Health issues and the effects of cannabis
Encyclopedia
The effects of cannabis are caused by cannabinoids
, most notably the chemical substance tetrahydrocannabinol
(THC). Cannabis
has both psychological and physiological effects on the human body. Five Europe
an countries, Canada
, and fifteen US states have legalized medical cannabis
if prescribed for nausea
, pain
, and alleviation of symptoms surrounding chronic illness.
Acute
effects while under the influence can include euphoria
and anxiety
. However, chronic
use is not associated with cardiovascular risk factors such as blood triglyceride
levels and blood pressure, as indicated in a longitudinal study. The evidence of long-term effects
on memory is preliminary and hindered by confounding factors. Concerns have been raised about the potential for long-term cannabis consumption to increase risk for schizophrenia
, bipolar disorders, and major depression, but the ultimate conclusions on these factors are disputed.
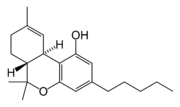
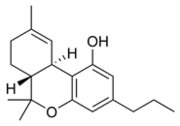
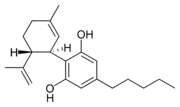
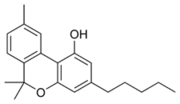
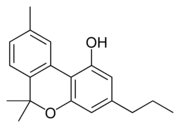
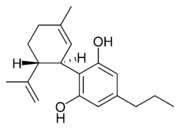
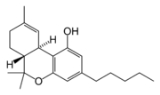
are cannabinoids
, including delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol
(Δ9-THC, commonly called simply THC). Some varieties, having undergone careful selection and growing techniques, can yield as much as 29% THC. Another psychoactive cannabinoid present in Cannabis sativa is tetrahydrocannabivarin
(THCV), but it is only found in small amounts and is in fact a cannabinoid antagonist.
In addition, there are also similar compounds contained in cannabis that do not exhibit any psychoactive response but are obligatory for functionality: cannabidiol
(CBD), an isomer
of THC; cannabinol
(CBN), an oxidation product of THC; cannabivarin
(CBV), an analog
of CBN with a different sidechain, cannabidivarin
(CBDV), an analog of CBD with a different side chain, and cannabinolic acid. How these other compounds interact with THC is not fully understood. Some clinical studies have proposed that CBD acts as a balancing force to regulate the strength of the psychoactive agent THC. Marijuana with relatively high ratios of CBD:THC is less likely to induce anxiety
than marijuana with low CBD:THC ratios. CBD is also believed to regulate the body’s metabolism of THC by inactivating cytochrome P450, an important class of enzymes that metabolize drugs. Experiments in which mice were treated with CBD followed by THC showed that CBD treatment was associated with a substantial increase in brain concentrations of THC and its major metabolites, most likely because it decreased the rate of clearance of THC from the body. Cannabis cofactor compounds have also been linked to lowering body temperature, modulating immune functioning, and cell protection. The essential oil
of cannabis contains many fragrant terpenoid
s which may synergize with the cannabinoids to produce their unique effects. THC is converted rapidly to 11-hydroxy-THC
, which is also pharmacologically active, so the drug effect outlasts measurable THC levels in blood.
THC and cannabidiol are also neuroprotective antioxidant
s. Research in rats has indicated that THC prevented hydroperoxide-induced oxidative damage as well as or better than other antioxidants in a chemical (Fenton reaction) system and neuron
al cultures. Cannabidiol was significantly more protective than either vitamin E
or vitamin C
.
The cannabinoid receptor is a typical member of the largest known family of receptors called a G protein-coupled receptor
. A signature of this type of receptor is the distinct pattern of how the receptor molecule spans the cell membrane
seven times. The location of cannabinoid receptors exists on the cell membrane, and both outside (extracellular
ly) and inside (intracellular
ly) the cell membrane. CB1 receptors, the bigger of the two, are extraordinarily abundant in the brain: 10 times more plentiful than μ-opioid receptor
s, the receptors responsible for the effects of morphine
. CB2 receptors are structurally different (the sequence similarity between the two subtypes of receptors is 44%), found only on cells of the immune system, and seems to function similarly to its CB1 counterpart. CB2 receptors are most commonly prevalent on B-cells, natural killer cells, and monocytes, but can also be found on polymorphonuclear neutrophil cells, T8 cells
, and T4 cells
. In the tonsils the CB2 receptors appear to be restricted to B-lymphocyte-enriched areas.
