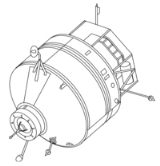
Kvant-1
Encyclopedia
Kvant-1 in 1995 |
|
| Module statistics | |
|---|---|
| Mission name | Mir Mir Mir was a space station operated in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001, at first by the Soviet Union and then by Russia. Assembled in orbit from 1986 to 1996, Mir was the first modular space station and had a greater mass than that of any previous spacecraft, holding the record for the... |
| Launch | March 31, 1987 00:06:16 UTC Coordinated Universal Time Coordinated Universal Time is the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time. It is one of several closely related successors to Greenwich Mean Time. Computer servers, online services and other entities that rely on having a universally accepted time use UTC for that purpose... LC-200/39 Baikonur Cosmodrome Site 200 Site 200 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome is a launch site used by Proton rockets. It consists of two launch pads, areas 39 and 40. Area 39 is currently used for Proton-M launches, including commercial flights conducted by International Launch Services. Area 40 is currently inactive, as it was slated to... , Baikonur Cosmodrome Baikonur Cosmodrome The Baikonur Cosmodrome , also called Tyuratam, is the world's first and largest operational space launch facility. It is located in the desert steppe of Kazakhstan, about east of the Aral Sea, north of the Syr Darya river, near Tyuratam railway station, at 90 meters above sea level... , USSR |
| Launch vehicle | Proton-K Proton-K The Proton-K, also designated Proton 8K82K after its GRAU index, 8K82K, is a Russian, previously Soviet, carrier rocket derived from the earlier Proton. It was built by Khrunichev, and is launched from sites 81 and 200 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan... |
| Docked | April 9, 1987 00:35:58 UTC Coordinated Universal Time Coordinated Universal Time is the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time. It is one of several closely related successors to Greenwich Mean Time. Computer servers, online services and other entities that rely on having a universally accepted time use UTC for that purpose... |
| Re-entry | March 23, 2001 05:50:00 UTC |
| Time in Orbit | 5106 days, 5 hours |
| Length | 5.3 m |
| Diameter | 4.35 m |
| Launch Mass (includes FSM): | 20,600 kg |
| Module Mass | 11,000 kg (at launch) |
| FSM Mass | 9,600 kg (at launch) |
| Habitable volume | 40 m3 |
Kvant-1 ' onMouseout='HidePop("27932")' href="/topics/English_language">English
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
: Quantum-I/1) (37KE) was the second module of the Soviet
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
space station
Space station
A space station is a spacecraft capable of supporting a crew which is designed to remain in space for an extended period of time, and to which other spacecraft can dock. A space station is distinguished from other spacecraft used for human spaceflight by its lack of major propulsion or landing...
Mir
Mir
Mir was a space station operated in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001, at first by the Soviet Union and then by Russia. Assembled in orbit from 1986 to 1996, Mir was the first modular space station and had a greater mass than that of any previous spacecraft, holding the record for the...
. It was the first addition to the Mir base block
Mir Core Module
Mir , DOS-7, was the first module of the Soviet/Russian Mir space station complex, in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001. Generally referred to as either the core module or base block, the module was launched on 20 February 1986 on a Proton-K rocket from LC-200/39 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome...
and contained scientific instruments for astrophysical observations and materials science experiments.
Kvant-1 conducted research into the physics of active galaxies, quasars and neutron stars. The module also supported biotechnology experiments in anti-viral preparations and fractions. Originally planned to dock with the Salyut 7
Salyut 7
Salyut 7 was a space station in low Earth orbit from April 1982 to February 1991. It was first manned in May 1982 with two crew via Soyuz T-5, and last visited in June 1986, by Soyuz T-15. Various crew and modules were used over its lifetime, including a total of 12 manned and 15 unmanned launches...
space station, Kvant-1 was the first, experimental version of a planned series of '37K' type modules with jettisonable TKS-E type propulsion module scheduled to be launched to Mir and on the Soviet Buran space shuttle
Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle was a manned orbital rocket and spacecraft system operated by NASA on 135 missions from 1981 to 2011. The system combined rocket launch, orbital spacecraft, and re-entry spaceplane with modular add-ons...
. The control system of Kvant-1 was developed by the NPO "Electropribor"
Khartron
JSC "Khartron" is a one of the leading design engineering bureaus of CIS , which develops and produces spacecraft control systems.- History and achievements :Khartron Corp...
