
Dithionite
Encyclopedia
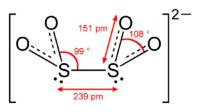
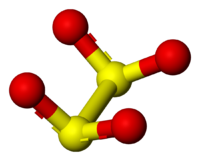
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
([S2O4]2−), is an oxoanion of sulfur
Sulfur
Sulfur or sulphur is the chemical element with atomic number 16. In the periodic table it is represented by the symbol S. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow...
formally derived from dithionous acid
Dithionous acid
Dithionous acid is a sulfur oxoacid with the chemical formula H2S2O4. It is unstable in pure form, but its salts, known as dithionites, are stable....
, H2S2O4.
Chemistry
Dithionous acid has not been detected either as a pure compound or in solution.Dithionite ions undergo both acid and alkaline hydrolysis
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction during which molecules of water are split into hydrogen cations and hydroxide anions in the process of a chemical mechanism. It is the type of reaction that is used to break down certain polymers, especially those made by condensation polymerization...
to thiosulfate
Thiosulfate
Thiosulfate is an oxyanion of sulfur. The prefix thio indicates that thiosulfate ion is a sulfate ion with one oxygen replaced by a sulfur. Thiosulfate occurs naturally and is produced by certain biochemical processes...
and bisulfite
Bisulfite
Bisulfite ion is the ion HSO3−. Salts containing the HSO3− ion are termed bisulfites also known as sulfite lyes...
, and sulfite
Sulfite
Sulfites are compounds that contain the sulfite ion SO. The sulfite ion is the conjugate base of bisulfite. Although the acid itself is elusive, its salts are widely used.-Structure:...
and sulfide
Sulfide
A sulfide is an anion of sulfur in its lowest oxidation state of 2-. Sulfide is also a slightly archaic term for thioethers, a common type of organosulfur compound that are well known for their bad odors.- Properties :...
, respectively
- 2 S2O + H2O → S2O + 2 HSO
- 3 Na2S2O4 + 6 NaOH → 5 Na2SO3 + Na2S + 3 H2O
Uses
The sodium salt of dithionous acid, sodium dithioniteSodium dithionite
Sodium dithionite is a white crystalline powder with a weak sulfurous odor. It is a sodium salt of dithionous acid. Although it is stable under most conditions, it will decompose in hot water and in acid solutions...
, finds widespread use in industry as a reducing agent
Reducing agent
A reducing agent is the element or compound in a reduction-oxidation reaction that donates an electron to another species; however, since the reducer loses an electron we say it is "oxidized"...
.
Dithionite is often used in conjunction with complexing agent (e.g., citric acid
Citric acid
Citric acid is a weak organic acid. It is a natural preservative/conservative and is also used to add an acidic, or sour, taste to foods and soft drinks...
) to reduce iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
(III) oxy-hydroxide into soluble iron(II) compounds and to remove amorphous iron(III)-bearing mineral phases in soil analyses (selective extraction).
The decomposition of dithionite produces reduced species of sulfur
Sulfur
Sulfur or sulphur is the chemical element with atomic number 16. In the periodic table it is represented by the symbol S. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow...
that can be very aggressive for the corrosion of steel and stainless steel. Thiosulfate
Thiosulfate
Thiosulfate is an oxyanion of sulfur. The prefix thio indicates that thiosulfate ion is a sulfate ion with one oxygen replaced by a sulfur. Thiosulfate occurs naturally and is produced by certain biochemical processes...
(S2O) is well known to induce pitting corrosion
Pitting corrosion
Pitting corrosion, or pitting, is a form of extremely localized corrosion that leads to the creation of small holes in the metal. The driving power for pitting corrosion is the depassivation of a small area, which becomes anodic while an unknown but potentially vast area becomes cathodic, leading...
while dissolved free sulfide
Sulfide
A sulfide is an anion of sulfur in its lowest oxidation state of 2-. Sulfide is also a slightly archaic term for thioethers, a common type of organosulfur compound that are well known for their bad odors.- Properties :...
(Na2S) is responsible for stress corrosion cracking
Stress corrosion cracking
Stress corrosion cracking is the unexpected sudden failure of normally ductile metals subjected to a tensile stress in a corrosive environment, especially at elevated temperature in the case of metals. SCC is highly chemically specific in that certain alloys are likely to undergo SCC only when...
(SCC).

