
Benzodiazepine
Encyclopedia
A benzodiazepine ˌ is a psychoactive drug
whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene
ring and a diazepine
ring. The first benzodiazepine, chlordiazepoxide
(Librium), was discovered accidentally
by Leo Sternbach
in 1955, and made available in 1960 by Hoffmann–La Roche, which has also marketed diazepam
(Valium) since 1963.
Benzodiazepines enhance the effect of the neurotransmitter
gamma-aminobutyric acid
(GABA), which results in sedative
, hypnotic
(sleep-inducing), anxiolytic
(anti-anxiety), anticonvulsant
, muscle relaxant
and amnesic
action. These properties make benzodiazepines useful in treating anxiety
, insomnia
, agitation
, seizure
s, muscle spasms
, alcohol withdrawal and as a premedication
for medical or dental procedures. Benzodiazepines are categorized as either short-, intermediate- or long-acting. Short- and intermediate-acting benzodiazepines are preferred for the treatment of insomnia; longer-acting benzodiazepines are recommended for the treatment of anxiety.
In general, benzodiazepines are safe and effective in the short term, although cognitive impairments and paradoxical effects such as aggression or behavioral disinhibition
occasionally occur. Long-term use is controversial due to concerns about adverse psychological and physical effects, increased questioning of effectiveness and because benzodiazepines are prone to cause tolerance, physical dependence
, and, upon cessation of use after long term use, a withdrawal syndrome
. Due to adverse effects associated with the long-term use of benzodiazepines, withdrawal from benzodiazepines, in general, leads to improved physical and mental health. The elderly are at an increased risk of suffering from both short- and long-term adverse effects
.
There is controversy concerning the safety of benzodiazepines in pregnancy. While they are not major teratogens, uncertainty remains as to whether they cause cleft palate in a small number of babies and whether neurobehavioural effects occur as a result of prenatal exposure; they are known to cause withdrawal symptoms in the newborn
. Benzodiazepines can be taken in overdoses and can cause dangerous deep unconsciousness
. However, they are much less toxic than their predecessors, the barbiturate
s, and death rarely results when a benzodiazepine is the only drug taken. When combined with other central nervous system depressants such as alcohol
and opiates, the potential for toxicity increases. Benzodiazepines are commonly misused and taken in combination with other drugs of abuse
.
, anticonvulsant, muscle relaxant, and amnesic
actions, which are useful in a variety of indications such as alcohol dependence
, seizures, anxiety
, panic
, agitation
and insomnia. Most are administered orally; however, they can also be given intravenously
, intramuscularly
or rectally. In general, benzodiazepines are well-tolerated and are safe and effective drugs in the short term for a wide range of conditions. Tolerance can develop to their effects and there is also a risk of dependence, and upon discontinuation a withdrawal syndrome may occur. These factors, combined with other possible secondary effects after prolonged use such as psychomotor, cognitive, or memory impairments, limit their long-term applicability. The effects of long-term use or misuse include the tendency to cause or worsen cognitive deficit
s, depression
and anxiety.
The American Psychiatric Association
(APA) guidelines note that, in general, benzodiazepines are well tolerated, and their use for the initial treatment for panic disorder is strongly supported by numerous controlled trials. APA states that there is insufficient evidence to recommend any of the established panic disorder treatments over another. The choice of treatment between benzodiazepines, SSRIs, serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressant
s, and psychotherapy should be based on the patient's history, preference, and other individual characteristics. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors are likely to be the best choice of pharmacotherapy for many patients with panic disorder, but benzodiazepines are also often used, and some studies suggest that these medications are still used with greater frequency than the SSRIs. One advantage of benzodiazepines is that they alleviate the anxiety symptoms much faster than antidepressants, and therefore may be preferred in patients for whom rapid symptom control is critical. However, this advantage is offset by the possibility of developing benzodiazepine dependence
. APA does not recommend benzodiazepines for persons with depressive symptoms or a recent history of substance abuse
. The APA guidelines state that, in general, pharmacotherapy of panic disorder should be continued for at least a year, and that clinical experience support continuing benzodiazepine treatment to prevent recurrence. Although major concerns about benzodiazepine tolerance and withdrawal have been raised, there is no evidence for significant dose escalation in patients using benzodiazepines long-term. For many such patients stable doses of benzodiazepines retain their efficacy over several years.
Guidelines issued by the UK-based National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
(NICE), carried out a systematic review using different methodology and came to a different conclusion. They questioned the accuracy of studies that were not placebo-controlled. And, based on the findings of placebo-controlled studies
, they do not recommend use of benzodiazepines beyond two to four weeks, as tolerance and physical dependence
develop rapidly, with withdrawal symptoms including rebound anxiety occurring after six weeks or more of use. Nevertheless, benzodiazepines continue to be prescribed for the long-term treatment of anxiety disorders, although specific antidepressants and psychological therapies are recommended as the first-line treatment options with the anticonvulsant
drug pregabalin
indicated as a second- or third-line treatment and suitable for long-term use. NICE stated that long-term use of benzodiazepines for panic disorder with or without agoraphobia
is an unlicensed indication, does not have long-term efficacy, and is, therefore, not recommended by clinical guidelines. Psychological therapies such as cognitive behavioural therapy are recommended as a first-line therapy for panic disorder; benzodiazepine use has been found to interfere with therapeutic gains from these therapies.
Benzodiazepines are usually administered orally; however, very occasionally lorazepam or diazepam may be given intravenously for the treatment of panic attacks.
(NICE), benzodiazepines can be used in the immediate management of GAD, if necessary. However, they should not usually be given for longer than 2–4 weeks. The only medications NICE recommends for the longer term management of GAD are antidepressants.
Likewise, Canadian Psychiatric Association (CPA) recommends benzodiazepines alprazolam
, bromazepam
, lorazepam
, and diazepam
only as a second-line choice, if the treatment with two different antidepressants was unsuccessful. Although they are second-line agents, benzodiazepines can be used for a limited time to relieve severe anxiety and agitation. CPA guidelines note that after 4–6 weeks the effect of benzodiazepines may decrease to the level of placebo, and that benzodiazepines are less effective than antidepressants in alleviating ruminative worry
, the core symptom of GAD. However, in some cases, a prolonged treatment with benzodiazepines as the add-on to an antidepressant may be justified.
and diazepam
have residual effects that may persist into the next day and are, in general, not recommended.
It is not clear as to whether the new nonbenzodiazepine
hypnotics (Z-drugs) are better than the short-acting benzodiazepines. The efficacy of these two groups of medications is similar. According to the US Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
, indirect comparison indicates that side-effects from benzodiazepines may be about twice as frequent as from nonbenzodiazepines. This may make the non-benzodiazepines preferable as the first-line long-term treatment of insomnia. However, the UK National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
did not find any convincing evidence in favor of Z-drugs. NICE review pointed out that short-acting Z-drugs were inappropriately compared in clinical trials with long-acting benzodiazepines. There have been no trials comparing short-acting Z-drugs with appropriate doses of short-acting benzodiazepines. Based on this, NICE recommended choosing the hypnotic based on cost and the patient's preference.
It has been argued that long-term use of hypnotics and overprescribing of these drugs represents an unjustifiable risk, especially to the elderly, and is harmful for the public health
in general.
that can usually be dealt with effectively by administering fast-acting benzodiazepines, which are potent anticonvulsants. In a hospital environment, intravenous clonazepam
, lorazepam
, and diazepam
are first-line choices, clonazepam due to its stronger and more potent anticonvulsant action, diazepam due to its faster onset and lorazepam for its longer duration of action. In the community, intravenous administration is not practical and so rectal diazepam or (more recently) buccal midazolam
are used, with a preference for midazolam as its administration is easier and more socially acceptable.
When benzodiazepines were first introduced, they were enthusiastically adopted for treating all forms of epilepsy
. However, drowsiness and tolerance become problems with continued use and none are now considered first-line choices for long-term epilepsy therapy. Clobazam is widely used by specialist epilepsy clinics worldwide (but it is not available in the US) and clonazepam is popular in the Netherlands, Belgium and France. In the UK, both clobazam and clonazepam are second-line choices for treating many forms of epilepsy. Clobazam also has a useful role for very short-term seizure prophylaxis and in catamenial epilepsy
. Discontinuation after long term use in epilepsy requires additional caution because of the risks of rebound seizures. Therefore, the dose is slowly tapered over a period of up to six months or longer.
is the most commonly used benzodiazepine for alcohol detoxification
, but diazepam
may be used as an alternative. Both are used in the detoxification of individuals who are motivated to stop drinking, and are prescribed for a short period of time to reduce the risks of developing tolerance and dependence to the benzodiazepine medication itself. The benzodiazepines with a longer half-life make detoxification more tolerable, and dangerous alcohol withdrawal effects are less likely to occur. On the other hand, short-acting benzodiazepines may lead to breakthrough seizure
s, and are, therefore, not recommended for detoxification in an outpatient setting. Oxazepam
and lorazepam
are often used in patients at risk of drug accumulation, in particular, the elderly and those with cirrhosis
, because they are metabolized differently from other benzodiazepines, through conjugation
.
Benzodiazepines are the preferred choice in the management of alcohol withdrawal syndrome
, in particular, for the prevention and treatment of the dangerous complication of seizures and in subduing severe delirium
. Lorazepam is the only benzodiazepine with predictable intramuscular absorption and it is the most effective in preventing and controlling acute seizures.
may result in falls and injuries, in particular, in the elderly. Another result is impairment of driving skills and increased likelihood of road traffic accidents. Decreased libido and erection problems are a common side effect. Depression and disinhibition
may emerge. Hypotension
and suppressed breathing may be encountered with intravenous use. Less common side effects include nausea and changes in appetite, blurred vision, confusion, euphoria
, depersonalization
and nightmares. Cases of liver toxicity have been described but are very rare.
, violence, impulsivity
, irritability
and suicidal behavior sometimes occur. These reactions have been explained as consequences of disinhibition, that is loss of control over socially unacceptable behavior. Paradoxical reactions are rare in the general population, with an incidence rate below 1% and similar to placebo. However, they occur with greater frequency in recreational abusers, individuals with borderline personality disorder
, children, and patients on high-dosage regimes. In these groups, impulse control problems are perhaps the most important risk factor for disinhibition; learning disabilities and neurological disorders are also significant risks. Most reports of disinhibition involve high doses of high-potency benzodiazepines. Paradoxical effects may also appear after chronic use of benzodiazepines.
While the definitive studies are lacking, the former view received support from a 2004 meta-analysis of 13 small studies. This meta-analysis found that long-term use of benzodiazepines was associated with moderate to large adverse effects on all areas of cognition, with visuospatial memory being the most commonly detected impairment. Some of the other impairments reported were decreased IQ, visiomotor coordination, information processing, verbal learning and concentration. The authors of the meta-analysis and a later reviewer noted that the applicability of this meta-analysis is limited because the subjects were taken mostly from withdrawal clinics; the coexisting drug, alcohol use, and psychiatric disorders were not defined; and several of the included studies conducted the cognitive measurements during the withdrawal period.
and tend to increase with time. Not everyone, however, experiences problems with long-term use. The adverse effects can include cognitive impairment, as well as affective and behavioural problems. Feelings of turmoil, difficulty in thinking constructively, loss of sex-drive, agoraphobia and social phobia, increasing anxiety and depression, loss of interest in leisure pursuits and interests, and an inability to experience or express feelings can also occur. Additionally an altered perception of self, environment and relationships may occur.

. Tolerance manifests itself as diminished pharmacological effect and develops relatively quickly to the sedative, hypnotic, anticonvulsant, and muscle relaxant actions of benzodiazepines. Tolerance to anti-anxiety effects develops more slowly with little evidence of continued effectiveness beyond four to six months of continued use. In general, tolerance to the amnesic effects does not occur. However, controversy exists as to tolerance to the anxiolytic effects with some evidence that benzodiazepines retain efficacy and opposing evidence from a systematic review of the literature that tolerance frequently occurs and some evidence that anxiety may worsen with long-term use. The question of tolerance to the amnesic effects of benzodiazepines is, likewise, unclear. Some evidence suggests that partial tolerance does develop, and "the memory impairment is limited to a narrow window within 90 minutes after each dose".
Discontinuation of benzodiazepines or abrupt reduction of the dose, even after a relatively short course of treatment (three to four weeks), may result in two groups of symptoms — rebound
and withdrawal
. Rebound symptoms are the return of the symptoms for which the patient was treated but worse than before. Withdrawal symptoms are the new symptoms that occur when the benzodiazepine is stopped. They are the main sign of physical dependence
.
 The most frequent symptoms of withdrawal from benzodiazepines are insomnia, gastric problems, tremor
The most frequent symptoms of withdrawal from benzodiazepines are insomnia, gastric problems, tremor
s, agitation, fearfulness, and muscle spasms
. The less frequent effects are irritability, sweating, depersonalization
, derealization
, hypersensitivity to stimuli, depression
, suicidal behavior, psychosis
, seizures, and delirium tremens
. Severe symptoms usually occur as a result of abrupt or over-rapid withdrawal. Abrupt withdrawal can be dangerous, therefore a gradual reduction regime is recommended.
Symptoms may also occur during a gradual dosage reduction, but are typically less severe and may persist as part of a protracted withdrawal syndrome
for months after cessation of benzodiazepines. Approximately 10% of patients will experience a notable protracted withdrawal syndrome, which can persist for many months or in some cases a year or longer. Protracted symptoms tend to resemble those seen during the first couple of months of withdrawal but usually are of a sub acute level of severity. Such symptoms do gradually lessen over time, eventually disappearing altogether.
Benzodiazepines have a reputation with patients and doctors for causing a severe and traumatic withdrawal; however, this is in large part due to the withdrawal process's being poorly managed. Over-rapid withdrawal from benzodiazepines increases the severity of the withdrawal syndrome and increases the failure rate. A slow and gradual withdrawal
customised to the individual and, if indicated, psychological support is the most effective way of managing the withdrawal. Opinion as to the time needed to complete withdrawal ranges from four weeks to several years. A goal of less than six months has been suggested, but due to factors such as dosage and type of benzodiazepine, reasons for prescription, lifestyle, personality, environmental stresses, and amount of available support, a year or more may be needed to withdraw. Withdrawal is best managed by transferring the physically dependent patient to an equivalent dose of diazepam because it has the longest half-life of all of the benzodiazepines, is metabolised into long-acting active metabolites and is available in low-potency tablets, which can be quartered for smaller doses. A further benefit is that it is available in liquid form, which allows for even smaller reductions. Chlordiazepoxide
, which also has a long half-life and long-acting active metabolites, can be used as an alternative. An alternate tapering procedure is to quantitatively reduce the tablet size on a periodic basis [ref]. Nonbenzodiazepine
s are contraindicated during benzodiazepine withdrawal as they are cross tolerant with benzodiazepines and can induce dependence. Alcohol is also cross tolerant with benzodiazepines and more toxic and thus caution is needed to avoid replacing one dependence with another. During withdrawal, fluoroquinolone-based antibiotics are best avoided if possible; they displace benzodiazepines from their binding site and reduce GABA function and, thus, may aggravate withdrawal symptoms. Antipsychotics are not recommended for benzodiazepine withdrawal (or other CNS depressant withdrawal states) especially clozapine
, olanzapine
or low potency phenothiazines e.g. chlorpromazine
as they lower the seizure threshold and can worsen withdrawal effects; if used extreme caution is required.
Withdrawal from long term benzodiazepines is beneficial for most individuals. Withdrawal of benzodiazepines from long-term users, in general, leads to improved physical and mental health
particularly in the elderly; although some long term users report continued benefit from taking benzodiazepines, this may be the result of suppression of withdrawal effects.
s, they can still cause problems in overdose. Taken alone, they rarely cause severe complications in overdose
; statistics in England showed that benzodiazepines were responsible for 3.8% of all deaths by poisoning from a single drug. However, combining these drugs with alcohol
, opiates or tricyclic antidepressants markedly raises the toxicity. The elderly are more sensitive to the side effects of benzodiazepines, and poisoning may even occur from their long-term use. The various benzodiazepines differ in their toxicity; temazepam
appears to be most toxic in overdose and when used with other drugs. The symptoms of a benzodiazepine overdose may include; drowsiness, slurred speech, nystagmus
, hypotension
, ataxia
, coma
, respiratory depression, and cardiorespiratory arrest.
