
John Tyler Morgan
Encyclopedia
John Tyler Morgan was a general
in the Confederate States Army
during the American Civil War
, and a six-term U.S. senator
from the state
of Alabama
after the war. He was a strong supporter of states rights and racial segregation
through the Reconstruction era. He was an expansionist, arguing for the annexation
of the Republic of Hawaii
and for U.S. construction of an interoceanic canal
in South America
.
into a family of Welsh origin whose ancestor James B. Morgan http://www.familysearch.org/eng/default.asp (1607–1704) settled in the Connecticut Colony
. John T. Morgan was initially educated by his mother. In 1833, he moved with his parents to Calhoun County, Alabama
, where he attended frontier schools and then studied law in Tuskegee
with justice William Parish Chilton, his brother-in-law. After admission to the bar he established a practice in Talledega
. Ten years later, Morgan moved to Dallas County
and resumed the practice of law in Selma
and Cahaba
.
Turning to politics, Morgan became a presidential elector on the Democratic
ticket in 1860, and supported John C. Breckinridge
. He was delegate from Dallas County to the State Convention of 1861, which passed the ordinance of secession
.
, at the age of 37 Morgan enlisted as a private in the Cahaba Rifles, which volunteered its services in the Confederate Army and was assigned to the 5th Alabama Infantry. He first saw action at the First Battle of Manassas in the summer of 1861. Morgan rose to major
and then lieutenant colonel
, serving under Col.
Robert E. Rodes
, a future Confederate general. Morgan resigned in 1862 and returned to Alabama
, where in August he recruited a new regiment
, the 51st Alabama Partisan Rangers
, becoming its colonel. He led it at the Battle of Stones River
, operating in cooperation with the cavalry of Nathan Bedford Forrest
.
When Rodes was promoted to major general
and given a division
in the Army of Northern Virginia
, Morgan declined an offer to command Rodes's old brigade
and instead remained in the Western Theater
, leading troops at the Battle of Chickamauga
. On November 16, 1863, he was appointed as a brigadier general
of cavalry and participated in the Knoxville Campaign
. His brigade consisted of the 1st, 3rd, 4th (Russell's), 9th, and 51st Alabama Cavalry regiments.
His men were routed and dispersed by Federal cavalry on January 27, 1864. He was reassigned to a new command and fought in the Atlanta Campaign
. Subsequently, his men harassed William T. Sherman's troops during the March to the Sea
. Later, he was assigned to administrative duty in Demopolis, Alabama
. When the Confederacy collapsed and the war ended, Morgan was trying to organize Alabama black troops for home defense.
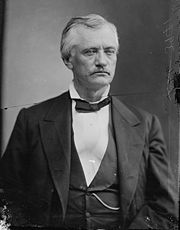 After the war, Morgan resumed the practicing of law in Selma, Alabama. He was once again presidential elector on the Democratic ticket in 1876 and was elected as a Democrat
After the war, Morgan resumed the practicing of law in Selma, Alabama. He was once again presidential elector on the Democratic ticket in 1876 and was elected as a Democrat
to the United States Senate in that year, being re-elected in 1882, 1888, 1894, 1900, and 1906, and serving from March 4, 1877, until his death. For much of his tenure, he served as Senator alongside a fellow former Confederate general, Edmund W. Pettus.
Morgan advocated for separating blacks and whites in the U.S. by encouraging the migration of black people out of the U.S. south. Hochschild wrote, "at various times in his long career Morgan also advocated sending them [negroes] to Hawaii, to Cuba, and to the Philippines - which, perhaps because the islands were so far away, he claimed were a "native home of the negro."
He introduced and fought for numerous legislative bills in support of legal lynching
. Morgan also staunchly worked for the repeal of the Fifteenth Amendment
to the U.S. Constitution that was intended to prevent the denial of voting rights based on race.
He was chairman of Committee on Rules
(Forty-sixth Congress), the Committee on Foreign Relations
(Fifty-third Congress), the Committee on Interoceanic Canals (Fifty-sixth and Fifty-seventh Congresses), and the Committee on Public Health and National Quarantine (Fifty-ninth Congress). In 1894, Morgan chaired an investigation, known as the Morgan Report
into the Hawaiian Revolution which concluded that the U.S. had remained completely neutral in the matter. He authored the introduction to the Morgan Report
based on the findings of the investigative committee.
