Ketogenic diet
Encyclopedia
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
, low-carbohydrate diet
Low-carbohydrate diet
Low-carbohydrate diets or low-carb diets are dietary programs that restrict carbohydrate consumption usually for weight control or for the treatment of obesity. Foods high in digestible carbohydrates are limited or replaced with foods containing a higher percentage of proteins and fats...
that in medicine is used primarily to treat difficult-to-control (refractory) epilepsy
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a common chronic neurological disorder characterized by seizures. These seizures are transient signs and/or symptoms of abnormal, excessive or hypersynchronous neuronal activity in the brain.About 50 million people worldwide have epilepsy, and nearly two out of every three new cases...
in children. The diet mimics aspects of starvation
Starvation
Starvation is a severe deficiency in caloric energy, nutrient and vitamin intake. It is the most extreme form of malnutrition. In humans, prolonged starvation can cause permanent organ damage and eventually, death...
by forcing the body to burn fats rather than carbohydrate
Carbohydrate
A carbohydrate is an organic compound with the empirical formula ; that is, consists only of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, with a hydrogen:oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 . However, there are exceptions to this. One common example would be deoxyribose, a component of DNA, which has the empirical...
s. Normally, the carbohydrates contained in food are converted into glucose
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar and an important carbohydrate in biology. Cells use it as the primary source of energy and a metabolic intermediate...
, which is then transported around the body and is particularly important in fuelling brain function. However, if there is very little carbohydrate in the diet, the liver
Liver
The liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
converts fat into fatty acid
Fatty acid
In chemistry, especially biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with a long unbranched aliphatic tail , which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have a chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are usually derived from...
s and ketone bodies
Ketone bodies
Ketone bodies are three water-soluble compounds that are produced as by-products when fatty acids are broken down for energy in the liver and kidney. They are used as a source of energy in the heart and brain. In the brain, they are a vital source of energy during fasting...
. The ketone bodies pass into the brain and replace glucose as an energy source. An elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood, a state known as ketosis
Ketosis
Ketosis is a state of elevated levels of ketone bodies in the body. It is almost always generalized throughout the body, with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when the liver glycogen stores are depleted...
, leads to a reduction in the frequency of epileptic seizures.
The original therapeutic diet for pediatric epilepsy provides just enough protein for body growth and repair, and sufficient calories
Food energy
Food energy is the amount of energy obtained from food that is available through cellular respiration.Food energy is expressed in food calories or kilojoules...
to maintain the correct weight for age and height. This classic ketogenic diet contains a 4:1 ratio by weight of fat to combined protein and carbohydrate. This is achieved by excluding high-carbohydrate foods such as starchy fruits and vegetables, bread, pasta, grains and sugar, while increasing the consumption of foods high in fat such as cream and butter.
Most dietary fat is made of molecules called long-chain triglycerides (LCTs). However, medium-chain triglycerides
Medium chain triglycerides
Medium-chain triglycerides are medium-chain fatty acid esters of glycerol.MCTs passively diffuse from the GI tract to the portal system without requirement for modification like long-chain fatty acids or very-long-chain fatty acids. In addition, MCTs do not require bile salts for digestion...
(MCTs)—made from fatty acids with shorter carbon chains than LCTs—are more ketogenic. A variant of the classic diet known as the MCT ketogenic diet uses a form of coconut oil
Coconut oil
Coconut oil is an edible oil extracted from the kernel or meat of matured coconuts harvested from the coconut palm . Throughout the tropical world, it has provided the primary source of fat in the diets of millions of people for generations. It has various applications in food, medicine, and industry...
, which is rich in MCTs, to provide around half the calories. As less overall fat is needed in this variant of the diet, a greater proportion of carbohydrate and protein can be consumed, allowing a greater variety of food choices.
The classic therapeutic ketogenic diet was developed for treatment of pediatric epilepsy in the 1920s and was widely used into the next decade, but its popularity waned with the introduction of effective anticonvulsant
Anticonvulsant
The anticonvulsants are a diverse group of pharmaceuticals used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of bipolar disorder, since many seem to act as mood stabilizers, and in the treatment of neuropathic pain. The goal of an...
drugs. In the mid 1990s, Hollywood producer Jim Abrahams
Jim Abrahams
Jim Abrahams is an American movie director and writer.Abrahams was born in Shorewood, Wisconsin, to a Jewish family, and attended Shorewood High School...
, whose son's severe epilepsy was effectively controlled by the diet, created the Charlie Foundation to promote it. Publicity included an appearance on NBC's Dateline
Dateline NBC
Dateline NBC, or Dateline, is a U.S. weekly television newsmagazine broadcast by NBC. It previously was NBC's flagship news magazine, but now focuses on true crime stories. It airs Friday at 9 p.m. EST and after football season on Sunday at 7 p.m. EST.-History:Dateline is historically notable for...
programme and ...First Do No Harm
...First Do No Harm
...First Do No Harm is a 1997 television film, directed by Jim Abrahams, about a boy whose severe epilepsy, unresponsive to medications with terrible side effects, is controlled by the ketogenic diet. Aspects of the story mirror Abrahams' own experience with his son Charlie.-Plot:The film tells a...
(1997), a made-for-television film
Television movie
A television film is a feature film that is a television program produced for and originally distributed by a television network, in contrast to...
starring Meryl Streep
Meryl Streep
Mary Louise "Meryl" Streep is an American actress who has worked in theatre, television and film.Streep made her professional stage debut in 1971's The Playboy of Seville, before her screen debut in the television movie The Deadliest Season in 1977. In that same year, she made her film debut with...
. The foundation sponsored a multicentre research study, the results of which—announced in 1996—marked the beginning of renewed scientific interest in the diet.
The diet is effective in half of the patients who try it, and very effective in one third of patients. In 2008, a randomised controlled trial showed a clear benefit for treating refractory epilepsy in children with the ketogenic diet. A treatment of 6 to 24 months duration frequently results in a ≥ 90% decrease or elimination of seizures.
There is some evidence that adults with epilepsy may benefit from the diet, and that a less strict regime, such as a modified Atkins diet, is similarly effective. Clinical trials and studies in animal models suggest that ketogenic diets provide neuroprotective and disease-modifying benefits for a number of adult neurodegenerative disorders. As of 2008, research in this area is regarded as having provided insufficient positive data to warrant clinical use.
Epilepsy
EpilepsyEpilepsy
Epilepsy is a common chronic neurological disorder characterized by seizures. These seizures are transient signs and/or symptoms of abnormal, excessive or hypersynchronous neuronal activity in the brain.About 50 million people worldwide have epilepsy, and nearly two out of every three new cases...
is one of the most common neurological
Neurology
Neurology is a medical specialty dealing with disorders of the nervous system. Specifically, it deals with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of disease involving the central, peripheral, and autonomic nervous systems, including their coverings, blood vessels, and all effector tissue,...
disorders after stroke
Stroke
A stroke, previously known medically as a cerebrovascular accident , is the rapidly developing loss of brain function due to disturbance in the blood supply to the brain. This can be due to ischemia caused by blockage , or a hemorrhage...
, and affects at least 50 million people worldwide. It is diagnosed in a person having recurrent unprovoked seizure
Seizure
An epileptic seizure, occasionally referred to as a fit, is defined as a transient symptom of "abnormal excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain". The outward effect can be as dramatic as a wild thrashing movement or as mild as a brief loss of awareness...
s. These occur when cortical
Cortex (anatomy)
In anatomy and zoology the cortex is the outermost layer of an organ. Organs with well-defined cortical layers include kidneys, adrenal glands, ovaries, the thymus, and portions of the brain, including the cerebral cortex, the most well-known of all cortices.The cerebellar cortex is the thin gray...
neuron
Neuron
A neuron is an electrically excitable cell that processes and transmits information by electrical and chemical signaling. Chemical signaling occurs via synapses, specialized connections with other cells. Neurons connect to each other to form networks. Neurons are the core components of the nervous...
s fire excessively, hypersynchronously, or both, leading to temporary disruption of normal brain function. This might affect, for example, the muscles, the senses, consciousness, or a combination. A seizure can be focal (confined to one part of the brain) or generalised (spread widely throughout the brain and leading to a loss of consciousness). Epilepsy may occur for a variety of reasons; some forms have been classified into epileptic syndrome
Syndrome
In medicine and psychology, a syndrome is the association of several clinically recognizable features, signs , symptoms , phenomena or characteristics that often occur together, so that the presence of one or more features alerts the physician to the possible presence of the others...
s, most of which begin in childhood. Epilepsy is considered refractory to treatment when two or three anticonvulsant
Anticonvulsant
The anticonvulsants are a diverse group of pharmaceuticals used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of bipolar disorder, since many seem to act as mood stabilizers, and in the treatment of neuropathic pain. The goal of an...
drugs have failed to control it. About 60% of patients will achieve control of their epilepsy with the first drug they use, whereas about 30% do not achieve control with drugs. When drugs fail, other options include epilepsy surgery
Epilepsy surgery
Approximately 60% of all patients with epilepsy suffer from focal epilepsy syndromes. In 15 to 20% of these patients, the condition is not adequately controlled with anticonvulsive drugs. Such patients are potential candidates for surgical epilepsy treatment...
, vagus nerve stimulation
Vagus nerve stimulation
Vagus nerve stimulation is an adjunctive treatment for certain types of intractable epilepsy and treatment-resistant depression.- Mechanism of action :...
and the ketogenic diet.
