
Manufacturing engineering
Encyclopedia
Manufacturing engineering is a field dealing with different manufacturing practices and the research and development of processes, machines and equipment.
 Manufacturing engineers develop and create physical artifacts, production processes, and technology. It is a very broad area which includes the design and development of products. The manufacturing engineering discipline has very strong overlaps with mechanical engineering
Manufacturing engineers develop and create physical artifacts, production processes, and technology. It is a very broad area which includes the design and development of products. The manufacturing engineering discipline has very strong overlaps with mechanical engineering
, industrial engineering
, electrical engineering
, electronic engineering
, computer science
, materials management
, and operations management
. Manufacturing engineers' success or failure directly impacts the advancement of technology and the spread of innovation. This field of engineering emerged in the mid to late 20th century, when industrialized countries introduced factories with:
1. Advanced statistical methods of quality control
: These factories were pioneered by the American mathematician William Edwards Deming, who was initially ignored by his home country. The same methods of quality control later turned Japanese factories into world leaders in cost-effectiveness and production quality.
2. Industrial robots on the factory floor, introduced in the late 1970s: These computer-controlled welding
arms and grippers could perform simple tasks such as attaching a car door quickly and flawlessly 24 hours a day. This cut costs and improved production speed.
, this factory mass-produced ships on assembly lines using manufactured parts. The Venice Arsenal apparently produced nearly one ship every day and, at its height, employed 16,000 people.
Many historians regard Matthew Boulton's Soho Manufactory (established in 1761 in Birmingham) as the first modern factory. Similar claims can be made for John Lombe's silk mill in Derby (1721), or Richard Arkwright's Cromford Mill (1771). The Cromford Mill was purpose-built to accommodate the equipment it held and to take the material through the various manufacturing processes. One historian, Murno Gladst, contends that the first factory was in Potosí
One historian, Murno Gladst, contends that the first factory was in Potosí
. The Potosi factory took advantage of the abundant silver that was mined nearby and processed silver ingot slugs into coins.
British colonies in the 19th century built factories simply as buildings where a large number of workers gathered to perform hand labor, usually in textile production. This proved more efficient for the administration and distribution of materials to individual workers than earlier methods of manufacturing, such as cottage industries or the putting-out system.
Cotton mills used inventions such as the steam engine
and the power loom
to pioneer the industrial factories of the 19th century, where precision machine tools and replaceable parts allowed greater efficiency and less waste. This experience formed the basis for the later studies of manufacturing engineering. Between 1820 and 1850, non-mechanized factories supplanted traditional artisan shops as the predominant form of manufacturing institution.
Henry Ford
further revolutionized the factory concept and thus manufacturing engineering in the early 20th century with the innovation of mass production. Highly specialized workers situated alongside a series of rolling ramps would build up a product such as (in Ford's case) an automobile. This concept dramatically decreased production costs for virtually all manufactured goods and brought about the age of consumerism.
Some industries, such as semiconductor
and steel
manufacturers use the term "fabrication" for these processes.
 Automation
Automation
is used in different processes of manufacturing such as machining and welding. Automated manufacturing refers to the application of automation to produce goods in a factory. The main advantages of automated manufacturing for the manufacturing process are realized with effective implementation of automation and include: higher consistency and quality, reduction of lead times, simplification of production, reduced handling, improved work flow, and improved worker morale.
Robotics
is the application of mechatronics and automation to create robots, which are often used in manufacturing to perform tasks that are dangerous, unpleasant, or repetitive. These robots may be of any shape and size, but all are preprogrammed and interact physically with the world. To create a robot, an engineer typically employs kinematics (to determine the robot's range of motion) and mechanics (to determine the stresses within the robot). Robots are used extensively in manufacturing engineering.
Robots allow businesses to save money on labor, perform tasks that are either too dangerous or too precise for humans to perform economically, and to insure better quality. Many companies employ assembly lines of robots, and some factories are so robotized that they can run by themselves. Outside the factory, robots have been employed in bomb disposal, space exploration, and many other fields. Robots are also sold for various residential applications.
Academic degrees for manufacturing engineers are usually the Bachelor of Engineering, [BE] or [BEng], and the Bachelor of Science, [BS] or [BSc]. For manufacturing technologists the required degrees are Bachelor of Technology [B.TECH] or Bachelor of Applied Science [BASc] in Manufacturing, depending upon the university. Masters degrees in engineering manufacturing include Master of Engineering [ME] or [MEng] in Manufacturing, Master of Science [M.Sc] in Manufacturing Management, Master of Science [M.Sc] in Industrial and Production Management, and Master of Science [M.Sc] as well as Master of Engineering [ME] in Design, which is a subdiscipline of manufacturing. Doctoral [PhD] or [DEng] level courses in manufacturing are also available depending on the university.
The undergraduate degree curriculum generally includes courses in physics, mathematics, computer science, project management, and specific topics in mechanical and manufacturing engineering. Initially such topics cover most, if not all, of the subdisciplines of manufacturing engineering. Students then choose to specialize in one or more subdisciplines towards the end of their degree work.
, and includes :
A bachelor's degree in these two areas will typically differ only by a few specialized classes, although the mechanical engineering degree requires much more mathematics expertise.
