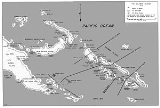
Solomon Islands campaign
Encyclopedia
The Solomon Islands campaign was a major campaign
of the Pacific War
of World War II
. The campaign began with Japanese
landings and occupation of several areas in the British Solomon Islands
and Bougainville
, in the Territory of New Guinea
, during the first six months of 1942. The Japanese occupied these locations and began the construction of several naval and air bases with the goals of protecting the flank of the Japanese offensive in New Guinea, establishing a security barrier for the major Japanese base at Rabaul
on New Britain
, and providing bases for interdicting supply lines between the Allied
powers of the United States and Australia
and New Zealand
.
The Allies, in order to defend their communication and supply lines in the South Pacific
, supported a counteroffensive in New Guinea, isolated the Japanese base at Rabaul, and counterattacked the Japanese in the Solomons with landings on Guadalcanal
(see Guadalcanal Campaign
) and small neighboring islands on 7 August 1942. These landings initiated a series of combined-arms battles between the two adversaries, beginning with the Guadalcanal landing and continuing with several battles in the central and northern Solomons, on and around New Georgia
Island, and Bougainville Island.
In a campaign of attrition fought on land, on sea, and in the air, the Allies wore the Japanese down, inflicting irreplaceable losses on Japanese military assets. The Allies retook some of the Solomon Islands (although resistance continued until the end of the war), and they also isolated and neutralized some Japanese positions, which were then bypassed. The Solomon Islands campaign then converged with the New Guinea campaign
.
and French Indochina
, the Japanese attacked
the US Pacific fleet
at Pearl Harbor
, Hawaii
. The attack crippled most of the U.S. Pacific Fleet's battleships and started a formal state of war between the two nations. Attacks on British Empire possessions in the Pacific, beginning with an attack on Hong Kong almost simultaneous with the Pearl Harbor attack, brought the United Kingdom, Australia and New Zealand into the conflict. In launching this war, Japanese leaders sought to neutralize the U.S. fleet, seize possessions rich in natural resources, and obtain strategic military bases to defend their far-flung empire. In the words of the Japanese Navy's
Combined Fleet
Secret Order Number One, dated November 1, 1941, the goals of the initial Japanese campaigns in the impending war were to, "(eject) British and American strength from the Netherlands Indies and the Philippines, (and) to establish a policy of autonomous self-sufficiency and economic independence."
The Empire of Japan accomplished its initial strategic objectives in the first six months of the war, capturing the Philippines
, Thailand
, Malaya
, Singapore
, the Dutch East Indies
, Wake Island
, New Britain
, Gilbert Islands
, and Guam
. A Japanese goal was to establish an effective defensive perimeter from British India on the west, through the Dutch East Indies
on the south, and to island bases in the south and central Pacific as its southeastern line of defense. Anchoring its defensive positions in the South Pacific was the major Japanese army and navy base at Rabaul
, New Britain
, which was captured in January 1942. In March and April, Japanese forces occupied and began constructing an airfield at Buka in northern Bougainville, as well as an airfield and naval base at Buin, in southern Bougainville.
, a joint plan to capture Port Moresby
in New Guinea. Also part of the plan was a navy operation to capture Tulagi
in the southern Solomons. The objective of the operation was for the Japanese to extend their southern perimeter and to establish bases to support possible future advances to seize Nauru
, Ocean Island
, New Caledonia
, Fiji
, and Samoa
and thereby cut the supply lines between Australia and the United States, with the goal of reducing or eliminating Australia as a threat to Japanese positions in the South Pacific. The Japanese Navy also proposed a future invasion of Australia, but the army answered that it currently lacked enough troops to support such an operation.
Japanese naval forces successfully captured Tulagi but its invasion of Port Moresby was repulsed at the Battle of the Coral Sea
. Shortly thereafter, the Japanese navy established small garrisons on the other northern and central Solomon Islands. One month later, the Japanese Combined Fleet lost four of its fleet aircraft carriers at the Battle of Midway
.