History
The ketogenic diet is a mainstream, nonpharmacologic therapy that was developed to reproduce the success and remove the limitations of the non-mainstream use of fastingFasting
Fasting is primarily the act of willingly abstaining from some or all food, drink, or both, for a period of time. An absolute fast is normally defined as abstinence from all food and liquid for a defined period, usually a single day , or several days. Other fasts may be only partially restrictive,...
to treat epilepsy
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a common chronic neurological disorder characterized by seizures. These seizures are transient signs and/or symptoms of abnormal, excessive or hypersynchronous neuronal activity in the brain.About 50 million people worldwide have epilepsy, and nearly two out of every three new cases...
. Although popular in the 1920s and 30s, it was largely abandoned in favour of new anticonvulsant
Anticonvulsant
The anticonvulsants are a diverse group of pharmaceuticals used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of bipolar disorder, since many seem to act as mood stabilizers, and in the treatment of neuropathic pain. The goal of an...
drugs. Most individuals with epilepsy can successfully control their seizures with medication. However, 20–30% fail to achieve such control despite trying a number of different drugs. For this group, and for children in particular, the diet has once again found a role in epilepsy management.
Fasting

Hippocratic Corpus
The Hippocratic Corpus , or Hippocratic Collection, is a collection of around 60 early Ancient Greek medical works strongly associated with the physician Hippocrates and his teachings...
, On the Sacred Disease, mentions the disease; it dates from . Its author argued against the prevailing view that epilepsy was supernatural in origin and cure, and proposed that dietary therapy had a rational and physical basis. In the same collection, the author of Epidemics describes the case of a man whose epilepsy is cured as quickly as it had appeared, through complete abstinence of food and drink. The royal physician Erasistratus
Erasistratus
Erasistratus was a Greek anatomist and royal physician under Seleucus I Nicator of Syria. Along with fellow physician Herophilus, he founded a school of anatomy in Alexandria, where they carried out anatomical research...
declared, "One inclining to epilepsy should be made to fast without mercy and be put on short rations." Galen
Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus , better known as Galen of Pergamon , was a prominent Roman physician, surgeon and philosopher...
believed an "attenuating diet" might afford a cure in mild cases and be helpful in others.
The first modern study of fasting as a treatment for epilepsy was in France in 1911. Twenty epilepsy patients of all ages were "detoxified" by consuming a low-calorie vegetarian diet, combined with periods of fasting and purging. Two benefited enormously, but most failed to maintain compliance with the imposed restrictions. The diet improved the patients' mental capabilities, in contrast to their medication, potassium bromide
Potassium bromide
Potassium bromide is a salt, widely used as an anticonvulsant and a sedative in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with over-the-counter use extending to 1975 in the United States. Its action is due to the bromide ion...
, which dulled the mind.
Around this time, Bernarr Macfadden
Bernarr Macfadden
Bernarr Macfadden was an influential American proponent of physical culture, a combination of bodybuilding with nutritional and health theories...
, an American exponent of physical culture
Physical culture
Physical culture is a term applied to health and strength training regimens, particularly those that originated during the 19th century. During the mid-late 20th century, the term "physical culture" became largely outmoded in most English-speaking countries, being replaced by terms such as...
, popularised the use of fasting to restore health. His disciple, the osteopathic physician Hugh Conklin, of Battle Creek, Michigan
Battle Creek, Michigan
Battle Creek is a city in the U.S. state of Michigan, in northwest Calhoun County, at the confluence of the Kalamazoo and Battle Creek Rivers. It is the principal city of the Battle Creek, Michigan Metropolitan Statistical Area , which encompasses all of Calhoun county...
, began to treat his epilepsy patients by recommending fasting. Conklin conjectured that epileptic seizures were caused when a toxin, secreted from the Peyer's patches in the intestines, was discharged into the bloodstream. He recommended a fast lasting 18 to 25 days to allow this toxin to dissipate. Conklin probably treated hundreds of epilepsy patients with his "water diet" and boasted of a 90% cure rate in children, falling to 50% in adults. Later analysis of Conklin's case records showed 20% of his patients achieved freedom from seizures and 50% had some improvement.
Conklin's fasting therapy was adopted by neurologists
Neurology
Neurology is a medical specialty dealing with disorders of the nervous system. Specifically, it deals with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of disease involving the central, peripheral, and autonomic nervous systems, including their coverings, blood vessels, and all effector tissue,...
in mainstream practice. In 1916, a Dr McMurray wrote to the New York Medical Journal claiming to have successfully treated epilepsy patients with a fast, followed by a starch- and sugar-free diet, since 1912. In 1921, prominent endocrinologist
Endocrinology
Endocrinology is a branch of biology and medicine dealing with the endocrine system, its diseases, and its specific secretions called hormones, the integration of developmental events such as proliferation, growth, and differentiation and the coordination of...
H. Rawle Geyelin reported his experiences to the American Medical Association
American Medical Association
The American Medical Association , founded in 1847 and incorporated in 1897, is the largest association of medical doctors and medical students in the United States.-Scope and operations:...
convention. He had seen Conklin's success first-hand and had attempted to reproduce the results in 36 of his own patients. He achieved similar results despite only having studied the patients for a short time. Further studies in the 1920s indicated that seizures generally returned after the fast. Charles Howland, the parent of one of Conklin's successful patients and a wealthy New York corporate lawyer, gave his brother John a gift of $5,000 to study "the ketosis of starvation". As professor of paediatrics at Johns Hopkins Hospital
Johns Hopkins Hospital
The Johns Hopkins Hospital is the teaching hospital and biomedical research facility of Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, located in Baltimore, Maryland . It was founded using money from a bequest by philanthropist Johns Hopkins...
, John Howland used the money to fund research undertaken by neurologist Stanley Cobb
Stanley Cobb
-External links:* can be found at The Center for the History of Medicine at the Countway Library, Harvard Medical School....
and his assistant William G. Lennox
William G. Lennox
William Gordon Lennox was an American neurologist who was a pioneer in the use of electroencephalography for the diagnosis and treatment of epilepsy.-Biography:...
.
Diet
In 1921, Rollin Woodyatt reviewed the research on diet and diabetes. He reported that three water-soluble compounds, β-hydroxybutyrate, acetoacetate and acetoneAcetone
Acetone is the organic compound with the formula 2CO, a colorless, mobile, flammable liquid, the simplest example of the ketones.Acetone is miscible with water and serves as an important solvent in its own right, typically as the solvent of choice for cleaning purposes in the laboratory...
(known collectively as ketone bodies
Ketone bodies
Ketone bodies are three water-soluble compounds that are produced as by-products when fatty acids are broken down for energy in the liver and kidney. They are used as a source of energy in the heart and brain. In the brain, they are a vital source of energy during fasting...
), were produced by the liver in otherwise healthy people when they were starved or if they consumed a very low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet. Russel Wilder, at the Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic is a not-for-profit medical practice and medical research group specializing in treating difficult patients . Patients are referred to Mayo Clinic from across the U.S. and the world, and it is known for innovative and effective treatments. Mayo Clinic is known for being at the top of...
, built on this research and coined the term ketogenic diet to describe a diet that produced a high level of ketones in the blood (ketonemia) through an excess of fat and lack of carbohydrate. Wilder hoped to obtain the benefits of fasting in a dietary therapy that could be maintained indefinitely. His trial on a few epilepsy patients in 1921 was the first use of the ketogenic diet as a treatment for epilepsy.
Wilder's colleague, paediatrician Mynie Peterman, later formulated the classic diet, with a ratio of one gram of protein per kilogram of body weight in children, 10–15 g of carbohydrate per day, and the remainder of calories from fat. Peterman's work in the 1920s established the techniques for induction and maintenance of the diet. Peterman documented positive effects (improved alertness, behaviour, and sleep) and adverse effects (nausea and vomiting due to excess ketosis). The diet proved to be very successful in children: Peterman reported in 1925 that 95% of 37 young patients had improved seizure control on the diet and 60% became seizure-free. By 1930, the diet had also been studied in 100 teenagers and adults. Clifford Barborka, also from the Mayo Clinic, reported that 56% of those older patients improved on the diet and 12% became seizure-free. Although the adult results are similar to modern studies of children, they did not compare as well to contemporary studies. Barborka concluded that adults were least likely to benefit from the diet, and the use of the ketogenic diet in adults was not studied again until 1999.
Anticonvulsants and decline
During the 1920s and 1930s, when the only anticonvulsant drugs were the sedative bromidesPotassium bromide
Potassium bromide is a salt, widely used as an anticonvulsant and a sedative in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with over-the-counter use extending to 1975 in the United States. Its action is due to the bromide ion...
(discovered 1857) and phenobarbital
Phenobarbital
Phenobarbital or phenobarbitone is a barbiturate, first marketed as Luminal by Friedr. Bayer et comp. It is the most widely used anticonvulsant worldwide, and the oldest still commonly used. It also has sedative and hypnotic properties but, as with other barbiturates, has been superseded by the...
(1912), the ketogenic diet was widely used and studied. This changed in 1938 when H. Houston Merritt
H. Houston Merritt
H. Houston Merritt was one of the pre-eminent academic neurologists of his day. As the chair of the Neurological Institute of New York from 1948 to 1967, he oversaw the training of hundreds of neurologists; 35 of his former students have become chairs of academic neurology departments across the...
and Tracy Putnam discovered phenytoin
Phenytoin
Phenytoin sodium is a commonly used antiepileptic. Phenytoin acts to suppress the abnormal brain activity seen in seizure by reducing electrical conductance among brain cells by stabilizing the inactive state of voltage-gated sodium channels...
