H-IIA
Encyclopedia

Expendable launch system
An expendable launch system is a launch system that uses an expendable launch vehicle to carry a payload into space. The vehicles used in expendable launch systems are designed to be used only once , and their components are not recovered for re-use after launch...
operated by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
, or MHI, is a Japanese company. It is one of the core companies of Mitsubishi Group.-History:In 1870 Yataro Iwasaki, the founder of Mitsubishi took a lease of Government-owned Nagasaki Shipyard. He named it Nagasaki Shipyard & Machinery Works, and started the shipbuilding business on a full scale...
(MHI) for the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency
Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency
The , or JAXA, is Japan's national aerospace agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on October 1, 2003, as an Independent Administrative Institution administered by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology and the...
(JAXA). The liquid-fueled H-IIA rocket
Rocket
A rocket is a missile, spacecraft, aircraft or other vehicle which obtains thrust from a rocket engine. In all rockets, the exhaust is formed entirely from propellants carried within the rocket before use. Rocket engines work by action and reaction...
s have been used to launch satellite
Satellite
In the context of spaceflight, a satellite is an object which has been placed into orbit by human endeavour. Such objects are sometimes called artificial satellites to distinguish them from natural satellites such as the Moon....
s into geostationary orbit
Geostationary orbit
A geostationary orbit is a geosynchronous orbit directly above the Earth's equator , with a period equal to the Earth's rotational period and an orbital eccentricity of approximately zero. An object in a geostationary orbit appears motionless, at a fixed position in the sky, to ground observers...
, to launch a lunar orbiting spacecraft, and to launch an interplanetary space probe
Space probe
A robotic spacecraft is a spacecraft with no humans on board, that is usually under telerobotic control. A robotic spacecraft designed to make scientific research measurements is often called a space probe. Many space missions are more suited to telerobotic rather than crewed operation, due to...
to Venus. Launches occur at the Tanegashima Space Center
Tanegashima Space Center
The is one of Japan's space development facilities. It is located on Tanegashima, an island located 115 km south of Kyūshū. It was established in 1969 when the National Space Development Agency of Japan was formed...
. Production and management of the H-IIA shifted from JAXA to MHI on April 1, 2007. Flight 13, which launched the lunar orbiter SELENE
SELENE
SELENE , better known in Japan by its nickname after the legendary Japanese moon princess, was the second Japanese lunar orbiter spacecraft. Produced by the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science and the National Space Development Agency , both now part of the Japan Aerospace Exploration...
, was the first H-IIA launched after this privatization.
The H-IIA is a derivative of the earlier H-II
H-II
The H-II rocket was a Japanese satellite launch system, which flew seven times between 1994 and 1999, with five successes. It was developed by NASDA in order to give Japan a capability to launch larger satellites in the 1990s. It was the first two-stage liquid-fuelled rocket Japan made using only...
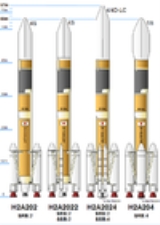
rocket, substantially redesigned to improve reliability and minimize costs. There are four different variants of the H-IIA for various purposes.
Vehicle description
The launch capability of an H-IIA launch vehicle can be enhanced by adding SRB-A (solid rocket boosterSolid rocket booster
Solid rocket boosters or Solid Rocket Motors, SRM, are used to provide thrust in spacecraft launches from the launchpad up to burnout of the SRBs. Many launch vehicles include SRBs, including the Ariane 5, Atlas V , and the NASA Space Shuttle...
or SRB) and Castor 4AXL
Castor (rocket stage)
The Castor family of solid-fuel rocket stages and boosters were built by Thiokol and used on a variety of launch vehicles. They were initially developed as the second stage motor of the Scout rocket...