The Allies countered the threats to Australia by a build-up of troops and aircraft, with the aim of implementing plans to approach and reconquer the Philippines
. In March 1942 Admiral Ernest King
, then Commander-in Chief of the U. S. Fleet, had advocated an offense from New Hebrides
through the Solomon Islands to the Bismarck Archipelago
. Following the victory at Midway, General Douglas MacArthur
, who had taken command of the South West Pacific Area
, proposed a lightning offense to retake Rabaul, which the Japanese were fortifying and using as a base of operations. The United States Navy advocated a more gradual approach from New Guinea and up the Solomon Island chain. These competing proposals were resolved by Admiral King and U.S. Army Chief of Staff General George C. Marshall, who adopted a three-task plan. Task One was the capture of the island of Tulagi
in the Solomons. Task Two was an advance along the New Guinea coast. Task Three was the capture of Rabaul. Task One, implemented by a directive of the Joint Chiefs of Staff on 2 July 1942 and named the initial attacks Operation Watchtower, became the Solomon Islands campaign.
, establishing air superiority during the daylight hours. The Japanese then resorted to nightly resupply missions which they called "Rat Transportation"
(and the Allies called "the Tokyo Express") through New Georgia Sound
("The Slot"). Many pitched battles were fought trying to stop Japanese supplies from getting through. So many ships were lost by both sides during the Guadalacanal campaign that the southern end of New Georgia Sound, the area north of Guadalcanal previously called Savo Sound, became known as "Ironbottom Sound
".
Allied success in the Solomon Islands campaign prevented the Japanese from cutting Australia and New Zealand off from the U.S. Operation Cartwheel
— the Allied grand strategy for the Solomons and New Guinea campaign
s — launched on June 30, 1943, isolated and neutralized Rabaul and destroyed much of Japan's sea and air supremacy. This opened the way for Allied forces to recapture the Philippines and cut off Japan from its crucial resource areas in the Netherlands East Indies.
The Solomons campaign culminated in the often bitter fighting of the Bougainville Campaign, which continued until the end of the war.
) Also available at: http://www.ibiblio.org/hyperwar/USMC/USMC-C-NSol/index.html
Military campaign
In the military sciences, the term military campaign applies to large scale, long duration, significant military strategy plan incorporating a series of inter-related military operations or battles forming a distinct part of a larger conflict often called a war...
of the Pacific War
Pacific War
The Pacific War, also sometimes called the Asia-Pacific War refers broadly to the parts of World War II that took place in the Pacific Ocean, its islands, and in East Asia, then called the Far East...
of World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
. The campaign began with Japanese
Empire of Japan
The Empire of Japan is the name of the state of Japan that existed from the Meiji Restoration on 3 January 1868 to the enactment of the post-World War II Constitution of...
landings and occupation of several areas in the British Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is a sovereign state in Oceania, east of Papua New Guinea, consisting of nearly one thousand islands. It covers a land mass of . The capital, Honiara, is located on the island of Guadalcanal...
and Bougainville
Bougainville Island
Bougainville Island is the main island of the Autonomous Region of Bougainville of Papua New Guinea. This region is also known as Bougainville Province or the North Solomons. The population of the province is 175,160 , which includes the adjacent island of Buka and assorted outlying islands...
, in the Territory of New Guinea
Territory of New Guinea
The Territory of New Guinea was the Australia-controlled, League of Nations-mandated territory in the north eastern part of the island of New Guinea, and surrounding islands, between 1920 and 1949...