THC and endogenous anandamide additionally interact with glycine receptor
s.
s located throughout the brain
and body, along with endogenous
cannabinoid neurotransmitters like anandamide
(a lipid
material derived ligand
from arachidonic acid
), suggested that the use of cannabis affects the brain in the same manner as a naturally occurring brain chemical. Cannabinoids usually contain a 1,1'-di-methyl-pyrane ring, a variedly derivatized aromatic ring and a variedly unsaturated
cyclohexyl
ring and their immediate chemical precursors, constituting a family of about 60 bi-cyclic and tri-cyclic compounds. Like most other neurological processes, the effects of cannabis on the brain follow the standard protocol of signal transduction
, the electrochemical system of sending signals through neurons for a biological response. It is now understood that cannabinoid receptors appear in similar forms in most vertebrates and invertebrates and have a long evolutionary history of 500 million years. The binding of cannabinoids to cannabinoid receptors decrease adenylyl cyclase activity, inhibit calcium N channels
, and disinhibit K+A channels
. There are two types of cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2).
The CB1 receptor is found primarily in the brain and mediates the psychological effects of THC. The CB2 receptor is most abundantly found on cells of the immune system
. Cannabinoids act as immunomodulators at CB2 receptors, meaning they increase some immune responses and decrease others. For example, nonpsychotropic cannabinoids can be used as a very effective anti-inflammatory
. The affinity of cannabinoids to bind to either receptor is about the same, with only a slight increase observed with the plant-derived compound CBD binding to CB2 receptors more frequently. Cannabinoids likely have a role in the brain’s control of movement
and memory
, as well as natural pain modulation. It is clear that cannabinoids can affect pain transmission and, specifically, that cannabinoids interact with the brain's endogenous opioid
system and may affect dopamine transmission. This is an important physiological pathway for the medical treatment of pain.
are lipophilic
(fat soluble) compounds that easily store in fat, thus yielding a long elimination half-life relative to other recreational drug
s. The THC molecule, and related compounds, are usually detectable in drug tests from 3 days up to 10 days according to Redwood Laboratories, heavy users can produce positive tests for up to 3 months after ceasing cannabis use (see drug test
).
and the amount that can enter the body through the consumption of cannabis plants poses no threat of death. In lab animal tests, scientists have had much difficulty administering a dosage of THC that is high enough to be lethal. Accordingly, there is little reason to believe a human would self-administer such doses. Indeed, a 1988 ruling from the United States Department of Justice concluded that "In practical terms, marijuana cannot induce a lethal response as a result of drug-related toxicity."
According to the Merck Index
, the of THC (the dose which causes the death of 50% of individuals) is 1270 mg/kg for male rats and 730 mg/kg for female rats from oral consumption in sesame oil, and 42 mg/kg for rats from inhalation.
The ratio of cannabis material required to produce a fatal overdose to the amount required to saturate cannabinoid receptors and cause intoxication is approximately 40,000:1. It is extremely difficult to overdose by smoking marijuana; a typical marijuana "joint" contains less than 10 mg of THC, and one would have to smoke thousands of those in a short period of time to approach toxic levels. According to a 2006 United Kingdom
government report, using cannabis is much less dangerous than tobacco, prescription drugs, and alcohol in social harms, physical harm, and addiction. It was found in 2007 that while tobacco and cannabis smoke are quite similar, cannabis smoke contained higher amounts of ammonia
, hydrogen cyanide, and nitrogen oxides, but lower levels of carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
s (PAHs). This study found that directly inhaled cannabis smoke contained as much as 20 times as much ammonia and 5 times as much hydrogen cyanide as tobacco smoke and compared the properties of both mainstream and sidestream (smoke emitted from a smouldering 'joint' or 'cone') smoke. Mainstream cannabis smoke was found to contain higher concentrations of selected polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) than sidestream tobacco smoke. However, other studies have found much lower disparities in ammonia and hydrogen cyanide between cannabis and tobacco, and that some other constituents (such as polonium-210, lead, arsenic, nicotine, and tobacco-specific nitrosamines) are either lower or non-existent in cannabis smoke.