He was a strong supporter of the annexation of Hawaii
and visited Hawaii in 1897 in support of annexation. He believed that the history of the U.S. clearly indicated it was unnecessary to hold a plebiscite in Hawaii as a condition for annexation. He was appointed by President William McKinley
in July 1898 to the commission created by the Newlands Resolution
to establish government in the Territory of Hawaii
. A strong advocate for a Central American canal, Morgan was also a staunch supporter of the Cuban revolutionaries in the 1890s.
The most recent study of Morgan by Joseph A. Fry suggests an alternate reason for Morgan's desires for American expansionism in the 1890s. Morgan may have figured that the expanded territories in Latin American would center their economic development in the Southern states, not the Northern ones, and this would undo the economic dominion of the North due to its victory of 1865. As it turned out the expansion in the wake of the Spanish American War did not lead to creating a southern United States economic domination.
while still in office. He was buried in Live Oak Cemetery in Selma, Alabama. The remainder of his term was served by John H. Bankhead
.
An article by history professor Thomas Adams Upchurch in the April 2004 Alabama Review says:
"It has become the solemn necessity on our part to protect the Caucasian race on this continent against the intrusion of Oriental people."
General (United States)
In the United States Army, United States Air Force, and United States Marine Corps, general is a four-star general officer rank, with the pay grade of O-10. General ranks above lieutenant general and below General of the Army or General of the Air Force; the Marine Corps does not have an...
in the Confederate States Army
Confederate States Army
The Confederate States Army was the army of the Confederate States of America while the Confederacy existed during the American Civil War. On February 8, 1861, delegates from the seven Deep South states which had already declared their secession from the United States of America adopted the...
during the American Civil War
American Civil War
The American Civil War was a civil war fought in the United States of America. In response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ; the other 25...
, and a six-term U.S. senator
United States Senate
The United States Senate is the upper house of the bicameral legislature of the United States, and together with the United States House of Representatives comprises the United States Congress. The composition and powers of the Senate are established in Article One of the U.S. Constitution. Each...
from the state
U.S. state
A U.S. state is any one of the 50 federated states of the United States of America that share sovereignty with the federal government. Because of this shared sovereignty, an American is a citizen both of the federal entity and of his or her state of domicile. Four states use the official title of...
of Alabama
Alabama
Alabama is a state located in the southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Tennessee to the north, Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gulf of Mexico to the south, and Mississippi to the west. Alabama ranks 30th in total land area and ranks second in the size of its inland...
after the war. He was a strong supporter of states rights and racial segregation
Racial segregation
Racial segregation is the separation of humans into racial groups in daily life. It may apply to activities such as eating in a restaurant, drinking from a water fountain, using a public toilet, attending school, going to the movies, or in the rental or purchase of a home...
through the Reconstruction era. He was an expansionist, arguing for the annexation
Annexation
Annexation is the de jure incorporation of some territory into another geo-political entity . Usually, it is implied that the territory and population being annexed is the smaller, more peripheral, and weaker of the two merging entities, barring physical size...
of the Republic of Hawaii
Republic of Hawaii
The Republic of Hawaii was the formal name of the government that controlled Hawaii from 1894 to 1898 when it was run as a republic. The republic period occurred between the administration of the Provisional Government of Hawaii which ended on July 4, 1894 and the adoption of the Newlands...
and for U.S. construction of an interoceanic canal
Canal
Canals are man-made channels for water. There are two types of canal:#Waterways: navigable transportation canals used for carrying ships and boats shipping goods and conveying people, further subdivided into two kinds:...
in South America
South America
South America is a continent situated in the Western Hemisphere, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere. The continent is also considered a subcontinent of the Americas. It is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east...
.
Early life and career
Morgan was born in Athens, TennesseeAthens, Tennessee
Athens is a city in McMinn County, Tennessee, United States. It is the county seat of McMinn County and the principal city of the Athens Micropolitan Statistical Area, which is part of the larger Chattanooga-Cleveland-Athens Combined Statistical Area. The population was 13,220 at the 2000...
into a family of Welsh origin whose ancestor James B. Morgan http://www.familysearch.org/eng/default.asp (1607–1704) settled in the Connecticut Colony
Connecticut Colony
The Connecticut Colony or Colony of Connecticut was an English colony located in British America that became the U.S. state of Connecticut. Originally known as the River Colony, it was organized on March 3, 1636 as a haven for Puritan noblemen. After early struggles with the Dutch, the English...