, during the first six months of 1942. The Japanese occupied these locations and began the construction of several naval and air bases with the goals of protecting the flank of the Japanese offensive in New Guinea, establishing a security barrier for the major Japanese base at Rabaul
Rabaul
Rabaul is a township in East New Britain province, Papua New Guinea. The town was the provincial capital and most important settlement in the province until it was destroyed in 1994 by falling ash of a volcanic eruption. During the eruption, ash was sent thousands of metres into the air and the...
on New Britain
New Britain
New Britain, or Niu Briten, is the largest island in the Bismarck Archipelago of Papua New Guinea. It is separated from the island of New Guinea by the Dampier and Vitiaz Straits and from New Ireland by St. George's Channel...
, and providing bases for interdicting supply lines between the Allied
Allies of World War II
The Allies of World War II were the countries that opposed the Axis powers during the Second World War . Former Axis states contributing to the Allied victory are not considered Allied states...
powers of the United States and Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
and New Zealand
New Zealand
New Zealand is an island country in the south-western Pacific Ocean comprising two main landmasses and numerous smaller islands. The country is situated some east of Australia across the Tasman Sea, and roughly south of the Pacific island nations of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga...
.
The Allies, in order to defend their communication and supply lines in the South Pacific
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
, supported a counteroffensive in New Guinea, isolated the Japanese base at Rabaul, and counterattacked the Japanese in the Solomons with landings on Guadalcanal
Guadalcanal
Guadalcanal is a tropical island in the South-Western Pacific. The largest island in the Solomons, it was discovered by the Spanish expedition of Alvaro de Mendaña in 1568...
(see Guadalcanal Campaign
Guadalcanal campaign
The Guadalcanal Campaign, also known as the Battle of Guadalcanal and codenamed Operation Watchtower by Allied forces, was a military campaign fought between August 7, 1942 and February 9, 1943 on and around the island of Guadalcanal in the Pacific theatre of World War II...
) and small neighboring islands on 7 August 1942. These landings initiated a series of combined-arms battles between the two adversaries, beginning with the Guadalcanal landing and continuing with several battles in the central and northern Solomons, on and around New Georgia
New Georgia
New Georgia is the largest island of the Western Province of the Solomon Islands.-Geography:This island is located in the New Georgia Group, an archipelago including most of the other larger islands in the province...
Island, and Bougainville Island.
In a campaign of attrition fought on land, on sea, and in the air, the Allies wore the Japanese down, inflicting irreplaceable losses on Japanese military assets. The Allies retook some of the Solomon Islands (although resistance continued until the end of the war), and they also isolated and neutralized some Japanese positions, which were then bypassed. The Solomon Islands campaign then converged with the New Guinea campaign
New Guinea campaign
The New Guinea campaign was one of the major military campaigns of World War II.Before the war, the island of New Guinea was split between:...
.
Strategic background
On December 7, 1941, after failing to resolve a dispute with the United States over Japan's actions in ChinaSecond Sino-Japanese War
The Second Sino-Japanese War was a military conflict fought primarily between the Republic of China and the Empire of Japan. From 1937 to 1941, China fought Japan with some economic help from Germany , the Soviet Union and the United States...
and French Indochina
French Indochina
French Indochina was part of the French colonial empire in southeast Asia. A federation of the three Vietnamese regions, Tonkin , Annam , and Cochinchina , as well as Cambodia, was formed in 1887....
, the Japanese attacked
Attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike conducted by the Imperial Japanese Navy against the United States naval base at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, on the morning of December 7, 1941...
the US Pacific fleet
United States Pacific Fleet
The United States Pacific Fleet is a Pacific Ocean theater-level component command of the United States Navy that provides naval resources under the operational control of the United States Pacific Command. Its home port is at Pearl Harbor Naval Base, Hawaii. It is commanded by Admiral Patrick M...
at Pearl Harbor
Pearl Harbor
Pearl Harbor, known to Hawaiians as Puuloa, is a lagoon harbor on the island of Oahu, Hawaii, west of Honolulu. Much of the harbor and surrounding lands is a United States Navy deep-water naval base. It is also the headquarters of the U.S. Pacific Fleet...