(Kharkiv
Kharkiv
Kharkiv or Kharkov is the second-largest city in Ukraine.The city was founded in 1654 and was a major centre of Ukrainian culture in the Russian Empire. Kharkiv became the first city in Ukraine where the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic was proclaimed in December 1917 and Soviet government was...
, Ukraine
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia...
).
Background
The Kvant spacecraft represented the first use of a new kind of Soviet space station module, designated 37K. An order authorising the beginning of development was issued on 17 September 1979. The basic 37K design consisted of a 4.2 m diameter pressurised cylinder with a docking port at the forward end. It was not equipped with its own propulsion system. The original authorisation was for a total of eight 37K's of various configurations:- One experimental 37KE (using a surplus FGB module of the cancelled Chelomei TKS manned ferry as a tug) which would be docked to the front port of the Salyut 7 space station.
- Four 37KS modules for Mir. These would be delivered and docked to the station by a new lighter weight FGO tug.
- Three 37KB modules. These would be carried in the payload bay of the Buran space shuttle. They could remain attached to the bay or (modified to the 37KBI configuration) be docked to the Mir or Mir-2 space stations using the Buran manipulator arm.
The 37KE was designated Kvant and was equipped with an astrophysics payload. It also used the Salyut-5B digital flight control computer and Gyrodyne flywheel orientation system developed for Almaz
Almaz
The Almaz program was a series of military space stations launched by the Soviet Union under cover of the civilian Salyut DOS-17K program after 1971....
. As the module neared completion Salyut 7 experienced numerous technical problems and Kvant was retargeted for a docking with Mir. But at that time Mir was planned to be in a 65 degree orbit, and Kvant was 800 kg too heavy for the Proton launch vehicle to place in such an orbit. In January 1985 Mir was changed to a 51.6 degree orbit, which solved one problem. But now it was planned that Kvant would dock with the rear port of Mir, requiring the addition of lines to conduct rocket propellant from Progress tanker spacecraft to Mir's storage tanks. This increased weigh again, forcing the FGB to have its propellant load reduced to 60% in the high pressure tanks and empty low pressure tanks. Still, at 22,797 kg, Kvant was the heaviest payload ever lofted by Proton, requiring special custom modifications to its launch vehicle.
Launch and docking
Soyuz TM-2
-Mission parameters:*Mass: 7100 kg*Perigee: 341 km*Apogee: 365 km*Inclination: 51.6°*Period: 91.6 minutes-Mission highlights:...
was already docked to the station. The FSM carried out major maneuvers on April 2 and April 5. On April 9, Kvant-1 achieved a soft dock with the aft port on Mir. However, the spacecraft was not able to achieve a hard dock which meant that the two spacecraft were only loosely connected. In this configuration, Mir could not orient itself or else damage would occur. The crew conducted an emergency EVA
Extra-vehicular activity
Extra-vehicular activity is work done by an astronaut away from the Earth, and outside of a spacecraft. The term most commonly applies to an EVA made outside a craft orbiting Earth , but also applies to an EVA made on the surface of the Moon...
on April 11 to investigate the problem. The crew found a piece of debris, probably a trash bag, that was left by Progress 28. After removing it, Kvant-1 was finally able to achieve a hard dock with the station. The FSM was jettisoned, revealing Kvant-1's rear docking port, on April 12.
Description
Kvant-1 was originally intended to be launched and docked to Salyut 7Salyut 7
Salyut 7 was a space station in low Earth orbit from April 1982 to February 1991. It was first manned in May 1982 with two crew via Soyuz T-5, and last visited in June 1986, by Soyuz T-15. Various crew and modules were used over its lifetime, including a total of 12 manned and 15 unmanned launches...
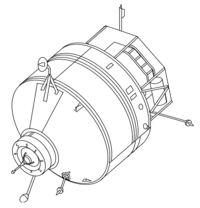
. But delays forced it to be launched to Mir instead. Kvant-1 consists of two pressurized working compartments and one unpressurized experiment compartment. Scientific equipment included an X-ray telescope, an ultraviolet telescope, a wide-angle camera, high-energy X-ray experiments, an X-ray/gamma ray detector, and the Svetlana electrophoresis unit.