In some countries, "professional engineer" is the term for registered or licensed engineers who are permitted to offer their professional services directly to the public. Professional Engineer
, abbreviatied (PE - USA) or (PEng - Canada), is the designation for licensure in North America. In order to qualify for this license, a candidate needs a bachelor's degree from an ABET
recognized university in the USA, a passing score on a state examination, and four years of work experience usually gained via a structured internship. In the USA, more recent graduates have the option of dividing this licensure process into two segments. The Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) exam is often taken immediately after graduation and the Principles and Practice of Engineering exam is taken after four years of working in a chosen engineering field.
Society of Manufacturing Engineers (SME) certifications (USA):
The SME administers qualifications specifically for the manufacturing industry. These are not degree level qualifications and are not recognized at the professional engineering level. The following discussion deals with qualifications in the USA only. Qualified candidates for the Certified Manufacturing Technologist Certificate (CMfgT) must pass a three-hour, 130-question multiple-choice exam. The exam covers math, manufacturing processes, manufacturing management, automation, and related subjects. Additionally, a candidate must have at least four years of combined education and manufacturing-related work experience.
Certified Manufacturing Engineering (CMfgE) is an engineering qualification administered by the Society of Manufacturing Engineers, Dearborn, Michigan, USA. Candidates qualifying for a Certified Manufacturing Engineering Certificate must pass a three-hour, 150 question multiple-choice exam which covers more in-depth topics than does the CMfgT exam. CMfgE candidates must also have eight years of combined education and manufacturing-related work experience, with a minimum of four years of work experience.
Certified Engineering Manager (CEM). The Certified Engineering Manager Certificate is also designed for engineers with eight years of combined education and manufacturing experience. The test is four hours long and has 160 multiple-choice questions. The CEM certification exam covers business processes, teamwork, responsibility, and other management-related categories.
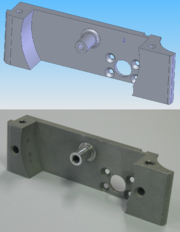 Many manufacturing companies, especially those in industrialized nations, have begun to incorporate computer-aided engineering
Many manufacturing companies, especially those in industrialized nations, have begun to incorporate computer-aided engineering
(CAE) programs into their existing design and analysis processes, including 2D and 3D solid modeling computer-aided design
(CAD). This method has many benefits, including easier and more exhaustive visualization of products, the ability to create virtual assemblies of parts, and ease of use in designing mating interfaces and tolerances.
Other CAE programs commonly used by product manufacturers include product life cycle management (PLM) tools and analysis tools used to perform complex simulations. Analysis tools may be used to predict product response to expected loads, including fatigue life and manufacturability. These tools include finite element analysis (FEA), computational fluid dynamics
(CFD), and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM).
Using CAE programs, a mechanical design team can quickly and cheaply iterate the design process to develop a product that better meets cost, performance, and other constraints. No physical prototype need be created until the design nears completion, allowing hundreds or thousands of designs to be evaluated, instead of relatively few. In addition, CAE analysis programs can model complicated physical phenomena which cannot be solved by hand, such as viscoelasticity, complex contact between mating parts, or non-Newtonian flows.
Just as manufacturing engineering is linked with other disciplines, such as mechatronics, multidisciplinary design optimization
(MDO) is also being used with other CAE programs to automate and improve the iterative design process. MDO tools wrap around existing CAE processes, allowing product evaluation to continue even after the analyst goes home for the day. They also utilize sophisticated optimization algorithms to more intelligently explore possible designs, often finding better, innovative solutions to difficult multidisciplinary design problems.
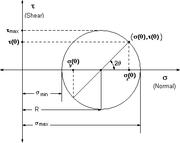 Mechanics, in the most general sense, is the study of forces and their effects on matter. Typically, engineering mechanics is used to analyze and predict the acceleration and deformation (both elastic and plastic) of objects under known forces (also called loads) or stresses. Subdisciplines of mechanics include:
Mechanics, in the most general sense, is the study of forces and their effects on matter. Typically, engineering mechanics is used to analyze and predict the acceleration and deformation (both elastic and plastic) of objects under known forces (also called loads) or stresses. Subdisciplines of mechanics include:
If the engineering project were to design a vehicle, statics might be employed to design the frame of the vehicle in order to evaluate where the stresses will be most intense. Dynamics might be used when designing the car's engine to evaluate the forces in the pistons and cams as the engine cycles. Mechanics of materials might be used to choose appropriate materials for the manufacture of the frame and engine. Fluid mechanics might be used to design a ventilation system for the vehicle or to design the intake system for the engine.
Engineers typically use kinematics in the design and analysis of mechanisms. Kinematics can be used to find the possible range of motion for a given mechanism, or, working in reverse, can be used to design a mechanism that has a desired range of motion.
 Drafting or technical drawing
Drafting or technical drawing
is the means by which manufacturers create instructions for manufacturing parts. A technical drawing can be a computer model or hand-drawn schematic showing all the dimensions necessary to manufacture a part, as well as assembly notes, a list of required materials, and other pertinent information. A U.S engineer or skilled worker who creates technical drawings may be referred to as a drafter or draftsman. Drafting has historically been a two-dimensional process, but computer-aided design (CAD) programs now allow the designer to create in three dimensions.
Instructions for manufacturing a part must be fed to the necessary machinery, either manually, through programmed instructions, or through the use of a computer-aided manufacturing
(CAM) or combined CAD/CAM program. Optionally, an engineer may also manually manufacture a part using the technical drawings, but this is becoming an increasing rarity with the advent of computer numerically controlled (CNC) manufacturing. Engineers primarily manufacture parts manually in the areas of applied spray coatings, finishes, and other processes that cannot economically or practically be done by a machine.
