
List of early East Slavic states
Encyclopedia
The following is a list of tribes who lived on the territories of contemporary Belarus
, Russia
, and Ukraine
. The tribes were later replaced or consolidated by Slavs, starting with the formation of Kievan Rus'
, including the semi-autonomous principalities of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
, that existed in the first half of the second millennium. The area was later expanded to become the Tsardom of Russia
, followed by the Russian Empire
, which became part of the Soviet Union
.
Clan
cultures of the Stone Age
and Bronze Age
, up to the Late Antiquity
period of the tribal societies that were replaced or incorporated into the Early Slavs
.
, Slavic peoples
and Balto-Slavic languages
The Slavs were a diverse group of tribal societies
in the Iron Age
and Migration Age
Europe whose tribal organizations created the foundations for today's Slavic nations
.
, Slavic peoples
, East Slavs
, West Slavs
, South Slavs
.png)
 After the battle of Kulikovo
After the battle of Kulikovo
Belarus
Belarus , officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe, bordered clockwise by Russia to the northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Its capital is Minsk; other major cities include Brest, Grodno , Gomel ,...
, Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
, and Ukraine
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia...
. The tribes were later replaced or consolidated by Slavs, starting with the formation of Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rus was a medieval polity in Eastern Europe, from the late 9th to the mid 13th century, when it disintegrated under the pressure of the Mongol invasion of 1237–1240....
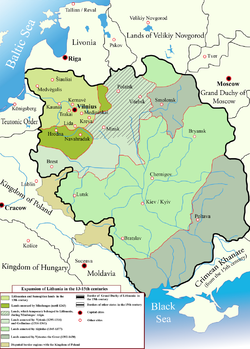
, including the semi-autonomous principalities of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state from the 12th /13th century until 1569 and then as a constituent part of Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth until 1791 when Constitution of May 3, 1791 abolished it in favor of unitary state. It was founded by the Lithuanians, one of the polytheistic...
, that existed in the first half of the second millennium. The area was later expanded to become the Tsardom of Russia
Tsardom of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year...
, followed by the Russian Empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
, which became part of the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
.
Proto-Slavic people
See Proto-Slavic languageProto-Slavic language
Proto-Slavic is the proto-language from which Slavic languages later emerged. It was spoken before the seventh century AD. As with most other proto-languages, no attested writings have been found; the language has been reconstructed by applying the comparative method to all the attested Slavic...
Clan
Clan
A clan is a group of people united by actual or perceived kinship and descent. Even if lineage details are unknown, clan members may be organized around a founding member or apical ancestor. The kinship-based bonds may be symbolical, whereby the clan shares a "stipulated" common ancestor that is a...
cultures of the Stone Age
Stone Age
The Stone Age is a broad prehistoric period, lasting about 2.5 million years , during which humans and their predecessor species in the genus Homo, as well as the earlier partly contemporary genera Australopithecus and Paranthropus, widely used exclusively stone as their hard material in the...
and Bronze Age
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a period characterized by the use of copper and its alloy bronze as the chief hard materials in the manufacture of some implements and weapons. Chronologically, it stands between the Stone Age and Iron Age...
, up to the Late Antiquity
Late Antiquity
Late Antiquity is a periodization used by historians to describe the time of transition from Classical Antiquity to the Middle Ages, in both mainland Europe and the Mediterranean world. Precise boundaries for the period are a matter of debate, but noted historian of the period Peter Brown proposed...
period of the tribal societies that were replaced or incorporated into the Early Slavs
Early Slavs
The early Slavs were a diverse group of tribal societies in Migration period and early medieval Europe whose tribal organizations indirectly created the foundations for today’s Slavic nations .The first mention of the name Slavs dates to the 6th century, by which time the Slavic tribes inhabited a...
.
- AlansAlansThe Alans, or the Alani, occasionally termed Alauni or Halani, were a group of Sarmatian tribes, nomadic pastoralists of the 1st millennium AD who spoke an Eastern Iranian language which derived from Scytho-Sarmatian and which in turn evolved into modern Ossetian.-Name:The various forms of Alan —...
- Bükk cultureBükk CultureBükk culture may have belonged to a dense pocket of Cro-magnon type people inhabiting the Bükk mountains of Hungary and the upper Tisza and its tributaries. The surrounding Neolithic was mainly of a more gracile Mediterranean type, with a Cro-magnon admixture as another possibility...
- Bug-Dniester cultureBug-Dniester cultureBug-Dniester culture, Dniester-Bug culture was the archaeological culture that developed in the chernozem region of Moldavia and Ukraine around the Dniester and Southern Bug rivers in the Neolithic....