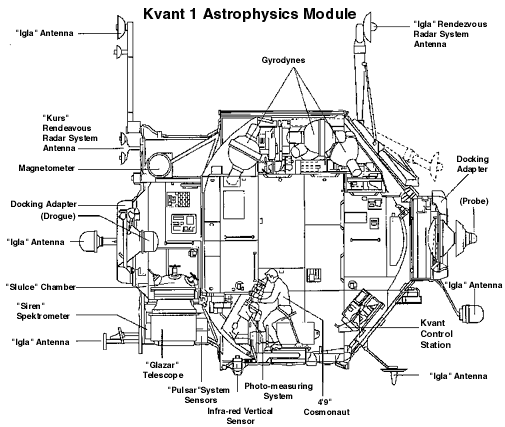
Gyroscope
A gyroscope is a device for measuring or maintaining orientation, based on the principles of angular momentum. In essence, a mechanical gyroscope is a spinning wheel or disk whose axle is free to take any orientation...
s which could be used to orient the station without using propellent. Kvant-1 also carried more life support systems including an Elektron oxygen generator and equipment for removing carbon dioxide from the air. Kvant-1 delivered an extra solar panel to the station which was deployed on the core module
Mir Core Module
Mir , DOS-7, was the first module of the Soviet/Russian Mir space station complex, in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001. Generally referred to as either the core module or base block, the module was launched on 20 February 1986 on a Proton-K rocket from LC-200/39 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome...
in June, 1987.
Kvant-1 did not have any propulsion systems. It was launched with a Functional Service Module (FSM) to act as a space tug to get Kvant-1 to Mir. The FSM carried propulsion and electrical systems. It was a modified version of the TKS spacecraft
TKS spacecraft
TKS spacecraft was a Soviet spacecraft design in the late 1960s intended to supply the military Almaz space station. The spacecraft was designed for manned or autonomous cargo resupply use...
. The TKS would later form the basis for the Kvant-2
Kvant-2
Kvant-2 was the third module and second major addition to the Mir space station. Its primary purpose was to deliver new science experiments, better life support systems, and an airlock to Mir. It was launched on November 26, 1989 on a Proton rocket. It docked to Mir on December 6...
, Kristall
Kristall
The Kristall module was the fourth module and the third major addition to the Mir space station. As with previous modules, its configuration was based on the 77K module, and was originally named "Kvant 3". It was launched on May 31, 1990 on a Proton rocket...
, Spektr
Spektr
Spektr was the fifth module of the Mir Space Station. The module was designed for remote observation of Earth's environment containing atmospheric and surface research equipment...
, and Priroda
Priroda
The Priroda module was the seventh and final module of the Mir Space Station. Its primary purpose was to conduct Earth resource experiments through remote sensing and to develop and verify remote sensing methods...
modules.
Later modifications
In January 1991, support structures that were designed to hold solar arrays were installed on Kvant-1. In July 1991, the crew constructed the Sofora girder during four EVAs. The Sofora girder was designed to test new construction techniques, mount a propulsion unit, and act as a place to hold experiments outside the station. In September, 1992, the crew installed the VDU propulsion unit on the end of the Sofora girder. It was delivered earlier by Progress M-14. The VDU was designed to increase the station's attitude control capability. In September 1993, the Rapana girder was constructed on Kvant-1 during two EVAs. The Rapana girder was designed to test girder assembly experiments for a possible Mir 2 space station. External experiments were also later held on the Rapana girder. On May 22, 1995, one of KristallKristall
The Kristall module was the fourth module and the third major addition to the Mir space station. As with previous modules, its configuration was based on the 77K module, and was originally named "Kvant 3". It was launched on May 31, 1990 on a Proton rocket...
's solar panels was re-deployed on Kvant-1. During May 1996, the Mir Cooperative Solar Array, which was delievered with the Mir Docking Module
Mir Docking Module
The Stykovochnyy Otsek , GRAU index 316GK, otherwise known as the Mir docking module or SO, was the sixth module of the Russian space station Mir, launched in November 1995 aboard the...
, was deployed on Kvant-1. In June, 1996, the Rapana girder was extended during an EVA. In November 1997, Kristall's old solar panel that was attached to Kvant-1 was disposed of and the all-Russian solar array, which was also delivered with the Docking Module, was attached in its place. In April 1998, the six-year-old VDU propulsion unit was replaced by a new one that was delivered by Progress M-38.
External links
- Russian Space Web
- Encyclopedia Astronautica
- Gunter's Space Page - information on Kvant-1

