
Nicrophorus americanus
Encyclopedia
Nicrophorus americanus, also known as the American burying beetle or giant carrion beetle, is a critically endangered species of beetle
endemic
to North America
. It belongs to the order Coleoptera and the family Silphidae. The carrion beetle
in North America is carnivorous, feeds on carrion
and requires carrion to breed. It is also one of the few species of beetle to exhibit parental care. The decline of the American burying beetle has been attributed to habitat loss, alteration, and degradation, and they now occur over less than 10% of their historic range.
. The beetle is nocturnal and is a strong flier, moving as far as a kilometer in one night.
in an adjacent tunnel. Within a few days, the larva
e develop and both parents feed and tend their young, an unusual activity among insects, but a characteristic shared with the. Brood size ranges from one to 30 young, but 12 to 15 is the average size.
The larvae spend about a week feeding off of the carcass then crawl into the soil to pupa
te, or develop. Mature N. americanus beetles emerge from the soil 45 to 60 days after their parents initially bury the carcass. Adult American burying beetles live for only 12 months.
s and open understory oak
hickory
forests. However, the beetles are carrion specialists in that they need carrion the size of a dove
or a chipmunk
in order to reproduce. Carrion availability may be the greatest factor determining where the species can survive.
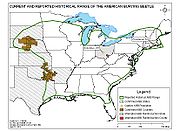 Historical records show that this beetle once lived in 35 states of the United States
Historical records show that this beetle once lived in 35 states of the United States
, the District of Columbia, and three Canadian
provinces: Ontario
, Quebec
, and Nova Scotia
. Now, natural populations are known to occur in only five states: on Block Island
in Rhode Island
, Oklahoma
, Arkansas
, South Dakota
and Nebraska
. They have also been reintroduced to Ohio
. N. americanus was listed as an endangered species in 1989; the IUCN lists the species as critically endangered. Biologists have not shown why N. americanus has disappeared from so many areas. Widespread use of pesticide
s may have caused local populations to disappear. The dramatic disappearance of this insect from many areas, however, took place before widespread use of DDT
. Lack of small carcasses to bury would prevent the species from reproducing, and changes in land use has reduced the quantity of small- to medium-sized birds and mammals preferred by N. americanus. Even the extinction of the once ubiquitous passenger pigeon
may have had a ripple effect
on carrion feeders like this beetle.
The immediate goal of conservation efforts is to reduce the threat of extinction
by creating captive and wild populations. Biologists have attempted to establish a beetle population releasing laboratory-raised American burying beetles on Penikese Island
in Massachusetts
. Biologists return each year to Penikese Island to study the survival and growth of the beetle population.
Beetle
Coleoptera is an order of insects commonly called beetles. The word "coleoptera" is from the Greek , koleos, "sheath"; and , pteron, "wing", thus "sheathed wing". Coleoptera contains more species than any other order, constituting almost 25% of all known life-forms...
endemic
Endemic (ecology)
Endemism is the ecological state of being unique to a defined geographic location, such as an island, nation or other defined zone, or habitat type; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, all species of lemur are endemic to the...
to North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
. It belongs to the order Coleoptera and the family Silphidae. The carrion beetle
Carrion beetle
Silphidae is a family of beetles that are known commonly as carrion or burying beetles. There are two subfamilies: Silphinae and Nicrophorinae. Both families feed on decaying organic matter such as dead animals. The families differ in which uses parental care and which types of carcasses they prefer...
in North America is carnivorous, feeds on carrion
Carrion
Carrion refers to the carcass of a dead animal. Carrion is an important food source for large carnivores and omnivores in most ecosystems. Examples of carrion-eaters include vultures, hawks, eagles, hyenas, Virginia Opossum, Tasmanian Devils, coyotes, Komodo dragons, and burying beetles...
and requires carrion to breed. It is also one of the few species of beetle to exhibit parental care. The decline of the American burying beetle has been attributed to habitat loss, alteration, and degradation, and they now occur over less than 10% of their historic range.