- Catacomb cultureCatacomb cultureThe Catacomb culture, ca. 2800-2200 BC, refers to an early Bronze Age culture occupying essentially what is present-day Ukraine. It is seen more as a term covering several smaller related archaeological cultures....
- Cernavodă cultureCernavoda cultureCernavodă culture, ca. 4000—3200 BC, a late copper age archaeological culture of the lower Eastern Bug River and Danube located along the coast of the Black Sea and somewhat inland...
- CimmeriansCimmeriansThe Cimmerians or Kimmerians were ancient equestrian nomads of Indo-European origin.According to the Greek historian Herodotus, of the 5th century BC, the Cimmerians inhabited the region north of the Caucasus and the Black Sea during the 8th and 7th centuries BC, in what is now Ukraine and Russia...
- Cucuteni-Trypillian culture
- Corded Ware cultureCorded Ware cultureThe Corded Ware culture , alternatively characterized as the Battle Axe culture or Single Grave culture, is an enormous European archaeological horizon that begins in the late Neolithic , flourishes through the Copper Age and culminates in the early Bronze Age.Corded Ware culture is associated with...
- Dnieper-Donets cultureDnieper-Donets cultureDnieper-Donets culture, ca. 5th—4th millennium BC. A neolithic culture in the area north of the Black Sea/Sea of Azov between the Dnieper and Donets River.There are parallels with the contemporaneous Samara culture...
- Globular Amphora cultureGlobular Amphora cultureThe Globular Amphora Culture , German Kugelamphoren-Kultur , ca. 3400-2800 BC, is an archaeological culture preceding the central area occupied by the Corded Ware culture. Somewhat to the south and west, it was bordered by the Baden culture. To the northeast was the Narva culture. It occupied much...
- GothsGothsThe Goths were an East Germanic tribe of Scandinavian origin whose two branches, the Visigoths and the Ostrogoths, played an important role in the fall of the Roman Empire and the emergence of Medieval Europe....
- HunsHunsThe Huns were a group of nomadic people who, appearing from east of the Volga River, migrated into Europe c. AD 370 and established the vast Hunnic Empire there. Since de Guignes linked them with the Xiongnu, who had been northern neighbours of China 300 years prior to the emergence of the Huns,...
- Khvalynsk cultureKhvalynsk cultureThe Khvalynsk culture was an Eneolithic culture of the first half of the 5th millennium BC, discovered at Khvalynsk on the Volga in Saratov Oblast, Russia. The culture also is termed the Middle Eneolithic or Developed Eneolithic or Proto-kurgan...
- Korchak cultureKorchak cultureKorchak culture is an archaeological culture of the sixth and seventh century East Slavs who settled along the southern tributaries of the Pripyat River and from the Dnieper River to the Southern Bug and Dniester rivers, throughout modern day northwestern Ukraine and southern Belarus...
- Lipiţa cultureLipiţa cultureLipiţa culture is the archaeological material culture representative of a Dacian tribe. It took its name from the Ukrainian village of Verkhnya Lypytsya Lipiţa culture (Romanian Lipiţa, Polish Lipica other spellings: Lipitsa, Lipitza) is the archaeological material culture representative of a...
- Lusatian cultureLusatian cultureThe Lusatian culture existed in the later Bronze Age and early Iron Age in most of today's Poland, parts of Czech Republic and Slovakia, parts of eastern Germany and parts of Ukraine...
- Mariupol cultureMariupol cultureThe Mariupol culture known as The Mariupol-type cemeteries was a transitional culture from Neolithic to Eneolithic of the second half of 5th millennium BCE at the Sea of Azov and neighbouring regions along rivers Dnieper, Don, Orel', Chir; Crimean peninsula, reaching as far as North Caucasus and...
- Middle Dnieper cultureMiddle Dnieper cultureThe Middle Dnieper culture is an eastern extension of the Corded Ware culture, ca. 3200—2300 BC of northern Ukraine and Belarus. As the name indicates, it was centered on the middle reach of the Dnieper River and is contemporaneous with the latter phase and then a successor to the...
- Pomeranian culturePomeranian cultureThe Pomeranian culture, also Pomeranian or Pomerelian Face Urn culture was an Iron Age culture in Pomerania, northern Poland. About 650 BC, it evolved from the Lusatian culture, often associated with the Nordic Bronze Age, and subsequently expanded southward...
