Leat
Encyclopedia

Wales
Wales is a country that is part of the United Kingdom and the island of Great Britain, bordered by England to its east and the Atlantic Ocean and Irish Sea to its west. It has a population of three million, and a total area of 20,779 km²...
, for an artificial watercourse
Watercourse
A watercourse is any flowing body of water. These include rivers, streams, anabranches, and so forth.-See also:* physical geography* Environmental flow* Waterway* Hydrology* Wadi-External links:...
or aqueduct
Aqueduct
An aqueduct is a water supply or navigable channel constructed to convey water. In modern engineering, the term is used for any system of pipes, ditches, canals, tunnels, and other structures used for this purpose....
dug into the ground, especially one supplying water to a watermill
Watermill
A watermill is a structure that uses a water wheel or turbine to drive a mechanical process such as flour, lumber or textile production, or metal shaping .- History :...
or its mill pond
Mill pond
A mill pond is any body of water used as a reservoir for a water-powered mill. Mill ponds were often created through the construction of a mill dam across a waterway. In many places, the common proper name Mill Pond name has remained even though the mill has long since gone...
. Other common uses for leats include delivery of water for mineral washing and concentration, for irrigation, to serve a dye works or other industrial plant, and provision of drinking water to a farm or household or as a catchment cut-off to improve the yield of a reservoir
Reservoir
A reservoir , artificial lake or dam is used to store water.Reservoirs may be created in river valleys by the construction of a dam or may be built by excavation in the ground or by conventional construction techniques such as brickwork or cast concrete.The term reservoir may also be used to...
.
According to the Oxford English Dictionary
Oxford English Dictionary
The Oxford English Dictionary , published by the Oxford University Press, is the self-styled premier dictionary of the English language. Two fully bound print editions of the OED have been published under its current name, in 1928 and 1989. The first edition was published in twelve volumes , and...
, leat is cognate
Cognate
In linguistics, cognates are words that have a common etymological origin. This learned term derives from the Latin cognatus . Cognates within the same language are called doublets. Strictly speaking, loanwords from another language are usually not meant by the term, e.g...
with let in the sense of "allow to pass through". Other names for the same thing include fleam (probably a leat supplying water to a mill that did not have a millpool). In parts of northern England, for example around Sheffield
Sheffield
Sheffield is a city and metropolitan borough of South Yorkshire, England. Its name derives from the River Sheaf, which runs through the city. Historically a part of the West Riding of Yorkshire, and with some of its southern suburbs annexed from Derbyshire, the city has grown from its largely...
, the equivalent word is goit. In southern England, a leat used to supply water for water-meadow
Water-meadow
A water-meadow is an area of grassland subject to controlled irrigation to increase agricultural productivity. Water-meadows were mainly used in Europe from the 16th to the early 20th centuries...
irrigation is often called a carrier, top carrier, or main.
Design and functions
Leats generally start some distance (a few hundred yards, or perhaps several miles) above the mill or other destination, where an offtake or sluiceSluice
A sluice is a water channel that is controlled at its head by a gate . For example, a millrace is a sluice that channels water toward a water mill...
gate diverts a proportion of the water from a river
River
A river is a natural watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, a lake, a sea, or another river. In a few cases, a river simply flows into the ground or dries up completely before reaching another body of water. Small rivers may also be called by several other names, including...
or stream
Stream
A stream is a body of water with a current, confined within a bed and stream banks. Depending on its locale or certain characteristics, a stream may be referred to as a branch, brook, beck, burn, creek, "crick", gill , kill, lick, rill, river, syke, bayou, rivulet, streamage, wash, run or...
. A weir
Weir
A weir is a small overflow dam used to alter the flow characteristics of a river or stream. In most cases weirs take the form of a barrier across the river that causes water to pool behind the structure , but allows water to flow over the top...
often serves to provide a reservoir of water adequate for diversion. The leat then runs along the edge or side of the valley, at a shallower slope than the main stream. The gradient determines the flow rate together with the quality of the wetted surface of the leat. The flow rate may be calculated using the Manning formula
Manning formula
The Manning formula, known also as the Gauckler–Manning formula, or Gauckler–Manning–Strickler formula in Europe, is an empirical formula for open channel flow, or free-surface flow driven by gravity...