(solid strap-on booster or SSB) to its basic configuration, creating a "family". The models are indicated by three or four numbers following the prefix "H2A". The first number in the sequence indicates the number of stages; the second the number of LRBs (Liquid rocket boosters); the third the number of SRBs; and, if present, the fourth number shows the number of SSBs. The first two figures are virtually fixed at "20", as H-IIA is always two-staged, and the plans for LRBs were cancelled and superseded by the H-IIB
H-IIB
H-IIB is an expendable launch system used to launch H-II Transfer Vehicles towards the International Space Station. H-IIB rockets are liquid-fuelled with solid-fuel strap-on boosters and are launched from the Tanegashima Space Center in Japan...
.
Variants
there are four different configurations shown in the following table.{| class="wikitable"
Geostationary transfer orbit
A geosynchronous transfer orbit or geostationary transfer orbit is a Hohmann transfer orbit used to reach geosynchronous or geostationary orbit....
)
Castor (rocket stage)
The Castor family of solid-fuel rocket stages and boosters were built by Thiokol and used on a variety of launch vehicles. They were initially developed as the second stage motor of the Scout rocket...
(SSB)
Launch history
The H-IIA was first launched on August 29, 2001, and the sixth launch on November 29, 2003 failed. The rocket was intended to launch two reconnaissance satellites to observe North Korea. JAXA announced that launches would resume in 2005, and indeed the first successful flight took place on February 26 with the launch of MTSAT-1RMulti-Functional Transport Satellite
Multifunctional Transport Satellites are a series of weather and aviation control satellites. They are geostationary satellites owned and operated by the Japanese Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport and the Japan Meteorological Agency , and provide coverage for the hemisphere centred on...
.
The first launch for a mission beyond Earth orbit was on September 14, 2007 for the SELENE
SELENE
SELENE , better known in Japan by its nickname after the legendary Japanese moon princess, was the second Japanese lunar orbiter spacecraft. Produced by the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science and the National Space Development Agency , both now part of the Japan Aerospace Exploration...
moon mission. The first foreign payload on the H-IIA was the Australian FedSat-1 in 2002. As of January 2011, 17 out of 18 launches were successful.
A rocket with increased launch capabilities, H-IIB
H-IIB
H-IIB is an expendable launch system used to launch H-II Transfer Vehicles towards the International Space Station. H-IIB rockets are liquid-fuelled with solid-fuel strap-on boosters and are launched from the Tanegashima Space Center in Japan...
, is a derivative of the H-IIA family. H-IIB uses two LE-7A engines in its first stage, as opposed to one in H-IIA. The first H-IIB was successfully launched on September 10, 2009.
{| class="wikitable"
!Date (UTC)!! Flight !! Type !! Payload !! Result
|-
|August 29, 2001
07:00:00 || TF1 ||H2A202||
 VEP 2
VEP 2 LRE || Success
LRE || Success|-
|February 4, 2002
02:45:00 || TF2 ||H2A2024 ||
 VEP 3
VEP 3 MDS-1
MDS-1MDS-1
Mission Demonstration Satellite 1 "Tsubasa" was a Japanese technology test mission. Its aim was to test commercial off the shelf components in space, especially in the radiation belt. The whole weight of the satellite was 475 kg....
(Tsubasa)
 DASH || Success
DASH || Success|-
|September 10, 2002
08:20:00 || F3 ||H2A2024||
 USERS
USERS DRTS (Kodama) || Success
DRTS (Kodama) || Success|-
|December 14, 2002
01:31:00 || F4 ||H2A202||
 ADEOS 2 (Midori 2)
ADEOS 2 (Midori 2) WEOS (Kanta-kun)
WEOS (Kanta-kun) FedSat
FedSatFedSat
FedSat is an Australian scientific research satellite launched from Tanegashima Space Center, Japan by a NASDA H-IIA launch vehicle in December 2002...
1
 Micro LabSat 1 || Success
Micro LabSat 1 || Success|-
|March 28, 2003
01:27:00 || F5 ||H2A2024||
 IGS
IGSInformation Gathering Satellite
An Information Gathering Satellite is a satellite in a Japanese spy satellite program. It was started as a response to the 1998 North Korean missile test over Japan. The satellite program's main mission is to provide early warning of impending hostile launches in the neighborhood...