A reversal agent for benzodiazepines exists, flumazenil
(Anexate). Its use as an antidote
is not routinely recommended due to the high risk of resedation and seizures. In a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of 326 patients, 4 patients suffered serious adverse events and 61% became resedated following the use of flumazenil. Numerous contraindications to its use exist. It is contraindicated in patients with a history of long-term use of benzodiazepines, those having ingested a substance that lowers the seizure threshold or may cause an arrhythmia, and in those with abnormal vital signs. One study found that only 10% of the patient population presenting with a benzodiazepine overdose
are suitable candidates for treatment with flumazenil.
in susceptible individuals. For that reason, they are contraindicated in people with myasthenia gravis
, sleep apnea
, bronchitis
, and COPD
. Caution is required when benzodiazepines are used in people with personality disorders or mental retardation
because of frequent paradoxical reactions. In major depression, they may precipitate suicidal tendencies
and are sometimes used for suicidal overdoses. Individuals with a history of alcohol, opioid
and barbiturate
abuse should avoid benzodiazepines, as there is a risk of life-threatening interactions with these drugs.
meaning potential for harm in the unborn has been demonstrated.
Exposure to benzodiazepines during pregnancy has been associated with a slightly increased (from 0.06 to 0.07%) risk of cleft palate in newborns, a controversial conclusion as some studies find no association between benzodiazepines and cleft palate. Their use by expectant mothers shortly before the delivery may result in a floppy infant syndrome, with the newborns suffering from hypotonia
, hypothermia
, lethargy, and breathing and feeding difficulties. Cases of neonatal withdrawal syndrome have been described in infants chronically exposed to benzodiazepines in utero
. This syndrome may be hard to recognize, as it starts several days after delivery, for example, as late as 21 day for chlordiazepoxide. The symptoms include tremor
s, hypertonia
, hyperreflexia
, hyperactivity, and vomiting and may last for up to three to six months. Tapering down the dose during pregnancy may lessen its severity. If used in pregnancy, those benzodiazepines with a better and longer safety record, such as diazepam
or chlordiazepoxide
, are recommended over potentially more harmful benzodiazepines, such as alprazolam
or triazolam
. Using the lowest effective dose for the shortest period of time minimizes the risks to the unborn child.
in the elderly can resemble dementia
, depression
, or anxiety syndromes, and progressively worsens over time. Adverse effects on cognition can be mistaken for the effects of old age. The benefits of withdrawal include improved cognition, alertness, mobility, reduced risk incontinance, and a reduced risk of falls and fractures. The success of gradual-tapering benzodiazepines is as great in the elderly as in younger people. Benzodiazepines should be prescribed to the elderly only with caution and only for a short period at low doses. Short to intermediate-acting benzodiazepines are preferred in the elderly such as oxazepam
and temazepam
. The high potency benzodiazepines alprazolam
and triazolam
and long-acting benzodiazepines are not recommended in the elderly due to increased adverse effects. Nonbenzodiazepines such as zaleplon
and zolpidem
and low doses of sedating antidepressants are sometimes used as alternatives to benzodiazepines.
Long-term use of benzodiazepines has been associated with increased risk of cognitive impairment, but its relationship with dementia remains inconclusive. The association of a past history of benzodiazepine use and cognitive decline is unclear, with some studies reporting a lower risk of cognitive decline in former users, some finding no association and some indicating an increased risk of cognitive decline.
Benzodiazepines are sometimes prescribed to treat behavioral symptoms of dementia. However, like antidepressant
s, they have little evidence of effectiveness, although antipsychotic
s have shown some benefit. Cognitive impairing effects of benzodiazepines that occur frequently in the elderly can also worsen dementia.
, the GABAA receptor, which increases the conductance of this inhibitory channel; this results in the various therapeutic effects as well as adverse effects of benzodiazepines. Other less important mechanisms of action are also known.
for the heterocyclic ring system (see figure to the right), which is a fusion between the benzene
and diazepine
ring systems. Under Hantzsch–Widman nomenclature
, a diazepine
is a heterocycle with two nitrogen
atoms, five carbon
atom and the maximum possible number of cumulative double bond
s. The "benzo" prefix indicates the benzene
ring fused onto the diazepine ring.
Benzodiazepine drugs are substituted 1,4-benzodiazepines, although the chemical term can refer to many other compounds that do not have useful pharmacological properties. Different benzodiazepine drugs have different side groups attached to this central structure. The different side groups affect the binding of the molecule to the GABAA receptor and so modulate the pharmacological properties. Many of the pharmacologically active "classical" benzodiazepine drugs contain the 5-phenyl-1H-benzo[e][1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one substructure (see figure to the right).
Nonbenzodiazepine
s also bind to the benzodiazepine binding site on the GABAA receptor and possess similar pharmacological properties. While the nonbenzodiazepines are by definition structurally unrelated to the benzodiazepines, both classes of drugs possess a common pharmacophore
(see figure to the lower-right), which explains their binding to a common receptor site.
 Benzodiazepines work by increasing the efficiency of a natural brain chemical, GABA
Benzodiazepines work by increasing the efficiency of a natural brain chemical, GABA
, to decrease the excitability of neuron
s. This reduces the communication between neurons and, therefore, has a calming effect on many of the functions of the brain.
GABA controls the excitability of neurons by binding to the GABAA receptor. The GABAA receptor is a protein complex located in the synapses
of neurons. All GABAA receptors contain an ion channel
that conducts chloride
ions across neuronal cell membrane
s and two binding sites for the neurotransmitter
gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), while a subset of GABAA receptor complexes also contain a single binding site for benzodiazepines. Binding of benzodiazepines to this receptor complex promotes binding of GABA, which in turn increases the conduction of chloride ions across the neuronal cell membrane. This increased conductance raises the membrane potential
of the neuron, resulting in inhibition of neuronal firing
. In addition, different GABAA receptor subtypes have varying distributions within different regions of the brain and, therefore, control distinct neuronal circuits
. Hence, activation of different GABAA receptor subtypes by benzodiazepines may result in distinct pharmacological actions. In terms of the mechanism of action of benzodiazepines, their similarities are too great to separate them into individual categories such as anxiolytic or hypnotic. For example, a hypnotic administered in low doses will produce anxiety-relieving effects, whereas a benzodiazepine marketed as an anti-anxiety drug will at higher doses induce sleep.
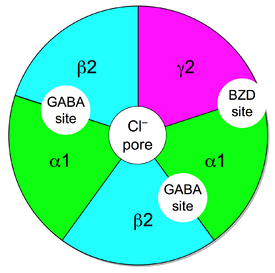
The subset of GABAA receptors that also bind benzodiazepines are referred to as benzodiazepine receptors (BzR). The GABAA receptor is a heteromer
composed of five subunits, the most common ones being two αs, two βs, and one γ (α2β2γ). For each subunit, many subtypes exist (α1-6, β1-3, and γ1-3). GABAA receptors that are made up of different combinations of subunit subtypes have different properties, different distributions in the brain and different activities relative to pharmacological and clinical effects. Benzodiazepines bind at the interface of the α and γ subunits on the GABAA receptor. Binding also requires that alpha subunits contain a histidine
amino acid residue, (i.e., α1
, α2
, α3
, and α5
containing GABAA receptors). For this reason, benzodiazepines show no affinity for GABAA receptors containing α4
and α6
subunits with an arginine
instead of a histidine residue.
Once bound to the benzodiazepine receptor, the benzodiazepine ligand
locks the benzodiazepine receptor into a conformation in which it has a greater affinity for the GABA
neurotransmitter
. This increases the frequency of the opening of the associated chloride ion channel
and hyperpolarizes
the membrane of the associated neuron. The inhibitory effect of the available GABA is potentiated, leading to sedatory and anxiolytic effects. Furthermore, different benzodiazepines can have different affinities for BzRs made up of different collection of subunits. For instance, those with high activity at the α1 are associated with stronger hypnotic
effects, whereas those with higher affinity for GABAA receptors containing α2 and/or α3 subunits have good anti-anxiety activity.
The benzodiazepine class of drugs also interact with peripheral benzodiazepine receptors. Peripheral benzodiazepine receptors are present in peripheral nervous system
tissues, glial cells, and to a lesser extent the central nervous system. These peripheral receptors are not structurally related nor coupled to GABAA receptors. They modulate the immune system
and are involved in the body response to injury. Benzodiazepines also function as weak adenosine reuptake inhibitor
s. It has been suggested that some of their anticonvulsant, anxiolytic and muscle relaxant effects may be in part mediated by this action.
with certain drugs. Depending on their metabolism
pathway, benzodiazepines can be roughly divided into two groups. The largest group consists of those that are metabolized by cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzymes and possess significant potential for interactions with other drugs. The other group comprises those that are metabolized through glucuronidation
, such as lorazepam
, oxazepam
, and temazepam
, and, in general, have few drug interactions.
Many drugs, including oral contraceptives, some antibiotic
s, antidepressant
s, and antifungal agents, inhibit cytochrome enzymes in the liver. They reduce the rate of elimination of the benzodiazepines that are metabolized by CYP450, leading to possibly excessive drug accumulation and increased side-effects. In contrast, drugs that induce cytochrome P450 enzymes, such as St John's wort
, the antibiotic rifampicin
, and the anticonvulsants carbamazepine
and phenytoin
, accelerate elimination of many benzodiazepines and decrease their action. Taking benzodiazepines with alcohol, opioid
s and other central nervous system depressants
potentiates their action. This often results in increased sedation, impaired motor coordination, suppressed breathing, and other adverse effects that have potential to be lethal. Antacids may slow down absorption of some benzodiazepines; however, this effect is marginal and inconsistent.
(Librium), was synthesized in 1955 by Leo Sternbach
while working at Hoffmann–La Roche on the development of tranquilizers. The pharmacological properties of the compounds prepared initially were disappointing, and Sternbach abandoned the project. Two years later, in April 1957, co-worker Earl Reeder noticed a "nicely crystalline" compound left over from the discontinued project while spring-cleaning in the lab. This compound, later named chlordiazepoxide, had not been tested in 1955 because of Sternbach's focus on other issues. Expecting the pharmacology results to be negative and hoping to publish the chemistry-related findings, researchers submitted it for a standard battery of animal tests. However, the compound showed very strong sedative
, anticonvulsant
, and muscle relaxant
effects. These impressive clinical findings led to its speedy introduction throughout the world in 1960 under the brand name Librium. Following chlordiazepoxide, diazepam
marketed by Hoffmann–La Roche under the brand name Valium in 1963, and for a while the two were the most commercially successful drugs. The introduction of benzodiazepines led to a decrease in the prescription of barbiturate
s, and by the 1970s they had largely replaced the older drugs for sedative and hypnotic
uses.
The new group of drugs was initially greeted with optimism by the medical profession, but gradually concerns arose; in particular, the risk of dependence became evident in the 1980s. Benzodiazepines have a unique history in that they were responsible for the largest-ever class-action lawsuit against drug manufacturers in the United Kingdom, involving 14,000 patients and 1,800 law firms that alleged the manufacturers knew of the dependence potential but intentionally withheld this information from doctors. At the same time, 117 general practitioners and 50 health authorities were sued by patients to recover damages for the harmful effects of dependence
and withdrawal
. This led some doctors to require a signed consent form from their patients and to recommend that all patients be adequately warned of the risks of dependence and withdrawal before starting treatment with benzodiazepines. The court case against the drug manufacturers never reached a verdict; legal aid
had been withdrawn and there were allegations that the consultant psychiatrists, the expert witnesses, had a conflict of interest. This litigation led to changes in the British law, making class action law suits more difficult.
In 2010, formerly classified documents from a Medical Research Council (UK)
meeting of experts emerged and revealed that the MRC was aware of research 30 years ago that suggested that benzodiazepines could cause brain damage in some people similar to that which occurs from alcohol abuse and failed to follow-up with larger clinical trials. The MRC turned down research proposals in the 1980s by Professor Lader and also proposals by Professor Ashton in 1995 to study whether benzodiazepines had permanent effects on the brain. The MRC responded that it has always been open to research proposals in this area that meet required standards. It was further alleged that the MRC documents were relevant to a large class-action lawsuit, which started in the mid-1980s against drug companies and one solicitor stated that it was strange that the MRC had 'hidden' the documents. Jim Dobbin
, MP and chair of the All-Party Parliamentary Group for Involuntary Tranquilliser Addiction, described the documents as a "huge scandal," given the large number of people who experience symptoms such as physical, cognitive, and psychological problems as a result of benzodiazepine use, which can persist even after withdrawing.
Although antidepressants with anxiolytic properties have been introduced, and there is increasing awareness of the adverse effects of benzodiazepines, prescriptions for short-term anxiety relief have not significantly dropped. For treatment of insomnia, benzodiazepines are now less popular than nonbenzodiazepine
s, which include zolpidem
, zaleplon
and eszopiclone
. Nonbenzodiazepines are molecularly distinct, but nonetheless, they work on the same benzodiazepine receptors and produce similar sedative effects.
which is Schedule III drugs under the Convention on Psychotropic Substances
. Some variation in drug scheduling exists in individual countries; for example, in the United Kingdom, midazolam
and temazepam
are Schedule III controlled drugs. British law requires temazepam (but not midazolam) to be stored in safe custody. Safe custody requirements ensures that pharmacists and doctors holding stock of temazepam must store it in securely fixed double-locked steel safety cabinets and maintain a written register, which must be bound and contain separate entries for temazepam and must be written in ink with no use of correction fluid. Disposal of expired stock must be witnessed by a designated inspector (either a local drug-enforcement police officer or official from health authority). Benzodiazepine abuse ranges from occasional binges on large doses, to chronic and compulsive drug abuse of high doses.
Benzodiazepines are used recreationally and by problematic drug misusers. Mortality
is higher among poly-drug misusers
that also use benzodiazepines. Heavy alcohol use also increases mortality
among poly-drug users. Dependence and tolerance, often coupled with dosage escalation, to benzodiazepines can develop rapidly among drug misusers; withdrawal syndrome may appear after as little as three weeks of continuous use. Long-term use has the potential to cause both physical and psychological dependence and severe withdrawal symptoms such as depression
, anxiety and panic attacks, and agoraphobia
. Benzodiazepines and, in particular, temazepam
are sometimes used intravenously, which, if done incorrectly or in an unsterile manner, can lead to medical complications including abscess
es, cellulitis
, thrombophlebitis
, arterial puncture, deep vein thrombosis
, and gangrene
. Sharing syringes and needles for this purpose also brings up the possibility of transmission of hepatitis
, HIV
, and other diseases. Benzodiazepines are also misused intranasally, which may have additional health consequences. Once benzodiazepine dependence has been established, a clinician usually converts the patient to an equivalent dose of diazepam before beginning a gradual reduction program.
A 1999–2005 Australian police survey of detainees reported preliminary findings that self-reported users of benzodiazepines were less likely than non-user detainees to work full-time and more likely to receive government benefits, use methamphetamine or heroin, and be arrested or imprisoned. Benzodiazepines are sometimes used for criminal purposes; they serve to incapacitate a victim in cases of drug assisted rape or robbery.
Overall, anecdotal evidence
suggests that temazepam
may be the most psychologically habit-forming (addictive)
benzodiazepine. Temazepam abuse reached epidemic proportions in some parts of the world, in particular, in Europe and Australia, and is a major drug of abuse in many Southeast Asian countries. This led authorities of various countries to place temazepam under a more restrictive legal status. Some countries banned the drug outright (i.e., Sweden). Temazepam also has certain pharmacokinetic properties of absorption, distribution, elimination, and clearance that make it more apt to abuse compared to many other benzodiazepines.
, and tetanus
, and as maintenance therapy in epilepsy (in particular, in cats). They are widely used in small and large animals (including horses, swine, cattle and exotic and wild animals) for their anxiolytic and sedative effects, as pre medication before surgery, for induction of anesthesia
and as adjuncts to anesthesia.