. John T. Morgan was initially educated by his mother. In 1833, he moved with his parents to Calhoun County, Alabama
Calhoun County, Alabama
Calhoun County is a county in the U.S. state of Alabama. Its name is in honor of John C. Calhoun, famous member of the United States Senate from South Carolina. As of 2010 the population was 118,572. It is included in the Anniston-Oxford Metropolitan Statistical Area...
, where he attended frontier schools and then studied law in Tuskegee
Tuskegee, Alabama
Tuskegee is a city in Macon County, Alabama, United States. At the 2000 census the population was 11,846 and is designated a Micropolitan Statistical Area. Tuskegee has been an important site in various stages of African American history....
with justice William Parish Chilton, his brother-in-law. After admission to the bar he established a practice in Talledega
Talladega, Alabama
Talladega is a city in Talladega County, Alabama, United States. At the 2000 census the population was 15,143. The city is the county seat of Talladega County. Talladega is approximately 50 miles east of Birmingham, Alabama....
. Ten years later, Morgan moved to Dallas County
Dallas County, Alabama
Dallas County is a county of the U.S. state of Alabama. Its name is in honor of United States Secretary of the Treasury Alexander J. Dallas. The county seat is Selma.- History :...
and resumed the practice of law in Selma
Selma, Alabama
Selma is a city in and the county seat of Dallas County, Alabama, United States, located on the banks of the Alabama River. The population was 20,512 at the 2000 census....
and Cahaba
Cahaba, Alabama
Cahaba, also spelled Cahawba, was the first permanent state capital of Alabama from 1820 to 1825. It is now a ghost town and state historic site. The site is located in Dallas County, southwest of Selma.-Capital:...
.
Turning to politics, Morgan became a presidential elector on the Democratic
Democratic Party (United States)
The Democratic Party is one of two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Republican Party. The party's socially liberal and progressive platform is largely considered center-left in the U.S. political spectrum. The party has the lengthiest record of continuous...
ticket in 1860, and supported John C. Breckinridge
John C. Breckinridge
John Cabell Breckinridge was an American lawyer and politician. He served as a U.S. Representative and U.S. Senator from Kentucky and was the 14th Vice President of the United States , to date the youngest vice president in U.S...
. He was delegate from Dallas County to the State Convention of 1861, which passed the ordinance of secession
Secession
Secession is the act of withdrawing from an organization, union, or especially a political entity. Threats of secession also can be a strategy for achieving more limited goals.-Secession theory:...
.
Civil War
With Alabama's vote to leave the UnionUnion (American Civil War)
During the American Civil War, the Union was a name used to refer to the federal government of the United States, which was supported by the twenty free states and five border slave states. It was opposed by 11 southern slave states that had declared a secession to join together to form the...
, at the age of 37 Morgan enlisted as a private in the Cahaba Rifles, which volunteered its services in the Confederate Army and was assigned to the 5th Alabama Infantry. He first saw action at the First Battle of Manassas in the summer of 1861. Morgan rose to major
Major (United States)
In the United States Army, Air Force, and Marine Corps, major is a field grade military officer rank just above the rank of captain and just below the rank of lieutenant colonel...
and then lieutenant colonel
Lieutenant Colonel (United States)
In the United States Army, United States Air Force, and United States Marine Corps, a lieutenant colonel is a field grade military officer rank just above the rank of major and just below the rank of colonel. It is equivalent to the naval rank of commander in the other uniformed services.The pay...
, serving under Col.
Colonel
Colonel , abbreviated Col or COL, is a military rank of a senior commissioned officer. It or a corresponding rank exists in most armies and in many air forces; the naval equivalent rank is generally "Captain". It is also used in some police forces and other paramilitary rank structures...
Robert E. Rodes
Robert E. Rodes
Robert Emmett Rodes was a railroad civil engineer and a promising young Confederate general in the American Civil War, killed in battle in the Shenandoah Valley.-Education, antebellum career:...
, a future Confederate general. Morgan resigned in 1862 and returned to Alabama
Alabama
Alabama is a state located in the southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Tennessee to the north, Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gulf of Mexico to the south, and Mississippi to the west. Alabama ranks 30th in total land area and ranks second in the size of its inland...
, where in August he recruited a new regiment
Regiment
A regiment is a major tactical military unit, composed of variable numbers of batteries, squadrons or battalions, commanded by a colonel or lieutenant colonel...