-Optical 1
 IGS-Radar 1 || Success
IGS-Radar 1 || Success|-
|November 29, 2003
04:33:00 || F6 || H2A2024 ||
 IGS
IGSInformation Gathering Satellite
An Information Gathering Satellite is a satellite in a Japanese spy satellite program. It was started as a response to the 1998 North Korean missile test over Japan. The satellite program's main mission is to provide early warning of impending hostile launches in the neighborhood...
-Optical 2
 IGS-Radar 2 || Failure
IGS-Radar 2 || Failure|-
|February 26, 2005
09:25:00 || F7 ||H2A2022 ||
 MTSAT-1R
MTSAT-1RMulti-Functional Transport Satellite
Multifunctional Transport Satellites are a series of weather and aviation control satellites. They are geostationary satellites owned and operated by the Japanese Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport and the Japan Meteorological Agency , and provide coverage for the hemisphere centred on...
(Himawari 6) || Success
|-
|January 24, 2006
01:33:00 || F8 ||H2A2022||
 ALOS
ALOSAlos
Alos can be:*Alos, Greece, an ancient city in Greece*Alos, Ariège, a commune of France*Alos, Tarn, a commune of France*ALOS , an initialism used in managed health care, meaning "average length of stay"...
(Daichi) || Success
|-
|February 18, 2006
06:27:00 || F9 ||H2A2024||
 MTSAT-2
MTSAT-2Multi-Functional Transport Satellite
Multifunctional Transport Satellites are a series of weather and aviation control satellites. They are geostationary satellites owned and operated by the Japanese Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport and the Japan Meteorological Agency , and provide coverage for the hemisphere centred on...
(Himawari 7) || Success
|-
|September 11, 2006
04:35:00 || F10 || H2A202||
 IGS
IGSInformation Gathering Satellite
An Information Gathering Satellite is a satellite in a Japanese spy satellite program. It was started as a response to the 1998 North Korean missile test over Japan. The satellite program's main mission is to provide early warning of impending hostile launches in the neighborhood...
-Optical 2 || Success
|-
|December 18, 2006
06:32:00 || F11 ||H2A204||
 ETS-VIII
ETS-VIIIETS-VIII
JAXA Engineering Test Satellite ETS-VIII is the eighth technology test satellite in a series which started with ETS-1 in 1975 by NASDA. It was launched with the H-2A on December 18, 2006....
(Kiku 8) || Success
|-
|February 24, 2007
04:41:00 || F12 ||H2A2024||
 IGS
IGSInformation Gathering Satellite
An Information Gathering Satellite is a satellite in a Japanese spy satellite program. It was started as a response to the 1998 North Korean missile test over Japan. The satellite program's main mission is to provide early warning of impending hostile launches in the neighborhood...
-Radar 2
 IGS
IGSInformation Gathering Satellite
An Information Gathering Satellite is a satellite in a Japanese spy satellite program. It was started as a response to the 1998 North Korean missile test over Japan. The satellite program's main mission is to provide early warning of impending hostile launches in the neighborhood...
-Experimentally Optical 3 || Success
|-
|September 14, 2007
01:31:01 || F13 ||H2A2022||
 SELENE
SELENESELENE
SELENE , better known in Japan by its nickname after the legendary Japanese moon princess, was the second Japanese lunar orbiter spacecraft. Produced by the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science and the National Space Development Agency , both now part of the Japan Aerospace Exploration...
(Kaguya) || Success
|-
|February 23, 2008
08:55:00 || F14 ||H2A2024 ||
 WINDS
WINDSWINDS
WINDS , is a Japanese communication satellite. Launch was originally scheduled for 2007. The launch date was eventually set for 15 February 2008, however a problem detected in a second stage manoeuvring thruster delayed it to 23 February...