Psychoactive drug
A psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, or psychotropic is a chemical substance that crosses the blood–brain barrier and acts primarily upon the central nervous system where it affects brain function, resulting in changes in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition, and behavior...
whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene
Benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound. It is composed of 6 carbon atoms in a ring, with 1 hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom, with the molecular formula C6H6....
ring and a diazepine
Diazepine
1,2-Diazepine is a seven-membered heterocyclic compound with two nitrogen atoms and three double bonds.-External links:*...
ring. The first benzodiazepine, chlordiazepoxide
Chlordiazepoxide
Chlordiazepoxide, is a sedative/hypnotic drug and benzodiazepine. It is marketed under the trade names Angirex, Klopoxid, Librax , Libritabs, Librium, Mesural, Multum, Novapam, Risolid, Silibrin, Sonimen and Tropium.Chlordiazepoxide was the first benzodiazepine to be synthesised and...
(Librium), was discovered accidentally
Serendipity
Serendipity means a "happy accident" or "pleasant surprise"; specifically, the accident of finding something good or useful without looking for it. The word has been voted as one of the ten English words hardest to translate in June 2004 by a British translation company. However, due to its...
by Leo Sternbach
Leo Sternbach
Leo Henryk Sternbach was a Polish-Jewish chemist who is credited with discovering benzodiazepines, main class of tranquilizers.-Biography:...
in 1955, and made available in 1960 by Hoffmann–La Roche, which has also marketed diazepam
Diazepam
Diazepam , first marketed as Valium by Hoffmann-La Roche is a benzodiazepine drug. Diazepam is also marketed in Australia as Antenex. It is commonly used for treating anxiety, insomnia, seizures including status epilepticus, muscle spasms , restless legs syndrome, alcohol withdrawal,...
(Valium) since 1963.
Benzodiazepines enhance the effect of the neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals that transmit signals from a neuron to a target cell across a synapse. Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles clustered beneath the membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse, and are released into the synaptic cleft, where they bind to...
gamma-aminobutyric acid
Gamma-aminobutyric acid
γ-Aminobutyric acid is the chief inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mammalian central nervous system. It plays a role in regulating neuronal excitability throughout the nervous system...
(GABA), which results in sedative
Sedative
A sedative or tranquilizer is a substance that induces sedation by reducing irritability or excitement....
, hypnotic
Hypnotic
Hypnotic drugs are a class of psychoactives whose primary function is to induce sleep and to be used in the treatment of insomnia and in surgical anesthesia...
(sleep-inducing), anxiolytic
Anxiolytic
An anxiolytic is a drug used for the treatment of anxiety, and its related psychological and physical symptoms...
(anti-anxiety), anticonvulsant
Anticonvulsant
The anticonvulsants are a diverse group of pharmaceuticals used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of bipolar disorder, since many seem to act as mood stabilizers, and in the treatment of neuropathic pain. The goal of an...
, muscle relaxant
Muscle relaxant
A muscle relaxant is a drug which affects skeletal muscle function and decreases the muscle tone. It may be used to alleviate symptoms such as muscle spasms, pain, and hyperreflexia. The term "muscle relaxant" is used to refer to two major therapeutic groups: neuromuscular blockers and spasmolytics...
and amnesic
Anterograde amnesia
Anterograde amnesia is a loss of the ability to create new memories after the event that caused the amnesia, leading to a partial or complete inability to recall the recent past, while long-term memories from before the event remain intact. This is in contrast to retrograde amnesia, where memories...
action. These properties make benzodiazepines useful in treating anxiety
Anxiety
Anxiety is a psychological and physiological state characterized by somatic, emotional, cognitive, and behavioral components. The root meaning of the word anxiety is 'to vex or trouble'; in either presence or absence of psychological stress, anxiety can create feelings of fear, worry, uneasiness,...
, insomnia
Insomnia
Insomnia is most often defined by an individual's report of sleeping difficulties. While the term is sometimes used in sleep literature to describe a disorder demonstrated by polysomnographic evidence of disturbed sleep, insomnia is often defined as a positive response to either of two questions:...
, agitation
Psychomotor agitation
Psychomotor agitation is a series of unintentional and purposeless motions that stem from mental tension and anxiety of an individual. This includes pacing around a room, wringing one's hands, pulling off clothing and putting it back on and other similar actions...
, seizure
Seizure
An epileptic seizure, occasionally referred to as a fit, is defined as a transient symptom of "abnormal excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain". The outward effect can be as dramatic as a wild thrashing movement or as mild as a brief loss of awareness...
s, muscle spasms
Spasm
In medicine a spasm is a sudden, involuntary contraction of a muscle, a group of muscles, or a hollow organ, or a similarly sudden contraction of an orifice. It is sometimes accompanied by a sudden burst of pain, but is usually harmless and ceases after a few minutes...
, alcohol withdrawal and as a premedication
Premedication
Premedication refer to a drug treatment given to a patient before a medical procedure. These drugs are typically sedative or analgesic....
for medical or dental procedures. Benzodiazepines are categorized as either short-, intermediate- or long-acting. Short- and intermediate-acting benzodiazepines are preferred for the treatment of insomnia; longer-acting benzodiazepines are recommended for the treatment of anxiety.
In general, benzodiazepines are safe and effective in the short term, although cognitive impairments and paradoxical effects such as aggression or behavioral disinhibition
Disinhibition
Disinhibition is a term in psychology used to describe a lack of restraint manifested in several ways, including disregard for social conventions, impulsivity, and poor risk assessment. Disinhibition affects motor, instinctual, emotional, cognitive and perceptual aspects with signs and symptoms...
occasionally occur. Long-term use is controversial due to concerns about adverse psychological and physical effects, increased questioning of effectiveness and because benzodiazepines are prone to cause tolerance, physical dependence
Physical dependence
Physical dependence refers to a state resulting from chronic use of a drug that has produced tolerance and where negative physical symptoms of withdrawal result from abrupt discontinuation or dosage reduction...
, and, upon cessation of use after long term use, a withdrawal syndrome
Benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome
Benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome—often abbreviated to benzo withdrawal—is the cluster of symptoms which appear when a person who has taken benzodiazepines long term and has developed benzodiazepine dependence stops taking benzodiazepine drug or during dosage reductions...
. Due to adverse effects associated with the long-term use of benzodiazepines, withdrawal from benzodiazepines, in general, leads to improved physical and mental health. The elderly are at an increased risk of suffering from both short- and long-term adverse effects
Adverse drug reaction
An adverse drug reaction is an expression that describes harm associated with the use of given medications at a normal dosage. ADRs may occur following a single dose or prolonged administration of a drug or result from the combination of two or more drugs...
.
There is controversy concerning the safety of benzodiazepines in pregnancy. While they are not major teratogens, uncertainty remains as to whether they cause cleft palate in a small number of babies and whether neurobehavioural effects occur as a result of prenatal exposure; they are known to cause withdrawal symptoms in the newborn
Neonatal withdrawal
Neonatal withdrawal or neonatal abstinence syndrome is a withdrawal syndrome of infants, caused by administration of drugs. Tolerance, dependence and withdrawal may occur as a result of repeated administration of drugs, or even after short-term high dose use for example during mechanical...
. Benzodiazepines can be taken in overdoses and can cause dangerous deep unconsciousness
Coma
In medicine, a coma is a state of unconsciousness, lasting more than 6 hours in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light or sound, lacks a normal sleep-wake cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. A person in a state of coma is described as...
. However, they are much less toxic than their predecessors, the barbiturate
Barbiturate
Barbiturates are drugs that act as central nervous system depressants, and can therefore produce a wide spectrum of effects, from mild sedation to total anesthesia. They are also effective as anxiolytics, as hypnotics, and as anticonvulsants...
s, and death rarely results when a benzodiazepine is the only drug taken. When combined with other central nervous system depressants such as alcohol
Alcoholic beverage
An alcoholic beverage is a drink containing ethanol, commonly known as alcohol. Alcoholic beverages are divided into three general classes: beers, wines, and spirits. They are legally consumed in most countries, and over 100 countries have laws regulating their production, sale, and consumption...
and opiates, the potential for toxicity increases. Benzodiazepines are commonly misused and taken in combination with other drugs of abuse
Drug abuse
Substance abuse, also known as drug abuse, refers to a maladaptive pattern of use of a substance that is not considered dependent. The term "drug abuse" does not exclude dependency, but is otherwise used in a similar manner in nonmedical contexts...
.
Medical uses
Benzodiazepines possess sedative, hypnotic, anxiolyticAnxiolytic
An anxiolytic is a drug used for the treatment of anxiety, and its related psychological and physical symptoms...
, anticonvulsant, muscle relaxant, and amnesic
Anterograde amnesia
Anterograde amnesia is a loss of the ability to create new memories after the event that caused the amnesia, leading to a partial or complete inability to recall the recent past, while long-term memories from before the event remain intact. This is in contrast to retrograde amnesia, where memories...
actions, which are useful in a variety of indications such as alcohol dependence
Alcohol dependence
Alcohol dependence, as described in the DSM-IV, is a psychiatric diagnosis describing an entity in which an individual uses alcohol despite significant areas of dysfunction, evidence of physical dependence, and/or related hardship.-Definition and diagnosis:According to the DSM-IV criteria for...
, seizures, anxiety
Anxiety
Anxiety is a psychological and physiological state characterized by somatic, emotional, cognitive, and behavioral components. The root meaning of the word anxiety is 'to vex or trouble'; in either presence or absence of psychological stress, anxiety can create feelings of fear, worry, uneasiness,...
, panic
Panic
Panic is a sudden sensation of fear which is so strong as to dominate or prevent reason and logical thinking, replacing it with overwhelming feelings of anxiety and frantic agitation consistent with an animalistic fight-or-flight reaction...
, agitation
Psychomotor agitation
Psychomotor agitation is a series of unintentional and purposeless motions that stem from mental tension and anxiety of an individual. This includes pacing around a room, wringing one's hands, pulling off clothing and putting it back on and other similar actions...
and insomnia. Most are administered orally; however, they can also be given intravenously
Intravenous therapy
Intravenous therapy or IV therapy is the infusion of liquid substances directly into a vein. The word intravenous simply means "within a vein". Therapies administered intravenously are often called specialty pharmaceuticals...
, intramuscularly
Intramuscular injection
Intramuscular injection is the injection of a substance directly into a muscle. In medicine, it is one of several alternative methods for the administration of medications . It is used for particular forms of medication that are administered in small amounts...
or rectally. In general, benzodiazepines are well-tolerated and are safe and effective drugs in the short term for a wide range of conditions. Tolerance can develop to their effects and there is also a risk of dependence, and upon discontinuation a withdrawal syndrome may occur. These factors, combined with other possible secondary effects after prolonged use such as psychomotor, cognitive, or memory impairments, limit their long-term applicability. The effects of long-term use or misuse include the tendency to cause or worsen cognitive deficit
Cognitive deficit
Cognitive deficit, also known as cognitive impairment is an inclusive term to describe any characteristic that acts as a barrier to cognitive performance...
s, depression
Clinical depression
Major depressive disorder is a mental disorder characterized by an all-encompassing low mood accompanied by low self-esteem, and by loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities...
and anxiety.
Panic disorder
Due to their effectiveness, tolerability, and rapid onset of anxiolytic action, benzodiazepines are frequently used for the treatment of anxiety associated with panic disorder. However, there is disagreement among expert bodies regarding the long-term use of benzodiazepines for panic disorder. The views range from those that hold that benzodiazepines are not effective long-term and that they should be reserved for treatment-resistant cases to that they are as effective in the long term as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors.The American Psychiatric Association
American Psychiatric Association
The American Psychiatric Association is the main professional organization of psychiatrists and trainee psychiatrists in the United States, and the most influential worldwide. Its some 38,000 members are mainly American but some are international...
(APA) guidelines note that, in general, benzodiazepines are well tolerated, and their use for the initial treatment for panic disorder is strongly supported by numerous controlled trials. APA states that there is insufficient evidence to recommend any of the established panic disorder treatments over another. The choice of treatment between benzodiazepines, SSRIs, serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressant
Tricyclic antidepressant
Tricyclic antidepressants are heterocyclic chemical compounds used primarily as antidepressants. The TCAs were first discovered in the early 1950s and were subsequently introduced later in the decade; they are named after their chemical structure, which contains three rings of atoms...
s, and psychotherapy should be based on the patient's history, preference, and other individual characteristics. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors are likely to be the best choice of pharmacotherapy for many patients with panic disorder, but benzodiazepines are also often used, and some studies suggest that these medications are still used with greater frequency than the SSRIs. One advantage of benzodiazepines is that they alleviate the anxiety symptoms much faster than antidepressants, and therefore may be preferred in patients for whom rapid symptom control is critical. However, this advantage is offset by the possibility of developing benzodiazepine dependence
Benzodiazepine dependence
Benzodiazepine dependence or benzodiazepine addiction is a condition during which a person is dependent on benzodiazepine drugs. Dependence can be either a psychological dependence, physical dependence, or a combination of the two...
. APA does not recommend benzodiazepines for persons with depressive symptoms or a recent history of substance abuse
Substance abuse
A substance-related disorder is an umbrella term used to describe several different conditions associated with several different substances .A substance related disorder is a condition in which an individual uses or abuses a...
. The APA guidelines state that, in general, pharmacotherapy of panic disorder should be continued for at least a year, and that clinical experience support continuing benzodiazepine treatment to prevent recurrence. Although major concerns about benzodiazepine tolerance and withdrawal have been raised, there is no evidence for significant dose escalation in patients using benzodiazepines long-term. For many such patients stable doses of benzodiazepines retain their efficacy over several years.
Guidelines issued by the UK-based National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
The National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence is a special health authority of the English National Health Service , serving both English NHS and the Welsh NHS...
(NICE), carried out a systematic review using different methodology and came to a different conclusion. They questioned the accuracy of studies that were not placebo-controlled. And, based on the findings of placebo-controlled studies
Placebo-controlled studies
A Placebo-controlled study is a way of testing a medical therapy in which, in addition to a group of subjects that receives the treatment to be evaluated, a separate control group receives a sham "placebo" treatment which is specifically designed to have no real effect...
, they do not recommend use of benzodiazepines beyond two to four weeks, as tolerance and physical dependence
Physical dependence
Physical dependence refers to a state resulting from chronic use of a drug that has produced tolerance and where negative physical symptoms of withdrawal result from abrupt discontinuation or dosage reduction...
develop rapidly, with withdrawal symptoms including rebound anxiety occurring after six weeks or more of use. Nevertheless, benzodiazepines continue to be prescribed for the long-term treatment of anxiety disorders, although specific antidepressants and psychological therapies are recommended as the first-line treatment options with the anticonvulsant
Anticonvulsant
The anticonvulsants are a diverse group of pharmaceuticals used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of bipolar disorder, since many seem to act as mood stabilizers, and in the treatment of neuropathic pain. The goal of an...
drug pregabalin
Pregabalin
Pregabalin is an anticonvulsant drug used for neuropathic pain and as an adjunct therapy for partial seizures with or without secondary generalization in adults. It has also been found effective for generalized anxiety disorder and is approved for this use in the European Union. It was designed...
indicated as a second- or third-line treatment and suitable for long-term use. NICE stated that long-term use of benzodiazepines for panic disorder with or without agoraphobia
Agoraphobia
Agoraphobia is an anxiety disorder defined as a morbid fear of having a panic attack or panic-like symptoms in a situation from which it is perceived to be difficult to escape. These situations can include, but are not limited to, wide-open spaces, crowds, or uncontrolled social conditions...
is an unlicensed indication, does not have long-term efficacy, and is, therefore, not recommended by clinical guidelines. Psychological therapies such as cognitive behavioural therapy are recommended as a first-line therapy for panic disorder; benzodiazepine use has been found to interfere with therapeutic gains from these therapies.
Benzodiazepines are usually administered orally; however, very occasionally lorazepam or diazepam may be given intravenously for the treatment of panic attacks.
Generalized anxiety disorder
Benzodiazepines have robust efficacy in the short-term management of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), but were not shown to be effective in producing long-term improvement overall. According to National Institute for Health and Clinical ExcellenceNational Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
The National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence is a special health authority of the English National Health Service , serving both English NHS and the Welsh NHS...
(NICE), benzodiazepines can be used in the immediate management of GAD, if necessary. However, they should not usually be given for longer than 2–4 weeks. The only medications NICE recommends for the longer term management of GAD are antidepressants.
