
List of orbital launch systems
Encyclopedia
This is a list of carrier rockets, and other systems used to place satellite
s into orbit
.


.jpg)



Satellite
In the context of spaceflight, a satellite is an object which has been placed into orbit by human endeavour. Such objects are sometimes called artificial satellites to distinguish them from natural satellites such as the Moon....
s into orbit
Orbit
In physics, an orbit is the gravitationally curved path of an object around a point in space, for example the orbit of a planet around the center of a star system, such as the Solar System...
.
China


- Feng Bao 1Feng Bao 1The Feng Bao 1 , also known as FB-1, was a Chinese carrier rocket launched between 1972 and 1981. It was replaced by the nearly identical Long March 2, which had been developed at the same time for political reasons related to China's Cultural Revolution.The Feng Bao was derived from the DF-5...
- Kaituozhe-1Kaituozhe-1The Kaituozhe-1 or is a Chinese commercial launch vehicle. Small and solid-fueled, its design was based on the road mobile DF-31 ICBM with an additional upper stage. The vehicle has performed two flights, the first in September 2002 and the second exactly one year later...
- Long March
- Long March 1
- Long March 1Long March 1Long March 1 is 1st member of China's Long March 1 .The study of Long March 1 began in 1965. Long March 1's first flight put China's first satellite Dong Fang Hong 1 to space on April 24, 1970.* Stages: 3...
- Long March 1DLong March 1DLong March 1D is the improved version of Long March 1 rocket stage for Chinese space agency craft, mainly for the thrustor of stage 1, from 1020 kilonewtons to 1101.2 kilonewtons, also improved the performance for stage 2 and stage 3. The improved Long March 1D can launch variant of LEO satellite;...
- Long March 1
- Long March 2
- Long March 2ALong March 2AThe Long March 2A, also known as the Chang Zheng 2A, CZ-2A and LM-2A, was a Chinese orbital carrier rocket. It was launched from Launch Area 2B at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Centre. It was a 2-stage rocket, and flew just once, on 5 November 1974...
- Long March 2CLong March 2CLong March 2C , or Chang Zheng 2C as in Chinese pinyin is a member of the Long March 2 rocket family, an expendable launch system operated by the People's Republic of China. This vehicle was developed by the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology, and the first launch occurred on November 26,...
- Long March 2DLong March 2DThe Long March 2D , also known as the Chang Zheng 2D, CZ-2D and LM-2D, is a Chinese orbital carrier rocket. It is a 2-stage carrier rocket mainly used for launching LEO and SSO satellites. It is mainly launched from areas 2B and 2S at Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center but can be launched from China's...
- Long March 2ELong March 2EThe Long March 2E, also known as the Chang Zheng 2E, CZ-2E and LM-2E, was a Chinese orbital carrier rocket. Designed to launch commercial communications satellites, the Long March 2E was retired in favour of the Long March 3B, after two launch failures. Launched from complex 2 at the Xichang...
- Long March 2E(A)
- Long March 2FLong March 2FThe Long March 2F , also known as the CZ-2F, LM-2F and Shenjian, is a Chinese manned orbital carrier rocket, part of the Long March rocket family. Designed to launch manned Shenzhou spacecraft, the Long March 2F is a man-rated two-stage version of the Long March 2E rocket, which in turn was based...
- Long March 2F/G
- Long March 2A
- Long March 3
- Long March 3Long March 3The Long March 3 , also known as the Chang Zheng 3, CZ-3 and LM-3, was a Chinese orbital carrier rocket. It was launched from Launch Complex 1 at the Xichang Satellite Launch Centre. It was a 3-stage rocket, and was mostly used to place DFH-2-class communications satellites into geosynchronous...
- Long March 3ALong March 3AThe Long March 3A , also known as the Chang Zheng 3A, CZ-3A and LM-3A, is a Chinese orbital carrier rocket. It is a 3-stage rocket, and is usually used to place communications satellites and Beidou navigation satellites into geosynchronous transfer orbits.It has formed the basis of the Long March...
- Long March 3BLong March 3BThe Long March 3B , also known as the Chang Zheng 3B, CZ-3B and LM-3B, is a Chinese orbital carrier rocket. Introduced in 1996, it is launched from Launch Area 2 at the Xichang Satellite Launch Centre...
- Long March 3B(A)
- Long March 3CLong March 3CThe Long March 3C , also known as the Chang Zheng 3C, CZ-3C and LM-3C, is a Chinese orbital carrier rocket. It is launched from Launch Complex 2 at the Xichang Satellite Launch Centre. A 3-stage rocket with two strapon liquid rocket boosters, it is a member of the Long March 3 rocket family, and...
- Long March 3
- Long March 4
- Long March 4ALong March 4AThe Long March 4A , also known as the Chang Zheng 4A, CZ-4A and LM-4A, sometimes misidentified as the Long March 4 due to the lack of any such designated rocket, was a Chinese orbital carrier rocket. It was launched from Launch Complex 1 at the Taiyuan Satellite Launch Centre. It was a 3-stage...