Physical description
N. americanus is between 25 and 45 mm long and can be identified by its striking, distinctive coloring. The body is shiny black, and on its wing covers are four scalloped, orange-red markings. Most distinctively, there is an orange-red marking on the beetle's pronotum, a large shield-like area just behind the head. N. americanus has orange facial markings and orange tips on their large antennaeAntenna (biology)
Antennae in biology have historically been paired appendages used for sensing in arthropods. More recently, the term has also been applied to cilium structures present in most cell types of eukaryotes....
. The beetle is nocturnal and is a strong flier, moving as far as a kilometer in one night.
Reproduction
During the winter months when temperatures are below 15 °C (60 °F) N. americanus adults bury themselves in the soil to overwinter. When temperatures are above 15 °C (60 °F) they emerge from the soil and begin the mating and reproduction process. Burying beetles are unusual in that both the male and female take part in raising the young. Male burying beetles often locate carcasses first and then attract a mate. Beetles often fight over the carcass, with usually the largest male and female individuals winning. The victors bury the carcass, the pair mates, and the female lays her eggsEgg (biology)
An egg is an organic vessel in which an embryo first begins to develop. In most birds, reptiles, insects, molluscs, fish, and monotremes, an egg is the zygote, resulting from fertilization of the ovum, which is expelled from the body and permitted to develop outside the body until the developing...
in an adjacent tunnel. Within a few days, the larva
Larva
A larva is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle...
e develop and both parents feed and tend their young, an unusual activity among insects, but a characteristic shared with the. Brood size ranges from one to 30 young, but 12 to 15 is the average size.
The larvae spend about a week feeding off of the carcass then crawl into the soil to pupa
Pupa
A pupa is the life stage of some insects undergoing transformation. The pupal stage is found only in holometabolous insects, those that undergo a complete metamorphosis, going through four life stages; embryo, larva, pupa and imago...
te, or develop. Mature N. americanus beetles emerge from the soil 45 to 60 days after their parents initially bury the carcass. Adult American burying beetles live for only 12 months.
Ecology and behavior
Historical records offer little insight into what type of habitat was preferred by the American burying beetle. Current information suggests that this species is a habitat generalist, or one that lives in many types of habitat, with a slight preference for grasslandGrassland
Grasslands are areas where the vegetation is dominated by grasses and other herbaceous plants . However, sedge and rush families can also be found. Grasslands occur naturally on all continents except Antarctica...
s and open understory oak
Oak
An oak is a tree or shrub in the genus Quercus , of which about 600 species exist. "Oak" may also appear in the names of species in related genera, notably Lithocarpus...
hickory
Hickory
Trees in the genus Carya are commonly known as hickory, derived from the Powhatan language of Virginia. The genus includes 17–19 species of deciduous trees with pinnately compound leaves and big nuts...
forests. However, the beetles are carrion specialists in that they need carrion the size of a dove
Dove
Pigeons and doves constitute the bird family Columbidae within the order Columbiformes, which include some 300 species of near passerines. In general terms "dove" and "pigeon" are used somewhat interchangeably...
or a chipmunk
Chipmunk
Chipmunks are small striped squirrels native to North America and Asia. They are usually classed either as a single genus with three subgenera, or as three genera.-Etymology and taxonomy:...
in order to reproduce. Carrion availability may be the greatest factor determining where the species can survive.
Conservation status

United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, the District of Columbia, and three Canadian
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
provinces: Ontario
Ontario
Ontario is a province of Canada, located in east-central Canada. It is Canada's most populous province and second largest in total area. It is home to the nation's most populous city, Toronto, and the nation's capital, Ottawa....
, Quebec
Quebec
Quebec or is a province in east-central Canada. It is the only Canadian province with a predominantly French-speaking population and the only one whose sole official language is French at the provincial level....