Likewise, Canadian Psychiatric Association (CPA) recommends benzodiazepines alprazolam
Alprazolam
Alprazolam is a short-acting anxiolytic of the benzodiazepine class of psychoactive drugs. Alprazolam, like other benzodiazepines, binds to specific sites on the GABAA gamma-amino-butyric acid receptor...
, bromazepam
Bromazepam
Bromazepam is a benzodiazepine derivative drug, patented by Roche in the 1963 and developed clinically in the 1970s...
, lorazepam
Lorazepam
Lorazepam is a high-potency short-to-intermediate-acting 3-hydroxy benzodiazepine drug that has all five intrinsic benzodiazepine effects: anxiolytic, amnesic, sedative/hypnotic, anticonvulsant, antiemetic and muscle relaxant...
, and diazepam
Diazepam
Diazepam , first marketed as Valium by Hoffmann-La Roche is a benzodiazepine drug. Diazepam is also marketed in Australia as Antenex. It is commonly used for treating anxiety, insomnia, seizures including status epilepticus, muscle spasms , restless legs syndrome, alcohol withdrawal,...
only as a second-line choice, if the treatment with two different antidepressants was unsuccessful. Although they are second-line agents, benzodiazepines can be used for a limited time to relieve severe anxiety and agitation. CPA guidelines note that after 4–6 weeks the effect of benzodiazepines may decrease to the level of placebo, and that benzodiazepines are less effective than antidepressants in alleviating ruminative worry
Rumination (psychology)
Rumination is a way of responding to distress that involves repetitively focusing on the symptoms of distress, and on its possible causes and consequences. Rumination is more common in people who are pessimistic, neurotic, and who have negative attributional styles. The tendency to ruminate is a...
, the core symptom of GAD. However, in some cases, a prolonged treatment with benzodiazepines as the add-on to an antidepressant may be justified.
Insomnia
Benzodiazepines can be useful for short-term treatment of insomnia. Their use beyond 2 to 4 weeks is not recommended due to the risk of dependence. It is preferred that benzodiazepines be taken intermittently and at the lowest effective dose. They improve sleep-related problems by shortening the time spent in bed before falling asleep, prolonging the sleep time, and, in general, reducing wakefulness. However, they worsen sleep quality by increasing light sleep and decreasing deep sleep. Other drawbacks of hypnotics, including benzodiazepines, are possible tolerance to their effects, rebound insomnia, and reduced slow-wave sleep and a withdrawal period typified by rebound insomnia and a prolonged period of anxiety and agitation. The list of benzodiazepines approved for the treatment of insomnia is fairly similar among most countries, but which benzodiazepines are officially designated as first-line hypnotics prescribed for the treatment of insomnia can vary distinctly between countries. Longer-acting benzodiazepines such as nitrazepamNitrazepam
Nitrazepam is a type of benzodiazepine drug and is marketed in English-speaking countries under the following brand names: Alodorm, Arem, Insoma, Mogadon, Nitrados, Nitrazadon, Ormodon, Paxadorm, Remnos, and Somnite...
and diazepam
Diazepam
Diazepam , first marketed as Valium by Hoffmann-La Roche is a benzodiazepine drug. Diazepam is also marketed in Australia as Antenex. It is commonly used for treating anxiety, insomnia, seizures including status epilepticus, muscle spasms , restless legs syndrome, alcohol withdrawal,...
have residual effects that may persist into the next day and are, in general, not recommended.
It is not clear as to whether the new nonbenzodiazepine
Nonbenzodiazepine
The nonbenzodiazepines, also called benzodiazepine-like drugs, are a class of psychoactive drugs pharmacologically resembling the benzodiazepines, with similar benefits, side effects and risks, despite having dissimilar or entirely different chemical structures.-Classes:There are currently three...
hypnotics (Z-drugs) are better than the short-acting benzodiazepines. The efficacy of these two groups of medications is similar. According to the US Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality is a part of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, which supports research designed to improve the outcomes and quality of health care, reduce its costs, address patient safety and medical errors, and broaden access to effective...
, indirect comparison indicates that side-effects from benzodiazepines may be about twice as frequent as from nonbenzodiazepines. This may make the non-benzodiazepines preferable as the first-line long-term treatment of insomnia. However, the UK National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
The National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence is a special health authority of the English National Health Service , serving both English NHS and the Welsh NHS...
did not find any convincing evidence in favor of Z-drugs. NICE review pointed out that short-acting Z-drugs were inappropriately compared in clinical trials with long-acting benzodiazepines. There have been no trials comparing short-acting Z-drugs with appropriate doses of short-acting benzodiazepines. Based on this, NICE recommended choosing the hypnotic based on cost and the patient's preference.
It has been argued that long-term use of hypnotics and overprescribing of these drugs represents an unjustifiable risk, especially to the elderly, and is harmful for the public health
Public health
Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals" . It is concerned with threats to health based on population health...
in general.
Seizures
Prolonged convulsive epileptic seizures are a medical emergencyMedical emergency
A medical emergency is an injury or illness that is acute and poses an immediate risk to a person's life or long term health. These emergencies may require assistance from another person, who should ideally be suitably qualified to do so, although some of these emergencies can be dealt with by the...
that can usually be dealt with effectively by administering fast-acting benzodiazepines, which are potent anticonvulsants. In a hospital environment, intravenous clonazepam
Clonazepam
Clonazepamis a benzodiazepine drug having anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, muscle relaxant, and hypnotic properties. It is marketed by Roche under the trade name Klonopin in the United States and Rivotril in Australia, Brazil, Canada and Europe...
, lorazepam
Lorazepam
Lorazepam is a high-potency short-to-intermediate-acting 3-hydroxy benzodiazepine drug that has all five intrinsic benzodiazepine effects: anxiolytic, amnesic, sedative/hypnotic, anticonvulsant, antiemetic and muscle relaxant...
, and diazepam
Diazepam
Diazepam , first marketed as Valium by Hoffmann-La Roche is a benzodiazepine drug. Diazepam is also marketed in Australia as Antenex. It is commonly used for treating anxiety, insomnia, seizures including status epilepticus, muscle spasms , restless legs syndrome, alcohol withdrawal,...
are first-line choices, clonazepam due to its stronger and more potent anticonvulsant action, diazepam due to its faster onset and lorazepam for its longer duration of action. In the community, intravenous administration is not practical and so rectal diazepam or (more recently) buccal midazolam
Midazolam
Midazolam is a short-acting drug in the benzodiazepine class developed by Hoffmann-La Roche in the 1970s. The drug is used for treatment of acute seizures, moderate to severe insomnia, and for inducing sedation and amnesia before medical procedures. It possesses profoundly potent anxiolytic,...
are used, with a preference for midazolam as its administration is easier and more socially acceptable.
When benzodiazepines were first introduced, they were enthusiastically adopted for treating all forms of epilepsy
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a common chronic neurological disorder characterized by seizures. These seizures are transient signs and/or symptoms of abnormal, excessive or hypersynchronous neuronal activity in the brain.About 50 million people worldwide have epilepsy, and nearly two out of every three new cases...
. However, drowsiness and tolerance become problems with continued use and none are now considered first-line choices for long-term epilepsy therapy. Clobazam is widely used by specialist epilepsy clinics worldwide (but it is not available in the US) and clonazepam is popular in the Netherlands, Belgium and France. In the UK, both clobazam and clonazepam are second-line choices for treating many forms of epilepsy. Clobazam also has a useful role for very short-term seizure prophylaxis and in catamenial epilepsy
Catamenial epilepsy
Catamenial epilepsy is a subtype of epilepsy, which is a chronic neurological condition characterized by recurrent seizures. Catamenial epilepsy is a subset of this population, which includes women of whom their seizure exacerbation is aligned with their menstrual cycle. Women with catamenial...
. Discontinuation after long term use in epilepsy requires additional caution because of the risks of rebound seizures. Therefore, the dose is slowly tapered over a period of up to six months or longer.
Alcohol withdrawal
ChlordiazepoxideChlordiazepoxide
Chlordiazepoxide, is a sedative/hypnotic drug and benzodiazepine. It is marketed under the trade names Angirex, Klopoxid, Librax , Libritabs, Librium, Mesural, Multum, Novapam, Risolid, Silibrin, Sonimen and Tropium.Chlordiazepoxide was the first benzodiazepine to be synthesised and...
is the most commonly used benzodiazepine for alcohol detoxification
Alcohol detoxification
Alcohol detoxification, or detox, for individuals with alcohol dependence, is the abrupt cessation of alcohol intake coupled with the substitution of alcohol with cross-tolerant drugs that have similar effects in order to prevent alcohol withdrawal...
, but diazepam
Diazepam
Diazepam , first marketed as Valium by Hoffmann-La Roche is a benzodiazepine drug. Diazepam is also marketed in Australia as Antenex. It is commonly used for treating anxiety, insomnia, seizures including status epilepticus, muscle spasms , restless legs syndrome, alcohol withdrawal,...
may be used as an alternative. Both are used in the detoxification of individuals who are motivated to stop drinking, and are prescribed for a short period of time to reduce the risks of developing tolerance and dependence to the benzodiazepine medication itself. The benzodiazepines with a longer half-life make detoxification more tolerable, and dangerous alcohol withdrawal effects are less likely to occur. On the other hand, short-acting benzodiazepines may lead to breakthrough seizure
Breakthrough seizure
A breakthrough seizure is an epileptic seizure that occurs, despite the use of anticonvulsants that have otherwise successfully prevented seizures in the patient...
s, and are, therefore, not recommended for detoxification in an outpatient setting. Oxazepam
Oxazepam
Oxazepam , is a drug which is a short to intermediate acting 3-hydroxy benzodiazepine derivative...
and lorazepam
Lorazepam
Lorazepam is a high-potency short-to-intermediate-acting 3-hydroxy benzodiazepine drug that has all five intrinsic benzodiazepine effects: anxiolytic, amnesic, sedative/hypnotic, anticonvulsant, antiemetic and muscle relaxant...
are often used in patients at risk of drug accumulation, in particular, the elderly and those with cirrhosis
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is a consequence of chronic liver disease characterized by replacement of liver tissue by fibrosis, scar tissue and regenerative nodules , leading to loss of liver function...
, because they are metabolized differently from other benzodiazepines, through conjugation
Glucuronidation
Glucuronidation is the addition of glucuronic acid to a substrate. Glucuronidation is often involved in xenobiotic metabolism of substances such as drugs, pollutants, bilirubin, androgens, estrogens, mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, fatty acid derivatives, retinoids, and bile acids...
.
Benzodiazepines are the preferred choice in the management of alcohol withdrawal syndrome
Alcohol withdrawal syndrome
-Protracted withdrawal:A protracted alcohol withdrawal syndrome occurs in many alcoholics where withdrawal symptoms continue beyond the acute withdrawal stage but usually at a subacute level of intensity and gradually decreasing with severity over time. This syndrome is also sometimes referred to...
, in particular, for the prevention and treatment of the dangerous complication of seizures and in subduing severe delirium
Delirium
Delirium or acute confusional state is a common and severe neuropsychiatric syndrome with core features of acute onset and fluctuating course, attentional deficits and generalized severe disorganization of behavior...
. Lorazepam is the only benzodiazepine with predictable intramuscular absorption and it is the most effective in preventing and controlling acute seizures.
Anxiety
Benzodiazepines are sometimes used in the treatment of acute anxiety, as they bring about rapid and marked or moderate relief of symptoms in most individuals; however, they are not recommended beyond 2–4 weeks of use due to risks of tolerance and dependence and a lack of long-term effectiveness. As for insomnia, they may also be used on an irregular/"as-needed" basis, such as in cases where said anxiety is at its worst. Compared to other pharmacological treatments, benzodiazepines are twice as likely to lead to a relapse of the underlying condition upon discontinuation. Psychological therapies and other pharmacological therapies are recommended for the long-term treatment of generalised anxiety disorder. Antidepressants have higher remission rates and are, in general, safe and effective in the short and long term.Other indications
Benzodiazepines are often prescribed for a wide range of conditions:- They can be very useful in intensive care to sedate patients receiving mechanical ventilationMechanical ventilationIn medicine, mechanical ventilation is a method to mechanically assist or replace spontaneous breathing. This may involve a machine called a ventilator or the breathing may be assisted by a physician, respiratory therapist or other suitable person compressing a bag or set of bellows...
or those in extreme distress. Caution is exercised in this situation due to the occasional occurrence of respiratory depression, and it is recommended that benzodiazepine overdoseBenzodiazepine overdoseBenzodiazepine overdose describes the ingestion of one of the drugs in the benzodiazepine class in quantities greater than are recommended or generally practiced. Death as a result of benzodiazepines is uncommon but does occasionally happen. Deaths after hospital admission are considered to be low...
treatment facilities should be available. - Benzodiazepines are effective as medication given a couple of hours before surgery to relieve anxiety. They also produce amnesiaAmnesiaAmnesia is a condition in which one's memory is lost. The causes of amnesia have traditionally been divided into categories. Memory appears to be stored in several parts of the limbic system of the brain, and any condition that interferes with the function of this system can cause amnesia...
, which can be useful, as patients will not be able to remember any unpleasantness from the procedure. They are also used in patients with dental phobia as well as some ophthalmic procedures like refractive surgery; although such use is controversial and only recommended for those who are very anxious. Midazolam is the most commonly prescribed for this use because of its strong sedative actions and fast recovery time, as well as its water solubility, which reduces pain upon injection. Diazepam and lorazepam are sometimes used. Lorazepam has particularly marked amnesic properties that may make it more effective when amnesia is the desired effect. - Benzodiazepines are well known for their strong muscle-relaxing properties and can be useful in the treatment of muscle spasms, although tolerance often develops to their muscle relaxant effects. BaclofenBaclofenBaclofen is a derivative of gamma-aminobutyric acid . It is primarily used to treat spasticity and is under investigation for the treatment of alcoholism....
or tizanidineTizanidineTizanidine is a drug that is used as a muscle relaxant. It is a centrally acting α2 adrenergic agonist. It is used to treat the spasms, cramping, and tightness of muscles caused by medical problems such as multiple sclerosis, spastic diplegia, back pain, or certain other injuries to the spine or...
are sometimes used as an alternative to benzodiazepines. Tizanidine has been found to have superior tolerability compared to diazepam and baclofen. - Benzodiazepines are also used to treat the acute panic caused by hallucinogen intoxication. Benzodiazepines are also used to calm the acutely agitated individual and can, if required, be given via an intramuscular injection. They can sometimes be effective in the short-term treatment of psychiatric emergencies such as acute psychosisPsychosisPsychosis means abnormal condition of the mind, and is a generic psychiatric term for a mental state often described as involving a "loss of contact with reality"...
as in schizophreniaSchizophreniaSchizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by a disintegration of thought processes and of emotional responsiveness. It most commonly manifests itself as auditory hallucinations, paranoid or bizarre delusions, or disorganized speech and thinking, and it is accompanied by significant social...
or maniaManiaMania, the presence of which is a criterion for certain psychiatric diagnoses, is a state of abnormally elevated or irritable mood, arousal, and/ or energy levels. In a sense, it is the opposite of depression...
, bringing about rapid tranquillization and sedation until the effects of lithiumLithium pharmacologyLithium pharmacology refers to use of the lithium ion, Li+, as a drug. A number of chemical salts of lithium are used medically as a mood stabilizing drug, primarily in the treatment of bipolar disorder, where they have a role in the treatment of depression and particularly of mania, both acutely...
or neuroleptics (antipsychotics) take effect. LorazepamLorazepamLorazepam is a high-potency short-to-intermediate-acting 3-hydroxy benzodiazepine drug that has all five intrinsic benzodiazepine effects: anxiolytic, amnesic, sedative/hypnotic, anticonvulsant, antiemetic and muscle relaxant...
is most commonly used but clonazepamClonazepamClonazepamis a benzodiazepine drug having anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, muscle relaxant, and hypnotic properties. It is marketed by Roche under the trade name Klonopin in the United States and Rivotril in Australia, Brazil, Canada and Europe...
is sometimes prescribed for acute psychosis or mania; their long-term use is not recommended due to risks of dependence. - ClonazepamClonazepamClonazepamis a benzodiazepine drug having anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, muscle relaxant, and hypnotic properties. It is marketed by Roche under the trade name Klonopin in the United States and Rivotril in Australia, Brazil, Canada and Europe...