, Hawaii
Hawaii
Hawaii is the newest of the 50 U.S. states , and is the only U.S. state made up entirely of islands. It is the northernmost island group in Polynesia, occupying most of an archipelago in the central Pacific Ocean, southwest of the continental United States, southeast of Japan, and northeast of...
. The attack crippled most of the U.S. Pacific Fleet's battleships and started a formal state of war between the two nations. Attacks on British Empire possessions in the Pacific, beginning with an attack on Hong Kong almost simultaneous with the Pearl Harbor attack, brought the United Kingdom, Australia and New Zealand into the conflict. In launching this war, Japanese leaders sought to neutralize the U.S. fleet, seize possessions rich in natural resources, and obtain strategic military bases to defend their far-flung empire. In the words of the Japanese Navy's
Imperial Japanese Navy
The Imperial Japanese Navy was the navy of the Empire of Japan from 1869 until 1947, when it was dissolved following Japan's constitutional renunciation of the use of force as a means of settling international disputes...
Combined Fleet
Combined Fleet
The was the main ocean-going component of the Imperial Japanese Navy. The Combined Fleet was not a standing force, but a temporary force formed for the duration of a conflict or major naval maneuvers from various units normally under separate commands in peacetime....
Secret Order Number One, dated November 1, 1941, the goals of the initial Japanese campaigns in the impending war were to, "(eject) British and American strength from the Netherlands Indies and the Philippines, (and) to establish a policy of autonomous self-sufficiency and economic independence."
The Empire of Japan accomplished its initial strategic objectives in the first six months of the war, capturing the Philippines
Philippines
The Philippines , officially known as the Republic of the Philippines , is a country in Southeast Asia in the western Pacific Ocean. To its north across the Luzon Strait lies Taiwan. West across the South China Sea sits Vietnam...
, Thailand
Thailand
Thailand , officially the Kingdom of Thailand , formerly known as Siam , is a country located at the centre of the Indochina peninsula and Southeast Asia. It is bordered to the north by Burma and Laos, to the east by Laos and Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the...
, Malaya
British Malaya
British Malaya loosely described a set of states on the Malay Peninsula and the Island of Singapore that were brought under British control between the 18th and the 20th centuries...
, Singapore
Singapore
Singapore , officially the Republic of Singapore, is a Southeast Asian city-state off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, north of the equator. An island country made up of 63 islands, it is separated from Malaysia by the Straits of Johor to its north and from Indonesia's Riau Islands by the...
, the Dutch East Indies
Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies was a Dutch colony that became modern Indonesia following World War II. It was formed from the nationalised colonies of the Dutch East India Company, which came under the administration of the Netherlands government in 1800....
, Wake Island
Wake Island
Wake Island is a coral atoll having a coastline of in the North Pacific Ocean, located about two-thirds of the way from Honolulu west to Guam east. It is an unorganized, unincorporated territory of the United States, administered by the Office of Insular Affairs, U.S. Department of the Interior...
, New Britain
New Britain
New Britain, or Niu Briten, is the largest island in the Bismarck Archipelago of Papua New Guinea. It is separated from the island of New Guinea by the Dampier and Vitiaz Straits and from New Ireland by St. George's Channel...
, Gilbert Islands
Gilbert Islands
The Gilbert Islands are a chain of sixteen atolls and coral islands in the Pacific Ocean. They are the main part of Republic of Kiribati and include Tarawa, the site of the country's capital and residence of almost half of the population.-Geography:The atolls and islands of the Gilbert Islands...
, and Guam
Guam
Guam is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States located in the western Pacific Ocean. It is one of five U.S. territories with an established civilian government. Guam is listed as one of 16 Non-Self-Governing Territories by the Special Committee on Decolonization of the United...