- Long March 4BLong March 4BThe Long March 4B , also known as the Chang Zheng 4B, CZ-4B and LM-4B is a Chinese orbital carrier rocket. Launched from Launch Complex 1 at the Taiyuan Satellite Launch Centre, it is a 3-stage rocket, used mostly to place satellites into low Earth and sun synchronous orbits...
- Long March 4CLong March 4CThe Long March 4C, also known as the Chang Zheng 4C, CZ-4C and LM-4C, previously designated Long March 4B-II, is a Chinese orbital carrier rocket. It is launched from the Jiuquan and Taiyuan Satellite Launch Centres, and consists of 3 stages...
- Long March 4A
- Long March 5 – under development
- CZ-NGLV-Light
- CZ-NGLV-Medium
- CZ-NGLV-A
- CZ-NGLV-B
- CZ-NGLV-C
- CZ-NGLV-D
- CZ-NGLV-E
- CZ-NGLV-F
- Long March 6Long March 6The Long March 6 or Chang Zheng 6 as in pinyin, abbreviated LM-6 for export or CZ-6 within China, is a Chinese liquid-fuelled carrier rocket, which is being developed by the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation and the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology, and is scheduled to...
– under development
- Long March 1
Europe
.jpg)
- Ariane
- Ariane 1Ariane 1Ariane 1 is the first version of the Ariane launcher family. Ariane 1 was designed primarily to put two telecommunications satellites at a time into orbit, thus reducing costs. As the size of the satellites grew Ariane 1 gave way to the more powerful Ariane 2 and Ariane 3 launchers.- Vehicle...
- Ariane 2Ariane 2 and Ariane 3Ariane 3 was a European expendable carrier rocket, which was used for eleven launches between 1984 and 1989. It was a member of the Ariane family of rockets, derived from the Ariane 2, although it flew before this...
- Ariane 3Ariane 2 and Ariane 3Ariane 3 was a European expendable carrier rocket, which was used for eleven launches between 1984 and 1989. It was a member of the Ariane family of rockets, derived from the Ariane 2, although it flew before this...
- Ariane 4Ariane 4Ariane 4 was an expendable launch system, designed by the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales and manufactured and marketed by its subsidiary Arianespace. Ariane 4 was justly known as the ‘workhorse’ of the Ariane family. Since its first flight on 15 June 1988 until the last, on 15 February 2003, it...
- Ariane 5Ariane 5Ariane 5 is, as a part of Ariane rocket family, an expendable launch system used to deliver payloads into geostationary transfer orbit or low Earth orbit . Ariane 5 rockets are manufactured under the authority of the European Space Agency and the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales...
- Ariane 1
- Europa (rocket)
- Vega (jointly with Italian Space AgencyItalian Space AgencyThe Italian Space Agency is a government agency established in 1988 to fund, regulate and coordinate space exploration activities in Italy...
) – under development - Ariane MAriane MAriane M is a hypothesized European expendable launch system designed to both place payloads in Low Earth Orbit and loft large payloads to lunar orbit.-History:The Ariane M was first hypothesized in 1991 as part of a CNES study...
– proposal only
India

- Satellite Launch VehicleSatellite Launch VehicleThe Indian Satellite Launch Vehicle or SLV was a project started in the early 1970s by Indian Space Research Organisation to develop the technology needed to launch satellites. The project was headed by Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam. SLV was intended to reach a height of 400 km and carry a payload of...
– Retired - Augmented Satellite Launch Vehicle – Retired
- Polar Satellite Launch VehiclePolar Satellite Launch VehicleThe Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle , commonly known by its abbreviation PSLV, is an expendable launch system developed and operated by the Indian Space Research Organisation . It was developed to allow India to launch its Indian Remote Sensing satellites into sun synchronous orbits, a service that...
- PSLVPolar Satellite Launch VehicleThe Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle , commonly known by its abbreviation PSLV, is an expendable launch system developed and operated by the Indian Space Research Organisation . It was developed to allow India to launch its Indian Remote Sensing satellites into sun synchronous orbits, a service that...
- PSLV-CAPolar Satellite Launch VehicleThe Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle , commonly known by its abbreviation PSLV, is an expendable launch system developed and operated by the Indian Space Research Organisation . It was developed to allow India to launch its Indian Remote Sensing satellites into sun synchronous orbits, a service that...
- PSLV-XLPolar Satellite Launch VehicleThe Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle , commonly known by its abbreviation PSLV, is an expendable launch system developed and operated by the Indian Space Research Organisation . It was developed to allow India to launch its Indian Remote Sensing satellites into sun synchronous orbits, a service that...
- PSLV-HPPolar Satellite Launch VehicleThe Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle , commonly known by its abbreviation PSLV, is an expendable launch system developed and operated by the Indian Space Research Organisation . It was developed to allow India to launch its Indian Remote Sensing satellites into sun synchronous orbits, a service that...
– Under development
- PSLV
- Geosynchronous Satellite Launch VehicleGeosynchronous Satellite Launch VehicleThe Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle is an expendable launch system operated by the Indian Space Research Organisation...