- Przeworsk culturePrzeworsk cultureThe Przeworsk culture is part of an Iron Age archaeological complex that dates from the 2nd century BC to the 5th century AD. It was located in what is now central and southern Poland, later spreading to parts of eastern Slovakia and Carpathian Ruthenia ranging between the Oder and the middle and...
- Samara cultureSamara cultureThe Samara culture was an eneolithic culture of the early 5th millennium BC at the Samara bend region of the middle Volga, discovered during archaeological excavations in 1973 near the village of Syezzheye in Russia...
- SarmatiansSarmatiansThe Iron Age Sarmatians were an Iranian people in Classical Antiquity, flourishing from about the 5th century BC to the 4th century AD....
- Scythians
- Srubna cultureSrubna cultureThe Srubna culture , was a Late Bronze Age culture. It is a successor to the Yamna culture, the Pit Grave culture and the Poltavka culture....
- Sredny Stog cultureSredny Stog cultureThe Sredny Stog culture dates from the 4500-3500 BC. It was situated just north of the Sea of Azov between the Dnieper and the Don...
- Trzciniec cultureTrzciniec cultureThe Trzciniec culture was an ancient tradition that subsisted in central Europe. Archeologists speculate its existence to have been between the years 1700 and 1200 BC....
- Usatovo cultureUsatovo cultureUsatovo culture, 3500—3000 BC, an archaeological culture facing the Black sea between the mouths of the Bug River and the Danube in present-day Romania, Moldavia, and southern Ukraine....
- Venethi
- Yamna cultureYamna cultureThe Yamna culture is a late copper age/early Bronze Age culture of the Southern Bug/Dniester/Ural region , dating to the 36th–23rd centuries BC...
Antiquity
See Early SlavsEarly Slavs
The early Slavs were a diverse group of tribal societies in Migration period and early medieval Europe whose tribal organizations indirectly created the foundations for today’s Slavic nations .The first mention of the name Slavs dates to the 6th century, by which time the Slavic tribes inhabited a...
, Slavic peoples
Slavic peoples
The Slavic people are an Indo-European panethnicity living in Eastern Europe, Southeast Europe, North Asia and Central Asia. The term Slavic represents a broad ethno-linguistic group of people, who speak languages belonging to the Slavic language family and share, to varying degrees, certain...
and Balto-Slavic languages
Balto-Slavic languages
The Balto-Slavic language group traditionally comprises Baltic and Slavic languages, belonging to the Indo-European family of languages. Baltic and Slavic languages share several linguistic traits not found in any other Indo-European branch, which points to the period of common development...
The Slavs were a diverse group of tribal societies
Tribe
A tribe, viewed historically or developmentally, consists of a social group existing before the development of, or outside of, states.Many anthropologists use the term tribal society to refer to societies organized largely on the basis of kinship, especially corporate descent groups .Some theorists...
in the Iron Age
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the archaeological period generally occurring after the Bronze Age, marked by the prevalent use of iron. The early period of the age is characterized by the widespread use of iron or steel. The adoption of such material coincided with other changes in society, including differing...
and Migration Age
Migration Period
The Migration Period, also called the Barbarian Invasions , was a period of intensified human migration in Europe that occurred from c. 400 to 800 CE. This period marked the transition from Late Antiquity to the Early Middle Ages...
Europe whose tribal organizations created the foundations for today's Slavic nations
Slavic peoples
The Slavic people are an Indo-European panethnicity living in Eastern Europe, Southeast Europe, North Asia and Central Asia. The term Slavic represents a broad ethno-linguistic group of people, who speak languages belonging to the Slavic language family and share, to varying degrees, certain...
.
- Antes people
- Carantanians
- Chernoles cultureChernoles cultureThe Chernoles culture is an Iron Age archaeological unit dating ca. 1025–700 BC. It was located in the forest-steppe between the Dniester and Dnieper Rivers, in what is now northern Ukraine. This location corresponds to where Herodotus later placed his Scythian ploughmen...
- Chernyakhov cultureChernyakhov cultureThe Sântana de Mureș–Chernyakhiv culture is the name given to an archaeological culture which flourished between the 2nd and 5th centuries in a wide area of Eastern Europe, specifically in what today constitutes Ukraine, Romania, Moldova, and parts of Belarus...
- Penkovka culturePenkovka cultureThe Penkovka culture is an archaeological culture dating from about the fifth to seventh/eights centuries CE, named after Penkovka , not far from Vinnytsia....
