Sulfur acids
Encyclopedia
The sulfur oxoacid
s are chemical compounds that contain sulfur
, oxygen
and hydrogen
. The best known and most important industrially is sulfuric acid
. Sulfur has a number of oxoacids; however, some of these are known only from their salts (these are shown in italics in the table below). The acids that have been characterised contain a variety of structural features, for example:
Oxoacid
An oxoacid is an acid that contains oxygen. To be more specific, it is an acid that:#contains oxygen#contains at least one other element#has at least one hydrogen atom bound to oxygen#forms an ion by the loss of one or more protons....
s are chemical compounds that contain sulfur
Sulfur
Sulfur or sulphur is the chemical element with atomic number 16. In the periodic table it is represented by the symbol S. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow...
, oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
and hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
. The best known and most important industrially is sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid is a strong mineral acid with the molecular formula . Its historical name is oil of vitriol. Pure sulfuric acid is a highly corrosive, colorless, viscous liquid. The salts of sulfuric acid are called sulfates...
. Sulfur has a number of oxoacids; however, some of these are known only from their salts (these are shown in italics in the table below). The acids that have been characterised contain a variety of structural features, for example:
- tetrahedral sulfur when coordinated to oxygen
- terminal and bridging oxygen atoms
- terminal peroxo groups
- terminal S=S
- chains of (-S-)n
| Acid | Formula | S oxdtn state | Structure | Related anions | Notes |
| Sulfuric acid Sulfuric acid Sulfuric acid is a strong mineral acid with the molecular formula . Its historical name is oil of vitriol. Pure sulfuric acid is a highly corrosive, colorless, viscous liquid. The salts of sulfuric acid are called sulfates... |
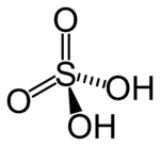
H2SO4 | VI | 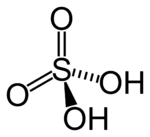 |
Sulfate Sulfate In inorganic chemistry, a sulfate is a salt of sulfuric acid.-Chemical properties:... , SO42 |
Best known and industrially significant |
| Polysulfuric acids including disulfuric acid Disulfuric acid Disulfuric acid is an oxoacid of sulfur. It is a major constituent of fuming sulfuric acid, oleum, and this is how most chemists encounter it. It is also a minor constituent of liquid anhydrous sulfuric acid due to the equilibria:... or pyrosulfuric acid |
H2SO4.nSO3 | VI | 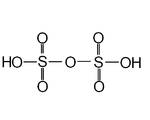 |
Disulfate (commonly known as pyrosulfate Pyrosulfate In chemistry, disulfate or pyrosulfate is the anion with the molecular formula [S2O7]2−. Disulfate is the IUPAC name. It has a dichromate like structure and can be visualised as two corner sharing SO4 tetrahedra, with a bridging oxygen atom.... ), S2O72 |
Pure disulfuric acid melts at 36°C. Present in fuming sulfuric acid, oleum Oleum Oleum , or fuming sulfuric acid refers to a solution of various compositions of sulfur trioxide in sulfuric acid or sometimes more specifically to disulfuric acid .... . Examples known for n=1,2. |
| Peroxymonosulfuric acid Peroxymonosulfuric acid Peroxymonosulfuric acid, also known as persulfuric acid, peroxysulfuric acid, or as Caro's acid, is H2SO5, a liquid at room temperature. In this acid, the S center adopts its characteristic tetrahedral geometry; the connectivity is indicated by the formula HO-O-S2-OH... |
H2SO5 | VI | 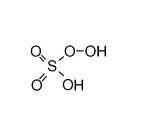 |
Peroxymonosulfate, OOSO32 |
"Caro's acid", a solid melting at 45°C |
| Peroxydisulfuric acid Peroxydisulfuric acid Peroxydisulfuric acid is a sulfur oxoacid with the chemical formula H2S2O8. It is also called Marshall's acid. In structural terms it can be written HO3SOOSO3H. It contains sulfur in its +6 oxidation state, but it also contains peroxide ions, which is why it appears to be in a higher oxidation... |
H2S2O8 | VI | 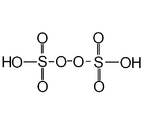 |
Peroxydisulfate, O3SOOSO32 |
A solid melting at 65°C. |
| Dithionic acid Dithionic acid Dithionic acid, H2S2O6, is a chemical compound known only in solution.- Salts :Dithionic acid is dibasic and salts called dithionates are known. No acid salts have been discovered. All dithionates are readily soluble in water. They are mild oxidizing and mild reducing agents. The structure of... |
H2S2O6 | V | 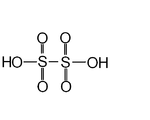 |