Cannabis is often considered an atypical, unique and sometimes paradoxical psychotropic due to its vast and sometimes contradictory array of effects. The subjective experience induced by imbibing in cannabis use can be considered stimulatory
and yet also sedative
or depressant
, while also having markedly mild psychedelic
and even dissociative characteristics.
Some effects may include a general alteration of conscious perception
, euphoria
, feelings of well-being, relaxation or stress reduction, increased appreciation of humor, music or the arts, joviality, metacognition
and introspection
, enhanced recollection (episodic memory
), increased sensuality, increased awareness of sensation, increased libido
, creative, abstract or philosophical thinking, disruption of linear memory and paranoia
or anxiety
. Anxiety
is the most commonly reported side effect of smoking marijuana. Between 20 and 30 percent of recreational users experience intense anxiety and/or panic attacks after smoking cannabis.
Cannabis also produces many subjective
and highly tangible effects, such as greater enjoyment of food taste and aroma (The Munchies), an enhanced enjoyment of music and comedy, and marked distortions in the perception of time and space (where experiencing a "rush" of ideas from the bank of long-term memory can create the subjective impression of long elapsed time, while a clock reveals that only a short time has passed). At higher doses, effects can include altered body image
, auditory and/or visual illusions, pseudo-hallucinatory or (rarely, at very high doses) fully hallucinatory experiences, and ataxia
from selective impairment of polysynaptic reflexes. In some cases, cannabis can lead to dissociative
states such as depersonalization
and derealization
; such effects are most often considered desirable, but have the potential to induce panic attack and paranoia in some unaccustomed users.
, dry mouth
(cotton mouth), reddening of the eyes
(congestion of the conjunctiva
l blood vessel
s), a reduction in intra-ocular pressure, muscle relaxation and a sensation of cold or hot hands and feet.
Electroencephalography
or EEG shows somewhat more persistent alpha wave
s of slightly lower frequency
than usual. Cannabinoids produce a "marked depression of motor activity" via activation of neuronal cannabinoid receptors belonging to the CB1
subtype.
A study of ten healthy, robust, male volunteers who resided in a residential research facility sought to examine both acute and residual subjective, physiologic, and performance effects of smoking marijuana cigarettes. On three separate days, subjects smoked one NIDA
marijuana cigarette containing either 0%, 1.8%, or 3.6% THC, documenting subjective, physiologic, and performance measures prior to smoking, five times following smoking on that day, and three times on the following morning. Subjects reported robust subjective effects following both active doses of marijuana, which returned to baseline levels within 3.5 hours. Heart rate increased and the pupillary light reflex decreased following active dose administration with return to baseline on that day. Additionally, marijuana smoking acutely produced decrements in smooth pursuit eye tracking. Although robust acute effects of marijuana were found on subjective and physiological measures, no effects were evident the day following administration, indicating that the residual effects of smoking a single marijuana cigarette are minimal.
A Dutch double blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, cross-over study examining male volunteers aged 18–45 years with a self-reported history of regular cannabis use concluded that smoking of cannabis with very high THC levels (marijuana with 9–23% THC), as currently sold in coffee shops in the Netherlands, may lead to higher THC blood-serum concentrations. This is reflected by an increase of the occurrence of impaired psychomotor skills, particularly among younger or inexperienced cannabis smokers, who do not always adapt their smoking-style to the higher THC content. High THC concentrations in cannabis were associated with a dose-related increase of physical effects (such as increase of heart rate, and decrease of blood pressure) and psychomotor effects (such as reacting more slowly, being less concentrated, making more mistakes during performance testing, having less motor control, and experiencing drowsiness). It was also observed during the study that the effects from a single joint
lasted for more than eight hours. Reaction times remained impaired five hours after smoking, when the THC serum concentrations were significantly reduced, but still present. However, it is important to note that the subjects (without knowing the potency) were told to finish their (unshared) joints rather than titrate their doses, leading in many cases to significantly higher doses than they would normally take. Also, when subjects smoke on several occasions per day, accumulation of THC in blood-serum may occur.