- GSLV Mk.I (a)Geosynchronous Satellite Launch VehicleThe Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle is an expendable launch system operated by the Indian Space Research Organisation...
- GSLV Mk.I (b)Geosynchronous Satellite Launch VehicleThe Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle is an expendable launch system operated by the Indian Space Research Organisation...
- GSLV Mk.IIGeosynchronous Satellite Launch VehicleThe Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle is an expendable launch system operated by the Indian Space Research Organisation...
- GSLV Mk.I (a)
- Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mk IIIGSLV IIIThe GSLV-III or Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle mark III is a launch vehicle currently under development by the Indian Space Research Organization...
– Under Development
Japan

- Lambda - Retired
- L-4SLambda 4SThe Lambda 4S or L-4S was an experimental Japanese expendable carrier rocket. It was produced by Nissan and the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science and launched five times between 1966 and 1970 with Ōsumi technology demonstration satellites...
- L-4S
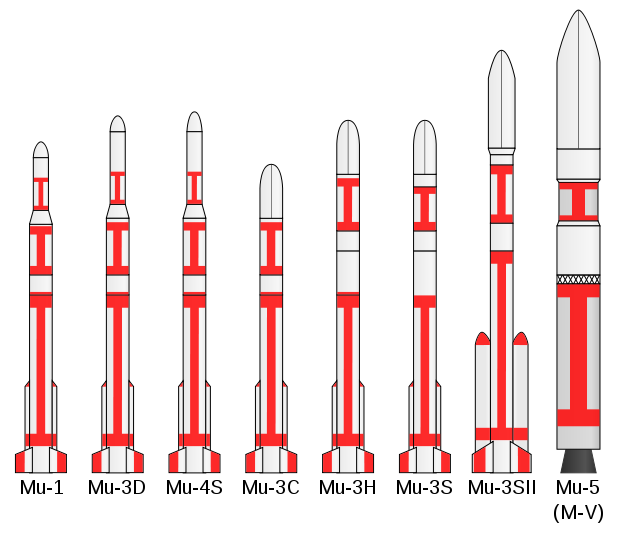
- MuMu (rocket)The Mu, also known as M, was a series of Japanese solid-fuelled carrier rockets, which were launched from Uchinoura between 1966 and 2006...
- Retired- M-4S
- M-3C
- M-3H
- M-3S
- M-3SII
- M-V
- N - Retired
- N-IN-I (rocket)The N-I or N-1 was a derivative of the American Delta rocket, produced under licence in Japan. It used a Thor-ELT first stage, a Mitsubishi Heavy Industries-designed LE-3 engine was used as a second stage, and three Castor SRMs. Seven were launched between 1975 and 1982, before it was replaced by...
- N-IIN-II (rocket)The N-II or N-2 was a derivative of the American Delta rocket, produced under licence in Japan. It used a Thor-ELT first stage, a Delta-F second stage, nine Castor SRMs, and on most flights either a Star-37E or Burner-2 upper stage, identical to the US Delta 0100 series configurations...
- N-I
- H-IH-IThe H-I or H-1 was a Japanese liquid-fuelled carrier rocket, consisting of a licence-produced American first stage and set of booster rockets, and all-Japanese upper stages. It was launched nine times between 1986 and 1992...
- Retired - H-II
- H-IIH-IIThe H-II rocket was a Japanese satellite launch system, which flew seven times between 1994 and 1999, with five successes. It was developed by NASDA in order to give Japan a capability to launch larger satellites in the 1990s. It was the first two-stage liquid-fuelled rocket Japan made using only...
- Retired - H-IIAH-IIAH-IIA is an active expendable launch system operated by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries for the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency . The liquid-fueled H-IIA rockets have been used to launch satellites into geostationary orbit, to launch a lunar orbiting spacecraft, and to launch an interplanetary...
- H-IIBH-IIBH-IIB is an expendable launch system used to launch H-II Transfer Vehicles towards the International Space Station. H-IIB rockets are liquid-fuelled with solid-fuel strap-on boosters and are launched from the Tanegashima Space Center in Japan...
- H-II
- J-IJ-IThe J-I was a Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency solid rocket expendable launch vehicle. It flew only once, in 1996, in a partial configuration, to launch the demonstrator Hyflex...
- Retired - GX – Cancelled
- Epsilon – under development (see M-V#Following program)
Russia
- Angara
- See also: Soviet Union
Soviet Union



- KosmosKosmos (rocket family)The Kosmos rockets are a series of Soviet and subsequently Russian rockets, derived from the R-12 and R-14 missiles, the most well known of which is the Kosmos-3M, which has made over 440 launches, and is still in service...
- Kosmos-1Kosmos-1The Kosmos-1 was a Soviet carrier rocket, derived from the R-14 missile, which was used to orbit satellites in 1964 and 1965. It served as an interim, and was quickly replaced by the Kosmos-3...
- Kosmos-2IKosmos-2IKosmos-2I is the designation applied to two Soviet carrier rockets, members of the R-12 family, which were used to orbit satellites between 1961 and 1977. They were superseded by the R-14 derived Kosmos-3 and Kosmos-3M.-References:* http://www.astronautix.com/lvs/koss63s1.htm*...