(Dilantin), and the focus of research shifted to discovering new drugs. With the introduction of sodium valproate
Sodium valproate
Sodium valproate or valproate sodium is the sodium salt of valproic acid and is an anticonvulsant used in the treatment of epilepsy, anorexia nervosa, panic attack, anxiety disorder, posttraumatic stress disorder, migraine and bipolar disorder, as well as other psychiatric conditions requiring...
in the 1970s, drugs were available to neurologists that were effective across a broad range of epileptic syndromes and seizure types. The use of the ketogenic diet, by this time restricted to difficult cases such as Lennox–Gastaut syndrome, declined further.
MCT diet
In the 1960s, it was discovered that medium-chain triglyceridesMedium chain triglycerides
Medium-chain triglycerides are medium-chain fatty acid esters of glycerol.MCTs passively diffuse from the GI tract to the portal system without requirement for modification like long-chain fatty acids or very-long-chain fatty acids. In addition, MCTs do not require bile salts for digestion...
(MCTs) produce more ketones per unit of energy than normal dietary fats (which are mostly long-chain triglycerides). MCTs are more efficiently absorbed and are rapidly transported to the liver via the hepatic portal system rather than the lymphatic system
Lymphatic system
The lymphoid system is the part of the immune system comprising a network of conduits called lymphatic vessels that carry a clear fluid called lymph unidirectionally toward the heart. Lymphoid tissue is found in many organs, particularly the lymph nodes, and in the lymphoid follicles associated...
. The severe carbohydrate restrictions of the classic ketogenic diet made it difficult for parents to produce palatable meals that their children would tolerate. In 1971, Peter Huttenlocher devised a ketogenic diet where about 60% of the calories came from the MCT oil, and this allowed more protein and up to three times as much carbohydrate as the classic ketogenic diet. The oil was mixed with at least twice its volume of skimmed milk, chilled, and sipped during the meal or incorporated into food. He tested it on twelve children and adolescents with intractable seizures. Most children improved in both seizure control and alertness, results that were similar to the classic ketogenic diet. Gastrointestinal upset was a problem, which led one patient to abandon the diet, but meals were easier to prepare and better accepted by the children. The MCT diet replaced the classic ketogenic diet in many hospitals, though some devised diets that were a combination of the two.
Revival
The ketogenic diet achieved national media exposure in the US in October 1994, when NBC's DatelineDateline NBC
Dateline NBC, or Dateline, is a U.S. weekly television newsmagazine broadcast by NBC. It previously was NBC's flagship news magazine, but now focuses on true crime stories. It airs Friday at 9 p.m. EST and after football season on Sunday at 7 p.m. EST.-History:Dateline is historically notable for...
television programme reported the case of Charlie Abrahams, son of Hollywood producer Jim Abrahams
Jim Abrahams
Jim Abrahams is an American movie director and writer.Abrahams was born in Shorewood, Wisconsin, to a Jewish family, and attended Shorewood High School...
. The two-year-old suffered from epilepsy that had remained uncontrolled by mainstream and alternative therapies. Abrahams discovered a reference to the ketogenic diet in an epilepsy guide for parents and brought Charlie to the Johns Hopkins Hospital, which had continued to offer the therapy. Under the diet, Charlie's epilepsy was rapidly controlled and his developmental progress resumed. This inspired Abrahams to create the Charlie Foundation to promote the diet and fund research. A multicentre prospective study began in 1994, the results were presented to the American Epilepsy Society in 1996 and were published in 1998. There followed an explosion of scientific interest in the diet. In 1997, Abrahams produced a TV movie, ...First Do No Harm
...First Do No Harm
...First Do No Harm is a 1997 television film, directed by Jim Abrahams, about a boy whose severe epilepsy, unresponsive to medications with terrible side effects, is controlled by the ketogenic diet. Aspects of the story mirror Abrahams' own experience with his son Charlie.-Plot:The film tells a...
, starring Meryl Streep
Meryl Streep
Mary Louise "Meryl" Streep is an American actress who has worked in theatre, television and film.Streep made her professional stage debut in 1971's The Playboy of Seville, before her screen debut in the television movie The Deadliest Season in 1977. In that same year, she made her film debut with...
, in which a young boy's intractable epilepsy is successfully treated by the ketogenic diet.
As of 2007, the ketogenic diet is available from around 75 centres in 45 countries. Less restrictive variants, such as the modified Atkins diet, have come into use, particularly among older children and adults. The ketogenic diet is also under investigation for the treatment of a wide variety of disorders other than epilepsy.
Efficacy
The ketogenic diet reduces seizure frequency by more than 50% in half of the patients who try it and by more than 90% in a third of patients. Three-quarters of children who respond do so within two weeks, though experts recommend a trial of at least three months before assuming it has been ineffective. Children with refractory epilepsy are more likely to find the ketogenic diet to be effective than to benefit from trying another anticonvulsant drug. There is some evidence that adolescents and adults may also benefit from the diet.Trial design
Early studies reported high success rates: in one study in 1925, 60% of patients became seizure-free, and another 35% of patients had a 50% reduction in seizure frequency. These studies generally examined a cohortCohort study
A cohort study or panel study is a form of longitudinal study used in medicine, social science, actuarial science, and ecology. It is an analysis of risk factors and follows a group of people who do not have the disease, and uses correlations to determine the absolute risk of subject contraction...
of patients recently treated by the physician (what is known as a retrospective study) and selected patients who had successfully maintained the dietary restrictions. However, these studies are difficult to compare to modern trials. One reason is that these older trials suffered from selection bias
Selection bias
Selection bias is a statistical bias in which there is an error in choosing the individuals or groups to take part in a scientific study. It is sometimes referred to as the selection effect. The term "selection bias" most often refers to the distortion of a statistical analysis, resulting from the...
, as they excluded patients who were unable to start or maintain the diet and thereby selected from patients who would generate better results. In an attempt to control for this bias, modern study design prefers a prospective cohort
Prospective cohort study
A prospective cohort study is a cohort study that follows over time a group of similar individuals who differ with respect to certain factors under study, to determine how these factors affect rates of a certain outcome...
(the patients in the study are chosen before therapy begins) in which the results are presented for all patients regardless of whether they started or completed the treatment (known as intent-to-treat analysis
Intention to treat analysis
In epidemiology, an intention to treat analysis is an analysis based on the initial treatment intent, not on the treatment eventually administered. ITT analysis is intended to avoid various misleading artifacts that can arise in intervention research...
).
Another difference between older and newer studies is that the type of patients treated with the ketogenic diet has changed over time. When first developed and used, the ketogenic diet was not a treatment of last resort; in contrast, the children in modern studies have already tried and failed a number of anticonvulsant drugs, so may be assumed to have more difficult-to-treat epilepsy. Early and modern studies also differ because the treatment protocol
Protocol (natural sciences)
In the natural sciences a protocol is a predefined written procedural method in the design and implementation of experiments. Protocols are written whenever it is desirable to standardize a laboratory method to ensure successful replication of results by others in the same laboratory or by other...
has changed. In older protocols, the diet was initiated with a prolonged fast
Fasting
Fasting is primarily the act of willingly abstaining from some or all food, drink, or both, for a period of time. An absolute fast is normally defined as abstinence from all food and liquid for a defined period, usually a single day , or several days. Other fasts may be only partially restrictive,...
, designed to lose 5–10% body weight
Body weight
The term body weight is used in daily English speech as well as in the contexts of biological and medical sciences to describe the mass of an organism's body. Body weight is measured in kilograms throughout the world, although in some countries it is still measured in pounds or stones and pounds...
, and heavily restricted the calorie intake. Concerns over child health and growth led to a relaxation of the diet's restrictions. Fluid restriction was once a feature of the diet, but this led to increased risk of constipation and kidney stones, and is no longer considered beneficial.
Outcomes
The largest modern study with an intent-to-treat prospective design was published in 1998 by a team from the Johns Hopkins HospitalJohns Hopkins Hospital
The Johns Hopkins Hospital is the teaching hospital and biomedical research facility of Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, located in Baltimore, Maryland . It was founded using money from a bequest by philanthropist Johns Hopkins...
and followed-up by a report published in 2001. As with most studies of the ketogenic diet, there was no control group (patients who did not receive the treatment). The study enrolled 150 children. After three months, 83% of them were still on the diet, 26% had experienced a good reduction in seizures, 31% had had an excellent reduction and 3% were seizure-free. At twelve months, 55% were still on the diet, 23% had a good response, 20% had an excellent response and 7% were seizure-free. Those who had discontinued the diet by this stage did so because it was ineffective, too restrictive or due to illness, and most of those who remained were benefiting from it. The percentage of those still on the diet at two, three and four years was 39%, 20% and 12% respectively. During this period the most common reason for discontinuing the diet was because the children had become seizure-free or significantly better. At four years, 16% of the original 150 children had a good reduction in seizure frequency, 14% had an excellent reduction and 13% were seizure-free, though these figures include many who were no longer on the diet. Those remaining on the diet after this duration were typically not seizure-free but had had an excellent response.
It is possible to combine the results of several small studies to produce evidence that is stronger than that available from each study alone—a statistical method known as meta-analysis
Meta-analysis
In statistics, a meta-analysis combines the results of several studies that address a set of related research hypotheses. In its simplest form, this is normally by identification of a common measure of effect size, for which a weighted average might be the output of a meta-analyses. Here the...
. One of four such analyses, conducted in 2006, looked at 19 studies on a total of 1,084 patients. It concluded that half the patients achieved a 50% reduction in seizures and a third achieved a 90% reduction.