effects produced by cannabinoids. Brain regions in which cannabinoid receptors are very abundant are the basal ganglia
, associated with movement control; the cerebellum
, associated with body movement coordination; the hippocampus
, associated with learning
, memory, and stress
control; the cerebral cortex
, associated with higher cognitive functions; and the nucleus accumbens
, regarded as the reward center of the brain. Other regions where cannabinoid receptors are moderately concentrated are the hypothalamus
, which regulates homeostatic functions; the amygdala
, associated with emotional responses and fear
s; the spinal cord
, associated with peripheral sensations like pain; the brain stem
, associated with sleep
, arousal
, and motor control; and the nucleus of the solitary tract
, associated with visceral sensations like nausea
and vomiting
.
Most notably, the two areas of motor control and memory are where the effects of cannabis are directly and irrefutably evident. Cannabinoids, depending on the dose, inhibit the transmission of neural signals through the basal ganglia and cerebellum. At lower doses, cannabinoids seem to stimulate locomotion while greater doses inhibit it, most commonly manifested by lack of steadiness (body sway and hand steadiness) in motor tasks that require a lot of attention. Other brain regions, like the cortex, the cerebellum, and the neural pathway from cortex to striatum
, are also involved in the control of movement and contain abundant cannabinoid receptors, indicating their possible involvement as well.
Experiments on animal and human tissue have demonstrated a disruption of short-term memory
formation, which is consistent with the abundance of CB1 receptors on the hippocampus, the region of the brain most closely associated with memory. Cannabinoids inhibit the release of several neurotransmitters in the hippocampus, like acetylcholine
, norepinephrine
, and glutamate, resulting in a major decrease in neuronal activity in that region. This decrease in activity resembles a "temporary hippocampal lesion." In the end, this procedure could lead to the blocking of cellular processes that are associated with memory formation.
In in-vitro experiments THC at extremely high concentrations, which could not be reached with commonly consumed doses, caused competitive inhibition
of the AChE
enzyme and inhibition of β-amyloid
peptide aggregation, the cause of Alzheimer's disease
. Compared to currently approved drugs prescribed for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, THC is a considerably superior inhibitor of A aggregation, and this study provides a previously unrecognized molecular mechanism through which cannabinoid molecules may directly impact the progression of this debilitating disease.
The study identified young males, amongst whom cannabis consumption is frequent and increasing, and in whom alcohol consumption is also common, as a risk group for traffic accidents. This is due to driving inexperience and factors associated with youth relating to risk
taking, delinquency
and motivation
. These demographic and psychosocial variables may relate to both drug use and accident risk, thereby presenting an artificial relationship between use of drugs and accident involvement.
The effects of cannabis on laboratory-based tasks show clear impairment with respect to tracking ability, attention
, and other tasks depending on the dose administered. Both simulation and road trials generally find that driving behavior shortly after consumption of larger doses of cannabis results in:
Kelly, Darke and Ross show similar results, with laboratory studies examining the effects of cannabis on skills utilised while driving showing impairments in tracking, attention, reaction time, short-term memory, hand-eye coordination, vigilance, time and distance perception, and decision making and concentration. An EMCDDA review concluded that "the acute effect of moderate or higher doses of cannabis impairs the skills related to safe driving and injury risk", specifically "attention, tracking and psychomotor skills".
In their review of driving simulator studies, Kelly et al. conclude that there is evidence of dose-dependent impairments in cannabis-affected drivers' ability to control a vehicle in the areas of steering, headway control, speed variability, car following, reaction time and lane positioning. The researchers note that "even in those who learn to compensate for a drug's impairing effects, substantial impairment in performance can still be observed under conditions of general task performance (i.e. when no contingencies are present to maintain compensated performance)."
. There were about 50 confirmed cases from 1960 to 2008, all of which occurred in Europe. However, all of the cases also involved tobacco (a known cause of Buerger's disease) in one way or another, and nearly all of the cannabis use was quite heavy. In Europe, cannabis is typically mixed with tobacco, in contrast to North America.