, and Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is one of Canada's three Maritime provinces and is the most populous province in Atlantic Canada. The name of the province is Latin for "New Scotland," but "Nova Scotia" is the recognized, English-language name of the province. The provincial capital is Halifax. Nova Scotia is the...
. Now, natural populations are known to occur in only five states: on Block Island
Block Island
Block Island is part of the U.S. state of Rhode Island and is located in the Atlantic Ocean approximately south of the coast of Rhode Island, east of Montauk Point on Long Island, and is separated from the Rhode Island mainland by Block Island Sound. The United States Census Bureau defines Block...
in Rhode Island
Rhode Island
The state of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations, more commonly referred to as Rhode Island , is a state in the New England region of the United States. It is the smallest U.S. state by area...
, Oklahoma
Oklahoma
Oklahoma is a state located in the South Central region of the United States of America. With an estimated 3,751,351 residents as of the 2010 census and a land area of 68,667 square miles , Oklahoma is the 28th most populous and 20th-largest state...
, Arkansas
Arkansas
Arkansas is a state located in the southern region of the United States. Its name is an Algonquian name of the Quapaw Indians. Arkansas shares borders with six states , and its eastern border is largely defined by the Mississippi River...
, South Dakota
South Dakota
South Dakota is a state located in the Midwestern region of the United States. It is named after the Lakota and Dakota Sioux American Indian tribes. Once a part of Dakota Territory, South Dakota became a state on November 2, 1889. The state has an area of and an estimated population of just over...
and Nebraska
Nebraska
Nebraska is a state on the Great Plains of the Midwestern United States. The state's capital is Lincoln and its largest city is Omaha, on the Missouri River....
. They have also been reintroduced to Ohio
Ohio
Ohio is a Midwestern state in the United States. The 34th largest state by area in the U.S.,it is the 7th‑most populous with over 11.5 million residents, containing several major American cities and seven metropolitan areas with populations of 500,000 or more.The state's capital is Columbus...
. N. americanus was listed as an endangered species in 1989; the IUCN lists the species as critically endangered. Biologists have not shown why N. americanus has disappeared from so many areas. Widespread use of pesticide
Pesticide
Pesticides are substances or mixture of substances intended for preventing, destroying, repelling or mitigating any pest.A pesticide may be a chemical unicycle, biological agent , antimicrobial, disinfectant or device used against any pest...
s may have caused local populations to disappear. The dramatic disappearance of this insect from many areas, however, took place before widespread use of DDT
DDT
DDT is one of the most well-known synthetic insecticides. It is a chemical with a long, unique, and controversial history....
. Lack of small carcasses to bury would prevent the species from reproducing, and changes in land use has reduced the quantity of small- to medium-sized birds and mammals preferred by N. americanus. Even the extinction of the once ubiquitous passenger pigeon
Passenger Pigeon
The Passenger Pigeon or Wild Pigeon was a bird, now extinct, that existed in North America and lived in enormous migratory flocks until the early 20th century...
may have had a ripple effect
Ripple effect
The ripple effect is a term used to describe a situation where, like the ever expanding ripples across water when an object is dropped into it, an effect from an initial state can be followed outwards incrementally....
on carrion feeders like this beetle.
The immediate goal of conservation efforts is to reduce the threat of extinction
Extinction
In biology and ecology, extinction is the end of an organism or of a group of organisms , normally a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and recover may have been lost before this point...
by creating captive and wild populations. Biologists have attempted to establish a beetle population releasing laboratory-raised American burying beetles on Penikese Island
Penikese Island
Penikese Island is a island off the coast of Massachusetts, United States, in Buzzards Bay. It is one of the Elizabeth Islands, which make up the town of Gosnold, Massachusetts...
in Massachusetts
Massachusetts
The Commonwealth of Massachusetts is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States of America. It is bordered by Rhode Island and Connecticut to the south, New York to the west, and Vermont and New Hampshire to the north; at its east lies the Atlantic Ocean. As of the 2010...
. Biologists return each year to Penikese Island to study the survival and growth of the beetle population.