The first randomised controlled trial was published in 2008, which had an intent-to-treat prospective design, but no blinding. This study enrolled 145 children, half of whom were randomly selected to start the ketogenic diet immediately and half to start after a three-month delay. The children who received delayed treatment acted as a control, which is particularly important for medical conditions such as epilepsy where patients may get better or worse regardless of treatment. Of the children in the diet group, 38% had at least a 50% reduction in seizure frequency, 7% had at least a 90% reduction, and one child became seizure-free. Only 6% of the control group saw a greater than 50% reduction in seizure frequency and no children had a 90% reduction. The mean
Arithmetic mean
In mathematics and statistics, the arithmetic mean, often referred to as simply the mean or average when the context is clear, is a method to derive the central tendency of a sample space...
seizure frequency of the diet group fell by a third; the control group's mean seizure frequency actually got worse.
Indications and contra-indications
The ketogenic diet is indicated as an adjunctive (additional) treatment in children with drug-resistant epilepsy. It is approved by national clinical guidelines in Scotland, England and Wales and reimbursed by nearly all US insurance companies. Children with a focal lesionLesion
A lesion is any abnormality in the tissue of an organism , usually caused by disease or trauma. Lesion is derived from the Latin word laesio which means injury.- Types :...
(a single point of brain abnormality causing the epilepsy) who would make suitable candidates for surgery
Epilepsy surgery
Approximately 60% of all patients with epilepsy suffer from focal epilepsy syndromes. In 15 to 20% of these patients, the condition is not adequately controlled with anticonvulsive drugs. Such patients are potential candidates for surgical epilepsy treatment...
are more likely to become seizure-free with surgery than with the ketogenic diet. In the UK, the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
The National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence is a special health authority of the English National Health Service , serving both English NHS and the Welsh NHS...
advises that the diet should not be recommended for adults with epilepsy. About a third of epilepsy centres that offer the ketogenic diet also offer a dietary therapy to adults. Some clinicians consider the two less restrictive dietary variants—the low glycemic index treatment and the modified Atkins diet—to be more appropriate for adolescents and adults. A liquid form of the ketogenic diet is particularly easy to prepare for, and well tolerated by, infants on formula and children who are tube-fed
Feeding tube
A feeding tube is a medical device used to provide nutrition to patients who cannot obtain nutrition by swallowing. The state of being fed by a feeding tube is called gavage, enteral feeding or tube feeding...
.
Advocates for the diet recommend that it be seriously considered after two medications have failed, as the chance of other drugs succeeding is only 10%. The diet can be considered earlier for some epilepsy and genetic syndromes where it has shown particular usefulness. These include Dravet syndrome, infantile spasms, myoclonic-astatic epilepsy and tuberous sclerosis complex.
A survey in 2005 of 88 paediatric neurologists in the US found that 36% regularly prescribed the diet after three or more drugs had failed; 24% occasionally prescribed the diet as a last resort; 24% had only prescribed the diet in a few rare cases; and 16% had never prescribed the diet. There are several possible explanations for this gap between evidence
Evidence-based medicine
Evidence-based medicine or evidence-based practice aims to apply the best available evidence gained from the scientific method to clinical decision making. It seeks to assess the strength of evidence of the risks and benefits of treatments and diagnostic tests...
and clinical practice. One major factor may be the lack of adequately trained dietitian
Dietitian
Dietitians supervise the preparation and service of food, develop modified diets, participate in research, and educate individuals and groups on good nutritional habits. The goals of dietitians are to provide medical nutritional intervention, and to obtain, safely prepare, serve and advise on...
s, who are needed to administer a ketogenic diet programme.
Because the ketogenic diet alters the body's metabolism, it is a first-line therapy in children with certain congenital metabolic diseases. However, it is absolutely contraindicated
Contraindication
In medicine, a contraindication is a condition or factor that serves as a reason to withhold a certain medical treatment.Some contraindications are absolute, meaning that there are no reasonable circumstances for undertaking a course of action...
in others. The diseases pyruvate dehydrogenase (E1) deficiency
Pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Deficiency is a genetic disease that involves human metabolism.-Inheritance and pathophysiology:It most commonly follows an X-linked inheritance pattern, but is approximately equally prevalent in both males and females. This is because heterozygote females commonly manifest...
and glucose transporter 1 deficiency syndrome
De Vivo disease
De Vivo disease is an autosomal dominant developmental disorder associated with a deficiency of GLUT1 also known as Glucose transporter type 1 deficiency syndrome -Presentation:...
prevent the body from using carbohydrates as fuel, which leads to a dependency on ketone bodies. The ketogenic diet is beneficial in treating the seizures and some other symptoms in these diseases and is an absolute indication. In contrast, the diseases pyruvate carboxylase deficiency
Pyruvate carboxylase deficiency
Pyruvate carboxylase deficiency is an inherited disorder that causes lactic acid and other potentially toxic compounds to accumulate in the blood. High levels of these substances can damage the body's organs and tissues, particularly in the nervous system. Pyruvate carboxylase deficiency is a rare...
, porphyria
Porphyria
Porphyrias are a group of inherited or acquired disorders of certain enzymes in the heme bio-synthetic pathway . They are broadly classified as acute porphyrias and cutaneous porphyrias, based on the site of the overproduction and accumulation of the porphyrins...
and other rare genetic disorders of fat metabolism prevent any use of the diet. A person with a disorder of fatty acid oxidation is unable to metabolise fatty acids, which replace carbohydrates as the major energy source on the diet. On the ketogenic diet, their body would consume its own protein stores for fuel, leading to acidosis
Acidosis
Acidosis is an increased acidity in the blood and other body tissue . If not further qualified, it usually refers to acidity of the blood plasma....
, and eventually coma and death.
Interactions
The ketogenic diet is usually initiated in combination with the patient's existing anticonvulsant regime, though patients may be weaned off anticonvulsants if the diet is successful. There is some evidence of synergistic benefits when the diet is combined with the vagus nerve stimulatorVagus nerve stimulation
Vagus nerve stimulation is an adjunctive treatment for certain types of intractable epilepsy and treatment-resistant depression.- Mechanism of action :...
or with the drug zonisamide
Zonisamide
Zonisamide is a sulfonamide anticonvulsant approved for use as an adjunctive therapy in adults with partial-onset seizures for adults; infantile spasm, mixed seizure types of Lennox-Gastaut syndrome, myoclonic, and generalized tonic clonic seizure.-History:...
, and that the diet may be less successful in children receiving phenobarbital
Phenobarbital
Phenobarbital or phenobarbitone is a barbiturate, first marketed as Luminal by Friedr. Bayer et comp. It is the most widely used anticonvulsant worldwide, and the oldest still commonly used. It also has sedative and hypnotic properties but, as with other barbiturates, has been superseded by the...
.
Adverse effects
The ketogenic diet is not a benign, holistic or natural treatment for epilepsy; as with any serious medical therapy, there may be complications. These are generally less severe and less frequent than with anticonvulsant medication or surgery. Common but easily treatable short-term side effects include constipationConstipation
Constipation refers to bowel movements that are infrequent or hard to pass. Constipation is a common cause of painful defecation...
, low-grade acidosis
Acidosis
Acidosis is an increased acidity in the blood and other body tissue . If not further qualified, it usually refers to acidity of the blood plasma....
, and hypoglycaemia if there is an initial fast. Cholesterol may increase
Hypercholesterolemia
Hypercholesterolemia is the presence of high levels of cholesterol in the blood. It is not a disease but a metabolic derangement that can be caused by many diseases, notably cardiovascular disease...
by around 30%. Long-term use of the ketogenic diet in children increases the risk of retarded growth, bone fractures, and kidney stone
Kidney stone
A kidney stone, also known as a renal calculus is a solid concretion or crystal aggregation formed in the kidneys from dietary minerals in the urine...
s. Supplements are necessary to counter the dietary deficiency of many micronutrient
Micronutrient
Micronutrients are nutrients required by humans and other living things throughout life in small quantities to orchestrate a whole range of physiological functions, but which the organism itself cannot produce. For people, they include dietary trace minerals in amounts generally less than 100...
s.
About 1 in 20 children on the ketogenic diet will develop kidney stones (compared with one in several thousand for the general population). A class of anticonvulsants known as carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are a class of pharmaceuticals that suppress the activity of carbonic anhydrase. Their clinical use has been established as antiglaucoma agents, diuretics, antiepileptics, in the management of mountain sickness, gastric and duodenal ulcers, neurological disorders, or...
(topiramate
Topiramate
Topiramate is an anticonvulsant drug. It was originally produced by Ortho-McNeil Neurologics and Noramco, Inc., both divisions of the Johnson & Johnson Corporation. This medication was discovered in 1979 by Bruce E. Maryanoff and Joseph F. Gardocki during their research work at McNeil...
, zonisamide
Zonisamide
Zonisamide is a sulfonamide anticonvulsant approved for use as an adjunctive therapy in adults with partial-onset seizures for adults; infantile spasm, mixed seizure types of Lennox-Gastaut syndrome, myoclonic, and generalized tonic clonic seizure.-History:...
) are known to increase the risk of kidney stones, but the combination of these anticonvulsants and the ketogenic diet does not appear to elevate the risk above that of the diet alone. The stones are treatable and do not justify discontinuation of the diet. Johns Hopkins Hospital now gives oral potassium citrate
Potassium citrate
Potassium citrate is a potassium salt of citric acid with the molecular formula C6H5K3O7. It is a white, slightly hygroscopic crystalline powder. It is odorless with a saline taste....
supplements to all ketogenic diet patients, resulting in a sevenfold decrease in the incidence of kidney stones. However, this empiric usage has not been tested in a prospective controlled trial. Kidney stone formation (nephrolithiasis) is associated with the diet for four reasons:
- Excess calcium in the urine (hypercalciuriaHypercalciuriaHypercalciuria or hypercalcinuria is the condition of elevated calcium in the urine. Chronic hypercalcinuria may lead to impairment of renal function, nephrocalcinosis, and renal insufficiency....