. By the time it arrives at the water mill the difference in levels between the leat and the main stream is great enough to provide a useful head
Hydraulic head
Hydraulic head or piezometric head is a specific measurement of water pressure above a geodetic datum. It is usually measured as a water surface elevation, expressed in units of length, at the entrance of a piezometer...
of water – several metres (perhaps 5 to 15 feet) for a watermill, or a metre or less (perhaps one to four feet) for a water-meadow
Water-meadow
A water-meadow is an area of grassland subject to controlled irrigation to increase agricultural productivity. Water-meadows were mainly used in Europe from the 16th to the early 20th centuries...
.
Water supply
Leats are used to increase the yield of a reservoir by trapping streams in nearby catchments by means of a contour leat. This captures part or all of the stream flow and transports it along the contour to the reservoir. Such leats are common around reservoirs in the uplands of Wales.Mining
Lead
Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed...
, tin
Tin
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn and atomic number 50. It is a main group metal in group 14 of the periodic table. Tin shows chemical similarity to both neighboring group 14 elements, germanium and lead and has two possible oxidation states, +2 and the slightly more stable +4...
and silver
Silver
Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal...
ores in mining areas of Wales
Wales
Wales is a country that is part of the United Kingdom and the island of Great Britain, bordered by England to its east and the Atlantic Ocean and Irish Sea to its west. It has a population of three million, and a total area of 20,779 km²...
, Cornwall
Cornwall
Cornwall is a unitary authority and ceremonial county of England, within the United Kingdom. It is bordered to the north and west by the Celtic Sea, to the south by the English Channel, and to the east by the county of Devon, over the River Tamar. Cornwall has a population of , and covers an area of...
, Devon
Devon
Devon is a large county in southwestern England. The county is sometimes referred to as Devonshire, although the term is rarely used inside the county itself as the county has never been officially "shired", it often indicates a traditional or historical context.The county shares borders with...
and the Pennines
Pennines
The Pennines are a low-rising mountain range, separating the North West of England from Yorkshire and the North East.Often described as the "backbone of England", they form a more-or-less continuous range stretching from the Peak District in Derbyshire, around the northern and eastern edges of...
from the 17th century onwards. They were used to supply water for hushing
Hushing
Hushing is an ancient and historic mining method using a flood or torrent of water to reveal mineral veins. The method was applied in several ways, both in prospecting for ores, and for their exploitation. Mineral veins are often hidden below soil and sub-soil, which must be stripped away to...
mineral deposits, washing ore and powering mills.
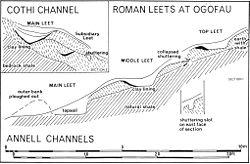
They were also used extensively by the Romans
Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome was a thriving civilization that grew on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to one of the largest empires in the ancient world....
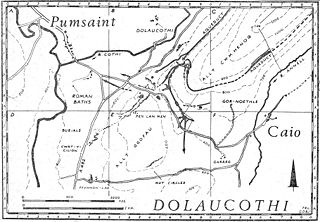
, and can still be seen at many sites, such as the Dolaucothi
Dolaucothi Gold Mines
The Dolaucothi Gold Mines , also known as the Ogofau Gold Mine, are Roman surface and deep mines located in the valley of the River Cothi, near Pumsaint, Carmarthenshire, Wales...
goldmines. They used the aqueduct
Aqueduct
An aqueduct is a water supply or navigable channel constructed to convey water. In modern engineering, the term is used for any system of pipes, ditches, canals, tunnels, and other structures used for this purpose....
s to prospect for ores by sluicing away the overburden of soil to reveal the bedrock in a method known as hushing
Hushing
Hushing is an ancient and historic mining method using a flood or torrent of water to reveal mineral veins. The method was applied in several ways, both in prospecting for ores, and for their exploitation. Mineral veins are often hidden below soil and sub-soil, which must be stripped away to...
. They could then attack the ore veins by fire-setting
Fire-setting
Fire-setting is a method of mining used since prehistoric times up to the Middle Ages. Fires were set against a rock face to heat the stone, which was then doused with water...