Drafting is used in nearly every subdiscipline of mechanical and manufacturing engineering, and by many other branches of engineering and architecture. Three-dimensional models created using CAD software are also commonly used in finite element analysis (FEA) and computational fluid dynamics
(CFD).
 Mechatronics is an engineering discipline which deals with the convergence of electrical, mechanical and manufacturing systems. Such combined systems are known as electromechanical systems and are widespread. Examples include automated manufacturing systems, heating, ventilation and air-conditioning systems, and various aircraft and automobile subsystems.
Mechatronics is an engineering discipline which deals with the convergence of electrical, mechanical and manufacturing systems. Such combined systems are known as electromechanical systems and are widespread. Examples include automated manufacturing systems, heating, ventilation and air-conditioning systems, and various aircraft and automobile subsystems.
The term mechatronics is typically used to refer to macroscopic systems, but futurists have predicted the emergence of very small electromechanical devices. Already such small devices, known as Microelectromechanical systems
(MEMS), are used in automobiles to initiate the deployment of airbags, in digital projectors to create sharper images, and in inkjet printers to create nozzles for high-definition printing. In the future it is hoped that such devices will be used in tiny implantable medical devices and to improve optical communication.
Manufacturing engineers are closely connected with engineering and industrial design efforts. Examples of major companies that employ manufacturing engineers in the United States include General Motors Corporation, Ford Motor Company, Chrysler, Boeing
, Gates Corporation and Pfizer. Examples in Europe include Airbus
, Daimler, BMW
, Fiat, and Michelin Tyre.
Industries where manufacturing engineers are generally employed include:
(FMS) is a manufacturing system in which there is some amount of flexibility that allows the system to react to changes, whether predicted or unpredicted. This flexibility is generally considered to fall into two categories, both of which have numerous subcategories.
The first category, machine flexibility, covers the system's ability to be changed to produce new product types and the ability to change the order of operations executed on a part. The second category, called routing flexibility, consists of the ability to use multiple machines to perform the same operation on a part, as well as the system's ability to absorb large-scale changes, such as in volume, capacity, or capability.
Most FMS systems comprise three main systems. The work machines, which are often automated CNC machines, are connected by a material handling system to optimize parts flow, and to a central control computer, which controls material movements and machine flow.
The main advantages of an FMS is its high flexibility in managing manufacturing resources like time and effort in order to manufacture a new product. The best application of an FMS is found in the production of small sets of products from a mass production.
(TWI). This innovative steady state (non-fusion) welding technique joins previously un-weldable materials, including several aluminum alloys. It may play an important role in the future construction of airplanes, potentially replacing rivets. Current uses of this technology to date include: welding the seams of the aluminum main space shuttle external tank, the Orion Crew Vehicle test article, Boeing Delta II and Delta IV Expendable Launch Vehicles and the SpaceX Falcon 1 rocket; armor plating for amphibious assault ships; and welding the wings and fuselage panels of the new Eclipse 500 aircraft from Eclipse Aviation, among an increasingly growing range of uses.
Other areas of research are :
Product Design
, MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems), Lean Manufacturing
, Intelligent Manufacturing Systems, Green Manufacturing,
Precision Engineering, Smart Materials, etc.
Overview
This field also deals with the integration of different facilities and systems for producing quality products (with optimal expenditure) by applying the principles of physics and the results of manufacturing systems studies, such as the following:- Craft or guild system
- Putting-out systemPutting-Out systemThe putting-out system was a means of subcontracting work. It was also known as the workshop system. In putting-out, work was contracted by a central agent to subcontractors who completed the work in their own facilities, usually their own homes....
- English system of manufacturingEnglish system of manufacturingThe English system of manufacturing was an early system of industrial production that required skilled machinists who were required to produce parts from a design or model. But however skilled the machinist, parts were never absolutely identical, and each part had to be manufactured separately to...
- American system of manufacturingAmerican system of manufacturingThe American system of manufacturing was a set of manufacturing methods that evolved in the 19th century. It involved semi-skilled labor using machine tools and jigs to make standardized, identical, interchangeable parts, manufactured to a tolerance, which could be assembled with a minimum of time...
- Soviet collectivism in manufacturing
- Mass productionMass productionMass production is the production of large amounts of standardized products, including and especially on assembly lines...
- Computer integrated manufacturingComputer Integrated ManufacturingComputer-integrated manufacturing is the manufacturing approach of using computers to control the entire production process. This integration allows individual processes to exchange information with each other and initiate actions...
- Computer-aided technologies in manufacturing
- Just in timeJust In TimeJust in time is a production strategy that strives to improve a business return on investment by reducing in-process inventory and associated carrying costs. Just-in-time production method is also called the Toyota Production System...
manufacturing - Lean manufacturingLean manufacturingLean manufacturing, lean enterprise, or lean production, often simply, "Lean," is a production practice that considers the expenditure of resources for any goal other than the creation of value for the end customer to be wasteful, and thus a target for elimination...
- Flexible manufacturing
- Mass customizationMass customizationMass customization, in marketing, manufacturing, call centres and management, is the use of flexible computer-aided manufacturing systems to produce custom output...
- Agile manufacturingAgile manufacturingAgile manufacturing is a term applied to an organization that has created the processes, tools, and training to enable it to respond quickly to customer needs and market changes while still controlling costs and quality....
- Rapid manufacturing
- PrefabricationPrefabricationPrefabrication is the practice of assembling components of a structure in a factory or other manufacturing site, and transporting complete assemblies or sub-assemblies to the construction site where the structure is to be located...