, the 51st Alabama Partisan Rangers
Partisan (military)
A partisan is a member of an irregular military force formed to oppose control of an area by a foreign power or by an army of occupation by some kind of insurgent activity...
, becoming its colonel. He led it at the Battle of Stones River
Battle of Stones River
The Battle of Stones River or Second Battle of Murfreesboro , was fought from December 31, 1862, to January 2, 1863, in Middle Tennessee, as the culmination of the Stones River Campaign in the Western Theater of the American Civil War...
, operating in cooperation with the cavalry of Nathan Bedford Forrest
Nathan Bedford Forrest
Nathan Bedford Forrest was a lieutenant general in the Confederate Army during the American Civil War. He is remembered both as a self-educated, innovative cavalry leader during the war and as a leading southern advocate in the postwar years...
.
When Rodes was promoted to major general
Major general (United States)
In the United States Army, United States Marine Corps, and United States Air Force, major general is a two-star general-officer rank, with the pay grade of O-8. Major general ranks above brigadier general and below lieutenant general...
and given a division
Division (military)
A division is a large military unit or formation usually consisting of between 10,000 and 20,000 soldiers. In most armies, a division is composed of several regiments or brigades, and in turn several divisions typically make up a corps...
in the Army of Northern Virginia
Army of Northern Virginia
The Army of Northern Virginia was the primary military force of the Confederate States of America in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War, as well as the primary command structure of the Department of Northern Virginia. It was most often arrayed against the Union Army of the Potomac...
, Morgan declined an offer to command Rodes's old brigade
Brigade
A brigade is a major tactical military formation that is typically composed of two to five battalions, plus supporting elements depending on the era and nationality of a given army and could be perceived as an enlarged/reinforced regiment...
and instead remained in the Western Theater
Western Theater of the American Civil War
This article presents an overview of major military and naval operations in the Western Theater of the American Civil War.-Theater of operations:...
, leading troops at the Battle of Chickamauga
Battle of Chickamauga
The Battle of Chickamauga, fought September 19–20, 1863, marked the end of a Union offensive in southeastern Tennessee and northwestern Georgia called the Chickamauga Campaign...
. On November 16, 1863, he was appointed as a brigadier general
Brigadier general (United States)
A brigadier general in the United States Army, Air Force, and Marine Corps, is a one-star general officer, with the pay grade of O-7. Brigadier general ranks above a colonel and below major general. Brigadier general is equivalent to the rank of rear admiral in the other uniformed...
of cavalry and participated in the Knoxville Campaign
Knoxville Campaign
The Knoxville Campaign was a series of American Civil War battles and maneuvers in East Tennessee during the fall of 1863. Union forces under Maj. Gen. Ambrose Burnside occupied Knoxville, Tennessee, and Confederate forces under Lt. Gen. James Longstreet were detached from Gen...
. His brigade consisted of the 1st, 3rd, 4th (Russell's), 9th, and 51st Alabama Cavalry regiments.
His men were routed and dispersed by Federal cavalry on January 27, 1864. He was reassigned to a new command and fought in the Atlanta Campaign
Atlanta Campaign
The Atlanta Campaign was a series of battles fought in the Western Theater of the American Civil War throughout northwest Georgia and the area around Atlanta during the summer of 1864. Union Maj. Gen. William T. Sherman invaded Georgia from the vicinity of Chattanooga, Tennessee, beginning in May...
. Subsequently, his men harassed William T. Sherman's troops during the March to the Sea
Sherman's March to the Sea
Sherman's March to the Sea is the name commonly given to the Savannah Campaign conducted around Georgia from November 15, 1864 to December 21, 1864 by Maj. Gen. William Tecumseh Sherman of the Union Army in the American Civil War...
. Later, he was assigned to administrative duty in Demopolis, Alabama
Demopolis, Alabama
Demopolis is the largest city in Marengo County, Alabama, United States. The population was 7,483 at the time of the 2010 United States Census....
. When the Confederacy collapsed and the war ended, Morgan was trying to organize Alabama black troops for home defense.