A 2008 study by the National Institutes of Health
Biomedical Research Centre in Baltimore found that heavy, chronic smoking of marijuana (138 joints per week) changed blood proteins
associated with heart disease
and stroke
. This is a result of raised carboxyhemoglobin levels from carbon monoxide. A similar increase in heart disease and ischemic strokes is observed in tobacco smokers, which suggests that the harmful effects come from combustion products, not marijuana.
A 2005 article in the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry reported on a 36-year-old man who suffered a stroke on three separate occasions after smoking a large amount of marijuana, despite having no known risk factors for the disorder, suggesting that a rare side effect of marijuana use may be an increase in the incidence of strokes among young smokers. A 2000 study by researchers at Boston's Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
, Massachusetts General Hospital
and Harvard School of Public Health
also found that a middle-age person's risk of heart attack rises nearly fivefold in the first hour after smoking marijuana, about the same elevated risk as vigorous exercise or sexual intercourse.
obtained from "soap bar"-type sources. The dried flowers of the plant may be contaminated by the plant taking up heavy metals and other toxins from its growing environment, or by the addition of lead or glass beads, used to increase the weight or to make the cannabis appear as if it has more crystal-looking trichomes indicating a higher THC content. Users who burn hot or mix cannabis with tobacco are at risk of failing to detect deviations from appropriate cannabis taste.
Despite cannabis being generally perceived as a natural or "chemical-free"
product, in a recent Australian survey one in four Australians consider cannabis grown indoors under hydroponic conditions to be a greater health risk due to increased contamination, added to the plant during cultivation to enhance the plant growth and quality.
and nicotine. Such complications demonstrate the need for studies on cannabis that have stronger controls, and investigations into alleged symptoms of cannabis use that may also be caused by tobacco. Some critics question whether agencies doing the research make an honest effort to present an accurate, unbiased summary of the evidence, or whether they "cherry-pick
" their data to please funding sources which may include the tobacco industry or governments dependent on cigarette tax revenue; others caution that the raw data, and not the final conclusions, are what should be examined.
Cannabis also has been shown to have a synergistic cytotoxic effect on lung cancer cell cultures in vitro with the food additive butylated hydroxyanisole
(BHA) and possibly the related compound butylated hydroxytoluene
(BHT). The study concluded, "Exposure to marijuana smoke in conjunction with BHA, a common food additive, may promote deleterious health effects in the lung." BHA & BHT are human-made fat preservatives, and are found in many packaged foods including: plastics in boxed cereal, Jello, Slim Jims, and more.
The Australian National Household Survey of 2001 showed that cannabis use in Australia is rarely used without other drugs. 95% of cannabis users also drank alcohol; 26% took amphetamines; 19% took ecstasy and only 2.7% reported not having used any other drug with cannabis. While research has been undertaken on the combined effects of alcohol and cannabis on performing certain tasks, little research has been conducted on the reasons why this combination is so popular. Evidence from a controlled experimental study undertaken by Lukas and Orozco suggests that alcohol causes THC to be absorbed more rapidly into the blood plasma of the user. Data from the Australian National Survey of Mental Health and Wellbeing found that three-quarters of recent cannabis users reported using alcohol when cannabis was not available.
A 2008 review of the evidence surrounding the acute impact on memory concluded that cannabinoids impair all aspects of short-term memory, especially short-term episodic and working memory. One small study found that no learning occurred during the 2 hour period in which the subjects (infrequent users) were "stoned".
has been documented for hundreds of years, and is commonly known as "the munchies" in popular culture. Clinical studies and survey data have found that cannabis increases food enjoyment and interest in food. Scientists have claimed to be able to explain what causes the increase in appetite, concluding that "endocannabinoids in the hypothalamus activate cannabinoid receptors that are responsible for maintaining food intake".
Endogenous cannabinoids have recently been discovered in foods such as chocolate and bovine milk.
It is widely accepted that the neonatal survival of many species "is largely dependent upon their suckling behavior, or appetite for breast milk" and recent research has identified the endogenous cannabinoid system to be the first neural system to display complete control over milk ingestion and neonatal survival. It is possible that "cannabinoid receptors in our body interact with the cannabinoids in milk to stimulate a suckling response in newborns so as to prevent growth failure".