- OwnershipOwnershipOwnership is the state or fact of exclusive rights and control over property, which may be an object, land/real estate or intellectual property. Ownership involves multiple rights, collectively referred to as title, which may be separated and held by different parties. The concept of ownership has...
- FabricationFabrication (metal)Fabrication as an industrial term refers to building metal structures by cutting, bending, and assembling. The cutting part of fabrication is via sawing, shearing, or chiseling ; torching with handheld torches ; and via CNC cutters...
- PublicationPublicationTo publish is to make content available to the public. While specific use of the term may vary among countries, it is usually applied to text, images, or other audio-visual content on any medium, including paper or electronic publishing forms such as websites, e-books, Compact Discs and MP3s...

Mechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering is a discipline of engineering that applies the principles of physics and materials science for analysis, design, manufacturing, and maintenance of mechanical systems. It is the branch of engineering that involves the production and usage of heat and mechanical power for the...
, industrial engineering
Industrial engineering
Industrial engineering is a branch of engineering dealing with the optimization of complex processes or systems. It is concerned with the development, improvement, implementation and evaluation of integrated systems of people, money, knowledge, information, equipment, energy, materials, analysis...
, electrical engineering
Electrical engineering
Electrical engineering is a field of engineering that generally deals with the study and application of electricity, electronics and electromagnetism. The field first became an identifiable occupation in the late nineteenth century after commercialization of the electric telegraph and electrical...
, electronic engineering
Electronic engineering
Electronics engineering, also referred to as electronic engineering, is an engineering discipline where non-linear and active electrical components such as electron tubes, and semiconductor devices, especially transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, are utilized to design electronic...
, computer science
Computer science
Computer science or computing science is the study of the theoretical foundations of information and computation and of practical techniques for their implementation and application in computer systems...
, materials management
Materials management
Materials management can deal with campus planning and building design for the movement of materials, or with logistics that deal with the tangible components of a supply chain...
, and operations management
Operations management
Operations management is an area of management concerned with overseeing, designing, and redesigning business operations in the production of goods and/or services. It involves the responsibility of ensuring that business operations are efficient in terms of using as little resources as needed, and...
. Manufacturing engineers' success or failure directly impacts the advancement of technology and the spread of innovation. This field of engineering emerged in the mid to late 20th century, when industrialized countries introduced factories with:
1. Advanced statistical methods of quality control
Quality control
Quality control, or QC for short, is a process by which entities review the quality of all factors involved in production. This approach places an emphasis on three aspects:...
: These factories were pioneered by the American mathematician William Edwards Deming, who was initially ignored by his home country. The same methods of quality control later turned Japanese factories into world leaders in cost-effectiveness and production quality.
2. Industrial robots on the factory floor, introduced in the late 1970s: These computer-controlled welding
Welding
Welding is a fabrication or sculptural process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, by causing coalescence. This is often done by melting the workpieces and adding a filler material to form a pool of molten material that cools to become a strong joint, with pressure sometimes...
arms and grippers could perform simple tasks such as attaching a car door quickly and flawlessly 24 hours a day. This cut costs and improved production speed.
History
The history of manufacturing engineering can be traced to factories in the mid 19th century USA and 18th century UK. Although large home production sites and workshops were established in ancient China, ancient Rome and the Middle East, the Venice Arsenal provides one of the first examples of a factory in the modern sense of the word. Founded in 1104 in the Republic of Venice several hundred years before the Industrial RevolutionIndustrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was a period from the 18th to the 19th century where major changes in agriculture, manufacturing, mining, transportation, and technology had a profound effect on the social, economic and cultural conditions of the times...
, this factory mass-produced ships on assembly lines using manufactured parts. The Venice Arsenal apparently produced nearly one ship every day and, at its height, employed 16,000 people.
Many historians regard Matthew Boulton's Soho Manufactory (established in 1761 in Birmingham) as the first modern factory. Similar claims can be made for John Lombe's silk mill in Derby (1721), or Richard Arkwright's Cromford Mill (1771). The Cromford Mill was purpose-built to accommodate the equipment it held and to take the material through the various manufacturing processes.

Potosí
Potosí is a city and the capital of the department of Potosí in Bolivia. It is one of the highest cities in the world by elevation at a nominal . and it was the location of the Spanish colonial mint, now the National Mint of Bolivia...
. The Potosi factory took advantage of the abundant silver that was mined nearby and processed silver ingot slugs into coins.
British colonies in the 19th century built factories simply as buildings where a large number of workers gathered to perform hand labor, usually in textile production. This proved more efficient for the administration and distribution of materials to individual workers than earlier methods of manufacturing, such as cottage industries or the putting-out system.
Cotton mills used inventions such as the steam engine
Steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid.Steam engines are external combustion engines, where the working fluid is separate from the combustion products. Non-combustion heat sources such as solar power, nuclear power or geothermal energy may be...
and the power loom
Power loom
A power loom is a mechanized loom powered by a line shaft. The first power loom was designed in 1784 by Edmund Cartwright and first built in 1785. It was refined over the next 47 years until a design by Kenworthy and Bullough, made the operation completely automatic. This was known as the...
to pioneer the industrial factories of the 19th century, where precision machine tools and replaceable parts allowed greater efficiency and less waste. This experience formed the basis for the later studies of manufacturing engineering. Between 1820 and 1850, non-mechanized factories supplanted traditional artisan shops as the predominant form of manufacturing institution.