, quench with water from a tank above the workings, and remove the debris with waves of water, a method still used in hydraulic mining
Hydraulic mining
Hydraulic mining, or hydraulicking, is a form of mining that uses high-pressure jets of water to dislodge rock material or move sediment. In the placer mining of gold or tin, the resulting water-sediment slurry is directed through sluice boxes to remove the gold.-Precursor - ground...
. The water supply could then be used for washing the ore after crushing by simple machines also driven by water.
The Romans also used them for supplying water to the bath-houses or thermae
Thermae
In ancient Rome, thermae and balnea were facilities for bathing...
and to drive vertical water-wheels.
Dartmoor

- Drake's LeatDrake's LeatDrake's Leat, also known as Plymouth Leat, was a watercourse constructed in the late 16th century to tap the River Meavy on Dartmoor, England in order to supply Plymouth with water. It was one of the first municipal water supplies in the country.-Plans:...
, constructed in 1591 under the management of Sir Francis DrakeFrancis DrakeSir Francis Drake, Vice Admiral was an English sea captain, privateer, navigator, slaver, and politician of the Elizabethan era. Elizabeth I of England awarded Drake a knighthood in 1581. He was second-in-command of the English fleet against the Spanish Armada in 1588. He also carried out the...
, as an agent of the Corporation of Plymouth, to carry water from DartmoorDartmoorDartmoor is an area of moorland in south Devon, England. Protected by National Park status, it covers .The granite upland dates from the Carboniferous period of geological history. The moorland is capped with many exposed granite hilltops known as tors, providing habitats for Dartmoor wildlife. The...
to PlymouthPlymouthPlymouth is a city and unitary authority area on the coast of Devon, England, about south-west of London. It is built between the mouths of the rivers Plym to the east and Tamar to the west, where they join Plymouth Sound...
.
- Devonport LeatDevonport LeatThe Devonport Leat was a leat constructed in the 1790s to carry fresh drinking water from the high ground of Dartmoor to the expanding dockyards at Devonport, Devon, England. It is fed by three Dartmoor rivers: the West Dart, the Cowsic and the Blackabrook...
constructed in the late 18th century to carry water to the expanding naval dockyard at DevonportDevonport, DevonDevonport, formerly named Plymouth Dock or just Dock, is a district of Plymouth in the English county of Devon, although it was, at one time, the more important settlement. It became a county borough in 1889...
(now a part of Plymouth). - Many leats on Dartmoor, mostly constructed to provide power for mining activities, although some were also sources of drinking water. The courses of many Dartmoor leats may still be followed.
- Many leats used for tin mining are marked on the 1/50000 and 1/25000 Ordnance SurveyOrdnance SurveyOrdnance Survey , an executive agency and non-ministerial government department of the Government of the United Kingdom, is the national mapping agency for Great Britain, producing maps of Great Britain , and one of the world's largest producers of maps.The name reflects its creation together with...
maps, such as that serving the now-defunct Vitifer mine near the Warren House InnWarren House InnThe Warren House Inn is a remote and isolated public house in the heart of Dartmoor, Devon, England. It is the highest pub in southern England at 1,425 feet above sea level...
.
See also
- AcequiaAcequiaAn acequia or séquia is a community-operated waterway used in Spain and former Spanish colonies in the Americas for irrigation. Particularly in Spain, the Andes, northern Mexico, and the modern-day American Southwest, acequias are usually historically engineered canals that carry snow runoff or...
- AqueductAqueductAn aqueduct is a water supply or navigable channel constructed to convey water. In modern engineering, the term is used for any system of pipes, ditches, canals, tunnels, and other structures used for this purpose....
s - FlumeFlumeA flume is an open artificial water channel, in the form of a gravity chute, that leads water from a diversion dam or weir completely aside a natural flow. Often, the flume is an elevated box structure that follows the natural contours of the land. These have been extensively used in hydraulic...
- Roman aqueductRoman aqueductThe Romans constructed numerous aqueducts to serve any large city in their empire, as well as many small towns and industrial sites. The city of Rome had the largest concentration of aqueducts, with water being supplied by eleven aqueducts constructed over a period of about 500 years...
s - Roman engineeringRoman engineeringRomans are famous for their advanced engineering accomplishments, although some of their own inventions were improvements on older ideas, concepts and inventions. Technology for bringing running water into cities was developed in the east, but transformed by the Romans into a technology...
- Roman mining