Postbellum career
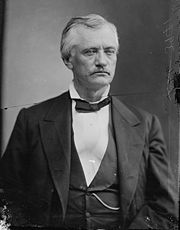
Democratic Party (United States)
The Democratic Party is one of two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Republican Party. The party's socially liberal and progressive platform is largely considered center-left in the U.S. political spectrum. The party has the lengthiest record of continuous...
to the United States Senate in that year, being re-elected in 1882, 1888, 1894, 1900, and 1906, and serving from March 4, 1877, until his death. For much of his tenure, he served as Senator alongside a fellow former Confederate general, Edmund W. Pettus.
Morgan advocated for separating blacks and whites in the U.S. by encouraging the migration of black people out of the U.S. south. Hochschild wrote, "at various times in his long career Morgan also advocated sending them [negroes] to Hawaii, to Cuba, and to the Philippines - which, perhaps because the islands were so far away, he claimed were a "native home of the negro."
He introduced and fought for numerous legislative bills in support of legal lynching
Lynching
Lynching is an extrajudicial execution carried out by a mob, often by hanging, but also by burning at the stake or shooting, in order to punish an alleged transgressor, or to intimidate, control, or otherwise manipulate a population of people. It is related to other means of social control that...
. Morgan also staunchly worked for the repeal of the Fifteenth Amendment
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution
The Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution prohibits each government in the United States from denying a citizen the right to vote based on that citizen's "race, color, or previous condition of servitude"...
to the U.S. Constitution that was intended to prevent the denial of voting rights based on race.
He was chairman of Committee on Rules
United States Senate Committee on Rules and Administration
The Senate Committee on Rules and Administration is responsible for the rules of the United States Senate, with administration of congressional buildings, and with credentials and qualifications of members of the Senate, including responsibility for dealing with contested elections.The committee...
(Forty-sixth Congress), the Committee on Foreign Relations
United States Senate Committee on Foreign Relations
The United States Senate Committee on Foreign Relations is a standing committee of the United States Senate. It is charged with leading foreign-policy legislation and debate in the Senate. The Foreign Relations Committee is generally responsible for overseeing and funding foreign aid programs as...
(Fifty-third Congress), the Committee on Interoceanic Canals (Fifty-sixth and Fifty-seventh Congresses), and the Committee on Public Health and National Quarantine (Fifty-ninth Congress). In 1894, Morgan chaired an investigation, known as the Morgan Report
Morgan Report
The Morgan Report was an 1894 report concluding an official U.S. Congressional investigation into the events surrounding the overthrow of the Hawaiian Kingdom, including the alleged role of U.S. military troops in the overthrow of Queen Liliuokalani...
into the Hawaiian Revolution which concluded that the U.S. had remained completely neutral in the matter. He authored the introduction to the Morgan Report
Morgan Report
The Morgan Report was an 1894 report concluding an official U.S. Congressional investigation into the events surrounding the overthrow of the Hawaiian Kingdom, including the alleged role of U.S. military troops in the overthrow of Queen Liliuokalani...
based on the findings of the investigative committee.
He was a strong supporter of the annexation of Hawaii
Hawaii
Hawaii is the newest of the 50 U.S. states , and is the only U.S. state made up entirely of islands. It is the northernmost island group in Polynesia, occupying most of an archipelago in the central Pacific Ocean, southwest of the continental United States, southeast of Japan, and northeast of...
and visited Hawaii in 1897 in support of annexation. He believed that the history of the U.S. clearly indicated it was unnecessary to hold a plebiscite in Hawaii as a condition for annexation. He was appointed by President William McKinley
William McKinley
William McKinley, Jr. was the 25th President of the United States . He is best known for winning fiercely fought elections, while supporting the gold standard and high tariffs; he succeeded in forging a Republican coalition that for the most part dominated national politics until the 1930s...
in July 1898 to the commission created by the Newlands Resolution
Newlands Resolution
The Newlands Resolution, was a joint resolution written by and named after United States Congressman Francis G. Newlands. It was an Act of Congress to annex the Republic of Hawaii and create the Territory of Hawaii....
to establish government in the Territory of Hawaii
Territory of Hawaii
The Territory of Hawaii or Hawaii Territory was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from July 7, 1898, until August 21, 1959, when its territory, with the exception of Johnston Atoll, was admitted to the Union as the fiftieth U.S. state, the State of Hawaii.The U.S...
. A strong advocate for a Central American canal, Morgan was also a staunch supporter of the Cuban revolutionaries in the 1890s.