Henry Ford
Henry Ford
Henry Ford was an American industrialist, the founder of the Ford Motor Company, and sponsor of the development of the assembly line technique of mass production. His introduction of the Model T automobile revolutionized transportation and American industry...
further revolutionized the factory concept and thus manufacturing engineering in the early 20th century with the innovation of mass production. Highly specialized workers situated alongside a series of rolling ramps would build up a product such as (in Ford's case) an automobile. This concept dramatically decreased production costs for virtually all manufactured goods and brought about the age of consumerism.
Modern developments
Modern manufacturing engineering studies include all intermediate processes required for the production and integration of a product's components.Some industries, such as semiconductor
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
and steel
Steel
Steel is an alloy that consists mostly of iron and has a carbon content between 0.2% and 2.1% by weight, depending on the grade. Carbon is the most common alloying material for iron, but various other alloying elements are used, such as manganese, chromium, vanadium, and tungsten...
manufacturers use the term "fabrication" for these processes.

Automation
Automation is the use of control systems and information technologies to reduce the need for human work in the production of goods and services. In the scope of industrialization, automation is a step beyond mechanization...
is used in different processes of manufacturing such as machining and welding. Automated manufacturing refers to the application of automation to produce goods in a factory. The main advantages of automated manufacturing for the manufacturing process are realized with effective implementation of automation and include: higher consistency and quality, reduction of lead times, simplification of production, reduced handling, improved work flow, and improved worker morale.
Robotics
Robotics
Robotics is the branch of technology that deals with the design, construction, operation, structural disposition, manufacture and application of robots...
is the application of mechatronics and automation to create robots, which are often used in manufacturing to perform tasks that are dangerous, unpleasant, or repetitive. These robots may be of any shape and size, but all are preprogrammed and interact physically with the world. To create a robot, an engineer typically employs kinematics (to determine the robot's range of motion) and mechanics (to determine the stresses within the robot). Robots are used extensively in manufacturing engineering.
Robots allow businesses to save money on labor, perform tasks that are either too dangerous or too precise for humans to perform economically, and to insure better quality. Many companies employ assembly lines of robots, and some factories are so robotized that they can run by themselves. Outside the factory, robots have been employed in bomb disposal, space exploration, and many other fields. Robots are also sold for various residential applications.
Certification programs in manufacturing engineering
Manufacturing engineers possess a bachelor's degree in engineering with a major in manufacturing engineering. The length of study for such a degree is usually four to five years followed by five more years of professional practice to qualify as a professional engineer. Working as a manufacturing engineering technologist involves a more applications-oriented qualification path.Academic degrees for manufacturing engineers are usually the Bachelor of Engineering, [BE] or [BEng], and the Bachelor of Science, [BS] or [BSc]. For manufacturing technologists the required degrees are Bachelor of Technology [B.TECH] or Bachelor of Applied Science [BASc] in Manufacturing, depending upon the university. Masters degrees in engineering manufacturing include Master of Engineering [ME] or [MEng] in Manufacturing, Master of Science [M.Sc] in Manufacturing Management, Master of Science [M.Sc] in Industrial and Production Management, and Master of Science [M.Sc] as well as Master of Engineering [ME] in Design, which is a subdiscipline of manufacturing. Doctoral [PhD] or [DEng] level courses in manufacturing are also available depending on the university.
The undergraduate degree curriculum generally includes courses in physics, mathematics, computer science, project management, and specific topics in mechanical and manufacturing engineering. Initially such topics cover most, if not all, of the subdisciplines of manufacturing engineering. Students then choose to specialize in one or more subdisciplines towards the end of their degree work.
Syllabus
The curriculum for a bachelor's degree in manufacturing is very similar to that for mechanical engineeringMechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering is a discipline of engineering that applies the principles of physics and materials science for analysis, design, manufacturing, and maintenance of mechanical systems. It is the branch of engineering that involves the production and usage of heat and mechanical power for the...
, and includes :
- Statics and dynamics
- Strength of materials and solid mechanics
- Instrumentation and measurement
- Thermodynamics, heat transfer, energy conversion, and HVACHVACHVAC refers to technology of indoor or automotive environmental comfort. HVAC system design is a major subdiscipline of mechanical engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer...
- Fluid mechanics and fluid dynamics
- Mechanism design (including kinematics and dynamics)
- Manufacturing technology or processes
- Hydraulics and pneumatics
- Mathematics - in particular, calculus, differential equations, statistics, and linear algebra.
- Engineering design
- Mechatronics and control theory
- Material engineering
- Drafting, CAD (including solid modeling), and CAM, etc.
A bachelor's degree in these two areas will typically differ only by a few specialized classes, although the mechanical engineering degree requires much more mathematics expertise.
Manufacturing engineering certification
Certification and licensure:In some countries, "professional engineer" is the term for registered or licensed engineers who are permitted to offer their professional services directly to the public. Professional Engineer
Professional Engineer
Regulation of the engineering profession is established by various jurisdictions of the world to protect the safety, well-being and other interests of the general public, and to define the licensure process through which an engineer becomes authorized to provide professional services to the...
, abbreviatied (PE - USA) or (PEng - Canada), is the designation for licensure in North America. In order to qualify for this license, a candidate needs a bachelor's degree from an ABET
Abet
Abet may refer to:* Abet Guidaben , former Philippine Basketball Association basketball player* ABET, Inc., a non-profit organization that accredits higher education programs in applied science, computing, engineering, and technology....
recognized university in the USA, a passing score on a state examination, and four years of work experience usually gained via a structured internship. In the USA, more recent graduates have the option of dividing this licensure process into two segments. The Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) exam is often taken immediately after graduation and the Principles and Practice of Engineering exam is taken after four years of working in a chosen engineering field.
