
Pomeranian culture
Encyclopedia
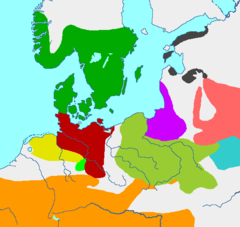
Pomerania
Pomerania is a historical region on the south shore of the Baltic Sea. Divided between Germany and Poland, it stretches roughly from the Recknitz River near Stralsund in the West, via the Oder River delta near Szczecin, to the mouth of the Vistula River near Gdańsk in the East...
n culture, also Pomeranian or Pomerelian Face Urn culture was an Iron Age
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the archaeological period generally occurring after the Bronze Age, marked by the prevalent use of iron. The early period of the age is characterized by the widespread use of iron or steel. The adoption of such material coincided with other changes in society, including differing...
culture in Pomerania
Pomerania
Pomerania is a historical region on the south shore of the Baltic Sea. Divided between Germany and Poland, it stretches roughly from the Recknitz River near Stralsund in the West, via the Oder River delta near Szczecin, to the mouth of the Vistula River near Gdańsk in the East...
, northern Poland
Poland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
. About 650 BC, it evolved from the Lusatian culture
Lusatian culture
The Lusatian culture existed in the later Bronze Age and early Iron Age in most of today's Poland, parts of Czech Republic and Slovakia, parts of eastern Germany and parts of Ukraine...
, often associated with the Nordic Bronze Age
Nordic Bronze Age
The Nordic Bronze Age is the name given by Oscar Montelius to a period and a Bronze Age culture in Scandinavian pre-history, c. 1700-500 BC, with sites that reached as far east as Estonia. Succeeding the Late Neolithic culture, its ethnic and linguistic affinities are unknown in the absence of...
, and subsequently expanded southward. Between 200 and 150 BC, it was succeeded by the Oksywie culture
Oksywie culture
The Oksywie Culture, was an archaeological culture which existed in the area of modern day Eastern Pomerania around the lower Vistula river, from the 2nd century BC to the early 1st century AD....
in eastern Pomerania
Pomerania
Pomerania is a historical region on the south shore of the Baltic Sea. Divided between Germany and Poland, it stretches roughly from the Recknitz River near Stralsund in the West, via the Oder River delta near Szczecin, to the mouth of the Vistula River near Gdańsk in the East...
and the Przeworsk culture
Przeworsk culture
The Przeworsk culture is part of an Iron Age archaeological complex that dates from the 2nd century BC to the 5th century AD. It was located in what is now central and southern Poland, later spreading to parts of eastern Slovakia and Carpathian Ruthenia ranging between the Oder and the middle and...
at the upper Vistula
Vistula
The Vistula is the longest and the most important river in Poland, at 1,047 km in length. The watershed area of the Vistula is , of which lies within Poland ....
and Oder
Oder
The Oder is a river in Central Europe. It rises in the Czech Republic and flows through western Poland, later forming of the border between Poland and Germany, part of the Oder-Neisse line...
rivers.
Features


Cist
A cist from ) is a small stone-built coffin-like box or ossuary used to hold the bodies of the dead. Examples can be found across Europe and in the Middle East....
s. The face-urns have lids in the form of hats, often miniature ear-rings of real bronze are added. The faces are sometimes modelled very naturalistically, and no two urns show the same face. Incised drawings on the urns show hunting scenes, chariot races or riders. Brooch
Brooch
A brooch ; also known in ancient times as a fibula; is a decorative jewelry item designed to be attached to garments. It is usually made of metal, often silver or gold but sometimes bronze or some other material...
es of Tłukom-type and necklaces of multiple bronze rings are typical examples of metal work.
The economy was similar to that of the Lusatian culture. Rye
Rye
Rye is a grass grown extensively as a grain and as a forage crop. It is a member of the wheat tribe and is closely related to barley and wheat. Rye grain is used for flour, rye bread, rye beer, some whiskeys, some vodkas, and animal fodder...
was systematically cultivated for the first time, but still formed a minor component of the cereals. There were fewer hill forts than in the area of the Lusatian culture
Lusatian culture
The Lusatian culture existed in the later Bronze Age and early Iron Age in most of today's Poland, parts of Czech Republic and Slovakia, parts of eastern Germany and parts of Ukraine...
further west. Southern imports were sparse as well.
Related cultures
A related culture of the same age was the House Urn culture in central Germany.Spread
In the later Iron Age, the Pomeranian culture spread southward, into areas formerly belonging to the LusatianLusatian culture
The Lusatian culture existed in the later Bronze Age and early Iron Age in most of today's Poland, parts of Czech Republic and Slovakia, parts of eastern Germany and parts of Ukraine...
, Wysoko- and Milograd culture
Milograd culture
The Milograd culture is an archaeological culture, lasting from about the 7th century BC to the 1st century AD. Geographically, it corresponds to present day southern Belarus and northern Ukraine, in the area of the confluence of the Dnieper and the Pripyat, north of Kiev...
s. In Masovia and Poland this mixture led to the development of the group with bell-shaped burials (Glockengräbergruppe).
See also
- Lusatian cultureLusatian cultureThe Lusatian culture existed in the later Bronze Age and early Iron Age in most of today's Poland, parts of Czech Republic and Slovakia, parts of eastern Germany and parts of Ukraine...
- Przeworsk culturePrzeworsk cultureThe Przeworsk culture is part of an Iron Age archaeological complex that dates from the 2nd century BC to the 5th century AD. It was located in what is now central and southern Poland, later spreading to parts of eastern Slovakia and Carpathian Ruthenia ranging between the Oder and the middle and...
- Nordic Bronze AgeNordic Bronze AgeThe Nordic Bronze Age is the name given by Oscar Montelius to a period and a Bronze Age culture in Scandinavian pre-history, c. 1700-500 BC, with sites that reached as far east as Estonia. Succeeding the Late Neolithic culture, its ethnic and linguistic affinities are unknown in the absence of...
Literature
- Hallstattzeit, Die Altertümer im Museum für Vor- und Frühgeschichte, Bd. 2 , 1999, ISBN 3-8053-2566-5
- TacitusTacitusPublius Cornelius Tacitus was a senator and a historian of the Roman Empire. The surviving portions of his two major works—the Annals and the Histories—examine the reigns of the Roman Emperors Tiberius, Claudius, Nero and those who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors...
: GermaniaGermania (book)The Germania , written by Gaius Cornelius Tacitus around 98, is an ethnographic work on the Germanic tribes outside the Roman Empire.-Contents:...