- KashubiansKashubiansKashubians/Kaszubians , also called Kashubs, Kashubes, Kaszubians, Kassubians or Cassubians, are a West Slavic ethnic group in Pomerelia, north-central Poland. Their settlement area is referred to as Kashubia ....
- Kiev cultureKiev cultureThe Kiev culture is an archaeological culture dating from about the 3rd to 5th centuries, named after Kiev, the capital of Ukraine. The dwellings are overwhelmingly of the semi-subterranean type, common among earlier Germanic tribes like the Scirii and Bastarnae, and later in Slavic cultures...
- KrivichKrivichThe Krivichi was one of the tribal unions of Early East Slavs between the 6th and the 12th centuries. They migrated to the mostly Finnic areas in the upper reaches of the Volga, Dnieper, Western Dvina, areas south of the lower reaches of river Velikaya and parts of the Neman basin.-Etymology:Many...
- KhazarsKhazarsThe Khazars were semi-nomadic Turkic people who established one of the largest polities of medieval Eurasia, with the capital of Atil and territory comprising much of modern-day European Russia, western Kazakhstan, eastern Ukraine, Azerbaijan, large portions of the northern Caucasus , parts of...
- Ilmen SlavsIlmen SlavsThe Ilmen Slavs was the northernmost tribe of the Early East Slavs, which inhabited the shores of the Lake Ilmen and the basin of the rivers of Volkhov, Lovat, Msta, and the upper stream of the Mologa River in the 8th to 10th centuries....
- LechitesLechitesLechites – an ethnic and linguistic group of West Slavs, the ancestors of modern Poles and the historical Pomeranians and Polabians.-History:...
- Milograd cultureMilograd cultureThe Milograd culture is an archaeological culture, lasting from about the 7th century BC to the 1st century AD. Geographically, it corresponds to present day southern Belarus and northern Ukraine, in the area of the confluence of the Dnieper and the Pripyat, north of Kiev...
- ObotritesObotritesThe Obotrites , also commonly known as the Obodrites, Abotrites, or Abodrites, were a confederation of medieval West Slavic tribes within the territory of modern Mecklenburg and Holstein in northern Germany . For decades they were allies of Charlemagne in his wars against Germanic Saxons and Slavic...
- Polabian SlavsPolabian SlavsPolabian Slavs - is a collective term applied to a number of Lechites tribes who lived along the Elbe river, between the Baltic Sea to the north, the Saale and the Limes Saxoniae to the west, the Ore Mountains and the Western Sudetes to the south, and Poland to the east. They have also been known...
- Roxolani
- SarmatiansSarmatiansThe Iron Age Sarmatians were an Iranian people in Classical Antiquity, flourishing from about the 5th century BC to the 4th century AD....
- Sclaveni or Sclaviniae
- VeletiVeletiThe Veleti or Wilzi were a group of medieval Lechites tribes within the territory of modern northeastern Germany; see Polabian Slavs. In common with other Slavic groups between the Elbe and Oder Rivers, they were often described by Germanic sources as Wends. In the late 10th century, they were...
- VlachsVlachsVlach is a blanket term covering several modern Latin peoples descending from the Latinised population in Central, Eastern and Southeastern Europe. English variations on the name include: Walla, Wlachs, Wallachs, Vlahs, Olahs or Ulahs...
- WendsWendsWends is a historic name for West Slavs living near Germanic settlement areas. It does not refer to a homogeneous people, but to various peoples, tribes or groups depending on where and when it is used...
Early Middle Ages (ca 800-1097)
See SlavicisationSlavicisation
Slavicisation is a term used to describe a cultural change in which something non-Slavic becomes Slavic. The process can either be voluntary, or applied with varying degrees of force.* Bulgarisation* Croatisation* Czechification* Polonization...
, Slavic peoples
Slavic peoples
The Slavic people are an Indo-European panethnicity living in Eastern Europe, Southeast Europe, North Asia and Central Asia. The term Slavic represents a broad ethno-linguistic group of people, who speak languages belonging to the Slavic language family and share, to varying degrees, certain...
, East Slavs
East Slavs
The East Slavs are Slavic peoples speaking East Slavic languages. Formerly the main population of the medieval state of Kievan Rus, by the seventeenth century they evolved into the Russian, Ukrainian, and Belarusian peoples.-Sources:...
, West Slavs
West Slavs
The West Slavs are Slavic peoples speaking West Slavic languages. They include Poles , Czechs, Slovaks, Lusatian Sorbs and the historical Polabians. The northern or Lechitic group includes, along with Polish, the extinct Polabian and Pomeranian languages...