Society of Manufacturing Engineers (SME) certifications (USA):
The SME administers qualifications specifically for the manufacturing industry. These are not degree level qualifications and are not recognized at the professional engineering level. The following discussion deals with qualifications in the USA only. Qualified candidates for the Certified Manufacturing Technologist Certificate (CMfgT) must pass a three-hour, 130-question multiple-choice exam. The exam covers math, manufacturing processes, manufacturing management, automation, and related subjects. Additionally, a candidate must have at least four years of combined education and manufacturing-related work experience.
Certified Manufacturing Engineering (CMfgE) is an engineering qualification administered by the Society of Manufacturing Engineers, Dearborn, Michigan, USA. Candidates qualifying for a Certified Manufacturing Engineering Certificate must pass a three-hour, 150 question multiple-choice exam which covers more in-depth topics than does the CMfgT exam. CMfgE candidates must also have eight years of combined education and manufacturing-related work experience, with a minimum of four years of work experience.
Certified Engineering Manager (CEM). The Certified Engineering Manager Certificate is also designed for engineers with eight years of combined education and manufacturing experience. The test is four hours long and has 160 multiple-choice questions. The CEM certification exam covers business processes, teamwork, responsibility, and other management-related categories.
Modern tools

Computer-aided engineering
Computer-aided engineering is the broad usage of computer software to aid in engineering tasks. It includes computer-aided design , computer-aided analysis , computer-integrated manufacturing , computer-aided manufacturing , material requirements planning , and computer-aided planning .- Overview...
(CAE) programs into their existing design and analysis processes, including 2D and 3D solid modeling computer-aided design
Computer-aided design
Computer-aided design , also known as computer-aided design and drafting , is the use of computer technology for the process of design and design-documentation. Computer Aided Drafting describes the process of drafting with a computer...
(CAD). This method has many benefits, including easier and more exhaustive visualization of products, the ability to create virtual assemblies of parts, and ease of use in designing mating interfaces and tolerances.
Other CAE programs commonly used by product manufacturers include product life cycle management (PLM) tools and analysis tools used to perform complex simulations. Analysis tools may be used to predict product response to expected loads, including fatigue life and manufacturability. These tools include finite element analysis (FEA), computational fluid dynamics
Computational fluid dynamics
Computational fluid dynamics, usually abbreviated as CFD, is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical methods and algorithms to solve and analyze problems that involve fluid flows. Computers are used to perform the calculations required to simulate the interaction of liquids and gases with...
(CFD), and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM).
Using CAE programs, a mechanical design team can quickly and cheaply iterate the design process to develop a product that better meets cost, performance, and other constraints. No physical prototype need be created until the design nears completion, allowing hundreds or thousands of designs to be evaluated, instead of relatively few. In addition, CAE analysis programs can model complicated physical phenomena which cannot be solved by hand, such as viscoelasticity, complex contact between mating parts, or non-Newtonian flows.
Just as manufacturing engineering is linked with other disciplines, such as mechatronics, multidisciplinary design optimization
Multidisciplinary design optimization
Multi-disciplinary design optimization is a field of engineering that uses optimization methods to solve design problems incorporating a number of disciplines. As defined by Prof. Carlo Poloni, MDO is "the art of finding the best compromise"...
(MDO) is also being used with other CAE programs to automate and improve the iterative design process. MDO tools wrap around existing CAE processes, allowing product evaluation to continue even after the analyst goes home for the day. They also utilize sophisticated optimization algorithms to more intelligently explore possible designs, often finding better, innovative solutions to difficult multidisciplinary design problems.
Mechanics

- StaticsStaticsStatics is the branch of mechanics concerned with the analysis of loads on physical systems in static equilibrium, that is, in a state where the relative positions of subsystems do not vary over time, or where components and structures are at a constant velocity...
, the study of non-moving bodies under known loads - DynamicsDynamics (mechanics)In the field of physics, the study of the causes of motion and changes in motion is dynamics. In other words the study of forces and why objects are in motion. Dynamics includes the study of the effect of torques on motion...
(or kinetics), the study of how forces affect moving bodies - Mechanics of materials, the study of how different materials deform under various types of stress
- Fluid mechanicsFluid mechanicsFluid mechanics is the study of fluids and the forces on them. Fluid mechanics can be divided into fluid statics, the study of fluids at rest; fluid kinematics, the study of fluids in motion; and fluid dynamics, the study of the effect of forces on fluid motion...
, the study of how fluids react to forces - Continuum mechanicsContinuum mechanicsContinuum mechanics is a branch of mechanics that deals with the analysis of the kinematics and the mechanical behavior of materials modelled as a continuous mass rather than as discrete particles...
, a method of applying mechanics that assumes that objects are continuous (rather than discrete)
If the engineering project were to design a vehicle, statics might be employed to design the frame of the vehicle in order to evaluate where the stresses will be most intense. Dynamics might be used when designing the car's engine to evaluate the forces in the pistons and cams as the engine cycles. Mechanics of materials might be used to choose appropriate materials for the manufacture of the frame and engine. Fluid mechanics might be used to design a ventilation system for the vehicle or to design the intake system for the engine.