) occurs due to increased bone demineralisation with acidosis. Bones are mainly composed of calcium phosphateCalcium phosphateCalcium phosphate is the name given to a family of minerals containing calcium ions together with orthophosphates , metaphosphates or pyrophosphates and occasionally hydrogen or hydroxide ions ....
. The phosphate reacts with the acid, and the calcium is excreted by the kidneys. - Hypocitraturia: the urine has an abnormally low concentration of citrate, which normally helps to dissolve free calcium.
- The urine has a low pH, which stops uric acidUric acidUric acid is a heterocyclic compound of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen with the formula C5H4N4O3. It forms ions and salts known as urates and acid urates such as ammonium acid urate. Uric acid is created when the body breaks down purine nucleotides. High blood concentrations of uric acid...
from dissolving, leading to crystals that act as a nidus for calcium stone formation. - Many institutions traditionally restricted the water intake of patients on the diet to 80% of normal daily needs; this practice is no longer encouraged.
In adults, common side effects include weight loss, constipation, raised cholesterol levels and, in women, menstrual irregularities
Menstrual disorder
-Disorders of ovulation:Infrequent or irregular ovulation -Disorders of ovulation:Infrequent or irregular ovulation -Disorders of ovulation:Infrequent or irregular ovulation (usually defined as cycles of ≥36 days or -Disorders of ovulation:Infrequent or irregular ovulation (usually defined as...
including amenorrhoea
Amenorrhoea
Amenorrhoea , amenorrhea , or amenorrhœa, is the absence of a menstrual period in a woman of reproductive age. Physiological states of amenorrhoea are seen during pregnancy and lactation , the latter also forming the basis of a form of contraception known as the lactational amenorrhoea method...
.
Implementation
The ketogenic diet is a medical nutrition therapyMedical nutrition therapy
Medical nutrition therapy is a therapeutic approach to treating medical conditions and their associated symptoms via the use of a specifically tailored diet devised and monitored by a registered dietician...
that involves participants from various disciplines. Team members include a registered paediatric dietitian
Dietitian
Dietitians supervise the preparation and service of food, develop modified diets, participate in research, and educate individuals and groups on good nutritional habits. The goals of dietitians are to provide medical nutritional intervention, and to obtain, safely prepare, serve and advise on...
who coordinates the diet programme; a paediatric neurologist
Neurologist
A neurologist is a physician who specializes in neurology, and is trained to investigate, or diagnose and treat neurological disorders.Neurology is the medical specialty related to the human nervous system. The nervous system encompasses the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. A specialist...
who is experienced in offering the ketogenic diet; and a registered nurse
Registered nurse
A registered nurse is a nurse who has graduated from a nursing program at a university or college and has passed a national licensing exam. A registered nurse helps individuals, families, and groups to achieve health and prevent disease...
who is familiar with childhood epilepsy. Additional help may come from a medical social worker who works with the family and a pharmacist
Pharmacist
Pharmacists are allied health professionals who practice in pharmacy, the field of health sciences focusing on safe and effective medication use...
who can advise on the carbohydrate content of medicines. Lastly, the parents and other caregivers must be educated in many aspects of the diet for it to be safely implemented.
Implementing the diet can present difficulties for caregivers and the patient due to the time commitment involved in measuring and planning meals. Since any unplanned eating can potentially break the nutritional balance required, some people find the discipline needed to maintain the diet challenging and unpleasant. Some people terminate the diet or switch to a less demanding diet, like the Modified Atkins Diet or the Low Glycemic Index Treatment, because they find the difficulties too great.
Initiation
The Johns Hopkins Hospital protocol for initiating the ketogenic diet has been widely adopted. It involves a consultation with the patient and their caregivers and, later, a short hospital admission. Because of the risk of complications during ketogenic diet initiation, most centres begin the diet under close medical supervision in hospital.At the initial consultation, patients are screened
Screening (medicine)
Screening, in medicine, is a strategy used in a population to detect a disease in individuals without signs or symptoms of that disease. Unlike what generally happens in medicine, screening tests are performed on persons without any clinical sign of disease....
for conditions that may contraindicate the diet. A dietary history
Medical history
The medical history or anamnesis of a patient is information gained by a physician by asking specific questions, either of the patient or of other people who know the person and can give suitable information , with the aim of obtaining information useful in formulating a diagnosis and providing...
is obtained and the parameters of the diet selected: the ketogenic ratio of fat to combined protein and carbohydrate, the calorie requirements, and the fluid intake.
The day before admission to hospital, the proportion of carbohydrate in the diet may be decreased and the patient begins fasting after his or her evening meal. On admission, only calorie- and caffeine-free fluids are allowed until dinner, which consists of "eggnog
Eggnog
Eggnog, or egg nog, is a sweetened dairy-based beverage traditionally made with milk and/or cream, sugar, beaten eggs , and liquor...
" restricted to one-third of the typical calories for a meal. The following breakfast and lunch are similar, and on the second day, the "eggnog" dinner is increased to two-thirds of a typical meal's caloric content. By the third day, dinner contains the full calorie quota and is a standard ketogenic meal (not "eggnog"). After a ketogenic breakfast on the fourth day, the patient is discharged. Where possible, the patient's current medicines are changed to carbohydrate-free formulations.
When in the hospital, glucose levels
Blood sugar
The blood sugar concentration or blood glucose level is the amount of glucose present in the blood of a human or animal. Normally in mammals, the body maintains the blood glucose level at a reference range between about 3.6 and 5.8 mM , or 64.8 and 104.4 mg/dL...
are checked several times daily and the patient is monitored for signs of symptomatic ketosis
Ketosis
Ketosis is a state of elevated levels of ketone bodies in the body. It is almost always generalized throughout the body, with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when the liver glycogen stores are depleted...
(which can be treated with a small quantity of orange juice). Lack of energy and lethargy are common but disappear within two weeks. The parents attend classes over the first three full days, which cover nutrition, managing the diet, preparing meals, avoiding sugar and handling illness. The level of parental education and commitment required is higher than with medication.
Variations on the Johns Hopkins protocol are common. The initiation can be performed using outpatient clinics rather than requiring a stay in hospital. Often there is no initial fast (fasting increases the risk of acidosis
Metabolic acidosis
In medicine, metabolic acidosis is a condition that occurs when the body produces too much acid or when the kidneys are not removing enough acid from the body. If unchecked, metabolic acidosis leads to acidemia, i.e., blood pH is low due to increased production of hydrogen by the body or the...
and hypoglycaemia and weight loss). Rather than increasing meal sizes over the three-day initiation, some institutions maintain meal size but alter the ketogenic ratio from 2:1 to 4:1.
For patients who benefit, half achieve a seizure reduction within five days (if the diet starts with an initial fast of one to two days), three-quarters achieve a reduction within two weeks, and 90% achieve a reduction within 23 days. If the diet does not begin with a fast, the time for half of the patients to achieve an improvement is longer (two weeks) but the long-term seizure reduction rates are unaffected. Parents are encouraged to persist with the diet for at least three months before any final consideration is made regarding efficacy.
Maintenance
After initiation, the child regularly visits the hospital outpatient clinic where they are seen by the dietitian and neurologist, and various tests and examinations are performed. These are held every three months for the first year and then every six months thereafter. Infants under one year old are seen more frequently, with the initial visit held after just two to four weeks. A period of minor adjustments is necessary to ensure consistent ketosis is maintained and to better adapt the meal plans to the patient. This fine-tuning is typically done over the telephone with the hospital dietitianDietitian
Dietitians supervise the preparation and service of food, develop modified diets, participate in research, and educate individuals and groups on good nutritional habits. The goals of dietitians are to provide medical nutritional intervention, and to obtain, safely prepare, serve and advise on...
and includes changing the number of calories, altering the ketogenic ratio, or adding some MCT or coconut oils to a classic diet. Urinary ketone levels
Ketonuria
Ketonuria is a medical condition in which ketone bodies are present in the urine.It is seen in conditions in which the body produces excess ketones as an alternative source of energy. It is seen during starvation or more commonly in type I diabetes mellitus...
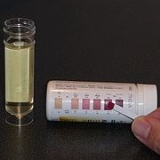
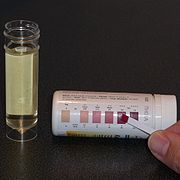
are checked daily to detect whether ketosis has been achieved and to confirm that the patient is following the diet, though the level of ketones does not correlate with an anticonvulsant effect. This is performed using ketone test strips containing nitroprusside, which change colour from buff-pink to maroon in the presence of acetoacetate (one of the three ketone bodies).
A short-lived increase in seizure frequency may occur during illness or if ketone
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure RCR', where R and R' can be a variety of atoms and groups of atoms. It features a carbonyl group bonded to two other carbon atoms. Many ketones are known and many are of great importance in industry and in biology...
levels fluctuate. The diet may be modified if seizure frequency remains high, or the child is losing weight. Loss of seizure-control may come from unexpected sources. Even "sugar-free" food can contain carbohydrates such as maltodextrin
Maltodextrin
Maltodextrin is a polysaccharide that is used as a food additive. It is produced from starch by partial hydrolysis and is usually found as a creamy-white hygroscopic spraydried powder. Maltodextrin is easily digestible, being absorbed as rapidly as glucose, and might be either moderately sweet or...