The most recent study of Morgan by Joseph A. Fry suggests an alternate reason for Morgan's desires for American expansionism in the 1890s. Morgan may have figured that the expanded territories in Latin American would center their economic development in the Southern states, not the Northern ones, and this would undo the economic dominion of the North due to its victory of 1865. As it turned out the expansion in the wake of the Spanish American War did not lead to creating a southern United States economic domination.
Death and legacy
Senator Morgan died in Washington, D.C.Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly referred to as Washington, "the District", or simply D.C., is the capital of the United States. On July 16, 1790, the United States Congress approved the creation of a permanent national capital as permitted by the U.S. Constitution....
while still in office. He was buried in Live Oak Cemetery in Selma, Alabama. The remainder of his term was served by John H. Bankhead
John H. Bankhead
John Hollis Bankhead was a U.S. senator from the state of Alabama.-Biography:He was born on September 13, 1842. He was appointed, then elected, to serve out the remainder of the term left by the death of John Tyler Morgan, and was later re-elected twice. He served in the Senate from June 18, 1907...
.
An article by history professor Thomas Adams Upchurch in the April 2004 Alabama Review says:
- His congressional speeches and published writings demonstrate the central role that Morgan played in the drama of racial politics on Capitol Hill and in the national press from 1889 to 1891. More importantly, they reveal his leadership in forging the ideology of white supremacyWhite supremacyWhite supremacy is the belief, and promotion of the belief, that white people are superior to people of other racial backgrounds. The term is sometimes used specifically to describe a political ideology that advocates the social and political dominance by whites.White supremacy, as with racial...
that dominated American race relations from the 1890s to the 1960s. Indeed, Morgan emerged as the most prominent and notorious racist ideologue of his day, a man who, as much as any other individual, set the tone for the coming Jim CrowJim Crow lawsThe Jim Crow laws were state and local laws in the United States enacted between 1876 and 1965. They mandated de jure racial segregation in all public facilities, with a supposedly "separate but equal" status for black Americans...
era."
Notable quotes
"The snows will fall from heaven in sooty blackness, sooner than the white women of the United States will consent to the maternity of negro families.""It has become the solemn necessity on our part to protect the Caucasian race on this continent against the intrusion of Oriental people."
Memorialization
- In 1953, Morgan was elected to membership in the Alabama Hall of FameAlabama Hall of FameThe Alabama Hall of Fame was established by Act of Alabama No. 646 to recognize "worthy citizens of the state who rendered outstanding service or who won fame on account of their achievements as to make them exceptional in the history of Alabama"...
.
- The John T. Morgan Academy in Selma is named for Morgan. Founded in 1965, the private school originally held classes in Morgan's old houseJohn Tyler Morgan HouseThe John Tyler Morgan House is a historic Greek Revival-style house in Selma, Alabama, United States. It was built by Thomas R. Wetmore in 1859 and sold to John Tyler Morgan in 1865. Morgan was an attorney and former Confederate general. Beginning in 1876, he was elected as a Democratic U.S....
.
- Morgan Hall on the campus of the University of AlabamaUniversity of AlabamaThe University of Alabama is a public coeducational university located in Tuscaloosa, Alabama, United States....
was also named in his honor. Senator Morgan had successfully led a fight in 1882 to obtain Federal funds in reparation for the university's destruction in 1865 by Union forces.
- Morgan's Rock Hacienda and Ecolodge, http://www.morgansrock.com in the country of NicaraguaNicaraguaNicaragua is the largest country in the Central American American isthmus, bordered by Honduras to the north and Costa Rica to the south. The country is situated between 11 and 14 degrees north of the Equator in the Northern Hemisphere, which places it entirely within the tropics. The Pacific Ocean...
was named for Morgan, who as a Senator had strongly advocated Nicaragua as the preferred location for an interoceanic canalCanalCanals are man-made channels for water. There are two types of canal:#Waterways: navigable transportation canals used for carrying ships and boats shipping goods and conveying people, further subdivided into two kinds:...
, instead of PanamaPanamaPanama , officially the Republic of Panama , is the southernmost country of Central America. Situated on the isthmus connecting North and South America, it is bordered by Costa Rica to the northwest, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean Sea to the north and the Pacific Ocean to the south. The...
.
- A memorial arch on the grounds of the Federal Building / U.S. Courthouse in Selma honors Senators Morgan and Pettus, who were instrumental in securing Federal appropriations for the State.
External links
- Men of Mark in America Biography & Portrait