, a benzodiazepine is used to treat many forms of parasomniaParasomniaFor the 2008 horror film, see Parasomnia Parasomnias are a category of sleep disorders that involve abnormal and unnatural movements, behaviors, emotions, perceptions, and dreams that occur while falling asleep, sleeping, between sleep stages, or during arousal from sleep...
. Rapid eye movement behavior disorderRapid eye movement behavior disorderRapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorder is a sleep disorder that involves abnormal behaviour during the sleep phase with rapid eye movement . It was first described in 1986....
responds well to low doses of clonazepam. Restless legs syndromeRestless legs syndromeRestless legs syndrome or Willis-Ekbom disease is a neurological disorder characterized by an irresistible urge to move one's body to stop uncomfortable or odd sensations. It most commonly affects the legs, but can affect the arms, torso, and even phantom limbs...
can be treated using clonazepam as a third line treatment option as the use of clonazepam is still investigational. - Benzodiazepines are sometimes used for obsessive compulsive disorder, although they are generally believed to be ineffective for this indication; effectiveness was, however, found in one small study. Benzodiazepines can be considered as a treatment option in treatment resistant cases.
- Antipsychotics are generally a first-line treatment for delirium; however, when deliriumDeliriumDelirium or acute confusional state is a common and severe neuropsychiatric syndrome with core features of acute onset and fluctuating course, attentional deficits and generalized severe disorganization of behavior...
is caused by alcohol or sedative hypnotic withdrawalWithdrawalWithdrawal can refer to any sort of separation, but is most commonly used to describe the group of symptoms that occurs upon the abrupt discontinuation/separation or a decrease in dosage of the intake of medications, recreational drugs, and alcohol...
, benzodiazepines are a first-line treatment.
Adverse effects
The most common side-effects of benzodiazepines are related to their sedating and muscle-relaxing action. They include drowsiness, dizziness, and decreased alertness and concentration. Lack of coordinationMotor coordination
thumb|right|Motor coordination is shown in this animated sequence by [[Eadweard Muybridge]] of himself throwing a diskMotor coordination is the combination of body movements created with the kinematic and kinetic parameters that result in intended actions. Such movements usually smoothly and...
may result in falls and injuries, in particular, in the elderly. Another result is impairment of driving skills and increased likelihood of road traffic accidents. Decreased libido and erection problems are a common side effect. Depression and disinhibition
Disinhibition
Disinhibition is a term in psychology used to describe a lack of restraint manifested in several ways, including disregard for social conventions, impulsivity, and poor risk assessment. Disinhibition affects motor, instinctual, emotional, cognitive and perceptual aspects with signs and symptoms...
may emerge. Hypotension
Hypotension
In physiology and medicine, hypotension is abnormally low blood pressure, especially in the arteries of the systemic circulation. It is best understood as a physiologic state, rather than a disease. It is often associated with shock, though not necessarily indicative of it. Hypotension is the...
and suppressed breathing may be encountered with intravenous use. Less common side effects include nausea and changes in appetite, blurred vision, confusion, euphoria
Euphoria (emotion)
Euphoria is medically recognized as a mental and emotional condition in which a person experiences intense feelings of well-being, elation, happiness, ecstasy, excitement and joy...
, depersonalization
Depersonalization
Depersonalization is an anomaly of the mechanism by which an individual has self-awareness. It is a feeling of watching oneself act, while having no control over a situation. Sufferers feel they have changed, and the world has become less real, vague, dreamlike, or lacking in significance...
and nightmares. Cases of liver toxicity have been described but are very rare.
Paradoxical effects
Paradoxical reactions, such as increased seizures in epileptics, aggressionAggression
In psychology, as well as other social and behavioral sciences, aggression refers to behavior between members of the same species that is intended to cause humiliation, pain, or harm. Ferguson and Beaver defined aggressive behavior as "Behavior which is intended to increase the social dominance of...
, violence, impulsivity
Impulsivity
Impulsivity is a personality trait characterized by the inclination of an individual to initiate behavior without adequate forethought as to the consequences of their actions, acting on the spur of the moment. Eysenck and Eysenck related impulsivity to risk-taking, lack of planning, and making up...
, irritability
Irritability
Irritability is an excessive response to stimuli. The term is used for both the physiological reaction to stimuli and for the pathological, abnormal or excessive sensitivity to stimuli; It is usually used to refer to anger or frustration....
and suicidal behavior sometimes occur. These reactions have been explained as consequences of disinhibition, that is loss of control over socially unacceptable behavior. Paradoxical reactions are rare in the general population, with an incidence rate below 1% and similar to placebo. However, they occur with greater frequency in recreational abusers, individuals with borderline personality disorder
Borderline personality disorder
Borderline personality disorder is a personality disorder described as a prolonged disturbance of personality function in a person , characterized by depth and variability of moods.The disorder typically involves unusual levels of instability in mood; black and white thinking, or splitting; the...
, children, and patients on high-dosage regimes. In these groups, impulse control problems are perhaps the most important risk factor for disinhibition; learning disabilities and neurological disorders are also significant risks. Most reports of disinhibition involve high doses of high-potency benzodiazepines. Paradoxical effects may also appear after chronic use of benzodiazepines.
Cognitive effects
The short-term use of benzodiazepines adversely affects multiple areas of cognition, the most notable one being that it interferes with the formation and consolidation of memories of new material and may induce complete anterograde amnesia. However, researchers hold contrary opinions regarding the effects of long-term administration. One view is that many of the short-term effects continue into the long-term and may even worsen, and are not resolved after quitting benzodiazepines. Another view maintains that cognitive deficits in chronic benzodiazepine users occur only for a short period after the dose, or that the anxiety disorders is the cause of these deficits.While the definitive studies are lacking, the former view received support from a 2004 meta-analysis of 13 small studies. This meta-analysis found that long-term use of benzodiazepines was associated with moderate to large adverse effects on all areas of cognition, with visuospatial memory being the most commonly detected impairment. Some of the other impairments reported were decreased IQ, visiomotor coordination, information processing, verbal learning and concentration. The authors of the meta-analysis and a later reviewer noted that the applicability of this meta-analysis is limited because the subjects were taken mostly from withdrawal clinics; the coexisting drug, alcohol use, and psychiatric disorders were not defined; and several of the included studies conducted the cognitive measurements during the withdrawal period.
Long-term effects
The long-term adverse effects of benzodiazepines include a general deterioration in physical and mental healthMental health
Mental health describes either a level of cognitive or emotional well-being or an absence of a mental disorder. From perspectives of the discipline of positive psychology or holism mental health may include an individual's ability to enjoy life and procure a balance between life activities and...
and tend to increase with time. Not everyone, however, experiences problems with long-term use. The adverse effects can include cognitive impairment, as well as affective and behavioural problems. Feelings of turmoil, difficulty in thinking constructively, loss of sex-drive, agoraphobia and social phobia, increasing anxiety and depression, loss of interest in leisure pursuits and interests, and an inability to experience or express feelings can also occur. Additionally an altered perception of self, environment and relationships may occur.
Withdrawal syndrome

Tolerance, dependence and withdrawal
The main problem of the chronic use of benzodiazepines is the development of tolerance and dependencePhysical dependence
Physical dependence refers to a state resulting from chronic use of a drug that has produced tolerance and where negative physical symptoms of withdrawal result from abrupt discontinuation or dosage reduction...
. Tolerance manifests itself as diminished pharmacological effect and develops relatively quickly to the sedative, hypnotic, anticonvulsant, and muscle relaxant actions of benzodiazepines. Tolerance to anti-anxiety effects develops more slowly with little evidence of continued effectiveness beyond four to six months of continued use. In general, tolerance to the amnesic effects does not occur. However, controversy exists as to tolerance to the anxiolytic effects with some evidence that benzodiazepines retain efficacy and opposing evidence from a systematic review of the literature that tolerance frequently occurs and some evidence that anxiety may worsen with long-term use. The question of tolerance to the amnesic effects of benzodiazepines is, likewise, unclear. Some evidence suggests that partial tolerance does develop, and "the memory impairment is limited to a narrow window within 90 minutes after each dose".
Discontinuation of benzodiazepines or abrupt reduction of the dose, even after a relatively short course of treatment (three to four weeks), may result in two groups of symptoms — rebound
Rebound effect
The rebound effect, or rebound phenomenon, is the tendency of some medications, when discontinued suddenly, to cause a return of the symptoms it relieved, and that, to a degree stronger than they were before treatment first began...
and withdrawal
Benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome
Benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome—often abbreviated to benzo withdrawal—is the cluster of symptoms which appear when a person who has taken benzodiazepines long term and has developed benzodiazepine dependence stops taking benzodiazepine drug or during dosage reductions...
. Rebound symptoms are the return of the symptoms for which the patient was treated but worse than before. Withdrawal symptoms are the new symptoms that occur when the benzodiazepine is stopped. They are the main sign of physical dependence
Physical dependence
Physical dependence refers to a state resulting from chronic use of a drug that has produced tolerance and where negative physical symptoms of withdrawal result from abrupt discontinuation or dosage reduction...
.
Withdrawal symptoms and management

Tremor
A tremor is an involuntary, somewhat rhythmic, muscle contraction and relaxation involving to-and-fro movements of one or more body parts. It is the most common of all involuntary movements and can affect the hands, arms, eyes, face, head, vocal folds, trunk, and legs. Most tremors occur in the...
s, agitation, fearfulness, and muscle spasms
Spasm
In medicine a spasm is a sudden, involuntary contraction of a muscle, a group of muscles, or a hollow organ, or a similarly sudden contraction of an orifice. It is sometimes accompanied by a sudden burst of pain, but is usually harmless and ceases after a few minutes...
. The less frequent effects are irritability, sweating, depersonalization
Depersonalization
Depersonalization is an anomaly of the mechanism by which an individual has self-awareness. It is a feeling of watching oneself act, while having no control over a situation. Sufferers feel they have changed, and the world has become less real, vague, dreamlike, or lacking in significance...
, derealization
Derealization
Derealization is an alteration in the perception or experience of the external world so that it seems unreal. Other symptoms include feeling as though one's environment is lacking in spontaneity, emotional coloring and depth. It is a dissociative symptom of many conditions, such as psychiatric and...
, hypersensitivity to stimuli, depression
Depression (mood)
Depression is a state of low mood and aversion to activity that can affect a person's thoughts, behaviour, feelings and physical well-being. Depressed people may feel sad, anxious, empty, hopeless, helpless, worthless, guilty, irritable, or restless...
, suicidal behavior, psychosis
Psychosis
Psychosis means abnormal condition of the mind, and is a generic psychiatric term for a mental state often described as involving a "loss of contact with reality"...
, seizures, and delirium tremens
Delirium tremens
Delirium tremens is an acute episode of delirium that is usually caused by withdrawal from alcohol, first described in 1813...
. Severe symptoms usually occur as a result of abrupt or over-rapid withdrawal. Abrupt withdrawal can be dangerous, therefore a gradual reduction regime is recommended.
Symptoms may also occur during a gradual dosage reduction, but are typically less severe and may persist as part of a protracted withdrawal syndrome
Benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome
Benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome—often abbreviated to benzo withdrawal—is the cluster of symptoms which appear when a person who has taken benzodiazepines long term and has developed benzodiazepine dependence stops taking benzodiazepine drug or during dosage reductions...
for months after cessation of benzodiazepines. Approximately 10% of patients will experience a notable protracted withdrawal syndrome, which can persist for many months or in some cases a year or longer. Protracted symptoms tend to resemble those seen during the first couple of months of withdrawal but usually are of a sub acute level of severity. Such symptoms do gradually lessen over time, eventually disappearing altogether.
Benzodiazepines have a reputation with patients and doctors for causing a severe and traumatic withdrawal; however, this is in large part due to the withdrawal process's being poorly managed. Over-rapid withdrawal from benzodiazepines increases the severity of the withdrawal syndrome and increases the failure rate. A slow and gradual withdrawal
Withdrawal
Withdrawal can refer to any sort of separation, but is most commonly used to describe the group of symptoms that occurs upon the abrupt discontinuation/separation or a decrease in dosage of the intake of medications, recreational drugs, and alcohol...
customised to the individual and, if indicated, psychological support is the most effective way of managing the withdrawal. Opinion as to the time needed to complete withdrawal ranges from four weeks to several years. A goal of less than six months has been suggested, but due to factors such as dosage and type of benzodiazepine, reasons for prescription, lifestyle, personality, environmental stresses, and amount of available support, a year or more may be needed to withdraw. Withdrawal is best managed by transferring the physically dependent patient to an equivalent dose of diazepam because it has the longest half-life of all of the benzodiazepines, is metabolised into long-acting active metabolites and is available in low-potency tablets, which can be quartered for smaller doses. A further benefit is that it is available in liquid form, which allows for even smaller reductions. Chlordiazepoxide
Chlordiazepoxide
Chlordiazepoxide, is a sedative/hypnotic drug and benzodiazepine. It is marketed under the trade names Angirex, Klopoxid, Librax , Libritabs, Librium, Mesural, Multum, Novapam, Risolid, Silibrin, Sonimen and Tropium.Chlordiazepoxide was the first benzodiazepine to be synthesised and...
, which also has a long half-life and long-acting active metabolites, can be used as an alternative. An alternate tapering procedure is to quantitatively reduce the tablet size on a periodic basis [ref]. Nonbenzodiazepine
Nonbenzodiazepine
The nonbenzodiazepines, also called benzodiazepine-like drugs, are a class of psychoactive drugs pharmacologically resembling the benzodiazepines, with similar benefits, side effects and risks, despite having dissimilar or entirely different chemical structures.-Classes:There are currently three...
s are contraindicated during benzodiazepine withdrawal as they are cross tolerant with benzodiazepines and can induce dependence. Alcohol is also cross tolerant with benzodiazepines and more toxic and thus caution is needed to avoid replacing one dependence with another. During withdrawal, fluoroquinolone-based antibiotics are best avoided if possible; they displace benzodiazepines from their binding site and reduce GABA function and, thus, may aggravate withdrawal symptoms. Antipsychotics are not recommended for benzodiazepine withdrawal (or other CNS depressant withdrawal states) especially clozapine
Clozapine
Clozapine is an antipsychotic medication used in the treatment of schizophrenia, and is also used off-label in the treatment of bipolar disorder. Wyatt. R and Chew...
, olanzapine
Olanzapine
Olanzapine is an atypical antipsychotic, approved by the FDA for the treatment of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder...
or low potency phenothiazines e.g. chlorpromazine
Chlorpromazine
Chlorpromazine is a typical antipsychotic...
as they lower the seizure threshold and can worsen withdrawal effects; if used extreme caution is required.
Withdrawal from long term benzodiazepines is beneficial for most individuals. Withdrawal of benzodiazepines from long-term users, in general, leads to improved physical and mental health
Mental health
Mental health describes either a level of cognitive or emotional well-being or an absence of a mental disorder. From perspectives of the discipline of positive psychology or holism mental health may include an individual's ability to enjoy life and procure a balance between life activities and...
particularly in the elderly; although some long term users report continued benefit from taking benzodiazepines, this may be the result of suppression of withdrawal effects.
Overdose
Although benzodiazepines are much safer in overdose than their predecessors, the barbiturateBarbiturate
Barbiturates are drugs that act as central nervous system depressants, and can therefore produce a wide spectrum of effects, from mild sedation to total anesthesia. They are also effective as anxiolytics, as hypnotics, and as anticonvulsants...
s, they can still cause problems in overdose. Taken alone, they rarely cause severe complications in overdose
Drug overdose
The term drug overdose describes the ingestion or application of a drug or other substance in quantities greater than are recommended or generally practiced...
; statistics in England showed that benzodiazepines were responsible for 3.8% of all deaths by poisoning from a single drug. However, combining these drugs with alcohol
Ethanol
Ethanol, also called ethyl alcohol, pure alcohol, grain alcohol, or drinking alcohol, is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid. It is a psychoactive drug and one of the oldest recreational drugs. Best known as the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, it is also used in thermometers, as a...