, South Slavs
South Slavs
The South Slavs are the southern branch of the Slavic peoples and speak South Slavic languages. Geographically, the South Slavs are native to the Balkan peninsula, the southern Pannonian Plain and the eastern Alps...
- ArsaniaArsaniaArtania or Arsania was one of the three centers of the Saqaliba described in a lost book by Abu Zayd al-Balkhi and mentioned in works by some of his followers...
- KuyabaKuyabaKuyavia, Kuyabia or Kuyaba was one of the three centers of the Saqaliba described in a lost book by Abu Zayd al-Balkhi Kuyavia, Kuyabia or Kuyaba was one of the three centers of the Saqaliba (early East Slavs) described in a lost book by Abu Zayd al-Balkhi Kuyavia, Kuyabia or Kuyaba was one of the...
- Rus' KhaganateRus' KhaganateRus' khaganate is a historiographical term for the formative phase of the Rus state in the 9th century AD....
(839-882) - Novgorod Rus'Administrative division of Novgorod LandThe administrative division of Novgorod Republic is not definitely known; the country was divided into several tysyachas and volosts. The city of Novgorod with its vicinity, as well as a few other towns were not part of any of those. Pskov achieved an autonomy from Novgorod in the 13th century;...
(862-882) - Kievan Rus'Kievan Rus'Kievan Rus was a medieval polity in Eastern Europe, from the late 9th to the mid 13th century, when it disintegrated under the pressure of the Mongol invasion of 1237–1240....
(882–1097)
Council of Liubech and after (1097-1237)
.png)
- Grand Duchy of KievKievan Rus'Kievan Rus was a medieval polity in Eastern Europe, from the late 9th to the mid 13th century, when it disintegrated under the pressure of the Mongol invasion of 1237–1240....
- Principality of SmolenskPrincipality of SmolenskThe Principality of Smolensk was a Kievan Rus' lordship from the eleventh to the fifteenth century...
(since 1127) - Principality of Turov and PinskPrincipality of Turov and PinskThe Duchy of Turov and Pinsk was a medieval principality and state on the territory of modern southern Belarus and northern Ukraine. The principality's capital was Turov or Pinsk, other important cities were Mazyr and Slutsk, Lutsk, Brest, and Volodymyr-Volynskyi...
(since 1132) - Novgorod RepublicNovgorod RepublicThe Novgorod Republic was a large medieval Russian state which stretched from the Baltic Sea to the Ural Mountains between the 12th and 15th centuries, centred on the city of Novgorod...
(since 1136)- Pskov RepublicPskov RepublicPskov, known at various times as the Principality of Pskov or the Pskov Republic , was a medieval state on the south shore of Lake Pskov. The capital city, also named Pskov, was located at the southern end of the Peipus–Pskov Lake system at the southeast corner of Ugandi, about southwest of...
(since ca.1200)
- Pskov Republic
- Principality of PereyaslavlPrincipality of PereyaslavlThe Principality of Pereslavl was a regional principality of Kievan Rus from the end of 9th to 1302 based on the city of Pereyaslavl on the Trubezh river. It was usually administrated by younger sons of the Grand Prince of Kiev...
(?) - Principality of Vladimir VolyhnPrincipality of HalychPrincipality of Halych was a Kievan Rus' principality established in around 1124 established by the grandson of Rostislav Ihor Vasylkovych . According to Mykhailo Hrushevsky the realm of Halych was passed to Rostislav upon the death of his father Vladimir Yaroslavich, but he was banished out of it...
(since 1154 to 1199; later created the Grand Duchy of Galicia-Volhynia)
- Principality of Smolensk
- Principality of Rostov-SuzdalVladimir-SuzdalThe Vladimir-Suzdal Principality or Vladimir-Suzdal Rus’ was one of the major principalities which succeeded Kievan Rus' in the late 12th century and lasted until the late 14th century. For a long time the Principality was a vassal of the Mongolian Golden Horde...
(since 1157 - The Grand Duchy of Vladimir-SuzdalVladimir-SuzdalThe Vladimir-Suzdal Principality or Vladimir-Suzdal Rus’ was one of the major principalities which succeeded Kievan Rus' in the late 12th century and lasted until the late 14th century. For a long time the Principality was a vassal of the Mongolian Golden Horde...
)- Principality of RostovVladimir-SuzdalThe Vladimir-Suzdal Principality or Vladimir-Suzdal Rus’ was one of the major principalities which succeeded Kievan Rus' in the late 12th century and lasted until the late 14th century. For a long time the Principality was a vassal of the Mongolian Golden Horde...