. A Japanese goal was to establish an effective defensive perimeter from British India on the west, through the Dutch East Indies
Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies was a Dutch colony that became modern Indonesia following World War II. It was formed from the nationalised colonies of the Dutch East India Company, which came under the administration of the Netherlands government in 1800....
on the south, and to island bases in the south and central Pacific as its southeastern line of defense. Anchoring its defensive positions in the South Pacific was the major Japanese army and navy base at Rabaul
Rabaul
Rabaul is a township in East New Britain province, Papua New Guinea. The town was the provincial capital and most important settlement in the province until it was destroyed in 1994 by falling ash of a volcanic eruption. During the eruption, ash was sent thousands of metres into the air and the...
, New Britain
New Britain
New Britain, or Niu Briten, is the largest island in the Bismarck Archipelago of Papua New Guinea. It is separated from the island of New Guinea by the Dampier and Vitiaz Straits and from New Ireland by St. George's Channel...
, which was captured in January 1942. In March and April, Japanese forces occupied and began constructing an airfield at Buka in northern Bougainville, as well as an airfield and naval base at Buin, in southern Bougainville.
Japanese advance into the Solomons
In April 1942, the Japanese army and navy together initiated Operation MoOperation Mo
Operation Mo or the Port Moresby Operation was the name of the Japanese plan to take control of the Australian Territory of New Guinea during World War II as well as other locations in the South Pacific with the goal of isolating Australia and New Zealand from their ally the United States...
, a joint plan to capture Port Moresby
Port Moresby
Port Moresby , or Pot Mosbi in Tok Pisin, is the capital and largest city of Papua New Guinea . It is located on the shores of the Gulf of Papua, on the southeastern coast of the island of New Guinea, which made it a prime objective for conquest by the Imperial Japanese forces during 1942–43...
in New Guinea. Also part of the plan was a navy operation to capture Tulagi
Tulagi
Tulagi, less commonly Tulaghi, is a small island in the Solomon Islands, just off the south coast of Florida Island. The town of the same name on the island Tulagi, less commonly Tulaghi, is a small island (5.5 km by 1 km) in the Solomon Islands, just off the south coast of Florida...
in the southern Solomons. The objective of the operation was for the Japanese to extend their southern perimeter and to establish bases to support possible future advances to seize Nauru
Nauru
Nauru , officially the Republic of Nauru and formerly known as Pleasant Island, is an island country in Micronesia in the South Pacific. Its nearest neighbour is Banaba Island in Kiribati, to the east. Nauru is the world's smallest republic, covering just...
, Ocean Island
Banaba Island
Banaba Island , an island in the Pacific Ocean, is a solitary raised coral island west of the Gilbert Island chain and 300 km east of Nauru. It is part of the Republic of Kiribati. It has an area of 6.5 km², and the highest point on the island is also the highest point in Kiribati, at 81...
, New Caledonia
New Caledonia
New Caledonia is a special collectivity of France located in the southwest Pacific Ocean, east of Australia and about from Metropolitan France. The archipelago, part of the Melanesia subregion, includes the main island of Grande Terre, the Loyalty Islands, the Belep archipelago, the Isle of...
, Fiji
Fiji
Fiji , officially the Republic of Fiji , is an island nation in Melanesia in the South Pacific Ocean about northeast of New Zealand's North Island...
, and Samoa
Samoa
Samoa , officially the Independent State of Samoa, formerly known as Western Samoa is a country encompassing the western part of the Samoan Islands in the South Pacific Ocean. It became independent from New Zealand in 1962. The two main islands of Samoa are Upolu and one of the biggest islands in...
and thereby cut the supply lines between Australia and the United States, with the goal of reducing or eliminating Australia as a threat to Japanese positions in the South Pacific. The Japanese Navy also proposed a future invasion of Australia, but the army answered that it currently lacked enough troops to support such an operation.
Japanese naval forces successfully captured Tulagi but its invasion of Port Moresby was repulsed at the Battle of the Coral Sea
Battle of the Coral Sea
The Battle of the Coral Sea, fought from 4–8 May 1942, was a major naval battle in the Pacific Theater of World War II between the Imperial Japanese Navy and Allied naval and air forces from the United States and Australia. The battle was the first fleet action in which aircraft carriers engaged...