, opiates or tricyclic antidepressants markedly raises the toxicity. The elderly are more sensitive to the side effects of benzodiazepines, and poisoning may even occur from their long-term use. The various benzodiazepines differ in their toxicity; temazepam
Temazepam
Temazepam is an intermediate-acting 3-hydroxy benzodiazepine. It is mostly prescribed for the short-term treatment of sleeplessness in patients who have difficulty maintaining sleep...
appears to be most toxic in overdose and when used with other drugs. The symptoms of a benzodiazepine overdose may include; drowsiness, slurred speech, nystagmus
Nystagmus
Nystagmus is a condition of involuntary eye movement, acquired in infancy or later in life, that may result in reduced or limited vision.There are two key forms of Nystagmus: pathological and physiological, with variations within each type. Nystagmus may be caused by congenital disorders,...
, hypotension
Hypotension
In physiology and medicine, hypotension is abnormally low blood pressure, especially in the arteries of the systemic circulation. It is best understood as a physiologic state, rather than a disease. It is often associated with shock, though not necessarily indicative of it. Hypotension is the...
, ataxia
Ataxia
Ataxia is a neurological sign and symptom that consists of gross lack of coordination of muscle movements. Ataxia is a non-specific clinical manifestation implying dysfunction of the parts of the nervous system that coordinate movement, such as the cerebellum...
, coma
Coma
In medicine, a coma is a state of unconsciousness, lasting more than 6 hours in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light or sound, lacks a normal sleep-wake cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. A person in a state of coma is described as...
, respiratory depression, and cardiorespiratory arrest.
A reversal agent for benzodiazepines exists, flumazenil
Flumazenil
Flumazenil is a benzodiazepine antagonist available for injection only, and the only benzodiazepine receptor antagonist on the market today.It was first introduced in 1987 by Hoffmann-La Roche under the trade name Anexate, but only approved by...
(Anexate). Its use as an antidote
Antidote
An antidote is a substance which can counteract a form of poisoning. The term ultimately derives from the Greek αντιδιδοναι antididonai, "given against"....
is not routinely recommended due to the high risk of resedation and seizures. In a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of 326 patients, 4 patients suffered serious adverse events and 61% became resedated following the use of flumazenil. Numerous contraindications to its use exist. It is contraindicated in patients with a history of long-term use of benzodiazepines, those having ingested a substance that lowers the seizure threshold or may cause an arrhythmia, and in those with abnormal vital signs. One study found that only 10% of the patient population presenting with a benzodiazepine overdose
Benzodiazepine overdose
Benzodiazepine overdose describes the ingestion of one of the drugs in the benzodiazepine class in quantities greater than are recommended or generally practiced. Death as a result of benzodiazepines is uncommon but does occasionally happen. Deaths after hospital admission are considered to be low...
are suitable candidates for treatment with flumazenil.
Contraindications
Because of their muscle relaxant action, benzodiazepines may cause respiratory depressionHypoventilation
In medicine, hypoventilation occurs when ventilation is inadequate to perform needed gas exchange...
in susceptible individuals. For that reason, they are contraindicated in people with myasthenia gravis
Myasthenia gravis
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune neuromuscular disease leading to fluctuating muscle weakness and fatiguability...
, sleep apnea
Sleep apnea
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by abnormal pauses in breathing or instances of abnormally low breathing, during sleep. Each pause in breathing, called an apnea, can last from a few seconds to minutes, and may occur 5 to 30 times or more an hour. Similarly, each abnormally low...
, bronchitis
Bronchitis
Acute bronchitis is an inflammation of the large bronchi in the lungs that is usually caused by viruses or bacteria and may last several days or weeks. Characteristic symptoms include cough, sputum production, and shortness of breath and wheezing related to the obstruction of the inflamed airways...
, and COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease , also known as chronic obstructive lung disease , chronic obstructive airway disease , chronic airflow limitation and chronic obstructive respiratory disease , is the co-occurrence of chronic bronchitis and emphysema, a pair of commonly co-existing diseases...
. Caution is required when benzodiazepines are used in people with personality disorders or mental retardation
Mental retardation
Mental retardation is a generalized disorder appearing before adulthood, characterized by significantly impaired cognitive functioning and deficits in two or more adaptive behaviors...
because of frequent paradoxical reactions. In major depression, they may precipitate suicidal tendencies
Suicidal tendencies
Suicidal tendencies is the propensity for a person to have suicidal ideation or to make suicide attempts. It may also refer to:* Suicidal Tendencies, a band that was founded in Venice, Los Angeles, California, in 1981 by the leader and only permanent member, singer Mike Muir* Suicide, the act of a...
and are sometimes used for suicidal overdoses. Individuals with a history of alcohol, opioid
Opioid
An opioid is a psychoactive chemical that works by binding to opioid receptors, which are found principally in the central and peripheral nervous system and the gastrointestinal tract...
and barbiturate
Barbiturate
Barbiturates are drugs that act as central nervous system depressants, and can therefore produce a wide spectrum of effects, from mild sedation to total anesthesia. They are also effective as anxiolytics, as hypnotics, and as anticonvulsants...
abuse should avoid benzodiazepines, as there is a risk of life-threatening interactions with these drugs.
Pregnancy
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration has categorized benzodiazepines into either category D or XPregnancy category
The pregnancy category of a pharmaceutical agent is an assessment of the risk of fetal injury due to the pharmaceutical, if it is used as directed by the mother during pregnancy. It does not include any risks conferred by pharmaceutical agents or their metabolites that are present in breast...
meaning potential for harm in the unborn has been demonstrated.
Exposure to benzodiazepines during pregnancy has been associated with a slightly increased (from 0.06 to 0.07%) risk of cleft palate in newborns, a controversial conclusion as some studies find no association between benzodiazepines and cleft palate. Their use by expectant mothers shortly before the delivery may result in a floppy infant syndrome, with the newborns suffering from hypotonia
Hypotonia
Hypotonia is a state of low muscle tone , often involving reduced muscle strength. Hypotonia is not a specific medical disorder, but a potential manifestation of many different diseases and disorders that affect motor nerve control by the brain or muscle strength...
, hypothermia
Hypothermia
Hypothermia is a condition in which core temperature drops below the required temperature for normal metabolism and body functions which is defined as . Body temperature is usually maintained near a constant level of through biologic homeostasis or thermoregulation...
, lethargy, and breathing and feeding difficulties. Cases of neonatal withdrawal syndrome have been described in infants chronically exposed to benzodiazepines in utero
In utero
In utero is a Latin term literally meaning "in the womb". In biology, the phrase describes the state of an embryo or fetus. In legal contexts, the phrase is used to refer to unborn children. Under common law, unborn children are still considered to exist for property transfer purposes.-See also:*...
. This syndrome may be hard to recognize, as it starts several days after delivery, for example, as late as 21 day for chlordiazepoxide. The symptoms include tremor
Tremor
A tremor is an involuntary, somewhat rhythmic, muscle contraction and relaxation involving to-and-fro movements of one or more body parts. It is the most common of all involuntary movements and can affect the hands, arms, eyes, face, head, vocal folds, trunk, and legs. Most tremors occur in the...
s, hypertonia
Hypertonia
Hypertonia a condition marked by an abnormal increase in muscle tension and a reduced ability of a muscle to stretch. It is caused by lesions to upper motor neurons in the central nervous system, which carry information from the central nervous system to the muscles and control posture, muscle...
, hyperreflexia
Hyperreflexia
Hyperreflexia is defined as overactive or overresponsive reflexes. Examples of this can include twitching or spastic tendencies, which are indicative of upper motor neuron disease as well as the lessening or loss of control ordinarily exerted by higher brain centers of lower neural pathways...
, hyperactivity, and vomiting and may last for up to three to six months. Tapering down the dose during pregnancy may lessen its severity. If used in pregnancy, those benzodiazepines with a better and longer safety record, such as diazepam
Diazepam
Diazepam , first marketed as Valium by Hoffmann-La Roche is a benzodiazepine drug. Diazepam is also marketed in Australia as Antenex. It is commonly used for treating anxiety, insomnia, seizures including status epilepticus, muscle spasms , restless legs syndrome, alcohol withdrawal,...
or chlordiazepoxide
Chlordiazepoxide
Chlordiazepoxide, is a sedative/hypnotic drug and benzodiazepine. It is marketed under the trade names Angirex, Klopoxid, Librax , Libritabs, Librium, Mesural, Multum, Novapam, Risolid, Silibrin, Sonimen and Tropium.Chlordiazepoxide was the first benzodiazepine to be synthesised and...
, are recommended over potentially more harmful benzodiazepines, such as alprazolam
Alprazolam
Alprazolam is a short-acting anxiolytic of the benzodiazepine class of psychoactive drugs. Alprazolam, like other benzodiazepines, binds to specific sites on the GABAA gamma-amino-butyric acid receptor...
or triazolam
Triazolam
Triazolam is a benzodiazepine drug. It possesses pharmacological properties similar to that of other benzodiazepines, but it is generally only used as a sedative to treat severe insomnia...
. Using the lowest effective dose for the shortest period of time minimizes the risks to the unborn child.
Elderly
The benefits of benzodiazepines are least and the risks are greatest in the elderly. The elderly are at an increased risk of dependence and are more sensitive to the adverse effects such as memory problems, daytime sedation, impaired motor coordination, and increased risk of motor vehicle accidents and falls. The long-term effects of benzodiazepines and benzodiazepine dependenceBenzodiazepine dependence
Benzodiazepine dependence or benzodiazepine addiction is a condition during which a person is dependent on benzodiazepine drugs. Dependence can be either a psychological dependence, physical dependence, or a combination of the two...
in the elderly can resemble dementia
Dementia
Dementia is a serious loss of cognitive ability in a previously unimpaired person, beyond what might be expected from normal aging...
, depression
Clinical depression
Major depressive disorder is a mental disorder characterized by an all-encompassing low mood accompanied by low self-esteem, and by loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities...
, or anxiety syndromes, and progressively worsens over time. Adverse effects on cognition can be mistaken for the effects of old age. The benefits of withdrawal include improved cognition, alertness, mobility, reduced risk incontinance, and a reduced risk of falls and fractures. The success of gradual-tapering benzodiazepines is as great in the elderly as in younger people. Benzodiazepines should be prescribed to the elderly only with caution and only for a short period at low doses. Short to intermediate-acting benzodiazepines are preferred in the elderly such as oxazepam
Oxazepam
Oxazepam , is a drug which is a short to intermediate acting 3-hydroxy benzodiazepine derivative...
and temazepam
Temazepam
Temazepam is an intermediate-acting 3-hydroxy benzodiazepine. It is mostly prescribed for the short-term treatment of sleeplessness in patients who have difficulty maintaining sleep...
. The high potency benzodiazepines alprazolam
Alprazolam
Alprazolam is a short-acting anxiolytic of the benzodiazepine class of psychoactive drugs. Alprazolam, like other benzodiazepines, binds to specific sites on the GABAA gamma-amino-butyric acid receptor...
and triazolam
Triazolam
Triazolam is a benzodiazepine drug. It possesses pharmacological properties similar to that of other benzodiazepines, but it is generally only used as a sedative to treat severe insomnia...
and long-acting benzodiazepines are not recommended in the elderly due to increased adverse effects. Nonbenzodiazepines such as zaleplon
Zaleplon
Zaleplon is a sedative/hypnotic, mainly used for insomnia. It is a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic from the pyrazolopyrimidine class. In terms of adverse effects zaleplon appears to offer little improvement compared to both benzodiazepines and other non-benzodiazepine Z-drugs.Sonata is manufactured by...
and zolpidem
Zolpidem
Zolpidem is a prescription medication used for the short-term treatment of insomnia, as well as some brain disorders. It is a short-acting nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic of the imidazopyridine class that potentiates gamma-aminobutyric acid , an inhibitory neurotransmitter, by binding to GABAA...
and low doses of sedating antidepressants are sometimes used as alternatives to benzodiazepines.
Long-term use of benzodiazepines has been associated with increased risk of cognitive impairment, but its relationship with dementia remains inconclusive. The association of a past history of benzodiazepine use and cognitive decline is unclear, with some studies reporting a lower risk of cognitive decline in former users, some finding no association and some indicating an increased risk of cognitive decline.
Benzodiazepines are sometimes prescribed to treat behavioral symptoms of dementia. However, like antidepressant
Antidepressant
An antidepressant is a psychiatric medication used to alleviate mood disorders, such as major depression and dysthymia and anxiety disorders such as social anxiety disorder. According to Gelder, Mayou &*Geddes people with a depressive illness will experience a therapeutic effect to their mood;...
s, they have little evidence of effectiveness, although antipsychotic
Antipsychotic
An antipsychotic is a tranquilizing psychiatric medication primarily used to manage psychosis , particularly in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. A first generation of antipsychotics, known as typical antipsychotics, was discovered in the 1950s...
s have shown some benefit. Cognitive impairing effects of benzodiazepines that occur frequently in the elderly can also worsen dementia.
Pharmacology
Benzodiazepines share a similar chemical structure, and their effects in humans are mainly produced by the allosteric modification of a specific kind of neurotransmitter receptorNeurotransmitter receptor
A Neurotransmitter receptor is a membrane receptor protein that is activated by a Neurotransmitter. A membrane protein interacts with the lipid bilayer that encloses the cell and a membrane receptor protein interacts with a chemical in the cells external environment, which binds to the cell...
, the GABAA receptor, which increases the conductance of this inhibitory channel; this results in the various therapeutic effects as well as adverse effects of benzodiazepines. Other less important mechanisms of action are also known.
Chemistry
The term benzodiazepine is the chemical nameIUPAC nomenclature
A chemical nomenclature is a set of rules to generate systematic names for chemical compounds. The nomenclature used most frequently worldwide is the one created and developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry ....
for the heterocyclic ring system (see figure to the right), which is a fusion between the benzene
Benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound. It is composed of 6 carbon atoms in a ring, with 1 hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom, with the molecular formula C6H6....
and diazepine
Diazepine
1,2-Diazepine is a seven-membered heterocyclic compound with two nitrogen atoms and three double bonds.-External links:*...
ring systems. Under Hantzsch–Widman nomenclature
Hantzsch–Widman nomenclature
Hantzsch–Widman nomenclature, also called the extended Hantzsch–Widman system, is a type of systematic chemical nomenclature used for naming heterocyclic parent hydrides having no more than ten ring members....
, a diazepine
Diazepine
1,2-Diazepine is a seven-membered heterocyclic compound with two nitrogen atoms and three double bonds.-External links:*...
is a heterocycle with two nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
atoms, five carbon
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
atom and the maximum possible number of cumulative double bond
Double bond
A double bond in chemistry is a chemical bond between two chemical elements involving four bonding electrons instead of the usual two. The most common double bond, that between two carbon atoms, can be found in alkenes. Many types of double bonds between two different elements exist, for example in...
s. The "benzo" prefix indicates the benzene
Benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound. It is composed of 6 carbon atoms in a ring, with 1 hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom, with the molecular formula C6H6....
ring fused onto the diazepine ring.
Benzodiazepine drugs are substituted 1,4-benzodiazepines, although the chemical term can refer to many other compounds that do not have useful pharmacological properties. Different benzodiazepine drugs have different side groups attached to this central structure. The different side groups affect the binding of the molecule to the GABAA receptor and so modulate the pharmacological properties. Many of the pharmacologically active "classical" benzodiazepine drugs contain the 5-phenyl-1H-benzo[e][1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one substructure (see figure to the right).
Nonbenzodiazepine
Nonbenzodiazepine
The nonbenzodiazepines, also called benzodiazepine-like drugs, are a class of psychoactive drugs pharmacologically resembling the benzodiazepines, with similar benefits, side effects and risks, despite having dissimilar or entirely different chemical structures.-Classes:There are currently three...
s also bind to the benzodiazepine binding site on the GABAA receptor and possess similar pharmacological properties. While the nonbenzodiazepines are by definition structurally unrelated to the benzodiazepines, both classes of drugs possess a common pharmacophore
Pharmacophore
thumb|right|300px|An example of a pharmacophore model.A pharmacophore is an abstract description of molecular features which are necessary for molecular recognition of a ligand by a biological macromolecule....
(see figure to the lower-right), which explains their binding to a common receptor site.
Mechanism of action

Gamma-aminobutyric acid
γ-Aminobutyric acid is the chief inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mammalian central nervous system. It plays a role in regulating neuronal excitability throughout the nervous system...