Higher rates of testicular cancer in western nations have been linked to use of cannabis. A study conducted by the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center
and funded by the National Institutes of Health
, published in the journal Cancer
March 15, 2009, linked long term use of cannabis to an increased risk of 70 percent for testicular cancer
with the scientists concluding that cannabis is harmful to the human endocrine and reproductive system.
More research is no guarantee of greater consensus in the field of cannabis studies, however; both advocates and opponents of the drug are able to call upon multiple scientific studies supporting their respective positions. Cannabis has been correlated with the development of various mental disorders in multiple studies, for example a recent 10 year study on 1923 individuals from the general population in Germany
, aged 14–24, concluded that cannabis use is a risk factor for the development of incident psychotic symptoms. Continued cannabis use might increase the risk for psychotic disorder.
Other studies differ widely as to whether cannabis use is the cause of the mental problems, whether the mental problems encourage cannabis use, or whether both the cannabis use and the mental problems are the effects of some other cause. Still other studies even encourage the use of cannabis in treating schizophrenia. Similarly, efforts to prove the "gateway drug" hypothesis that cannabis and alcohol makes users more inclined to become addicted to "harder" drugs like cocaine and heroin have produced mixed results, with different studies finding varying degrees of correlation between the use of cannabis and other drugs, and some finding none. Some, however, believe the "gateway effect," currently being pinned on the use of marijuana, should not be attributed to the drug itself but rather the illegality of the drug in most countries. Supporters of this theory believe that the grouping of marijuana and harder drugs in law is, in fact, the cause of users of marijuana to move on to those harder drugs.
s found in cannabis only affect plants and not humans, but some microorganisms, especially those that proliferate when the herb is not correctly dried and stored, can be harmful to humans. Some users may store marijuana in an airtight bag or jar in a refrigerator
to prevent fungi and bacterial growth.
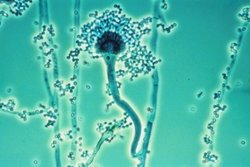 The fungi Aspergillus flavus
The fungi Aspergillus flavus
, Aspergillus fumigatus
, Aspergillus niger
, Aspergillus parasiticus
, Aspergillus tamarii, Aspergillus sulphureus, Aspergillus repens, Mucor hiemalis
(not a human pathogen), Penicillium chrysogenum
, Penicillium italicum
and Rhizopus nigrans have been found in moldy cannabis. Aspergillus
mold species can infect the lungs via smoking or handling of infected cannabis and cause opportunistic and sometimes deadly aspergillosis
. Some of the microorganisms found create aflatoxin
s, which are toxic and carcinogenic. Researchers suggest that moldy cannabis thus be discarded.
Mold is also found in smoke from mold infected cannabis, and the lungs and nasal passages are a major means of contracting fungal infections. Levitz and Diamond (1991) suggested baking marijuana in home ovens at 150 °C [302 °F], for five minutes before smoking. Oven treatment killed conidia of A. fumigatus, A. flavus and A. niger, and did not degrade the active component of marijuana, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)."
with dozens of cases of salmonellosis
in 1981. "Thermophilic actinomycetes" were also found in cannabis.
 In many countries, experimental science regarding cannabis is restricted due to its illegality
In many countries, experimental science regarding cannabis is restricted due to its illegality
. Thus, cannabis as a drug is often hard to fit into the structural confines of medical research because appropriate, research-grade samples are difficult to obtain for research purposes, unless granted under authority of national governments.
by the clash between Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies
(MAPS), an independent research group, and the National Institute on Drug Abuse
(NIDA), a federal agency
charged with the application of science to the study of drug abuse. The NIDA largely operates under the general control of the Office of National Drug Control Policy
(ONDCP), a White House office
responsible for the direct coordination of all legal, legislative, scientific, social and political aspects of federal drug control policy.
The cannabis that is available for research studies in the United States is grown at the University of Mississippi
and solely controlled by the NIDA, which has veto power over the Food and Drug Administration
(FDA) to define accepted protocols. Since 1942, when cannabis was removed from the U.S. Pharmacopoeia and its medical use was prohibited, there have been no legal (under federal law) privately funded cannabis production projects. This has resulted in a limited amount of research being done and possibly in NIDA producing cannabis which has been alleged to be of very low potency and inferior quality.