. Shortly thereafter, the Japanese navy established small garrisons on the other northern and central Solomon Islands. One month later, the Japanese Combined Fleet lost four of its fleet aircraft carriers at the Battle of Midway
Battle of Midway
The Battle of Midway is widely regarded as the most important naval battle of the Pacific Campaign of World War II. Between 4 and 7 June 1942, approximately one month after the Battle of the Coral Sea and six months after Japan's attack on Pearl Harbor, the United States Navy decisively defeated...
.
The Allies countered the threats to Australia by a build-up of troops and aircraft, with the aim of implementing plans to approach and reconquer the Philippines
Philippines
The Philippines , officially known as the Republic of the Philippines , is a country in Southeast Asia in the western Pacific Ocean. To its north across the Luzon Strait lies Taiwan. West across the South China Sea sits Vietnam...
. In March 1942 Admiral Ernest King
Ernest King
Fleet Admiral Ernest Joseph King was Commander in Chief, United States Fleet and Chief of Naval Operations during World War II. As COMINCH, he directed the United States Navy's operations, planning, and administration and was a member of the Joint Chiefs of Staff. He was the U.S...
, then Commander-in Chief of the U. S. Fleet, had advocated an offense from New Hebrides
New Hebrides
New Hebrides was the colonial name for an island group in the South Pacific that now forms the nation of Vanuatu. The New Hebrides were colonized by both the British and French in the 18th century shortly after Captain James Cook visited the islands...
through the Solomon Islands to the Bismarck Archipelago
Bismarck Archipelago
The Bismarck Archipelago is a group of islands off the northeastern coast of New Guinea in the western Pacific Ocean and is part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea.-History:...
. Following the victory at Midway, General Douglas MacArthur
Douglas MacArthur
General of the Army Douglas MacArthur was an American general and field marshal of the Philippine Army. He was a Chief of Staff of the United States Army during the 1930s and played a prominent role in the Pacific theater during World War II. He received the Medal of Honor for his service in the...
, who had taken command of the South West Pacific Area
South West Pacific Area
South West Pacific Area was the name given to the Allied supreme military command in the South West Pacific Theatre of World War II. It was one of four major Allied commands in the Pacific theatres of World War II, during 1942–45...
, proposed a lightning offense to retake Rabaul, which the Japanese were fortifying and using as a base of operations. The United States Navy advocated a more gradual approach from New Guinea and up the Solomon Island chain. These competing proposals were resolved by Admiral King and U.S. Army Chief of Staff General George C. Marshall, who adopted a three-task plan. Task One was the capture of the island of Tulagi
Tulagi
Tulagi, less commonly Tulaghi, is a small island in the Solomon Islands, just off the south coast of Florida Island. The town of the same name on the island Tulagi, less commonly Tulaghi, is a small island (5.5 km by 1 km) in the Solomon Islands, just off the south coast of Florida...
in the Solomons. Task Two was an advance along the New Guinea coast. Task Three was the capture of Rabaul. Task One, implemented by a directive of the Joint Chiefs of Staff on 2 July 1942 and named the initial attacks Operation Watchtower, became the Solomon Islands campaign.
Course of campaign
The Allies created a combined air formation, Cactus Air ForceCactus Air Force
Cactus Air Force refers to the ensemble of Allied air power assigned to the island of Guadalcanal from August 1942 until December 1942 during the early stages of the Guadalcanal Campaign, particularly those operating from Henderson Field...
, establishing air superiority during the daylight hours. The Japanese then resorted to nightly resupply missions which they called "Rat Transportation"
Tokyo Express
The Tokyo Express was the name given by Allied forces to the use of Imperial Japanese Navy ships at night to deliver personnel, supplies, and equipment to Japanese forces operating in and around New Guinea and the Solomon Islands during the Pacific campaign of World War II...