, to decrease the excitability of neuron
Neuron
A neuron is an electrically excitable cell that processes and transmits information by electrical and chemical signaling. Chemical signaling occurs via synapses, specialized connections with other cells. Neurons connect to each other to form networks. Neurons are the core components of the nervous...
s. This reduces the communication between neurons and, therefore, has a calming effect on many of the functions of the brain.
GABA controls the excitability of neurons by binding to the GABAA receptor. The GABAA receptor is a protein complex located in the synapses
Chemical synapse
Chemical synapses are specialized junctions through which neurons signal to each other and to non-neuronal cells such as those in muscles or glands. Chemical synapses allow neurons to form circuits within the central nervous system. They are crucial to the biological computations that underlie...
of neurons. All GABAA receptors contain an ion channel
Ion channel
Ion channels are pore-forming proteins that help establish and control the small voltage gradient across the plasma membrane of cells by allowing the flow of ions down their electrochemical gradient. They are present in the membranes that surround all biological cells...
that conducts chloride
Chloride
The chloride ion is formed when the element chlorine, a halogen, picks up one electron to form an anion Cl−. The salts of hydrochloric acid HCl contain chloride ions and can also be called chlorides. The chloride ion, and its salts such as sodium chloride, are very soluble in water...
ions across neuronal cell membrane
Cell membrane
The cell membrane or plasma membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. It basically protects the cell...
s and two binding sites for the neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals that transmit signals from a neuron to a target cell across a synapse. Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles clustered beneath the membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse, and are released into the synaptic cleft, where they bind to...
gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), while a subset of GABAA receptor complexes also contain a single binding site for benzodiazepines. Binding of benzodiazepines to this receptor complex promotes binding of GABA, which in turn increases the conduction of chloride ions across the neuronal cell membrane. This increased conductance raises the membrane potential
Membrane potential
Membrane potential is the difference in electrical potential between the interior and exterior of a biological cell. All animal cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane composed of a lipid bilayer with a variety of types of proteins embedded in it...
of the neuron, resulting in inhibition of neuronal firing
Action potential
In physiology, an action potential is a short-lasting event in which the electrical membrane potential of a cell rapidly rises and falls, following a consistent trajectory. Action potentials occur in several types of animal cells, called excitable cells, which include neurons, muscle cells, and...
. In addition, different GABAA receptor subtypes have varying distributions within different regions of the brain and, therefore, control distinct neuronal circuits
Biological neural network
In neuroscience, a biological neural network describes a population of physically interconnected neurons or a group of disparate neurons whose inputs or signalling targets define a recognizable circuit. Communication between neurons often involves an electrochemical process...
. Hence, activation of different GABAA receptor subtypes by benzodiazepines may result in distinct pharmacological actions. In terms of the mechanism of action of benzodiazepines, their similarities are too great to separate them into individual categories such as anxiolytic or hypnotic. For example, a hypnotic administered in low doses will produce anxiety-relieving effects, whereas a benzodiazepine marketed as an anti-anxiety drug will at higher doses induce sleep.
The subset of GABAA receptors that also bind benzodiazepines are referred to as benzodiazepine receptors (BzR). The GABAA receptor is a heteromer
Heteromer
-Pharmacology:* Ligand-gated ion channels such as the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor and GABAA receptor are composed of five subunits arranged around a central pore that opens to allow ions to pass through. There are a large number of different subunits available, which can come together in a...
composed of five subunits, the most common ones being two αs, two βs, and one γ (α2β2γ). For each subunit, many subtypes exist (α1-6, β1-3, and γ1-3). GABAA receptors that are made up of different combinations of subunit subtypes have different properties, different distributions in the brain and different activities relative to pharmacological and clinical effects. Benzodiazepines bind at the interface of the α and γ subunits on the GABAA receptor. Binding also requires that alpha subunits contain a histidine
Histidine
Histidine Histidine, an essential amino acid, has a positively charged imidazole functional group. It is one of the 22 proteinogenic amino acids. Its codons are CAU and CAC. Histidine was first isolated by German physician Albrecht Kossel in 1896. Histidine is an essential amino acid in humans...
amino acid residue, (i.e., α1
GABRA1
Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit alpha-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GABRA1 gene.-Further reading:...
, α2
GABRA2
Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit alpha-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GABRA2 gene....
, α3
GABRA3
Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit alpha-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GABRA3 gene.- Function :GABA is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mammalian brain where it acts at GABAA receptors, which are ligand-gated chloride channels...
, and α5
GABRA5
Gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptor, alpha 5, also known as GABRA5, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the GABRA5 gene.-Function:...
containing GABAA receptors). For this reason, benzodiazepines show no affinity for GABAA receptors containing α4
GABRA4
Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit alpha-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GABRA4 gene....
and α6
GABRA6
Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit alpha-6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GABRA6 gene.One study has found a genetic variant in the gene to be associated with the personality trait neuroticism....
subunits with an arginine
Arginine
Arginine is an α-amino acid. The L-form is one of the 20 most common natural amino acids. At the level of molecular genetics, in the structure of the messenger ribonucleic acid mRNA, CGU, CGC, CGA, CGG, AGA, and AGG, are the triplets of nucleotide bases or codons that codify for arginine during...
instead of a histidine residue.
Once bound to the benzodiazepine receptor, the benzodiazepine ligand
Ligand (biochemistry)
In biochemistry and pharmacology, a ligand is a substance that forms a complex with a biomolecule to serve a biological purpose. In a narrower sense, it is a signal triggering molecule, binding to a site on a target protein.The binding occurs by intermolecular forces, such as ionic bonds, hydrogen...
locks the benzodiazepine receptor into a conformation in which it has a greater affinity for the GABA
Gamma-aminobutyric acid
γ-Aminobutyric acid is the chief inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mammalian central nervous system. It plays a role in regulating neuronal excitability throughout the nervous system...
neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals that transmit signals from a neuron to a target cell across a synapse. Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles clustered beneath the membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse, and are released into the synaptic cleft, where they bind to...
. This increases the frequency of the opening of the associated chloride ion channel
Ion channel
Ion channels are pore-forming proteins that help establish and control the small voltage gradient across the plasma membrane of cells by allowing the flow of ions down their electrochemical gradient. They are present in the membranes that surround all biological cells...
and hyperpolarizes
Hyperpolarization (biology)
Hyperpolarization is a change in a cell's membrane potential that makes it more negative. It is the opposite of a depolarization.Hyperpolarization is often caused by efflux of K+ through K+ channels, or influx of Cl– through Cl– channels. On the other hand, influx of cations, e.g...
the membrane of the associated neuron. The inhibitory effect of the available GABA is potentiated, leading to sedatory and anxiolytic effects. Furthermore, different benzodiazepines can have different affinities for BzRs made up of different collection of subunits. For instance, those with high activity at the α1 are associated with stronger hypnotic
Hypnotic
Hypnotic drugs are a class of psychoactives whose primary function is to induce sleep and to be used in the treatment of insomnia and in surgical anesthesia...
effects, whereas those with higher affinity for GABAA receptors containing α2 and/or α3 subunits have good anti-anxiety activity.
The benzodiazepine class of drugs also interact with peripheral benzodiazepine receptors. Peripheral benzodiazepine receptors are present in peripheral nervous system
Peripheral nervous system
The peripheral nervous system consists of the nerves and ganglia outside of the brain and spinal cord. The main function of the PNS is to connect the central nervous system to the limbs and organs. Unlike the CNS, the PNS is not protected by the bone of spine and skull, or by the blood–brain...
tissues, glial cells, and to a lesser extent the central nervous system. These peripheral receptors are not structurally related nor coupled to GABAA receptors. They modulate the immune system
Immune system
An immune system is a system of biological structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease by identifying and killing pathogens and tumor cells. It detects a wide variety of agents, from viruses to parasitic worms, and needs to distinguish them from the organism's own...
and are involved in the body response to injury. Benzodiazepines also function as weak adenosine reuptake inhibitor
Adenosine reuptake inhibitor
An adenosine reuptake inhibitor is a type of drug which acts as a reuptake inhibitor for the purine nucleoside and neurotransmitter adenosine by blocking the action of one or more of the equilibrative nucleoside transporters . This in turn leads to increased extracellular concentrations of...
s. It has been suggested that some of their anticonvulsant, anxiolytic and muscle relaxant effects may be in part mediated by this action.
Pharmacokinetics
A benzodiazepine can be placed into one of three groups by its elimination half-life, or time it takes for the body to eliminate half of the dose. Some benzodiazepines have long-acting active metabolites, such as diazepam and chlordiazepoxide, which are metabolised into desmethyldiazepam. Desmethyldiazepam has a half-life of 36–200 hours, and flurazepam, with the main active metabolite of desalkylflurazepam, with a half-life of 40–250 hours. These long-acting metabolites are partial agonists.- Short-acting compounds have a median half-life of 1–12 hours. They have few residual effects if taken before bedtime, rebound insomnia may occur upon discontinuation, and they might cause daytime withdrawal symptoms such as next day rebound anxiety with prolonged usage. Examples are brotizolamBrotizolamBrotizolam is a sedative-hypnotic thienodiazepine drug which is a benzodiazepine analog. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, hypnotic, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties, and is considered to be similar in effect to short-acting benzodiazepines such as triazolam...
, midazolamMidazolamMidazolam is a short-acting drug in the benzodiazepine class developed by Hoffmann-La Roche in the 1970s. The drug is used for treatment of acute seizures, moderate to severe insomnia, and for inducing sedation and amnesia before medical procedures. It possesses profoundly potent anxiolytic,...
, and triazolamTriazolamTriazolam is a benzodiazepine drug. It possesses pharmacological properties similar to that of other benzodiazepines, but it is generally only used as a sedative to treat severe insomnia...
. - Intermediate-acting compounds have a median half-life of 12–40 hours. They may have some residual effects in the first half of the day if used as a hypnoticHypnoticHypnotic drugs are a class of psychoactives whose primary function is to induce sleep and to be used in the treatment of insomnia and in surgical anesthesia...
. Rebound insomnia, however, is more common upon discontinuation of intermediate-acting benzodiazepines than longer-acting benzodiazepines. Examples are alprazolamAlprazolamAlprazolam is a short-acting anxiolytic of the benzodiazepine class of psychoactive drugs. Alprazolam, like other benzodiazepines, binds to specific sites on the GABAA gamma-amino-butyric acid receptor...
, estazolamEstazolamEstazolam is a benzodiazepine derivative drug developed by Upjohn in the 1970s. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties...
, flunitrazepamFlunitrazepamFlunitrazepam is marketed as a potent hypnotic, sedative, anticonvulsant, anxiolytic, amnestic, and skeletal muscle relaxant drug most commonly known as Rohypnol...
, clonazepamClonazepamClonazepamis a benzodiazepine drug having anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, muscle relaxant, and hypnotic properties. It is marketed by Roche under the trade name Klonopin in the United States and Rivotril in Australia, Brazil, Canada and Europe...
, lormetazepamLormetazepamLormetazepam Lormetazepam Lormetazepam (INN, or methyl-lorazepam, is a drug which is a short to intermediate acting 3-hydroxy benzodiazepine derivative. It possesses hypnotic, anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties....
, lorazepamLorazepamLorazepam is a high-potency short-to-intermediate-acting 3-hydroxy benzodiazepine drug that has all five intrinsic benzodiazepine effects: anxiolytic, amnesic, sedative/hypnotic, anticonvulsant, antiemetic and muscle relaxant...
, nitrazepamNitrazepamNitrazepam is a type of benzodiazepine drug and is marketed in English-speaking countries under the following brand names: Alodorm, Arem, Insoma, Mogadon, Nitrados, Nitrazadon, Ormodon, Paxadorm, Remnos, and Somnite...
, and temazepamTemazepamTemazepam is an intermediate-acting 3-hydroxy benzodiazepine. It is mostly prescribed for the short-term treatment of sleeplessness in patients who have difficulty maintaining sleep...
. - Long-acting compounds have a half-life of 40–250 hours. They have a risk of accumulation in the elderly and in individuals with severely impaired liver function, but they have a reduced severity of rebound effects and withdrawalWithdrawalWithdrawal can refer to any sort of separation, but is most commonly used to describe the group of symptoms that occurs upon the abrupt discontinuation/separation or a decrease in dosage of the intake of medications, recreational drugs, and alcohol...
. Examples are diazepamDiazepamDiazepam , first marketed as Valium by Hoffmann-La Roche is a benzodiazepine drug. Diazepam is also marketed in Australia as Antenex. It is commonly used for treating anxiety, insomnia, seizures including status epilepticus, muscle spasms , restless legs syndrome, alcohol withdrawal,...
, clorazepateClorazepateClorazepate , also known as clorazepate dipotassium, is a drug that is a benzodiazepine derivative. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative, hypnotic and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. Clorazepate is a prodrug for desmethyldiazepam, which is rapidly produced as an active metabolite...
, chlordiazepoxideChlordiazepoxideChlordiazepoxide, is a sedative/hypnotic drug and benzodiazepine. It is marketed under the trade names Angirex, Klopoxid, Librax , Libritabs, Librium, Mesural, Multum, Novapam, Risolid, Silibrin, Sonimen and Tropium.Chlordiazepoxide was the first benzodiazepine to be synthesised and...
, and flurazepamFlurazepamFlurazepam is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. It produces a metabolite with a very long half-life , which may stay in the bloodstream for up to four days...
.
Interactions
Individual benzodiazepines may have different interactionsDrug interaction
A drug interaction is a situation in which a substance affects the activity of a drug, i.e. the effects are increased or decreased, or they produce a new effect that neither produces on its own. Typically, interaction between drugs come to mind...
with certain drugs. Depending on their metabolism
Metabolism
Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that happen in the cells of living organisms to sustain life. These processes allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. Metabolism is usually divided into two categories...
pathway, benzodiazepines can be roughly divided into two groups. The largest group consists of those that are metabolized by cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzymes and possess significant potential for interactions with other drugs. The other group comprises those that are metabolized through glucuronidation
Glucuronidation
Glucuronidation is the addition of glucuronic acid to a substrate. Glucuronidation is often involved in xenobiotic metabolism of substances such as drugs, pollutants, bilirubin, androgens, estrogens, mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, fatty acid derivatives, retinoids, and bile acids...
, such as lorazepam
Lorazepam
Lorazepam is a high-potency short-to-intermediate-acting 3-hydroxy benzodiazepine drug that has all five intrinsic benzodiazepine effects: anxiolytic, amnesic, sedative/hypnotic, anticonvulsant, antiemetic and muscle relaxant...
, oxazepam
Oxazepam
Oxazepam , is a drug which is a short to intermediate acting 3-hydroxy benzodiazepine derivative...
, and temazepam
Temazepam
Temazepam is an intermediate-acting 3-hydroxy benzodiazepine. It is mostly prescribed for the short-term treatment of sleeplessness in patients who have difficulty maintaining sleep...
, and, in general, have few drug interactions.
Many drugs, including oral contraceptives, some antibiotic
Antibiotic
An antibacterial is a compound or substance that kills or slows down the growth of bacteria.The term is often used synonymously with the term antibiotic; today, however, with increased knowledge of the causative agents of various infectious diseases, antibiotic has come to denote a broader range of...
s, antidepressant
Antidepressant
An antidepressant is a psychiatric medication used to alleviate mood disorders, such as major depression and dysthymia and anxiety disorders such as social anxiety disorder. According to Gelder, Mayou &*Geddes people with a depressive illness will experience a therapeutic effect to their mood;...
s, and antifungal agents, inhibit cytochrome enzymes in the liver. They reduce the rate of elimination of the benzodiazepines that are metabolized by CYP450, leading to possibly excessive drug accumulation and increased side-effects. In contrast, drugs that induce cytochrome P450 enzymes, such as St John's wort
St John's wort
St John's wort is the plant species Hypericum perforatum, and is also known as Tipton's Weed, Chase-devil, or Klamath weed....
, the antibiotic rifampicin
Rifampicin
Rifampicin or rifampin is a bactericidal antibiotic drug of the rifamycin group. It is a semisynthetic compound derived from Amycolatopsis rifamycinica ...