(since 1207) - Principality of YaroslavlPrincipality of YaroslavlThe Principality of Yaroslavl was an eastern Slavic principality, which existed in 1218—1463.Its first independent prince was Vsyevolod Konstantinovich, who died fighting the Mongols on the Siti river, March 4th 1238. Yaroslavl had been sacked in February...
(since 1218)
- Principality of Rostov
- Principality of Chernigov
- Principality of Novgorod-SeverskPrincipality of Novgorod-SeverskThe Principality of Novgorod-Seversk was a medieval Rus' principality centered on the town now called Novhorod-Siverskyi. The principality was aligned to the Principality of Chernigov. It may have been created in 1139, the date of one modern authority...
(personal union with Chernigov) - Principality of Ryazan
- Principality of MuromPrincipality of MuromThe Principality of Murom was a medieval Rus' lordship based on the city of Murom, now in Vladimir Oblast, Russia. Murom lay in an area that was strongly Finno-Ugric for much of its medieval history, located in the homeland of the Muromians...
(since 1127)
- Principality of Murom
- Principality of Terebovl (since 1097 to 1141; incorporated to Principality of HalychPrincipality of HalychPrincipality of Halych was a Kievan Rus' principality established in around 1124 established by the grandson of Rostislav Ihor Vasylkovych . According to Mykhailo Hrushevsky the realm of Halych was passed to Rostislav upon the death of his father Vladimir Yaroslavich, but he was banished out of it...
)- Principality of HalychPrincipality of HalychPrincipality of Halych was a Kievan Rus' principality established in around 1124 established by the grandson of Rostislav Ihor Vasylkovych . According to Mykhailo Hrushevsky the realm of Halych was passed to Rostislav upon the death of his father Vladimir Yaroslavich, but he was banished out of it...
(since 1124 to 1199; later - Grand Duchy of Galicia-Volhynia)
- Principality of Halych
- Principality of PeremyshlPrincipality of PeremyshlThe Principality of Peremyshl was a medieval petty principality centred on Peremyshl in the Cherven lands .-First mentioning:...
(to Grand Duchy of Galicia-Volhynia, later incorporated to Kingdom of Poland) - Principality of TmutarakanTmutarakanTmutarakan was a Mediaeval Russian principality and trading town that controlled the Cimmerian Bosporus, the passage from the Black Sea to the Sea of Azov. Its site was the ancient Greek colony of Hermonassa . It was situated on the Taman peninsula, in the present-day Krasnodar Krai of Russia,...
(destroyed by CumansCumansThe Cumans were Turkic nomadic people comprising the western branch of the Cuman-Kipchak confederation. After Mongol invasion , they decided to seek asylum in Hungary, and subsequently to Bulgaria...
at 1097)
Mongol invasion and yoke (1237-1380)
From the Mongol invasion of Rus' to the battle of KulikovoBattle of Kulikovo
The Battle of Kulikovo was a battle between Tatar Mamai and Muscovy Dmitriy and portrayed by Russian historiography as a stand-off between Russians and the Golden Horde. However, the political situation at the time was much more complicated and concerned the politics of the Northeastern Rus'...
- Grand Duchy of KievKievan Rus'Kievan Rus was a medieval polity in Eastern Europe, from the late 9th to the mid 13th century, when it disintegrated under the pressure of the Mongol invasion of 1237–1240....
(to Lithuania at 1362) - Grand Duchy of Galicia–Volhynia (since 1253 - Kingdom; to Grand Duchy of LithuaniaGrand Duchy of LithuaniaThe Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state from the 12th /13th century until 1569 and then as a constituent part of Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth until 1791 when Constitution of May 3, 1791 abolished it in favor of unitary state. It was founded by the Lithuanians, one of the polytheistic...
and Kingdom of Poland at 1349) - Grand Duchy of Vladimir-SuzdalVladimir-SuzdalThe Vladimir-Suzdal Principality or Vladimir-Suzdal Rus’ was one of the major principalities which succeeded Kievan Rus' in the late 12th century and lasted until the late 14th century. For a long time the Principality was a vassal of the Mongolian Golden Horde...
- Principality of VladimirVladimir-SuzdalThe Vladimir-Suzdal Principality or Vladimir-Suzdal Rus’ was one of the major principalities which succeeded Kievan Rus' in the late 12th century and lasted until the late 14th century. For a long time the Principality was a vassal of the Mongolian Golden Horde...