Dithionate, O3SSO32 |
Not obtained pure, only concentrated solutions |
| Thiosulfuric acid Thiosulfuric acid Thiosulfuric acid is a sulfur oxoacid. The acid cannot be made by acidifying thiosulfate salts as the acid readily decomposes in water. The decomposition products can include sulfur, sulfur dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, polysulfanes, sulfuric acid and polythionates, depending on the exact reaction... |
H2S2O3 | II | 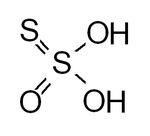 |
Thiosulfate Thiosulfate Thiosulfate is an oxyanion of sulfur. The prefix thio indicates that thiosulfate ion is a sulfate ion with one oxygen replaced by a sulfur. Thiosulfate occurs naturally and is produced by certain biochemical processes... , S2O32 Hydrogenthiosulfate HS2O3− (ammonium salt prepared in anhydrous methanol at -80 °C ) |
Aqueous solutions decompose. |
| Disulfurous acid Disulfurous acid Disulfurous acid or pyrosulfurous acid is an oxoacid of sulfur with the formula H2S2O5. The salts of disulfurous acid are called disulfites or metabisulfites. Disulfurous acid is, like sulfurous acid , a phantom acid, which does not exist in the free state.In contrast to disulfate , disulfite has... or pyrosulfurous acid |
H2S2O5 | IV | 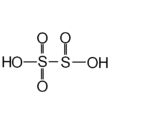 |
Disulfite commonly known as metabisulfite Metabisulfite A disulfite, commonly known as metabisulfite, is a chemical compound containing the disulfite ion [S2O52−].-Production of the disulfite ion:The disulfite ion is a dimer of the bisulfite ion... , S2O52 |
Not known |
| Sulfurous acid Sulfurous acid Sulfurous acid is the chemical compound with the formula H2SO3. There is no evidence that sulfurous acid exists in solution, but the molecule has been detected in the gas phase... |
H2SO3 | IV | 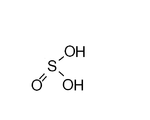 |
Bisulfite Bisulfite Bisulfite ion is the ion HSO3−. Salts containing the HSO3− ion are termed bisulfites also known as sulfite lyes... , HSO3 Sulfite Sulfites are compounds that contain the sulfite ion SO. The sulfite ion is the conjugate base of bisulfite. Although the acid itself is elusive, its salts are widely used.-Structure:... , SO32 |
Not known. |
| Dithionous acid Dithionous acid Dithionous acid is a sulfur oxoacid with the chemical formula H2S2O4. It is unstable in pure form, but its salts, known as dithionites, are stable.... |
H2S2O4 | III | Dithionite Dithionite The dithionite anion , is an oxoanion of sulfur formally derived from dithionous acid, H2S2O4.-Chemistry:Dithionous acid has not been detected either as a pure compound or in solution.... , O2SSO22 |
Not known. | |
| Polythionic acid Polythionic acid Polythionic acid is an oxoacid which has a straight chain of sulfur atoms and has the chemical formula H2SnO6 . Trithionic acid , tetrathionic acid are simple examples. The compounds of n... s |
H2SxO6 | 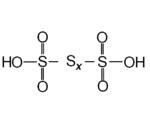 |
Polythionates, O3S(Sx-2)SO32 Tetrathionate The tetrathionate anion, S4O62−, is a sulfur oxoanion derived from the compound tetrathionic acid, H2S4O6. Two of the sulfur atoms present in the ion are in oxidation state 0 and two are in oxidation state +5. Alternatively, the compound can be viewed as the adduct resulting from the binding of... , pentathionate, hexathionate, heptathionate, octathionate, nonathionate, decathionate, undecathionate, dodecathionate, tridecathionate and tetradecathionate. |
Examples known with x= 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, 12, 14. |
See also
- Sulfinic acids
- Sulfonic acidSulfonic acidSulfonic acid usually refers to a member of the class of organosulfur compounds with the general formula RS2–OH, where R is an alkyl or aryl. The formal part of acid, HS2–OH, are formally derivatives of the "parent" inorganic compound with the formula HSO2.-Preparation:Sulfonic acid is...
s - Chlorosulfuric acidChlorosulfuric acidChlorosulfuric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula HSO3Cl. It is also known as chlorosulfonic acid. It is a distillable, colorless liquid that should be handled with care. It is a hygroscopic and a powerful lachrymator.-Structure and properties:Chlorosulfuric acid is a tetrahedral...
- Fluorosulfuric acidFluorosulfuric acidFluorosulfuric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula HSO3F. It is one of the strongest acids commercially available and is a superacid. The formula HFSO3 emphasizes its relationship to sulfuric acid, H2SO4; HSO3F is a tetrahedral molecule.-Chemical properties:Fluorosulfuric acid is a...