, sorbitol
Sorbitol
Sorbitol, also known as glucitol, Sorbogem® and Sorbo®, is a sugar alcohol that the human body metabolizes slowly. It can be obtained by reduction of glucose, changing the aldehyde group to a hydroxyl group. Sorbitol is found in apples, pears, peaches, and prunes...
, starch
Starch
Starch or amylum is a carbohydrate consisting of a large number of glucose units joined together by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by all green plants as an energy store...
and fructose
Fructose
Fructose, or fruit sugar, is a simple monosaccharide found in many plants. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and galactose, that are absorbed directly into the bloodstream during digestion. Fructose was discovered by French chemist Augustin-Pierre Dubrunfaut in 1847...
. The sorbitol content of suntan lotion and other skincare products may be high enough for some to be absorbed through the skin and thus negate ketosis.
Discontinuation
About 20% of children on the ketogenic diet achieve freedom from seizures, and many are able to reduce the use of anticonvulsant drugs or eliminate them altogether. Commonly, at around two years on the diet, or after six months of being seizure-free, the diet may be gradually discontinued over two or three months. This is done by lowering the ketogenic ratio until urinary ketosis is no longer detected, and then lifting all calorie restrictions. This timing and method of discontinuation mimics that of anticonvulsant drug therapy in children, where the child has become seizure free. When the diet is required to treat certain metabolic diseases, the duration will be longer. The total diet duration is up to the treating ketogenic diet team and parents; durations up to 12 years have been studied and found beneficial.Children who discontinue the diet after achieving seizure freedom have about a 20% risk of seizures returning. The length of time until recurrence is highly variable but averages two years. This risk of recurrence compares with 10% for resective surgery (where part of the brain is removed) and 30–50% for anticonvulsant therapy. Of those that have a recurrence, just over half can regain freedom from seizures either with anticonvulsants or by returning to the ketogenic diet. Recurrence is more likely if, despite seizure freedom, an electroencephalogram (EEG) shows epileptiform spikes, which indicate epileptic activity in the brain but are below the level that will cause a seizure. Recurrence is also likely if an MRI scan shows focal abnormalities (for example, as in children with tuberous sclerosis
Tuberous sclerosis
Tuberous sclerosis or tuberous sclerosis complex is a rare multi-system genetic disease that causes non-malignant tumors to grow in the brain and on other vital organs such as the kidneys, heart, eyes, lungs, and skin. A combination of symptoms may include seizures, developmental delay, behavioral...
). Such children may remain on the diet longer than average, and it has been suggested that children with tuberous sclerosis who achieve seizure freedom could remain on the ketogenic diet indefinitely.
Classic
The ketogenic diet is calculated by a dietitianDietitian
Dietitians supervise the preparation and service of food, develop modified diets, participate in research, and educate individuals and groups on good nutritional habits. The goals of dietitians are to provide medical nutritional intervention, and to obtain, safely prepare, serve and advise on...
for each child. Age, weight, activity levels, culture and food preferences all affect the meal plan. First, the energy requirements are set at 80–90% of the recommended daily amounts (RDA) for the child's age (the high-fat diet requires less energy to process than a typical high-carbohydrate diet). Highly active children or those with muscle spasticity
Spasticity
Spasticity is a feature of altered skeletal muscle performance in muscle tone involving hypertonia, which is also referred to as an unusual "tightness" of muscles...
require more calories than this; immobile children require less. The ketogenic ratio of the diet compares the weight of fat to the combined weight of carbohydrate and protein. This is typically 4:1, but children who are younger than 18 months, older than 12 years, or who are obese may be started on a 3:1 ratio. Fat is energy-rich, with 9 kcal/g (38 kJ/g) compared to 4 kcal/g (17 kJ/g) for carbohydrate or protein, so portions on the ketogenic diet are smaller than normal. The quantity of fat in the diet can be calculated from the overall energy requirements and the chosen ketogenic ratio. Next, the protein levels are set to allow for growth and body maintenance, and are around 1 g protein for each kg of body weight. Lastly, the amount of carbohydrate is set according to what allowance is left while maintaining the chosen ratio. Any carbohydrate in medications or supplements
Dietary supplement
A dietary supplement, also known as food supplement or nutritional supplement, is a preparation intended to supplement the diet and provide nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, fiber, fatty acids, or amino acids, that may be missing or may not be consumed in sufficient quantities in a person's diet...
must be subtracted from this allowance. The total daily amount of fat, protein and carbohydrate is then evenly divided across the meals.
A computer program such as KetoCalculator may be used to help generate recipes. The meals often have four components: heavy whipping cream
Cream
Cream is a dairy product that is composed of the higher-butterfat layer skimmed from the top of milk before homogenization. In un-homogenized milk, over time, the lighter fat rises to the top. In the industrial production of cream this process is accelerated by using centrifuges called "separators"...
, a protein-rich food (typically meat), a fruit or vegetable, and butter, vegetable oil or mayonnaise. Only low-carbohydrate fruits and vegetables are allowed, which excludes bananas, potatoes, peas and corn. Suitable fruits are divided into two groups based on the amount of carbohydrate they contain, and vegetables are similarly divided into two groups. Foods within each of these four groups may be freely substituted to allow for variation without needing to recalculate portion sizes. For example, cooked broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cauliflower and green beans are all equivalent. Fresh, canned or frozen foods are equivalent, but raw and cooked vegetables differ, and processed foods are an additional complication. Parents are required to be precise when measuring food quantities on an electronic scale
Weighing scale
A weighing scale is a measuring instrument for determining the weight or mass of an object. A spring scale measures weight by the distance a spring deflects under its load...
accurate to 1 g. The child must eat the whole meal and cannot have extra portions; any snacks must be incorporated into the meal plan. A small amount of MCT oil may be used to help with constipation or to increase ketosis.
The ketogenic diet is not a balanced diet and only contains tiny portions of fresh fruit and vegetables, fortified
Food fortification
Food fortification or enrichment is the process of adding micronutrients to food. It can be purely a commercial choice to provide extra nutrients in a food, or sometimes it is a public health policy which aims to reduce numbers of people with dietary deficiencies in a population.Diets that lack...
cereals and calcium-rich foods. In particular, the B vitamins
B vitamins
B vitamins are a group of water-soluble vitamins that play important roles in cell metabolism. The B vitamins were once thought to be a single vitamin, referred to as vitamin B . Later research showed that they are chemically distinct vitamins that often coexist in the same foods...
, calcium
Calcium
Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
and vitamin D
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids. In humans, vitamin D is unique both because it functions as a prohormone and because the body can synthesize it when sun exposure is adequate ....
must be artificially supplemented. This is achieved by taking two sugar-free supplements designed for the patient's age: a multivitamin
Multivitamin
A multivitamin is a preparation intended to supplement a human diet with vitamins, dietary minerals, and other nutritional elements. Such preparations are available in the form of tablets, capsules, pastilles, powders, liquids, and injectable formulations...
with minerals
Dietary mineral
Dietary minerals are the chemical elements required by living organisms, other than the four elements carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen present in common organic molecules. Examples of mineral elements include calcium, magnesium, potassium, sodium, zinc, and iodine...
, and calcium
Calcium
Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
with vitamin D
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids. In humans, vitamin D is unique both because it functions as a prohormone and because the body can synthesize it when sun exposure is adequate ....
. A typical day of food for a child on a 4:1 ratio, 1,500 kcal (6,300 kJ) ketogenic diet comprises:
- Breakfast: egg with bacon
28 g egg, 11 g bacon, 37 g of 36% heavy whipping cream, 23 g butter and 9 g apple. - Snack: peanut butter ball
6 g peanut butter and 9 g butter. - Lunch: tuna salad
28 g tuna fish, 30 g mayonnaise, 10 g celery, 36 g of 36% heavy whipping cream and 15 g lettuce. - Snack: keto yogurt
18 g of 36% heavy whipping cream, 17 g sour cream, 4 g strawberries and artificial sweetener. - Dinner: cheeseburger (no bun)
22 g minced (ground) beef, 10 g American cheeseAmerican cheeseAmerican cheese is a processed cheese. It is orange, yellow, or white in color and mild in flavor, with a medium-firm consistency, and melts easily. American cheese was originally only white, but is usually now modified to yellow. In the past it was made from a blend of cheeses, most often Colby...
, 26 g butter, 38 g cream, 10 g lettuce and 11 g green beans. - Snack: keto custard
25 g of 36% heavy whipping cream, 9 g egg and pure vanilla flavouring.
MCT oil
Normal dietary fat contains mostly long-chain triglycerideTriglyceride
A triglyceride is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids. There are many triglycerides, depending on the oil source, some are highly unsaturated, some less so....
s (LCT). Medium-chain triglycerides
Medium chain triglycerides
Medium-chain triglycerides are medium-chain fatty acid esters of glycerol.MCTs passively diffuse from the GI tract to the portal system without requirement for modification like long-chain fatty acids or very-long-chain fatty acids. In addition, MCTs do not require bile salts for digestion...
are more ketogenic than LCTs because they generate more ketones per unit of energy when metabolised. Their use allows for a diet with a lower proportion of fat and a greater proportion of protein and carbohydrate, leading to more food choices and larger portion sizes. The original MCT diet developed by Peter Huttenlocher in the 1970s derived 60% of its calories from MCT oil. Consuming that quantity of MCT oil caused abdominal cramps, diarrhoea and vomiting in some children. A figure of 45% is regarded as a balance between achieving good ketosis and minimising gastrointestinal complaints. The classical and modified MCT ketogenic diets are equally effective and differences in tolerability are not statistically significant. The MCT diet is less popular in the United States; MCT oil is more expensive than other dietary fats and is not covered by insurance companies.