(since 1238; to Moscow at 1364) - Principality of Beloozero (since 1238)
- Principality of Tver (since 1246)
- Principality of Moscow (since 1276; since 1330 - The Grand Duchy)
- Principality of Suzdal—Nizhny NovgorodPrincipality of Suzdal—Nizhny NovgorodThe Principality of Suzdal—Nizhny Novgorod was an East Slavic principality, which formed in 1341. Its main towns were Suzdal, Nizhny Novgorod, Gorokhovets, Gorodets and Kurmysh. Since 1350 Nizhny Novgorod has been the capital of the principality....
(since 1341)
- Principality of Vladimir
- Grand Duchy of Chernigov
- Novgorod RepublicNovgorod RepublicThe Novgorod Republic was a large medieval Russian state which stretched from the Baltic Sea to the Ural Mountains between the 12th and 15th centuries, centred on the city of Novgorod...
- Principality of Great Perm (since 1323)
- Pskov RepublicPskov RepublicPskov, known at various times as the Principality of Pskov or the Pskov Republic , was a medieval state on the south shore of Lake Pskov. The capital city, also named Pskov, was located at the southern end of the Peipus–Pskov Lake system at the southeast corner of Ugandi, about southwest of...
- Principality of SmolenskPrincipality of SmolenskThe Principality of Smolensk was a Kievan Rus' lordship from the eleventh to the fifteenth century...
- Principality of Toropets (personal union with Smolensk; to Lithuania at 1362)
- Principality of Polotsk (to Lithuania at 1307)
- Principality of Grodno (to Lithuania at 1315)
- Principality of Vitebsk (to Lithuania at 1320)
- Principality of Minsk (to Lithuania at 1326)
- Principality of Turov and PinskPrincipality of Turov and PinskThe Duchy of Turov and Pinsk was a medieval principality and state on the territory of modern southern Belarus and northern Ukraine. The principality's capital was Turov or Pinsk, other important cities were Mazyr and Slutsk, Lutsk, Brest, and Volodymyr-Volynskyi...
(to Lithuania at 1336) - Principality of Ryazan
- Principality of Novgorod-SeverskPrincipality of Novgorod-SeverskThe Principality of Novgorod-Seversk was a medieval Rus' principality centered on the town now called Novhorod-Siverskyi. The principality was aligned to the Principality of Chernigov. It may have been created in 1139, the date of one modern authority...
(to Lithuania at 1356)- Principality of TrubetskPrincipality of TrubetskThe Principality of Trubetsk was a small, landlocked Rus' principality in Eastern Europe. In the later Middle Ages it was bordered by the Grand Duchy of Lithuania to its west and by Muscovy to its east. The Principality of Trubetsk was a principality within modern Bryansk Oblast, about 50 miles ...
(since 1357)
- Principality of Trubetsk
- Principality of RostovRostovRostov is a town in Yaroslavl Oblast, Russia, one of the oldest in the country and a tourist center of the Golden Ring. It is located on the shores of Lake Nero, northeast of Moscow. Population:...
- Principality of YaroslavlPrincipality of YaroslavlThe Principality of Yaroslavl was an eastern Slavic principality, which existed in 1218—1463.Its first independent prince was Vsyevolod Konstantinovich, who died fighting the Mongols on the Siti river, March 4th 1238. Yaroslavl had been sacked in February...
- Principality of PereyaslavlPrincipality of PereyaslavlThe Principality of Pereslavl was a regional principality of Kievan Rus from the end of 9th to 1302 based on the city of Pereyaslavl on the Trubezh river. It was usually administrated by younger sons of the Grand Prince of Kiev...
(destroyed by the Mongols at 1239)
The rise of Muscovy (1380-1480)

Battle of Kulikovo
The Battle of Kulikovo was a battle between Tatar Mamai and Muscovy Dmitriy and portrayed by Russian historiography as a stand-off between Russians and the Golden Horde. However, the political situation at the time was much more complicated and concerned the politics of the Northeastern Rus'...
- Grand Duchy of MoscowGrand Duchy of MoscowThe Grand Duchy of Moscow or Grand Principality of Moscow, also known in English simply as Muscovy , was a late medieval Rus' principality centered on Moscow, and the predecessor state of the early modern Tsardom of Russia....
- Principality of MuromPrincipality of MuromThe Principality of Murom was a medieval Rus' lordship based on the city of Murom, now in Vladimir Oblast, Russia. Murom lay in an area that was strongly Finno-Ugric for much of its medieval history, located in the homeland of the Muromians...