- Kosmos-3Kosmos-3The Kosmos-3 was a Soviet carrier rocket, derived from the R-14 missile, which was used to orbit satellites between 1966 and 1968. It was quickly replaced by the modernised Kosmos-3M. Six were flown, four as orbital carrier rockets, and two on sub-orbital flights...
- Kosmos-3M
- Kosmos-1
- EnergiaEnergiaEnergia was a Soviet rocket that was designed by NPO Energia to serve as a heavy-lift expendable launch system as well as a booster for the Buran spacecraft. Control system main developer enterprise was the NPO "Electropribor"...
- Zenit
- Zenit 2
- Zenit 3
- Zenit-3SL
- Zenit 3SLB
- Zenit
- N1
- R-7
- LunaLuna (rocket)The Luna 8K72 vehicles were carrier rockets used by the Soviet Union for nine space probe launch attempts in the Luna programme between 1958-09-23 and 1960-04-16...
- MolniyaMolniya (rocket)Molniya 8K78 was a modification of the well-known R-7 Semyorka rocket and had four stages.This derivative of the original three stage Vostok rocket was especially designed to bring high flying satellites into orbit or to launch probes to other planets. The first launch of this rocket was on...
- Molniya-MMolniya-MThe Molniya-M , designation 8K78M, was a Russian carrier rocket derived from the R-7 Semyorka ICBM. First launched in 1964, it had replaced its predecessor, Molniya, by the end of 1965...
- Molniya-M
- PolyotPolyot (rocket)The Polyot was an interim orbital carrier rocket, built to test ASAT spacecraft. It was required as a stopgap after the cancellation of the UR-200 programme, but before the Tsyklon could enter service. Only two were ever launched, the first on 1 November 1963, and the last on 12 April 1964...
- Soyuz family
- SoyuzSoyuz (rocket)The Soyuz was a Soviet expendable carrier rocket designed by OKB-1 and manufactured by State Aviation Plant No. 1 in Samara, Russia. It was used to launch Soyuz spacecraft as part of the Soyuz programme, initially on unmanned test flights, followed by the first 19 manned launches of the...
- Soyuz-LSoyuz-LThe Soyuz-L , GRAU index 11A511L was a Soviet expendable carrier rocket designed by OKB-1 and manufactured by State Aviation Plant No. 1 in Samara, Russia. It was used for tests of the LK Lunar lander in low Earth orbit, as part of the Soviet lunar programme.The Soyuz-L was essentially a two stage...
- Soyuz-MSoyuz-MThe Soyuz-M , GRAU index 11A511M was a Soviet expendable carrier rocket designed by OKB-1 and manufactured by State Aviation Plant No. 1 in Samara, Russia. It was originally built to launch manned Soyuz 7K-VI spacecraft for the Soviet armed forces. Following the cancellation of this programme,...
- Soyuz-L
- Soyuz-USoyuz-UThe Soyuz-U launch vehicle is an improved version of the original Soyuz LV. Soyuz-U is part of the R-7 family of rockets based on the R-7 Semyorka missile. Members of this rocket family were designed by the TsSKB design bureau and constructed at the Progress Factory in Samara, Russia....
- Soyuz-U2Soyuz-U2The Soyuz-U2 was a Soviet, later Russian, carrier rocket. It was derived from the Soyuz-U, and a member of the R-7 family of rockets...
- Soyuz-FGSoyuz-FGThe Soyuz-FG launch vehicle is an improved version of the Soyuz-U, from the R-7 family of rockets, designed and constructed by TsSKB-Progress in Samara...
- Soyuz-U2
- Soyuz-2
- Soyuz
- Sputnik
- Voskhod
- Vostok
- Luna
- Shtil'Shtil'Space launch vehicle Shtil Space launch vehicle Shtil Space launch vehicle Shtil (Russian: (Штиль - calm (weather)), is a converted SLBM used for launching artificial satellites into orbit. It is based on the R-29RM designed by State Rocket Center Makeyev and related to the Volna Launch Vehicle....
- Start-1START-1Start-1 is a Russian satellite launch vehicle based on the RT-2PM Topol, a Soviet intercontinental ballistic missile developed by Moscow Institute of Thermal Technology.- History :...
- Universal RocketUniversal RocketThe Universal Rocket or UR family of missiles and carrier rockets is a Russian, previously Soviet rocket family. Intended to allow the same technology to be used in all Soviet rockets, the UR is produced by the Khrunichev State Research and Production Space Centre. Several variants were originally...
- Proton
- RockotRockotThe Rokot , also transliterated as a the pun Rockot, is a Russian space launch vehicle that can launch a payload of 1,950 kilograms into a 200 kilometre high Earth orbit with 63° inclination. It is a derivative of the UR-100N intercontinental ballistic missile , supplied and operated by Eurockot...
