
Kvant-2
Encyclopedia
Kvant-2 (77KSD, TsM-D, 11F77D) was the third module and second major addition to the Mir space station
. Its primary purpose was to deliver new science experiments, better life support systems, and an airlock to Mir. It was launched on November 26, 1989 on a Proton rocket
. It docked to Mir on December 6. Its control system has been designed by the NPO "Electropribor"
(Kharkiv
, Ukraine
).
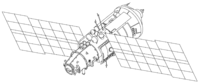
 Kvant-2 was the first Mir module based on the TKS spacecraft
Kvant-2 was the first Mir module based on the TKS spacecraft
. Kvant-2 was divided into three compartments. They were the EVA
airlock, the instrument/cargo compartment, and the instrument/experiment compartment. The instrument/cargo compartment could be sealed off and act as an extension or a back-up to the airlock. Before Kvant-2 docked to the station, EVAs had to be carried by depressurizing the docking node on the Core Module
. Kvant-2 also carried the Soviet version of the Manned Maneuvering Unit
for the Orlan space suit. It delievered the Salyut 5B computer which was an improvement over the Argon 16B computer already on the station. Kvant-2 had a system for regenerating water from urine and a shower for personal hygiene. It carried six gyrodines to augment those already located in Kvant-1
. Unlike Kvant-1, Kvant-2's gyrodines were only accessible from the exterior which turned out to make replacement of failed ones more difficult.
Scientific equipment on Kvant-2 included a high-resolution camera, spectrometers, X-ray sensors, the Volna 2 fluid flow experiment, and the Inkubator-2 unit which was used for hatching and raising quail
. A list of experiments and equipment follows:
Mir
Mir was a space station operated in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001, at first by the Soviet Union and then by Russia. Assembled in orbit from 1986 to 1996, Mir was the first modular space station and had a greater mass than that of any previous spacecraft, holding the record for the...
. Its primary purpose was to deliver new science experiments, better life support systems, and an airlock to Mir. It was launched on November 26, 1989 on a Proton rocket
Proton rocket
Proton is an expendable launch system used for both commercial and Russian government space launches. The first Proton rocket was launched in 1965 and the launch system is still in use as of 2011, which makes it one of the most successful heavy boosters in the history of spaceflight...
. It docked to Mir on December 6. Its control system has been designed by the NPO "Electropribor"
Khartron
JSC "Khartron" is a one of the leading design engineering bureaus of CIS , which develops and produces spacecraft control systems.- History and achievements :Khartron Corp...
(Kharkiv
Kharkiv
Kharkiv or Kharkov is the second-largest city in Ukraine.The city was founded in 1654 and was a major centre of Ukrainian culture in the Russian Empire. Kharkiv became the first city in Ukraine where the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic was proclaimed in December 1917 and Soviet government was...
, Ukraine
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia...
).
Specifications
- Length: 12.2 m
- Diameter: 4.35 m
- Mass: 19,640 kg
- Habitable volume: 61.9 m3
- Wingspan: 24 m
- Configuration: 77K (TKS) based module
Description


TKS spacecraft
TKS spacecraft was a Soviet spacecraft design in the late 1960s intended to supply the military Almaz space station. The spacecraft was designed for manned or autonomous cargo resupply use...
. Kvant-2 was divided into three compartments. They were the EVA
Extra-vehicular activity
Extra-vehicular activity is work done by an astronaut away from the Earth, and outside of a spacecraft. The term most commonly applies to an EVA made outside a craft orbiting Earth , but also applies to an EVA made on the surface of the Moon...
airlock, the instrument/cargo compartment, and the instrument/experiment compartment. The instrument/cargo compartment could be sealed off and act as an extension or a back-up to the airlock. Before Kvant-2 docked to the station, EVAs had to be carried by depressurizing the docking node on the Core Module
Mir Core Module
Mir , DOS-7, was the first module of the Soviet/Russian Mir space station complex, in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001. Generally referred to as either the core module or base block, the module was launched on 20 February 1986 on a Proton-K rocket from LC-200/39 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome...
. Kvant-2 also carried the Soviet version of the Manned Maneuvering Unit
Manned Maneuvering Unit
The Manned Maneuvering Unit is an astronaut propulsion unit which was used by NASA on three space shuttle missions in 1984. The MMU allowed the astronauts to perform untethered EVA spacewalks at a distance from the shuttle. The MMU was used in practice to retrieve a pair of faulty communications...
for the Orlan space suit. It delievered the Salyut 5B computer which was an improvement over the Argon 16B computer already on the station. Kvant-2 had a system for regenerating water from urine and a shower for personal hygiene. It carried six gyrodines to augment those already located in Kvant-1
Kvant-1
Kvant-1 was the second module of the Soviet space station Mir. It was the first addition to the Mir base block and contained scientific instruments for astrophysical observations and materials science experiments....
. Unlike Kvant-1, Kvant-2's gyrodines were only accessible from the exterior which turned out to make replacement of failed ones more difficult.
Scientific equipment on Kvant-2 included a high-resolution camera, spectrometers, X-ray sensors, the Volna 2 fluid flow experiment, and the Inkubator-2 unit which was used for hatching and raising quail
Quail
Quail is a collective name for several genera of mid-sized birds generally considered in the order Galliformes. Old World quail are found in the family Phasianidae, while New World quail are found in the family Odontophoridae...
. A list of experiments and equipment follows:
- ARIZ X-ray spectrometer
- ASPG-M scan platform carrying ITS-7D IR spectrometer (using the Czech sensor platform first used on Vega spacecraft).
- Cosmic dust detectors
- Gamma 2 spectrometer package
- Ikar EVA unit
- Inkubator 2 - bird egg incubator
- KAP-350 topographic camera
- MKF-6MA Earth resources film camera - 6 spectral bands. Provided by East Germany.
- MKS-M2 optical spectrometer
- Phaza AFM-2 spectrometer
- Spektr-256 spectrometer
- Sprut 5 charged particle spectrometer (installed 1991).
- TV cameras
- Volna 2 propellant tank demonstration (250kg)
External links
- Russian Space Web
- Encyclopedia Astronautica
- Gunter's Space Page - information on Kvant-2