, and the anticonvulsants carbamazepine
Carbamazepine
Carbamazepine is an anticonvulsant and mood-stabilizing drug used primarily in the treatment of epilepsy and bipolar disorder, as well as trigeminal neuralgia...
and phenytoin
Phenytoin
Phenytoin sodium is a commonly used antiepileptic. Phenytoin acts to suppress the abnormal brain activity seen in seizure by reducing electrical conductance among brain cells by stabilizing the inactive state of voltage-gated sodium channels...
, accelerate elimination of many benzodiazepines and decrease their action. Taking benzodiazepines with alcohol, opioid
Opioid
An opioid is a psychoactive chemical that works by binding to opioid receptors, which are found principally in the central and peripheral nervous system and the gastrointestinal tract...
s and other central nervous system depressants
Depressant
A depressant, or central depressant, is a drug or endogenous compound that depresses the function or activity of a specific part of the brain...
potentiates their action. This often results in increased sedation, impaired motor coordination, suppressed breathing, and other adverse effects that have potential to be lethal. Antacids may slow down absorption of some benzodiazepines; however, this effect is marginal and inconsistent.
History
The first benzodiazepine, chlordiazepoxideChlordiazepoxide
Chlordiazepoxide, is a sedative/hypnotic drug and benzodiazepine. It is marketed under the trade names Angirex, Klopoxid, Librax , Libritabs, Librium, Mesural, Multum, Novapam, Risolid, Silibrin, Sonimen and Tropium.Chlordiazepoxide was the first benzodiazepine to be synthesised and...
(Librium), was synthesized in 1955 by Leo Sternbach
Leo Sternbach
Leo Henryk Sternbach was a Polish-Jewish chemist who is credited with discovering benzodiazepines, main class of tranquilizers.-Biography:...
while working at Hoffmann–La Roche on the development of tranquilizers. The pharmacological properties of the compounds prepared initially were disappointing, and Sternbach abandoned the project. Two years later, in April 1957, co-worker Earl Reeder noticed a "nicely crystalline" compound left over from the discontinued project while spring-cleaning in the lab. This compound, later named chlordiazepoxide, had not been tested in 1955 because of Sternbach's focus on other issues. Expecting the pharmacology results to be negative and hoping to publish the chemistry-related findings, researchers submitted it for a standard battery of animal tests. However, the compound showed very strong sedative
Sedative
A sedative or tranquilizer is a substance that induces sedation by reducing irritability or excitement....
, anticonvulsant
Anticonvulsant
The anticonvulsants are a diverse group of pharmaceuticals used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of bipolar disorder, since many seem to act as mood stabilizers, and in the treatment of neuropathic pain. The goal of an...
, and muscle relaxant
Muscle relaxant
A muscle relaxant is a drug which affects skeletal muscle function and decreases the muscle tone. It may be used to alleviate symptoms such as muscle spasms, pain, and hyperreflexia. The term "muscle relaxant" is used to refer to two major therapeutic groups: neuromuscular blockers and spasmolytics...
effects. These impressive clinical findings led to its speedy introduction throughout the world in 1960 under the brand name Librium. Following chlordiazepoxide, diazepam
Diazepam
Diazepam , first marketed as Valium by Hoffmann-La Roche is a benzodiazepine drug. Diazepam is also marketed in Australia as Antenex. It is commonly used for treating anxiety, insomnia, seizures including status epilepticus, muscle spasms , restless legs syndrome, alcohol withdrawal,...
marketed by Hoffmann–La Roche under the brand name Valium in 1963, and for a while the two were the most commercially successful drugs. The introduction of benzodiazepines led to a decrease in the prescription of barbiturate
Barbiturate
Barbiturates are drugs that act as central nervous system depressants, and can therefore produce a wide spectrum of effects, from mild sedation to total anesthesia. They are also effective as anxiolytics, as hypnotics, and as anticonvulsants...
s, and by the 1970s they had largely replaced the older drugs for sedative and hypnotic
Hypnotic
Hypnotic drugs are a class of psychoactives whose primary function is to induce sleep and to be used in the treatment of insomnia and in surgical anesthesia...
uses.
The new group of drugs was initially greeted with optimism by the medical profession, but gradually concerns arose; in particular, the risk of dependence became evident in the 1980s. Benzodiazepines have a unique history in that they were responsible for the largest-ever class-action lawsuit against drug manufacturers in the United Kingdom, involving 14,000 patients and 1,800 law firms that alleged the manufacturers knew of the dependence potential but intentionally withheld this information from doctors. At the same time, 117 general practitioners and 50 health authorities were sued by patients to recover damages for the harmful effects of dependence
Benzodiazepine dependence
Benzodiazepine dependence or benzodiazepine addiction is a condition during which a person is dependent on benzodiazepine drugs. Dependence can be either a psychological dependence, physical dependence, or a combination of the two...
and withdrawal
Withdrawal
Withdrawal can refer to any sort of separation, but is most commonly used to describe the group of symptoms that occurs upon the abrupt discontinuation/separation or a decrease in dosage of the intake of medications, recreational drugs, and alcohol...
. This led some doctors to require a signed consent form from their patients and to recommend that all patients be adequately warned of the risks of dependence and withdrawal before starting treatment with benzodiazepines. The court case against the drug manufacturers never reached a verdict; legal aid
Legal aid
Legal aid is the provision of assistance to people otherwise unable to afford legal representation and access to the court system. Legal aid is regarded as central in providing access to justice by ensuring equality before the law, the right to counsel and the right to a fair trial.A number of...
had been withdrawn and there were allegations that the consultant psychiatrists, the expert witnesses, had a conflict of interest. This litigation led to changes in the British law, making class action law suits more difficult.
In 2010, formerly classified documents from a Medical Research Council (UK)
Medical Research Council (UK)
The Medical Research Council is a publicly-funded agency responsible for co-ordinating and funding medical research in the United Kingdom. It is one of seven Research Councils in the UK and is answerable to, although politically independent from, the Department for Business, Innovation and Skills...
meeting of experts emerged and revealed that the MRC was aware of research 30 years ago that suggested that benzodiazepines could cause brain damage in some people similar to that which occurs from alcohol abuse and failed to follow-up with larger clinical trials. The MRC turned down research proposals in the 1980s by Professor Lader and also proposals by Professor Ashton in 1995 to study whether benzodiazepines had permanent effects on the brain. The MRC responded that it has always been open to research proposals in this area that meet required standards. It was further alleged that the MRC documents were relevant to a large class-action lawsuit, which started in the mid-1980s against drug companies and one solicitor stated that it was strange that the MRC had 'hidden' the documents. Jim Dobbin
Jim Dobbin
James "Jim" Dobbin is a British Labour Co-operative politician and microbiologist, who has been the Member of Parliament for Heywood and Middleton since 1997.-Education and career:...
, MP and chair of the All-Party Parliamentary Group for Involuntary Tranquilliser Addiction, described the documents as a "huge scandal," given the large number of people who experience symptoms such as physical, cognitive, and psychological problems as a result of benzodiazepine use, which can persist even after withdrawing.
Although antidepressants with anxiolytic properties have been introduced, and there is increasing awareness of the adverse effects of benzodiazepines, prescriptions for short-term anxiety relief have not significantly dropped. For treatment of insomnia, benzodiazepines are now less popular than nonbenzodiazepine
Nonbenzodiazepine
The nonbenzodiazepines, also called benzodiazepine-like drugs, are a class of psychoactive drugs pharmacologically resembling the benzodiazepines, with similar benefits, side effects and risks, despite having dissimilar or entirely different chemical structures.-Classes:There are currently three...
s, which include zolpidem
Zolpidem
Zolpidem is a prescription medication used for the short-term treatment of insomnia, as well as some brain disorders. It is a short-acting nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic of the imidazopyridine class that potentiates gamma-aminobutyric acid , an inhibitory neurotransmitter, by binding to GABAA...
, zaleplon
Zaleplon
Zaleplon is a sedative/hypnotic, mainly used for insomnia. It is a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic from the pyrazolopyrimidine class. In terms of adverse effects zaleplon appears to offer little improvement compared to both benzodiazepines and other non-benzodiazepine Z-drugs.Sonata is manufactured by...
and eszopiclone
Eszopiclone
Eszopiclone, marketed by Sepracor under the brand-name Lunesta, is a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic used as a treatment for insomnia. Eszopiclone is the active dextrorotatory stereoisomer of zopiclone, and belongs to the class of drugs known as cyclopyrrolones.Eszopiclone is a short acting...
. Nonbenzodiazepines are molecularly distinct, but nonetheless, they work on the same benzodiazepine receptors and produce similar sedative effects.
Recreational use
Benzodiazepines are considered to be major drugs of abuse. Benzodiazepine abuse is mostly limited to individuals who abuse other drugs, i.e., poly-drug abusers. The majority of prescribed users do not abuse their medication. On the international scene, benzodiazepines are categorized as Schedule IV controlled drugs by the INCB, apart from flunitrazepamFlunitrazepam
Flunitrazepam is marketed as a potent hypnotic, sedative, anticonvulsant, anxiolytic, amnestic, and skeletal muscle relaxant drug most commonly known as Rohypnol...
which is Schedule III drugs under the Convention on Psychotropic Substances
Convention on Psychotropic Substances
The Convention on Psychotropic Substances of 1971 is a United Nations treaty designed to control psychoactive drugs such as amphetamines, barbiturates, benzodiazepines, and psychedelics signed at Vienna on February 21, 1971...
. Some variation in drug scheduling exists in individual countries; for example, in the United Kingdom, midazolam
Midazolam
Midazolam is a short-acting drug in the benzodiazepine class developed by Hoffmann-La Roche in the 1970s. The drug is used for treatment of acute seizures, moderate to severe insomnia, and for inducing sedation and amnesia before medical procedures. It possesses profoundly potent anxiolytic,...
and temazepam
Temazepam
Temazepam is an intermediate-acting 3-hydroxy benzodiazepine. It is mostly prescribed for the short-term treatment of sleeplessness in patients who have difficulty maintaining sleep...
are Schedule III controlled drugs. British law requires temazepam (but not midazolam) to be stored in safe custody. Safe custody requirements ensures that pharmacists and doctors holding stock of temazepam must store it in securely fixed double-locked steel safety cabinets and maintain a written register, which must be bound and contain separate entries for temazepam and must be written in ink with no use of correction fluid. Disposal of expired stock must be witnessed by a designated inspector (either a local drug-enforcement police officer or official from health authority). Benzodiazepine abuse ranges from occasional binges on large doses, to chronic and compulsive drug abuse of high doses.
Benzodiazepines are used recreationally and by problematic drug misusers. Mortality
Death
Death is the permanent termination of the biological functions that sustain a living organism. Phenomena which commonly bring about death include old age, predation, malnutrition, disease, and accidents or trauma resulting in terminal injury....
is higher among poly-drug misusers
Poly drug use
Polydrug use refers to the use of two or more psychoactive drugs in combination to achieve a particular effect. In many cases one drug is used as a base or primary drug, with additional drugs to leaven or compensate for the side effects of the primary drug and make the experience more enjoyable...
that also use benzodiazepines. Heavy alcohol use also increases mortality
Mortality rate
Mortality rate is a measure of the number of deaths in a population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit time...
among poly-drug users. Dependence and tolerance, often coupled with dosage escalation, to benzodiazepines can develop rapidly among drug misusers; withdrawal syndrome may appear after as little as three weeks of continuous use. Long-term use has the potential to cause both physical and psychological dependence and severe withdrawal symptoms such as depression
Clinical depression
Major depressive disorder is a mental disorder characterized by an all-encompassing low mood accompanied by low self-esteem, and by loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities...
, anxiety and panic attacks, and agoraphobia
Agoraphobia
Agoraphobia is an anxiety disorder defined as a morbid fear of having a panic attack or panic-like symptoms in a situation from which it is perceived to be difficult to escape. These situations can include, but are not limited to, wide-open spaces, crowds, or uncontrolled social conditions...
. Benzodiazepines and, in particular, temazepam
Temazepam
Temazepam is an intermediate-acting 3-hydroxy benzodiazepine. It is mostly prescribed for the short-term treatment of sleeplessness in patients who have difficulty maintaining sleep...
are sometimes used intravenously, which, if done incorrectly or in an unsterile manner, can lead to medical complications including abscess
Abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus that has accumulated in a cavity formed by the tissue in which the pus resides due to an infectious process or other foreign materials...
es, cellulitis
Cellulitis
Cellulitis is a diffuse inflammation of connective tissue with severe inflammation of dermal and subcutaneous layers of the skin. Cellulitis can be caused by normal skin flora or by exogenous bacteria, and often occurs where the skin has previously been broken: cracks in the skin, cuts, blisters,...
, thrombophlebitis
Thrombophlebitis
Thrombophlebitis is phlebitis related to a thrombus . When it occurs repeatedly in different locations, it is known as "Thrombophlebitis migrans" or "migrating thrombophlebitis".-Signs and symptoms:...
, arterial puncture, deep vein thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein. Deep vein thrombosis commonly affects the leg veins or the deep veins of the pelvis. Occasionally the veins of the arm are affected...
, and gangrene
Gangrene
Gangrene is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that arises when a considerable mass of body tissue dies . This may occur after an injury or infection, or in people suffering from any chronic health problem affecting blood circulation. The primary cause of gangrene is reduced blood...
. Sharing syringes and needles for this purpose also brings up the possibility of transmission of hepatitis
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is a medical condition defined by the inflammation of the liver and characterized by the presence of inflammatory cells in the tissue of the organ. The name is from the Greek hepar , the root being hepat- , meaning liver, and suffix -itis, meaning "inflammation"...
, HIV
HIV
Human immunodeficiency virus is a lentivirus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome , a condition in humans in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive...
, and other diseases. Benzodiazepines are also misused intranasally, which may have additional health consequences. Once benzodiazepine dependence has been established, a clinician usually converts the patient to an equivalent dose of diazepam before beginning a gradual reduction program.
A 1999–2005 Australian police survey of detainees reported preliminary findings that self-reported users of benzodiazepines were less likely than non-user detainees to work full-time and more likely to receive government benefits, use methamphetamine or heroin, and be arrested or imprisoned. Benzodiazepines are sometimes used for criminal purposes; they serve to incapacitate a victim in cases of drug assisted rape or robbery.
Overall, anecdotal evidence
Anecdotal evidence
The expression anecdotal evidence refers to evidence from anecdotes. Because of the small sample, there is a larger chance that it may be true but unreliable due to cherry-picked or otherwise unrepresentative of typical cases....
suggests that temazepam
Temazepam
Temazepam is an intermediate-acting 3-hydroxy benzodiazepine. It is mostly prescribed for the short-term treatment of sleeplessness in patients who have difficulty maintaining sleep...
may be the most psychologically habit-forming (addictive)
Substance dependence
The section about substance dependence in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders does not use the word addiction at all. It explains:...
benzodiazepine. Temazepam abuse reached epidemic proportions in some parts of the world, in particular, in Europe and Australia, and is a major drug of abuse in many Southeast Asian countries. This led authorities of various countries to place temazepam under a more restrictive legal status. Some countries banned the drug outright (i.e., Sweden). Temazepam also has certain pharmacokinetic properties of absorption, distribution, elimination, and clearance that make it more apt to abuse compared to many other benzodiazepines.
Veterinary use
Benzodiazepines are used in veterinary practice in the treatment of various disorders and conditions. As in humans, they are used in the first-line management of seizures, status epilepticusStatus epilepticus
Status epilepticus is a life-threatening condition in which the brain is in a state of persistent seizure. Definitions vary, but traditionally it is defined as one continuous unremitting seizure lasting longer than 5 minutes, or recurrent seizures without regaining consciousness between seizures...
, and tetanus
Tetanus
Tetanus is a medical condition characterized by a prolonged contraction of skeletal muscle fibers. The primary symptoms are caused by tetanospasmin, a neurotoxin produced by the Gram-positive, rod-shaped, obligate anaerobic bacterium Clostridium tetani...
, and as maintenance therapy in epilepsy (in particular, in cats). They are widely used in small and large animals (including horses, swine, cattle and exotic and wild animals) for their anxiolytic and sedative effects, as pre medication before surgery, for induction of anesthesia
Anesthesia
Anesthesia, or anaesthesia , traditionally meant the condition of having sensation blocked or temporarily taken away...
and as adjuncts to anesthesia.
Further reading
- Benzodiazepines - information from mental health charity The Royal College of Psychiatrists