- Strela
Ukraine
- R-36 derivatives
- Dnepr
- TsyklonTsyklonThe Tsyklon , GRAU index 11K67, was a Soviet/Ukrainian-designed expendable launch system, primarily used to put Cosmos satellites into low Earth orbit. It is based on the R-36 intercontinental ballistic missile designed by Mikhail Yangel and made eight launches, with seven successes, and one failure...
- Tsyklon-2Tsyklon-2The Tsyklon-2, also known as Tsiklon-2 and Tsyklon-M, GRAU index 11K69, was a Soviet, and subsequently Ukrainian orbital carrier rocket. A derivative of the R-36 ICBM, and a member of the Tsyklon family, it made its maiden flight on 6 August 1969, and after 106 launches, made its final flight on 24...
- Tsyklon-3Tsyklon-3The Tsyklon-3, also known as Tsiklon-3, GRAU index 11K68, was a Soviet, and subsequently Ukrainian orbital carrier rocket. A derivative of the R-36 ICBM, and a member of the Tsyklon family, it made its maiden flight on 24 June 1977, and was retired on 30 January 2009...
- Tsyklon-4Tsyklon-4The Tsyklon-4 or Cyclone-4, also known as Tsiklon-4, is a Ukrainian carrier rocket which is being developed for commercial satellite launches. Derived from the Tsyklon-3, it has a new third stage, a larger payload fairing, and a modernised flight control system compared to its predecessor...
– under development
- Tsyklon-2
- EnergiaEnergiaEnergia was a Soviet rocket that was designed by NPO Energia to serve as a heavy-lift expendable launch system as well as a booster for the Buran spacecraft. Control system main developer enterprise was the NPO "Electropribor"...
- Zenit
- Zenit 2
- Zenit 3
- Zenit-3SL
- Zenit 3SLB
- Zenit
- See also: Soviet Union
United States
bold denotes active OLS



- AresAres (rocket)In terms of rocketry, Ares could mean:*Three Shuttle-Derived Launch Vehicles under development for NASA's Project Constellation program:**The Ares I Crew Launch Vehicle , designed to launch the Orion ....
– under development/to be cancelled- Ares IAres IAres I was the crew launch vehicle that was being developed by NASA as part of the Constellation Program. The name "Ares" refers to the Greek deity Ares, who is identified with the Roman god Mars...
- Ares IV
- Ares VAres VThe Ares V was the planned cargo launch component of the Constellation program, which was to have replaced the Space Shuttle after its retirement in 2011. Ares V was also planned to carry supplies for a human presence on Mars...
- Ares I
- Athena
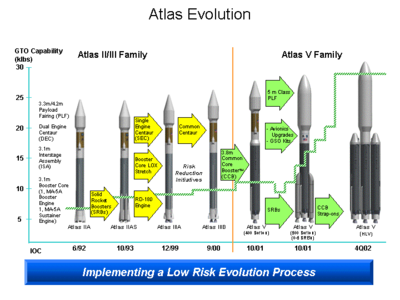
- AtlasAtlas (rocket family)Atlas is a family of U.S. space launch vehicles. The original Atlas missile was designed in the late 1950s and produced by the Convair Division of General Dynamics, to be used as an intercontinental ballistic missile...
- Atlas BSM-65B AtlasThe SM-65B Atlas, or Atlas B, also designated X-12 was a prototype of the Atlas missile. First flown on 19 July 1958, the Atlas B was the first version of the Atlas rocket to use the stage and a half design....
- retired - Atlas-AbleAtlas-AbleThe Atlas-Able was an American expendable launch system derived from the SM-65 Atlas missile. It was a member of the Atlas family of rockets, and was used to launch several Pioneer spacecraft towards the Moon...
- retired - Atlas-AgenaAtlas-AgenaThe Atlas-Agena was an American expendable launch system derived from the SM-65 Atlas missile. It was a member of the Atlas family of rockets, and was used for 119 orbital launches between 1960 and 1978....
- retired - Atlas E/FAtlas E/FThe Atlas E/F, also designated SB-1A was an American expendable launch system and sounding rocket built using parts of decommissioned SM-65 Atlas missiles...
- retired - Atlas HAtlas HThe Atlas H was an American expendable launch system derived from the SM-65 Atlas missile. It was a member of the Atlas family of rockets, and was used to launch five clusters of NOSS satellites for the US National Reconnaissance Office...
- retired - Atlas LV-3BAtlas LV-3BThe Atlas LV-3B, Atlas D Mercury Launch Vehicle or Mercury-Atlas Launch Vehicle, was a man-rated expendable launch system used as part of the United States Project Mercury to send astronauts into low Earth orbit. It was derived from the SM-65D Atlas missile, and was a member of the Atlas family of...
- retired - Atlas SLV-3Atlas SLV-3The Atlas SLV-3, or SLV-3 Atlas was an American expendable launch system derived from the SM-65 Atlas missile. It was a member of the Atlas family of rockets, and was used for three suborbital tests of X-23 Prime re-entry vehicles...
- retired - Atlas-CentaurAtlas-CentaurThe Atlas-Centaur was an American expendable launch system designed and built by General Dynamics Convair Division in San Diego, CA. It was derived from the SM-65 Atlas missile. It was a member of the Atlas family of rockets, and was used for 61 orbital launches between 1962 and 1983. It was...