Modified Atkins
First reported in 2003, the idea of using a form of the Atkins diet to treat epilepsy came about after parents and patients discovered that the induction phase of the Atkins diet controlled seizures. The ketogenic diet team at Johns Hopkins Hospital modified the Atkins diet by removing the aim of achieving weight loss, extending the induction phase indefinitely, and specifically encouraging fat consumption. Compared with the ketogenic diet, the modified Atkins diet (MAD) places no limit on calories or protein, and the lower overall ketogenic ratio (approximately 1:1) does not need to be consistently maintained by all meals of the day. The MAD does not begin with a fast or with a stay in hospital and requires less dietitian support than the ketogenic diet. Carbohydrates are initially limited to 10 g per day in children or 20 g per day in adults, and are increased to 20–30 g per day after a month or so, depending on the effect on seizure control or tolerance of the restrictions. Like the ketogenic diet, the MAD requires vitamin and mineral supplements and children are carefully and periodically monitored at outpatient clinics.The modified Atkins diet reduces seizure frequency by more than 50% in 43% of patients who try it and by more than 90% in 27% of patients. Few adverse effects have been reported, though cholesterol is increased and the diet has not been studied long term. Although based on a smaller data set (126 adults and children from 11 studies over five centres), these results from 2009 compare favourably with the traditional ketogenic diet.
Low glycemic index treatment
The low glycemic index treatment (LGIT) is an attempt to achieve the stable blood glucose levels seen in children on the classic ketogenic diet while using a much less restrictive regime. The hypothesis is that stable blood glucose may be one of the mechanisms of action involved in the ketogenic diet, which occurs because the absorption of the limited carbohydrates is slowed by the high fat content. Although it is also a high-fat diet (with approximately 60% calories from fat), the LGIT allows more carbohydrate than either the classic ketogenic diet or the modified Atkins diet, approximately 40–60 g per day. However, the types of carbohydrates consumed are restricted to those that have a glycemic indexGlycemic index
The glycemic index, glycaemic index, or GI is a measure of the effects of carbohydrates on blood sugar levels. Carbohydrates that break down quickly during digestion and release glucose rapidly into the bloodstream have a high GI; carbohydrates that break down more slowly, releasing glucose more...
lower than 50. Like the modified Atkins diet, the LGIT is initiated and maintained at outpatient clinics and does not require precise weighing of food or intensive dietitian support. Both are offered at most centres that run ketogenic diet programmes, and in some centres they are often the primary dietary therapy for adolescents.
Short-term results for the LGIT indicate that at one month approximately half of the patients experience a greater than 50% reduction in seizure frequency, with overall figures approaching that of the ketogenic diet. The data (coming from one centre's experience with 76 children up to the year 2009) also indicate fewer side effects than the ketogenic diet and that it is better tolerated, with more palatable meals.
Prescribed formulations

Feeding tube
A feeding tube is a medical device used to provide nutrition to patients who cannot obtain nutrition by swallowing. The state of being fed by a feeding tube is called gavage, enteral feeding or tube feeding...
can also be given a ketogenic diet. Parents make up a prescribed
Medical prescription
A prescription is a health-care program implemented by a physician or other medical practitioner in the form of instructions that govern the plan of care for an individual patient. Prescriptions may include orders to be performed by a patient, caretaker, nurse, pharmacist or other therapist....
powdered formula, such as KetoCal, into a liquid feed. Gastrostomy feeding avoids any issues with palatability, and bottle-fed infants readily accept the ketogenic formula. Some studies have found this liquid feed to be more efficacious and associated with lower total cholesterol
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a complex isoprenoid. Specifically, it is a waxy steroid of fat that is produced in the liver or intestines. It is used to produce hormones and cell membranes and is transported in the blood plasma of all mammals. It is an essential structural component of mammalian cell membranes...
than a solid ketogenic diet. KetoCal is a nutritionally complete food containing milk protein and is supplemented with amino acids, fat, carbohydrate, vitamins, minerals and trace elements. It is used to administer the 4:1 ratio classic ketogenic diet in children over one year. The formula is available in both 3:1 and 4:1 ratios, either unflavoured or in an artificially sweetened vanilla flavour and is suitable for tube or oral feeding. Other formula products include KetoVolve and Ketonia. Alternatively, a liquid ketogenic diet may be produced by combining Ross Carbohydrate Free soy formula with Microlipid and Polycose.
Worldwide
There are theoretically no restrictions on where the ketogenic diet might be used, and it can cost less than modern anticonvulsants. However, fasting and dietary changes are affected by religious and cultural issues. A culture where food is often prepared by grandparents or hired help means more people must be educated about the diet. When families dine together, sharing the same meal, it can be difficult to separate the child's meal. In many countries, food labelling is not mandatory so calculating the proportions of fat, protein and carbohydrate is difficult. In some countries, it may be hard to find sugar-free forms of medicines and supplements, to purchase an accurate electronic scale, or to afford MCT oils.Jewish dietary laws
Kashrut
Kashrut is the set of Jewish dietary laws. Food in accord with halakha is termed kosher in English, from the Ashkenazi pronunciation of the Hebrew term kashér , meaning "fit" Kashrut (also kashruth or kashrus) is the set of Jewish dietary laws. Food in accord with halakha (Jewish law) is termed...
prevent mixing meat and milk in one dish. In Asia, the normal diet includes rice and noodles as the main energy source, making their elimination difficult. Therefore the MCT-oil form of the diet, which allows more carbohydrate, has proved useful. In India, religious beliefs commonly affect the diet: some patients are vegetarians, or will not eat root vegetables, or avoid beef. The Indian ketogenic diet is started without a fast due to cultural opposition towards fasting in children. The low-fat, high-carbohydrate nature of the normal Indian and Asian diet means that their ketogenic diets typically have a lower ketogenic ratio (1:1) than in America and Europe. However, they appear to be just as effective.
In many developing countries, the ketogenic diet is expensive because dairy fats and meat are dearer than grain, fruit and vegetables. The modified Atkins diet has been proposed as a lower-cost alternative for those countries; the slightly more expensive food bill can be offset by a reduction in pharmaceutical costs if the diet is successful. The modified Atkins diet is less complex to explain and prepare and requires less support from a dietitian.
Seizure pathology
The brain is composed of a network of neurons that transmit signalsNeurotransmission
Neurotransmission , also called synaptic transmission, is the process by which signaling molecules called neurotransmitters are released by a neuron , and bind to and activate the receptors of another neuron...
by propagating nerve impulses. The propagation of this impulse from one neuron's synapse
Chemical synapse
Chemical synapses are specialized junctions through which neurons signal to each other and to non-neuronal cells such as those in muscles or glands. Chemical synapses allow neurons to form circuits within the central nervous system. They are crucial to the biological computations that underlie...
to another is typically controlled by neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals that transmit signals from a neuron to a target cell across a synapse. Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles clustered beneath the membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse, and are released into the synaptic cleft, where they bind to...
s, though there are also electrical pathways
Electrical synapse
An electrical synapse is a mechanical and electrically conductive link between two abutting neurons that is formed at a narrow gap between the pre- and postsynaptic neurons known as a gap junction. At gap junctions, such cells approach within about 3.5 nm of each other, a much shorter...
between some neurons. Neurotransmitters can inhibit impulse firing (primarily done by γ-aminobutyric acid
Gamma-aminobutyric acid
γ-Aminobutyric acid is the chief inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mammalian central nervous system. It plays a role in regulating neuronal excitability throughout the nervous system...
, or GABA) or they can excite the neuron into firing (primarily done by glutamate). A neuron that releases inhibitory neurotransmitters from its terminals is called an inhibitory neuron, while one that releases excitatory neurotransmitters is an excitatory neuron. When the normal balance between inhibition and excitation is significantly disrupted in all or part of the brain, a seizure can occur. The GABA system is an important target for anticonvulsant drugs, since seizures may be discouraged by increasing GABA synthesis, decreasing its breakdown, or enhancing its effect on neurons.
The nerve impulse is characterised by a great influx of sodium ions through channels in the neuron's cell membrane
Cell membrane
The cell membrane or plasma membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. It basically protects the cell...
followed by an efflux of potassium ions through other channels. The neuron is unable to fire again for a short time (known as the refractory period), which is mediated by another potassium channel
Calcium-activated potassium channel
Calcium-activated potassium channels are divided into BK channels, IK channels, and SK channels based on their conductance ....
. The flow through these ion channel
Ion channel
Ion channels are pore-forming proteins that help establish and control the small voltage gradient across the plasma membrane of cells by allowing the flow of ions down their electrochemical gradient. They are present in the membranes that surround all biological cells...
s is governed by a "gate" which is opened by either a voltage change or a chemical messenger
Ligand-gated ion channel
Ligand-gated ion channels are one type of ionotropic receptor or channel-linked receptor. They are a group of transmembrane ion channels that are opened or closed in response to the binding of a chemical messenger , such as a neurotransmitter.The binding site of endogenous ligands on LGICs...
known as a ligand
Ligand (biochemistry)
In biochemistry and pharmacology, a ligand is a substance that forms a complex with a biomolecule to serve a biological purpose. In a narrower sense, it is a signal triggering molecule, binding to a site on a target protein.The binding occurs by intermolecular forces, such as ionic bonds, hydrogen...