Kinematics
Kinematics is the study of the motion of bodies (objects) and systems (groups of objects), while ignoring the forces that cause the motion. The movement of a crane and the oscillations of a piston in an engine are both simple kinematic systems. The crane is a type of open kinematic chain, while the piston is part of a closed four-bar linkage.Engineers typically use kinematics in the design and analysis of mechanisms. Kinematics can be used to find the possible range of motion for a given mechanism, or, working in reverse, can be used to design a mechanism that has a desired range of motion.
Drafting

Technical drawing
Technical drawing, also known as drafting or draughting, is the act and discipline of composing plans that visually communicate how something functions or has to be constructed.Drafting is the language of industry....
is the means by which manufacturers create instructions for manufacturing parts. A technical drawing can be a computer model or hand-drawn schematic showing all the dimensions necessary to manufacture a part, as well as assembly notes, a list of required materials, and other pertinent information. A U.S engineer or skilled worker who creates technical drawings may be referred to as a drafter or draftsman. Drafting has historically been a two-dimensional process, but computer-aided design (CAD) programs now allow the designer to create in three dimensions.
Instructions for manufacturing a part must be fed to the necessary machinery, either manually, through programmed instructions, or through the use of a computer-aided manufacturing
Computer-aided manufacturing
Computer-aided manufacturing is the use of computer software to control machine tools and related machinery in the manufacturing of workpieces. This is not the only definition for CAM, but it is the most common; CAM may also refer to the use of a computer to assist in all operations of a...
(CAM) or combined CAD/CAM program. Optionally, an engineer may also manually manufacture a part using the technical drawings, but this is becoming an increasing rarity with the advent of computer numerically controlled (CNC) manufacturing. Engineers primarily manufacture parts manually in the areas of applied spray coatings, finishes, and other processes that cannot economically or practically be done by a machine.
Drafting is used in nearly every subdiscipline of mechanical and manufacturing engineering, and by many other branches of engineering and architecture. Three-dimensional models created using CAD software are also commonly used in finite element analysis (FEA) and computational fluid dynamics
Computational fluid dynamics
Computational fluid dynamics, usually abbreviated as CFD, is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical methods and algorithms to solve and analyze problems that involve fluid flows. Computers are used to perform the calculations required to simulate the interaction of liquids and gases with...
(CFD).
Mechatronics

The term mechatronics is typically used to refer to macroscopic systems, but futurists have predicted the emergence of very small electromechanical devices. Already such small devices, known as Microelectromechanical systems
Microelectromechanical systems
Microelectromechanical systems is the technology of very small mechanical devices driven by electricity; it merges at the nano-scale into nanoelectromechanical systems and nanotechnology...
(MEMS), are used in automobiles to initiate the deployment of airbags, in digital projectors to create sharper images, and in inkjet printers to create nozzles for high-definition printing. In the future it is hoped that such devices will be used in tiny implantable medical devices and to improve optical communication.
Textile engineering
Textile engineering courses deal with the application of scientific and engineering principles to the design and control of all aspects of fiber, textile, and apparel processes, products, and machinery. These include natural and man-made materials, interaction of materials with machines, safety and health, energy conservation, and waste and pollution control. Additionally, students are given experience in plant design and layout, machine and wet process design and improvement, and designing and creating textile products. Throughout the textile engineering curriculum, students take classes from other engineering and disciplines including: mechanical, chemical, materials and industrial engineering.Employment
Manufacturing engineering is just one facet of the engineering industry. Manufacturing engineers enjoy improving the production process from start to finish. They have the ability to keep the whole production process in mind as they focus on a particular portion of the process. Successful students in manufacturing engineering degree programs are inspired by the notion of starting with a natural resource, such as a block of wood, and ending with a usable, valuable product, such as a desk, produced efficiently and economically.Manufacturing engineers are closely connected with engineering and industrial design efforts. Examples of major companies that employ manufacturing engineers in the United States include General Motors Corporation, Ford Motor Company, Chrysler, Boeing
Boeing
The Boeing Company is an American multinational aerospace and defense corporation, founded in 1916 by William E. Boeing in Seattle, Washington. Boeing has expanded over the years, merging with McDonnell Douglas in 1997. Boeing Corporate headquarters has been in Chicago, Illinois since 2001...
, Gates Corporation and Pfizer. Examples in Europe include Airbus
Airbus
Airbus SAS is an aircraft manufacturing subsidiary of EADS, a European aerospace company. Based in Blagnac, France, surburb of Toulouse, and with significant activity across Europe, the company produces around half of the world's jet airliners....
, Daimler, BMW
BMW
Bayerische Motoren Werke AG is a German automobile, motorcycle and engine manufacturing company founded in 1916. It also owns and produces the Mini marque, and is the parent company of Rolls-Royce Motor Cars. BMW produces motorcycles under BMW Motorrad and Husqvarna brands...
, Fiat, and Michelin Tyre.
Industries where manufacturing engineers are generally employed include:
- Aerospace industry
- Automotive industryAutomotive industryThe automotive industry designs, develops, manufactures, markets, and sells motor vehicles, and is one of the world's most important economic sectors by revenue....
- Chemical industryChemical industryThe chemical industry comprises the companies that produce industrial chemicals. Central to the modern world economy, it converts raw materials into more than 70,000 different products.-Products:...
- Computer industryComputer industryComputer industry is a collective term used to describe the whole range of businesses involved in developing computer software, designing computer hardware and computer networking infrastructures, the manufacture of computer components and the provision of information technology services.-See...
- Electronics industry
- Food processing industry
- Garment industry
- Pharmaceutical industry
- Pulp and paper industryPulp and paper industryThe global pulp and paper industry is dominated by North American , northern European and East Asian countries...