(to Moscow at 1393) - Principality of Suzdal—Nizhny NovgorodPrincipality of Suzdal—Nizhny NovgorodThe Principality of Suzdal—Nizhny Novgorod was an East Slavic principality, which formed in 1341. Its main towns were Suzdal, Nizhny Novgorod, Gorokhovets, Gorodets and Kurmysh. Since 1350 Nizhny Novgorod has been the capital of the principality....
(to Moscow at 1425)- Principality of SuzdalVladimir-SuzdalThe Vladimir-Suzdal Principality or Vladimir-Suzdal Rus’ was one of the major principalities which succeeded Kievan Rus' in the late 12th century and lasted until the late 14th century. For a long time the Principality was a vassal of the Mongolian Golden Horde...
(to Moscow at 1451)
- Principality of Suzdal
- Principality of YaroslavlPrincipality of YaroslavlThe Principality of Yaroslavl was an eastern Slavic principality, which existed in 1218—1463.Its first independent prince was Vsyevolod Konstantinovich, who died fighting the Mongols on the Siti river, March 4th 1238. Yaroslavl had been sacked in February...
(to Moscow at 1471) - Principality of RostovRostovRostov is a town in Yaroslavl Oblast, Russia, one of the oldest in the country and a tourist center of the Golden Ring. It is located on the shores of Lake Nero, northeast of Moscow. Population:...
(to Moscow at 1474) - Novgorod RepublicNovgorod RepublicThe Novgorod Republic was a large medieval Russian state which stretched from the Baltic Sea to the Ural Mountains between the 12th and 15th centuries, centred on the city of Novgorod...
(to Moscow at 1478) - Principality of Great Perm
- Grand Duchy of Tver
- Grand Duchy of Ryazan
- Pskov RepublicPskov RepublicPskov, known at various times as the Principality of Pskov or the Pskov Republic , was a medieval state on the south shore of Lake Pskov. The capital city, also named Pskov, was located at the southern end of the Peipus–Pskov Lake system at the southeast corner of Ugandi, about southwest of...
- Principality of Beloozero
- Principality of TrubetskPrincipality of TrubetskThe Principality of Trubetsk was a small, landlocked Rus' principality in Eastern Europe. In the later Middle Ages it was bordered by the Grand Duchy of Lithuania to its west and by Muscovy to its east. The Principality of Trubetsk was a principality within modern Bryansk Oblast, about 50 miles ...
- Principality of Starodub (to Lithuania at 1406)
- Principality of SmolenskPrincipality of SmolenskThe Principality of Smolensk was a Kievan Rus' lordship from the eleventh to the fifteenth century...
(to Lithuania at 1404) - Grand Duchy of Chernigov (to Lithuania at 1406)
since 1480
- Grand Duchy of MoscowGrand Duchy of MoscowThe Grand Duchy of Moscow or Grand Principality of Moscow, also known in English simply as Muscovy , was a late medieval Rus' principality centered on Moscow, and the predecessor state of the early modern Tsardom of Russia....
- Grand Duchy of Tver (to Moscow at 1485)
- Principality of Beloozero (to Moscow at 1485)
- Pskov RepublicPskov RepublicPskov, known at various times as the Principality of Pskov or the Pskov Republic , was a medieval state on the south shore of Lake Pskov. The capital city, also named Pskov, was located at the southern end of the Peipus–Pskov Lake system at the southeast corner of Ugandi, about southwest of...
(to Moscow at 1510) - Grand Duchy of Ryazan (to Moscow at 1521)
- Principality of TrubetskPrincipality of TrubetskThe Principality of Trubetsk was a small, landlocked Rus' principality in Eastern Europe. In the later Middle Ages it was bordered by the Grand Duchy of Lithuania to its west and by Muscovy to its east. The Principality of Trubetsk was a principality within modern Bryansk Oblast, about 50 miles ...
(to Tsardom of RussiaTsardom of RussiaThe Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year...
at 1566) - Grand Duchy of LithuaniaGrand Duchy of LithuaniaThe Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state from the 12th /13th century until 1569 and then as a constituent part of Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth until 1791 when Constitution of May 3, 1791 abolished it in favor of unitary state. It was founded by the Lithuanians, one of the polytheistic...
(to Russian EmpireRussian EmpireThe Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
at 1772-1795)
See also
- Historical states of ItalyHistorical states of ItalyItaly, until the present era, was a conglomeration of city-states and other small independent entities. The following is a list of the various states that made up what we now know as Italy during the past...
- Historical states of Germany
- List of Medieval Slavic tribes
- Lech, Čech, and Rus

