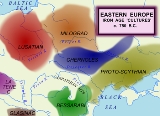
Chernoles culture
Encyclopedia
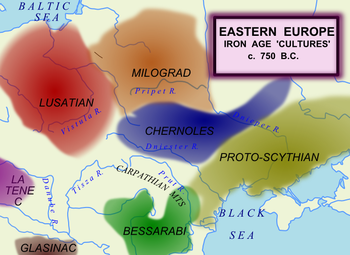
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the archaeological period generally occurring after the Bronze Age, marked by the prevalent use of iron. The early period of the age is characterized by the widespread use of iron or steel. The adoption of such material coincided with other changes in society, including differing...
archaeological unit dating ca. 1025–700 BC. It was located in the forest-steppe between the Dniester
Dniester
The Dniester is a river in Eastern Europe. It runs through Ukraine and Moldova and separates most of Moldova's territory from the breakaway de facto state of Transnistria.-Names:...
and Dnieper River
Dnieper River
The Dnieper River is one of the major rivers of Europe that flows from Russia, through Belarus and Ukraine, to the Black Sea.The total length is and has a drainage basin of .The river is noted for its dams and hydroelectric stations...
s, in what is now northern Ukraine
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia...
. This location corresponds to where Herodotus
Herodotus
Herodotus was an ancient Greek historian who was born in Halicarnassus, Caria and lived in the 5th century BC . He has been called the "Father of History", and was the first historian known to collect his materials systematically, test their accuracy to a certain extent and arrange them in a...
later placed his Scythian ploughmen. From 200 BC, the culture was overrun by the arrival of Germanic
Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples are an Indo-European ethno-linguistic group of Northern European origin, identified by their use of the Indo-European Germanic languages which diversified out of Proto-Germanic during the Pre-Roman Iron Age.Originating about 1800 BCE from the Corded Ware Culture on the North...
and Celtic settlers to the region.
Features
Chernolian settlements include, both, open and fortified sites surrounded by multiple banks and ditches. Houses were usually surface-dwellings and of substantial size, ~ 10 x 6 m. Artifacts found in settlements include stone and bronze axes, weapons, bronze ornaments, and iron tools. Cult wheat, barley and millet were staples. The economy was agricultural with added stockbreeding. Bronze artefacts betray significant contacts with Scythian nomads, and finds of finer ceramic wares suggest contacts with Thrace and Black SeaBlack Sea
The Black Sea is bounded by Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus and is ultimately connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Mediterranean and the Aegean seas and various straits. The Bosphorus strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean...
Greek colonies. Inhabitants practiced biritual burials: inhumation under barrows and cremation in urnfields (the latter predominated in later periods).

