naturally occurring ridge or artificially constructed fill or wall, which regulates water levels...
and similar control structures using concrete and masonry materials. Use of these hard materials destroys habitat for fish and other animals. Such a project may stabilize the immediate area where flood damage occurred, but often it simply shifts the problem to an upstream or downstream segment of the stream. See River engineering
River engineering
River engineering is the process of planned human intervention in the course, characteristics or flow of a river with the intention of producing some defined benefit. People have intervened in the natural course and behaviour of rivers since before recorded history - to manage the water resources,...
.
Pollution prevention practices include low impact development
Low impact development
Low-impact development is a term used in the United States to describe a land planning and engineering design approach to managing stormwater runoff. LID emphasizes conservation and use of on-site natural features to protect water quality...
techniques, installation of green roof
Green roof
A green roof is a roof of a building that is partially or completely covered with vegetation and a growing medium, planted over a waterproofing membrane. It may also include additional layers such as a root barrier and drainage and irrigation systems...
s and improved chemical handling (e.g. management of motor fuels & oil, fertilizers and pesticides). Runoff mitigation systems include infiltration basin
Infiltration basin
An infiltration basin , is a type of best management practice that is used to manage stormwater runoff, prevent flooding and downstream erosion, and improve water quality in an adjacent river, stream, lake or bay...
s, bioretention
Bioretention
Bioretention is the process in which contaminants and sedimentation are removed from stormwater runoff. Stormwater is collected into the treatment area which consists of a grass buffer strip, sand bed, ponding area, organic layer or mulch layer, planting soil, and plants...
systems, constructed wetland
Constructed wetland
A constructed wetland or wetpark is an artificial wetland, marsh or swamp created as a new or restored habitat for native and migratory wildlife, for anthropogenic discharge such as wastewater, stormwater runoff, or sewage treatment, for land reclamation after mining, refineries, or other...
s, retention basin
Retention basin
A retention basin is used to manage stormwater runoff to prevent flooding and downstream erosion, and improve water quality in an adjacent river, stream, lake or bay. Sometimes called a wet pond or wet detention basin, it is an artificial lake with vegetation around the perimeter, and includes a...
s and similar devices.
See also
- Agricultural surface runoff
- Agricultural nutrient runoff
- First flushFirst flushFirst flush is the initial surface runoff of a rainstorm. During this phase, water pollution entering storm drains in areas with high proportions of impervious surfaces is typically more concentrated compared to the remainder of the storm...
- Nonpoint source pollutionNonpoint source pollutionNonpoint source pollution refers to both water and air pollution from diffuse sources. Nonpoint source water pollution affects a water body from sources such as polluted runoff from agricultural areas draining into a river, or wind-borne debris blowing out to sea. Nonpoint source air pollution...
- List of environmental issues
- Nationwide Urban Runoff Program, a research project conducted by the US Environmental Protection Agency
Further reading
- Landers, Jay (2006). "Selecting Stormwater BMPs." Stormwater: May–June 2006.