(and the Allies called "the Tokyo Express") through New Georgia Sound
New Georgia Sound
New Georgia Sound is the body of water that runs approximately through the middle of the Solomon Islands. The Sound is bounded by Choiseul Island, Santa Isabel Island, and Florida Island to the north, and by Vella Lavella, Kolombangara, New Georgia, and the Russell Islands to the south...
("The Slot"). Many pitched battles were fought trying to stop Japanese supplies from getting through. So many ships were lost by both sides during the Guadalacanal campaign that the southern end of New Georgia Sound, the area north of Guadalcanal previously called Savo Sound, became known as "Ironbottom Sound
Ironbottom Sound
"Ironbottom Sound" is the name given by Allied sailors to Savo Sound, the stretch of water at the southern end of The Slot between Guadalcanal, Savo Island, and Florida Island of the Solomon Islands, because of the dozens of ships and planes that sank there during the Battle of Guadalcanal in...
".
Allied success in the Solomon Islands campaign prevented the Japanese from cutting Australia and New Zealand off from the U.S. Operation Cartwheel
Operation Cartwheel
Operation Cartwheel was a major military strategy for the Allies in the Pacific theater of World War II. Cartwheel was a twin-axis of advance operation, aimed at militarily neutralizing the major Japanese base at Rabaul...
— the Allied grand strategy for the Solomons and New Guinea campaign
New Guinea campaign
The New Guinea campaign was one of the major military campaigns of World War II.Before the war, the island of New Guinea was split between:...
s — launched on June 30, 1943, isolated and neutralized Rabaul and destroyed much of Japan's sea and air supremacy. This opened the way for Allied forces to recapture the Philippines and cut off Japan from its crucial resource areas in the Netherlands East Indies.
The Solomons campaign culminated in the often bitter fighting of the Bougainville Campaign, which continued until the end of the war.
See also
- New Guinea campaignNew Guinea campaignThe New Guinea campaign was one of the major military campaigns of World War II.Before the war, the island of New Guinea was split between:...
- New Britain Campaign
- Gilbert and Marshall Islands campaignGilbert and Marshall Islands campaignIn the Pacific Theater of World War II, the Gilbert and Marshall Islands campaign, from November 1943 through February 1944, were key strategic operations of the United States Pacific Fleet and Marine Corps in the Central Pacific. The campaign was preceded by a raid on Makin Island by U.S...
- Guadalcanal CampaignGuadalcanal campaignThe Guadalcanal Campaign, also known as the Battle of Guadalcanal and codenamed Operation Watchtower by Allied forces, was a military campaign fought between August 7, 1942 and February 9, 1943 on and around the island of Guadalcanal in the Pacific theatre of World War II...
- AirSolsAirSolsAirSols was an abbreviation of Air Solomons, the Allied air units in the Solomon Islands campaign of World War II, from April 1943 to June 1944. Its units came from the United States Navy , United States Marine Corps , United States Army Air Forces and the Royal New Zealand Air Force . AirSols...
External links
(translation of excerpts from the Senshi SōshōSenshi Sōshō
The , also called the , is a military history of Imperial Japan's involvement in the Pacific War from 1937 to 1945. The history was compiled and is currently kept by the War History Office of Japan's Ministry of Defense in Tokyo, Japan...
) Also available at: http://www.ibiblio.org/hyperwar/USMC/USMC-C-NSol/index.html
- WW2DB: Solomons Campaign- Translation of the official record by the Japanese Demobilization Bureaux detailing the Imperial Japanese Army and Navy's participation in the Southwest Pacific area of the Pacific WarPacific WarThe Pacific War, also sometimes called the Asia-Pacific War refers broadly to the parts of World War II that took place in the Pacific Ocean, its islands, and in East Asia, then called the Far East...
.
Further reading
- Hungerford, T.A.G.. (1952). The Ridge and the River. Sydney: Angus & Roberston. Republished by Penguin, 1992; ISBN 0-14-300174-4.