MAPS, in conjunction with Professor Lyle Craker
, PhD, the director of the Medicinal Plant Program at the University of Massachusetts Amherst
, sought to provide independently grown cannabis of more appropriate research quality for FDA-approved research studies, and encountered opposition by NIDA, the ONDCP, and the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration
(DEA).
Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids are a class of chemical compounds that include the phytocannabinoids , and chemical compounds that mimic the actions of phytocannabinoids or have a similar structure...
, most notably the chemical substance tetrahydrocannabinol
Tetrahydrocannabinol
Tetrahydrocannabinol , also known as delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol , Δ1-THC , or dronabinol, is the main chemical psychoactive substance found in the cannabis plant. It was first isolated in 1964. In pure form, it is a glassy solid when cold, and becomes viscous and sticky if warmed...
(THC). Cannabis
Cannabis (drug)
Cannabis, also known as marijuana among many other names, refers to any number of preparations of the Cannabis plant intended for use as a psychoactive drug or for medicinal purposes. The English term marijuana comes from the Mexican Spanish word marihuana...
has both psychological and physiological effects on the human body. Five Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
an countries, Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
, and fifteen US states have legalized medical cannabis
Medical cannabis
Medical cannabis refers to the use of parts of the herb cannabis as a physician-recommended form of medicine or herbal therapy, or to synthetic forms of specific cannabinoids such as THC as a physician-recommended form of medicine...
if prescribed for nausea
Nausea
Nausea , is a sensation of unease and discomfort in the upper stomach with an involuntary urge to vomit. It often, but not always, precedes vomiting...
, pain
Pain
Pain is an unpleasant sensation often caused by intense or damaging stimuli such as stubbing a toe, burning a finger, putting iodine on a cut, and bumping the "funny bone."...
, and alleviation of symptoms surrounding chronic illness.
Acute
Acute toxicity
Acute toxicity describes the adverse effects of a substance that result either from a single exposure or from multiple exposures in a short space of time...
effects while under the influence can include euphoria
Euphoria
Euphoria is an emotional and mental state defined as a sense of great elation and well being.Euphoria may also refer to:* Euphoria , a genus of scarab beetles* Euphoria, a genus name previously used for the longan and other trees...
and anxiety
Anxiety
Anxiety is a psychological and physiological state characterized by somatic, emotional, cognitive, and behavioral components. The root meaning of the word anxiety is 'to vex or trouble'; in either presence or absence of psychological stress, anxiety can create feelings of fear, worry, uneasiness,...
. However, chronic
Chronic toxicity
Chronic toxicity is a property of a substance that has toxic effects on a living organism, when that organism is exposed to the substance continuously or repeatedly. Compared with acute toxicity.Two distinct situations need to be considered:...
use is not associated with cardiovascular risk factors such as blood triglyceride
Triglyceride
A triglyceride is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids. There are many triglycerides, depending on the oil source, some are highly unsaturated, some less so....
levels and blood pressure, as indicated in a longitudinal study. The evidence of long-term effects
Long-term effects of cannabis
Though the long-term effects of cannabis have been studied, there remains much to be concluded. Because use of cannabis ranges widely from users who try it once, to people using it frequently in a year, as well as users who use it daily, it is hard to measure the health effects it has on the human...
on memory is preliminary and hindered by confounding factors. Concerns have been raised about the potential for long-term cannabis consumption to increase risk for schizophrenia
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by a disintegration of thought processes and of emotional responsiveness. It most commonly manifests itself as auditory hallucinations, paranoid or bizarre delusions, or disorganized speech and thinking, and it is accompanied by significant social...
, bipolar disorders, and major depression, but the ultimate conclusions on these factors are disputed.
Biochemical effects






Cannabinoids and cannabinoid receptors
The most prevalent psychoactive substances in cannabisCannabis
Cannabis is a genus of flowering plants that includes three putative species, Cannabis sativa, Cannabis indica, and Cannabis ruderalis. These three taxa are indigenous to Central Asia, and South Asia. Cannabis has long been used for fibre , for seed and seed oils, for medicinal purposes, and as a...
are cannabinoids
Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids are a class of chemical compounds that include the phytocannabinoids , and chemical compounds that mimic the actions of phytocannabinoids or have a similar structure...