- Atlas GAtlas GThe Atlas G, also known as Atlas G Centaur-D1AR was an American expendable launch system derived from the Atlas-Centaur. It was a member of the Atlas family of rockets, and was used to launch seven communication satellites during the mid to late 1980s...
- retired - Atlas IAtlas IThe Atlas I was an American expendable launch system, used in the 1990s to launch a variety of different satellites. The "I" in "Atlas I" can cause confusion, as all previous Atlas rockets were designated using letters, ending with the Atlas H, however subsequent rockets were designated using roman...
- retired - Atlas IIAtlas IIAtlas II was a member of the Atlas family of launch vehicles, which evolved from the successful Atlas missile program of the 1950s. Atlas II was the last Atlas to use a three engine, "stage-and-a-half" design: two of its three engines were jettisoned during ascent, but its fuel tanks and other...
- retired - Atlas IIIAtlas IIIThe Lockheed Martin Atlas III was an American orbital launch vehicle, used between 2000 and 2005. It was the first member of the Atlas family since the Atlas A to feature a "normal" staging method, compared to the previous Atlas family members, which were equipped with jettisonable engines on the...
- retired - Atlas VAtlas VAtlas V is an active expendable launch system in the Atlas rocket family. Atlas V was formerly operated by Lockheed Martin, and is now operated by the Lockheed Martin-Boeing joint venture United Launch Alliance...
- Atlas G
- Atlas B
- ConestogaConestoga (rocket)The Conestoga was a rocket consisting originally of surplus Minuteman missile stages with additional strap-on boosters, as required, for larger payloads. It was the world's first privately-funded commercial rocket, but was used only three times before the program was shut down due to a lack of...
- retired - Falcon
- Falcon 1Falcon 1The Falcon 1 is a partially reusable launch system designed and manufactured by SpaceX, a space transportation company in Hawthorne, California. The two-stage-to-orbit rocket uses LOX/RP-1 for both stages, the first powered by a single Merlin engine and the second powered by a single Kestrel engine...
- Falcon 9Falcon 9Falcon 9 is a rocket-powered spaceflight launch system designed and manufactured by SpaceX. Both stages of its two-stage-to-orbit vehicle use liquid oxygen and rocket-grade kerosene propellants...
- Falcon 1
- Juno IIJuno IIJuno II was an American space launch vehicle used during the late 1950s and early 1960s. It was derived from the Jupiter missile, which was used as the first stage.-Development:...
- retired - MinotaurMinotaur (rocket)The Minotaur is a family of American solid fuel rockets derived from converted Minuteman and Peacekeeper intercontinental ballistic missiles. They are built by Orbital Sciences Corporation....
- Minotaur IMinotaur IThe Minotaur I, or just Minotaur is an American expendable launch system derived from the Minuteman II missile. It is used to launch small satellites for the US Government, and is a member of the Minotaur family of rockets produced by Orbital Sciences Corporation.Minotaur I rockets consist of the...
- Minotaur IVMinotaur IVMinotaur IV, also known as Peacekeeper SLV and OSP-2 PK is an active expendable launch system derived from the Peacekeeper missile. It is operated by Orbital Sciences Corporation, and made its maiden flight on 22 April 2010, carrying the HTV-2a Hypersonic Test Vehicle...
- under development - Minotaur VMinotaur VThe Minotaur V is an American expendable launch system derived from the Minotaur IV, itself a derivative of the Peacekeeper missile. It is being developed by Orbital Sciences Corporation, and is scheduled to make its maiden flight in 2012 carrying the LADEE spacecraft for NASA.The Minotaur V is a...
- in concept
- Minotaur I
- Pegasus
- PilotNOTS-EV-1 PilotThe NOTS-EV-1 Pilot, also known as NOTSNIK was an expendable launch system and anti-satellite weapon developed by the United States Navy United States Naval Ordnance Test Station . Ten were launched during July and August 1958, all of which failed. It was the first air-launched rocket to be used...
- retired - RedstoneRedstone (rocket)The PGM-11 Redstone was the first large American ballistic missile. A short-range surface-to-surface rocket, it was in active service with the U.S. Army in West Germany from June 1958 to June 1964 as part of NATO's Cold War defense of Western Europe...
- Juno IJuno IThe Juno I was a four-stage American booster rocket which launched America's first satellite, Explorer 1, in 1958. A member of the Redstone rocket family, it was derived from the Jupiter-C sounding rocket...
- retired - SpartaSparta (rocket)The Sparta was a three-stage rocket that launched Australia's first Earth satellite, WRESAT, on 29 November 1967.Sparta used a surplus American Redstone as its first stage, an Antares as a second stage, and a BE-3 as a third stage...
- retired
- Juno I
- SaturnSaturn (rocket family)The Saturn family of American rocket boosters was developed by a team of mostly German rocket scientists led by Wernher von Braun to launch heavy payloads to Earth orbit and beyond. Originally proposed as a military satellite launcher, they were adopted as the launch vehicles for the Apollo moon...