(Kizuna) || Success
|-
|January 23, 2009
12:54:00 || F15 || H2A202||
 GOSAT (Ibuki)
GOSAT (Ibuki)  SDS-1
SDS-1SDS-1
The Small Demonstration Satellite , nicknamed the "Sun Devil Satellite", is a spacecraft or satellite which is built as part of a JAXA programme to develop and demonstrate technology for and through small satellites. One of the mid-term goals is also to demonstrate formation flying. SDS-1...
 STARS (Kūkai)
STARS (Kūkai)  KKS-1 (Kiseki)
KKS-1 (Kiseki)  PRISM (Hitomi)
PRISM (Hitomi)  Sohla
SohlaSohla
Sohla-1 and Sohla-2 are two 50 kg small demonstration satellites in development by Japan. The project was initiated by the SOHLA organisation in 2003. The aim of this group is to revitalize local economy by developing space technologies...
-1 (Maido 1)
 SORUNSAT-1 (Kagayaki)
SORUNSAT-1 (Kagayaki)  SPRITE-SAT (Raijin) || Success
SPRITE-SAT (Raijin) || Success|-
|November 28, 2009
01:21:00 || F16 ||H2A202||
 IGS
IGSInformation Gathering Satellite
An Information Gathering Satellite is a satellite in a Japanese spy satellite program. It was started as a response to the 1998 North Korean missile test over Japan. The satellite program's main mission is to provide early warning of impending hostile launches in the neighborhood...
-Optical 3
|| Success
|-
|May 20, 2010
21:58:22 || F17 || H2A202 ||
 PLANET-C
PLANET-CPLANET-C
, formerly known as the Venus Climate Orbiter and Planet-C, is a Japanese unmanned spacecraft which was intended to explore Venus. It was launched aboard an H-IIA 202 rocket on 20 May 2010, after being delayed because of weather from its initial 18 May scheduled target...
(Akatsuki)
 IKAROS
IKAROSIKAROS
IKAROS is a Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency experimental spacecraft. The spacecraft was launched on 21 May, 2010, aboard an H-IIA rocket, together with the Akatsuki probe and four other small spacecraft...
 UNITEC-1 (Shin'en)
UNITEC-1 (Shin'en)  Waseda-SAT2
Waseda-SAT2Waseda-SAT2
Waseda-SAT2 is a Japanese satellite which launched in May 2010. It is a student-built spacecraft, which will be operated by Waseda University, and is intended to be used for Earth observation and technology demonstration. It will test the use of extendible paddles to provide attitude control...
 K-Sat (Hayato)
K-Sat (Hayato)  Negai☆
Negai☆Negai (satellite)
is a Japanese satellite which launched in May 2010. It is a student-built spacecraft, which will be operated by Soka University, and is intended to be used for technology demonstration. The satellite is a single unit CubeSat, and will be used to test a field programmable gate array in orbit...
|| Success
|-
|September 11, 2010
11:17:00 || F18 || H2A202 ||
 QZS-1 (Michibiki) || Success
QZS-1 (Michibiki) || Success|-
|September 23, 2011
04:36:50 || F19 || H2A202 ||
 IGS
IGSInformation Gathering Satellite
An Information Gathering Satellite is a satellite in a Japanese spy satellite program. It was started as a response to the 1998 North Korean missile test over Japan. The satellite program's main mission is to provide early warning of impending hostile launches in the neighborhood...
-Optical 4 || Success
|-
|colspan="8" |Planned launches
|-
|December 11, 2011 || F20 || H2A202 ||
 IGS
IGSInformation Gathering Satellite
An Information Gathering Satellite is a satellite in a Japanese spy satellite program. It was started as a response to the 1998 North Korean missile test over Japan. The satellite program's main mission is to provide early warning of impending hostile launches in the neighborhood...
-Radar 3 ||
|-
|FY2011
|| F21 || ||
 GCOM-W1
GCOM-W1GCOM-W
GCOM is a series of JAXA Earth Observation Missions as a successor to the ill-fated ADEOS 2 satellite and to the Aqua Mission. GCOM is, together with the GPM Mission, Japan's contribution to the GEOSS ....
 KOMPSAT-3 ||
KOMPSAT-3 |||}