(such as a neurotransmitter). These channels are another target for anticonvulsant drugs.
There are many ways in which epilepsy occurs. Examples of pathological physiology include: unusual excitatory connections within the neuronal network of the brain; abnormal neuron structure leading to altered current flow; decreased inhibitory neurotransmitter synthesis; ineffective receptors for inhibitory neurotransmitters; insufficient breakdown of excitatory neurotransmitters leading to excess; immature synapse development; and impaired function of ionic channels.
Seizure control
Although many hypotheses have been put forward to explain how the ketogenic diet works, it remains a mystery. Disproven hypotheses include systemic acidosisMetabolic acidosis
In medicine, metabolic acidosis is a condition that occurs when the body produces too much acid or when the kidneys are not removing enough acid from the body. If unchecked, metabolic acidosis leads to acidemia, i.e., blood pH is low due to increased production of hydrogen by the body or the...
(high levels of acid in the blood), electrolyte changes
Electrolyte disturbance
Electrolytes play a vital role in maintaining homeostasis within the body. They help to regulate myocardial and neurological function, fluid balance, oxygen delivery, acid-base balance and much more. Electrolyte imbalances can develop by the following mechanisms: excessive ingestion; diminished...
and hypoglycaemia (low blood glucose). Although many biochemical changes are known to occur in the brain of a patient on the ketogenic diet, it is not known which of these has an anticonvulsant effect. The lack of understanding in this area is similar to the situation with many anticonvulsant drugs.
On the ketogenic diet, carbohydrates are restricted and so cannot provide for all the metabolic needs of the body. Instead, fatty acids are used as the major source of fuel. These are used through fatty-acid oxidation
Fatty acid metabolism
Fatty acids are an important source of energy and adenosine triphosphate for many cellular organisms. Excess fatty acids, glucose, and other nutrients can be stored efficiently as fat. Triglycerides yield more than twice as much energy for the same mass as do carbohydrates or proteins. All cell...
in the cell's mitochondria (the energy-producing part of the cell). Humans can convert some amino acid
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
s into glucose by a process called gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis is a metabolic pathway that results in the generation of glucose from non-carbohydrate carbon substrates such as lactate, glycerol, and glucogenic amino acids....
, but cannot do this for fatty acids. Since amino acids are needed to make proteins, which are essential for growth and repair of body tissues, these cannot be used only to produce glucose. This could pose a problem for the brain, since it is normally fuelled solely by glucose, and fatty acids do not cross the blood–brain barrier. Fortunately, the liver can use fatty acids to synthesise the three ketone bodies
Ketone bodies
Ketone bodies are three water-soluble compounds that are produced as by-products when fatty acids are broken down for energy in the liver and kidney. They are used as a source of energy in the heart and brain. In the brain, they are a vital source of energy during fasting...
β-hydroxybutyrate, acetoacetate and acetone
Acetone
Acetone is the organic compound with the formula 2CO, a colorless, mobile, flammable liquid, the simplest example of the ketones.Acetone is miscible with water and serves as an important solvent in its own right, typically as the solvent of choice for cleaning purposes in the laboratory...
. These ketone bodies enter the brain and substitute for glucose.
The ketone bodies are possibly anticonvulsant in themselves; in animal model
Animal model
An animal model is a living, non-human animal used during the research and investigation of human disease, for the purpose of better understanding the disease without the added risk of causing harm to an actual human being during the process...
s, acetoacetate and acetone protect against seizures. The ketogenic diet results in adaptive changes to brain energy metabolism that increase the energy reserves; ketone bodies are a more efficient fuel than glucose, and the number of mitochondria is increased. This may help the neuron
Neuron
A neuron is an electrically excitable cell that processes and transmits information by electrical and chemical signaling. Chemical signaling occurs via synapses, specialized connections with other cells. Neurons connect to each other to form networks. Neurons are the core components of the nervous...
s to remain stable in the face of increased energy demand during a seizure, and may confer a neuroprotective effect.
The ketogenic diet has been studied in at least 14 rodent animal models of seizures. It is protective in many of these models and has a different protection profile than any known anticonvulsant. Conversely, fenofibrate
Fenofibrate
Fenofibrate is a drug of the fibrate class. Fenofibrate was developed by Groupe Fournier SA, before it was acquired in 2005 by Solvay Pharmaceutical, a business unit owned by the Belgian corporation, Solvay S.A. In 2009 Solvay Pharmaceutical was acquired by Abbott Laboratories. It is mainly used to...
, not used clinically as an antiepileptic, exhibits experimental anticonvulsant
Anticonvulsant
The anticonvulsants are a diverse group of pharmaceuticals used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of bipolar disorder, since many seem to act as mood stabilizers, and in the treatment of neuropathic pain. The goal of an...
properties in adult rats comparable to the ketogenic diet. This, together with studies showing its efficacy in patients who have failed to achieve seizure control on half a dozen drugs, suggests a unique mechanism of action.
Anticonvulsants suppress epileptic seizures, but they neither cure nor prevent the development of seizure susceptibility. The development of epilepsy (epileptogenesis) is a process that is poorly understood. A few anticonvulsants (valproate, levetiracetam and benzodiazepine
Benzodiazepine
A benzodiazepine is a psychoactive drug whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring...
s) have shown antiepileptogenic properties in animal models of epileptogenesis. However, no anticonvulsant has ever achieved this in a clinical trial in humans. The ketogenic diet has been found to have antiepileptogenic properties in rats.
Other applications
The ketogenic diet may be a successful treatment for several rare metabolic diseases. Case reports of two children indicate that it may be a possible treatment for astrocytomaAstrocytoma
Astrocytomas are a type of neoplasm of the brain. They originate in a particular kind of glial-cells, star-shaped brain cells in the cerebrum called astrocytes. This type of tumor does not usually spread outside the brain and spinal cord and it does not usually affect other organs...
s, a type of brain tumour. Autism
Autism
Autism is a disorder of neural development characterized by impaired social interaction and communication, and by restricted and repetitive behavior. These signs all begin before a child is three years old. Autism affects information processing in the brain by altering how nerve cells and their...
, depression
Clinical depression
Major depressive disorder is a mental disorder characterized by an all-encompassing low mood accompanied by low self-esteem, and by loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities...
, migraine
Migraine
Migraine is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by moderate to severe headaches, and nausea...
headaches, polycystic ovary syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome is one of the most common female endocrine disorders. PCOS is a complex, heterogeneous disorder of uncertain aetiology, but there is strong evidence that it can to a large degree be classified as a genetic disease....
, and type 2 diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, often simply referred to as diabetes, is a group of metabolic diseases in which a person has high blood sugar, either because the body does not produce enough insulin, or because cells do not respond to the insulin that is produced...
have also been shown to improve in small case studies. There is evidence from uncontrolled clinical trials and studies in animal models that the ketogenic diet can provide symptomatic and disease-modifying activity in a broad range of neurodegenerative disorders including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis , also referred to as Lou Gehrig's disease, is a form of motor neuron disease caused by the degeneration of upper and lower neurons, located in the ventral horn of the spinal cord and the cortical neurons that provide their efferent input...
, Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease also known in medical literature as Alzheimer disease is the most common form of dementia. There is no cure for the disease, which worsens as it progresses, and eventually leads to death...
and Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease is a degenerative disorder of the central nervous system...
, and may be protective in traumatic brain injury
Traumatic brain injury
Traumatic brain injury , also known as intracranial injury, occurs when an external force traumatically injures the brain. TBI can be classified based on severity, mechanism , or other features...
and stroke
Stroke
A stroke, previously known medically as a cerebrovascular accident , is the rapidly developing loss of brain function due to disturbance in the blood supply to the brain. This can be due to ischemia caused by blockage , or a hemorrhage...
. Because tumour cells are inefficient in processing ketone bodies for energy, the ketogenic diet has also been suggested as a treatment for cancer. , there is insufficient evidence to support the use of the ketogenic diet as a treatment for these conditions; however, clinical trials for many of them are ongoing.
In March 2009, caprylidene
Caprylidene
Caprylidene is a medical food that was approved in March 2009 by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for the "clinical dietary management of the metabolic processes associated with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease"...
(Axona) was approved as a medical food
Medical food
Medical foods are foods that are specially formulated and intended for the dietary management of a disease that has distinctive nutritional needs that cannot be met by normal diet alone...
by the US Food and Drug Administration for the "dietary
management of the metabolic processes and nutritional requirements associated with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease". Glucose metabolism by the brain is impaired in Alzheimer's disease, and it is proposed that ketone bodies may provide an alternative energy source. Caprylidene is a powdered form of the MCT caprylic triglyceride.
Further reading
- Freeman JM, Kossoff EH, Freeman JB, Kelly MT. The Ketogenic Diet: A Treatment for Children and Others with Epilepsy. 4th ed. New York: Demos; 2007. ISBN 1-932603-18-2.
External links
- Matthew's Friends. A UK charity and information resource.
- The Charlie Foundation. A US charity and information resource, set up by Jim AbrahamsJim AbrahamsJim Abrahams is an American movie director and writer.Abrahams was born in Shorewood, Wisconsin, to a Jewish family, and attended Shorewood High School...
. - epilepsy.com: Dietary Therapies & Ketogenic News. Information and regular research news updates.
- A Talk with John Freeman: Tending the Flame. An interview discussing the ketogenic diet that appeared in BrainWaves, Fall 2003, Volume 16, Number 2.