- retired- Saturn ISaturn IThe Saturn I was the United States' first heavy-lift dedicated space launcher, a rocket designed specifically to launch large payloads into low Earth orbit. Most of the rocket's power came from a clustered lower stage consisting of tanks taken from older rocket designs and strapped together to make...
- Saturn IBSaturn IBThe Saturn IB was an American launch vehicle commissioned by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration for use in the Apollo program...
- Saturn IB
- Saturn VSaturn VThe Saturn V was an American human-rated expendable rocket used by NASA's Apollo and Skylab programs from 1967 until 1973. A multistage liquid-fueled launch vehicle, NASA launched 13 Saturn Vs from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida with no loss of crew or payload...
- Saturn INT-21Saturn INT-21The Saturn INT-21 was a study for an American orbital launch vehicle of the 1970s. It was derived from the Saturn V rocket used for the Apollo program, using its first and second stages, but lacking the third stage. The guidance unit would be moved from the top of the third stage to the top of the...
- Saturn INT-21
- Saturn I
- Scout - retired
- Space ShuttleSpace ShuttleThe Space Shuttle was a manned orbital rocket and spacecraft system operated by NASA on 135 missions from 1981 to 2011. The system combined rocket launch, orbital spacecraft, and re-entry spaceplane with modular add-ons...
- retired - Taurus
- Taurus IITaurus IITaurus II is an expendable launch system being developed by Orbital Sciences Corporation. It is a two stage vehicle designed to launch payloads weighing up to into low-Earth orbit...
– under development
- Taurus II
- Thor - retired
- Thor-AbleThor-AbleThe Thor-Able was an American expendable launch system and sounding rocket used for a series of re-entry vehicle tests and satellite launches between 1958 and 1960. It was a two stage rocket, consisting of a Thor IRBM as a first stage, and a Vanguard-derived Able second stage. On some flights, an...
- retired - Thor-AblestarThor-AblestarThe Thor-Ablestar, or Thor Able-Star, also known as Thor-Epsilon was an American expendable launch system consisting of a PGM-17 Thor missile, with an Ablestar upper stage...
- retired - Thor-AgenaThor-AgenaThor-Agena was a series of orbital launch vehicles. The rockets used Thor first stages and Agena second stages. They are thus cousins of the more famous Thor-Deltas, which founded the Delta rocket family. The first attempted launch of a Thor-Agena was in January 1959...
- retired- Thorad-AgenaThorad-AgenaThe Thorad-Agena was an American expendable launch system, derived from the Thor and Delta rockets. The first stage of the rocket was the stretched variant of the Thor which had been developed for the Delta programme. The second stage was the Agena-D, which had already been used in conjunction with...
- retired
- Thorad-Agena
- Thor-BurnerThor-BurnerThe Thor-Burner was an American expendable launch system, a member of the Thor family. It consisted of a Thor missile, with one or two Burner upper stages. It was used between 1965 and 1976, to orbit a number of satellites, most commonly DMSP weather satellites. Twenty-four were launched, of which...
- retired - Thor DSV-2UThor DSV-2UThe Thor DSV-2U or Thor LV-2F Star-37XE Star-37S-ISS was an American expendable launch system used to launch five DMSP weather satellites between 1976 and 1980. It was a member of the Thor family of rockets, and a derivative of the Thor DSV-2....
- retired - Delta - retired
- Thor-DeltaThor-DeltaThe Thor-Delta, also known as Delta DM-19 or just Delta was an early American expendable launch system used for 12 orbital launches in the early 1960s. A derivative of the Thor-Able, it was a member of the Thor family of rockets, and the first member of the Delta family.The first stage was a Thor...
- retired - Delta ADelta AThe Delta A, or Thor-Delta A was an American expendable launch system used to launch two Explorer spacecraft in October 1962. A derivative of the Thor-Delta, it was a member of the Delta family of rockets....
- retired - Delta BDelta BThe Delta B, or Thor-Delta B was an American expendable launch system used for nine orbital launches between 1962 and 1964. A derivative of the Thor-Delta, it was a member of the Delta family of rockets....
- retired - Delta CDelta CThe Delta C, or Thor-Delta C was an American expendable launch system used for thirteen orbital launches between 1963 and 1969. It was a member of the Delta family of rockets....
- retired - Delta DDelta DThe Delta D, Thrust Augmented Delta or Thor-Delta D was an American expendable launch system used to launch two communications satellites in 1964 and 1965. It was derived from the Delta C, and was a member of the Delta family of rockets....
- retired - Delta EDelta EThe Delta E, or Thor-Delta E was an American expendable launch system used for twenty-three orbital launches between 1965 and 1971. It was a member of the Delta family of rockets....
- retired - Delta GDelta GThe Delta G, or Thor-Delta G was an American expendable launch system used to launch two biological research satellites in 1966 and 1967. It was a member of the Delta family of rockets....
- retired - Delta JDelta JThe Delta J, or Thor-Delta J was an American expendable launch system of the late 1960s. Only one was launched, with the Explorer 38 spacecraft. It was a member of the Delta family of rockets....