- Toy industryToy industryThe toy industry is an economic sector that produces small goods in any material. The production of toys is called toymaking. Hinges, buttons, belt buckles and hooks are all examples of goods that were once considered "toys" and could be produced in metal, leather or glass, amongst others...
Flexible manufacturing systems
A flexible manufacturing systemFlexible manufacturing system
A flexible manufacturing system is a manufacturing system in which there is some amount of flexibility that allows the system to react in the case of changes, whether predicted or unpredicted...
(FMS) is a manufacturing system in which there is some amount of flexibility that allows the system to react to changes, whether predicted or unpredicted. This flexibility is generally considered to fall into two categories, both of which have numerous subcategories.
The first category, machine flexibility, covers the system's ability to be changed to produce new product types and the ability to change the order of operations executed on a part. The second category, called routing flexibility, consists of the ability to use multiple machines to perform the same operation on a part, as well as the system's ability to absorb large-scale changes, such as in volume, capacity, or capability.
Most FMS systems comprise three main systems. The work machines, which are often automated CNC machines, are connected by a material handling system to optimize parts flow, and to a central control computer, which controls material movements and machine flow.
The main advantages of an FMS is its high flexibility in managing manufacturing resources like time and effort in order to manufacture a new product. The best application of an FMS is found in the production of small sets of products from a mass production.
Computer integrated manufacturing
Computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM) in engineering is a method of manufacturing in which the entire production process is controlled by computer. Traditionally separated process methods are joined through a computer by CIM. This integration allows the processes to exchange information and to initiate actions. Through this integration, manufacturing can be faster and less error-prone, although the main advantage is the ability to create automated manufacturing processes. Typically CIM relies on closed-loop control processes based on real-time input from sensors. It is also known as flexible design and manufacturing.Friction stir welding
Friction stir welding was discovered in 1991 by The Welding InstituteThe Welding Institute
The Welding Institute or TWI is a research and technology organisation with a specialty in welding. The Welding Institute is based in Cambridgeshire, England, since 1946, and has several offices around the world....
(TWI). This innovative steady state (non-fusion) welding technique joins previously un-weldable materials, including several aluminum alloys. It may play an important role in the future construction of airplanes, potentially replacing rivets. Current uses of this technology to date include: welding the seams of the aluminum main space shuttle external tank, the Orion Crew Vehicle test article, Boeing Delta II and Delta IV Expendable Launch Vehicles and the SpaceX Falcon 1 rocket; armor plating for amphibious assault ships; and welding the wings and fuselage panels of the new Eclipse 500 aircraft from Eclipse Aviation, among an increasingly growing range of uses.
Other areas of research are :
Product Design
Product design
-Introduction:Product design is the process of creating a new product to be sold by a business or enterprise to its customers. It is concerned with the efficient and effective generation and development of ideas through a process that leads to new products.Product designers conceptualize and...
, MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems), Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing
Lean manufacturing, lean enterprise, or lean production, often simply, "Lean," is a production practice that considers the expenditure of resources for any goal other than the creation of value for the end customer to be wasteful, and thus a target for elimination...
, Intelligent Manufacturing Systems, Green Manufacturing,
Precision Engineering, Smart Materials, etc.
See also
- Automotive engineeringAutomotive engineeringModern automotive engineering, along with aerospace engineering and marine engineering, is a branch of vehicle engineering, incorporating elements of mechanical, electrical, electronic, software and safety engineering as applied to the design, manufacture and operation of motorcycles, automobiles,...
- Computer-aided designComputer-aided designComputer-aided design , also known as computer-aided design and drafting , is the use of computer technology for the process of design and design-documentation. Computer Aided Drafting describes the process of drafting with a computer...
- Computer numerically controlled
- Industrial revolutionIndustrial RevolutionThe Industrial Revolution was a period from the 18th to the 19th century where major changes in agriculture, manufacturing, mining, transportation, and technology had a profound effect on the social, economic and cultural conditions of the times...
- KinematicsKinematicsKinematics is the branch of classical mechanics that describes the motion of bodies and systems without consideration of the forces that cause the motion....
- MechanicsMechanicsMechanics is the branch of physics concerned with the behavior of physical bodies when subjected to forces or displacements, and the subsequent effects of the bodies on their environment....
- ManufacturingManufacturingManufacturing is the use of machines, tools and labor to produce goods for use or sale. The term may refer to a range of human activity, from handicraft to high tech, but is most commonly applied to industrial production, in which raw materials are transformed into finished goods on a large scale...
- Manufacturing Engineering Education
- MechatronicsMechatronicsMechatronics is the combination of mechanical engineering, electronic engineering, computer engineering, software engineering, control engineering, and systems design engineering in order to design, and manufacture useful products. Mechatronics is a multidisciplinary field of engineering, that is...
- Mechanical engineeringMechanical engineeringMechanical engineering is a discipline of engineering that applies the principles of physics and materials science for analysis, design, manufacturing, and maintenance of mechanical systems. It is the branch of engineering that involves the production and usage of heat and mechanical power for the...
- Occupational health and safety
- Package engineering
- RoboticsRoboticsRobotics is the branch of technology that deals with the design, construction, operation, structural disposition, manufacture and application of robots...
- Technical drawingTechnical drawingTechnical drawing, also known as drafting or draughting, is the act and discipline of composing plans that visually communicate how something functions or has to be constructed.Drafting is the language of industry....