- retired - Delta LDelta LThe Delta L, Thor-Delta L, or Thrust-Augmented Long Tank Thor-Delta was an American expendable launch system used to launch the Pioneer E and TETR satellites in 1969 and HEOS satellite in 1972. It was a member of the Delta family of rockets.The Delta L was a three stage rocket...
- retired - Delta MDelta MThe Delta M or Thor-Delta M was an American expendable launch system used for thirteen orbital launches between 1968 and 1971. It was a member of the Delta family of rockets....
- retired - Delta NDelta NThe Delta N or Thor-Delta N was an American expendable launch system used for nine orbital launches between 1968 and 1972. It was a member of the Delta family of rockets, and the last Delta to be given an alphabetical designation - subsequent rockets were designated using a four digit numerical...
- retired - Delta 0100Delta 0100The Delta 0100 series, also Delta 100, 0300 or 300 series, was an American expendable launch system which conducted orbital launches between 1968 and 1972. It was a member of the Delta family of rockets, and the first to be designated using a four digit numerical code...
- retired - Delta 1000Delta 1000The Delta 1000 series was an American expendable launch system which was used to conduct eight orbital launches between 1972 and 1975. It was a member of the Delta family of rockets. Several variants existed, differentiated by a four digit numerical code....
- retired - Delta 2000Delta 2000The Delta 2000 series was an American expendable launch system which was used to conduct forty-four orbital launches between 1974 and 1981. It was a member of the Delta family of rockets. Several variants existed, which were differentiated by a four digit numerical code.The first stage was an...
- retired - Delta 3000Delta 3000The Delta 3000 series was an American expendable launch system which was used to conduct thirty five orbital launches between 1975 and 1989. It was a member of the Delta family of rockets. Several variants existed, which were differentiated by a four digit numerical code.The first stage was the...
- retired - Delta 4000Delta 4000The Delta 4000 series was an American expendable launch system which was used to conduct two orbital launches in 1989 and 1990. It was a member of the Delta family of rockets. Although several variants were put forward, only the Delta 4925 was launched. The designations used a four digit numerical...
- retired - Delta 5000Delta 5000The Delta 5000 series was an American expendable launch system which was used to conduct an orbital launch in 1989. It was a member of the Delta family of rockets. Although several variants were put forward, only the Delta 5920 was launched. The designation used a four digit numerical code to store...
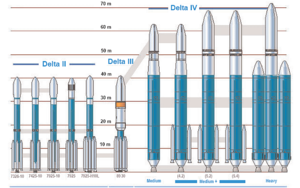
- retired - Delta IIDelta IIDelta II was an American space launch system, originally designed and built by McDonnell Douglas. Delta II is part of the Delta rocket family and was in service from 1989 until November 1, 2011...
- Delta II 6000 - retired
- Delta II 7000
- Delta III - retired
- Delta IV
- Thor-Delta
- Thor-Able
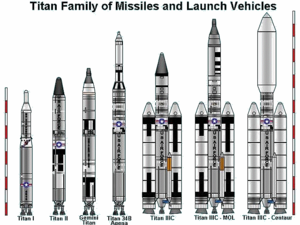
- TitanTitan (rocket family)Titan was a family of U.S. expendable rockets used between 1959 and 2005. A total of 368 rockets of this family were launched, including all the Project Gemini manned flights of the mid-1960s...
- retired- Titan II GLVTitan II GLVThe Titan II GLV or Gemini-Titan was an American expendable launch system derived from the Titan II missile, which was used to launch twelve Gemini missions for NASA between 1964 and 1966...
- Titan 23GTitan 23GThe Titan 23G, Titan IIG, Titan 2G or Titan II SLV was an American expendable launch system derived from the LGM-25C Titan II intercontinental ballistic missile. Retired Titan II missiles were converted by Martin Marietta, into which the Glenn L. Martin Company, which built the original Titan II,...
- Titan IIIB
- Titan IIITitan IIIThe Titan IIIC was a space booster used by the United States Air Force. It was launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, FL., and Vandenberg Air Force Base, CA. It was planned to be used as a launch vehicle in the cancelled Dyna-Soar and Manned Orbiting Laboratory programs...
- Titan 34DTitan 34DThe Titan 34D was an American rocket, used to launch a number of satellites for mostly military applications. After its retirement from military service, a small number were converted to the Commercial Titan III configuration, which included a stretched second stage, and a larger fairing...
- Commercial Titan IIICommercial Titan IIIThe Commercial Titan III, also known as CT-3 or CT-III was an American expendable launch system, developed by Martin Marietta during the late 1980s and flown four times during the early 1990s. It was derived from the Titan 34D, and was originally proposed as a medium-lift expendable launch system...
- Titan IVTitan IVThe Titan IV family of space boosters were used by the U.S. Air Force. They were launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida, and Vandenberg Air Force Base, California. At the time of its introduction, the Titan IV was the "largest unmanned space booster used by the Air Force."The...
- Titan II GLV
- Vanguard - retired