, including delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol
Tetrahydrocannabinol
Tetrahydrocannabinol , also known as delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol , Δ1-THC , or dronabinol, is the main chemical psychoactive substance found in the cannabis plant. It was first isolated in 1964. In pure form, it is a glassy solid when cold, and becomes viscous and sticky if warmed...
(Δ9-THC, commonly called simply THC). Some varieties, having undergone careful selection and growing techniques, can yield as much as 29% THC. Another psychoactive cannabinoid present in Cannabis sativa is tetrahydrocannabivarin
Tetrahydrocannabivarin
Tetrahydrocannabivarin , also known as tetrahydrocannabivarol, is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid found naturally in Cannabis sativa. It is an analogue of tetrahydrocannabinol...
(THCV), but it is only found in small amounts and is in fact a cannabinoid antagonist.
In addition, there are also similar compounds contained in cannabis that do not exhibit any psychoactive response but are obligatory for functionality: cannabidiol
Cannabidiol
Cannabidiol is a cannabinoid found in Cannabis. It is a major constituent of the plant, representing up to 40% in its extracts.It has displayed sedative effects in animal tests...
(CBD), an isomer
Isomer
In chemistry, isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. Isomers do not necessarily share similar properties, unless they also have the same functional groups. There are many different classes of isomers, like stereoisomers, enantiomers, geometrical...
of THC; cannabinol
Cannabinol
Cannabinol is a psychoactive substance cannabinoid found in Cannabis sativa and Cannabis indica/afghanica. It is also a metabolite of tetrahydrocannabinol . CBN acts as a weak agonist of the CB1 and CB2 receptors, with lower affinity in comparison to THC.- External links :* Compounds found in...
(CBN), an oxidation product of THC; cannabivarin
Cannabivarin
Cannabivarin, also known as cannabivarol or CBV, is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid found in minor amounts in the hemp plant Cannabis sativa. It is an analog of cannabinol with the sidechain shortened by two CH2 groups. CBV is an oxidation product of tetrahydrocannabivarin .- External links :* ...
(CBV), an analog
Analog (chemistry)
In chemistry, a structural analog , also known as chemical analog or simply analog, is a compound having a structure similar to that of another one, but differing from it in respect of a certain component. It can differ in one or more atoms, functional groups, or substructures, which are replaced...
of CBN with a different sidechain, cannabidivarin
Cannabidivarin
Cannabidivarine , also known as cannabidivarol, is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid found in low amounts in Cannabis sativa. It is an analog of cannabidiol , with the side-chain shortened by two CH2 groups...
(CBDV), an analog of CBD with a different side chain, and cannabinolic acid. How these other compounds interact with THC is not fully understood. Some clinical studies have proposed that CBD acts as a balancing force to regulate the strength of the psychoactive agent THC. Marijuana with relatively high ratios of CBD:THC is less likely to induce anxiety
Anxiety
Anxiety is a psychological and physiological state characterized by somatic, emotional, cognitive, and behavioral components. The root meaning of the word anxiety is 'to vex or trouble'; in either presence or absence of psychological stress, anxiety can create feelings of fear, worry, uneasiness,...
than marijuana with low CBD:THC ratios. CBD is also believed to regulate the body’s metabolism of THC by inactivating cytochrome P450, an important class of enzymes that metabolize drugs. Experiments in which mice were treated with CBD followed by THC showed that CBD treatment was associated with a substantial increase in brain concentrations of THC and its major metabolites, most likely because it decreased the rate of clearance of THC from the body. Cannabis cofactor compounds have also been linked to lowering body temperature, modulating immune functioning, and cell protection. The essential oil
Essential oil
An essential oil is a concentrated hydrophobic liquid containing volatile aroma compounds from plants. Essential oils are also known as volatile oils, ethereal oils or aetherolea, or simply as the "oil of" the plant from which they were extracted, such as oil of clove...
of cannabis contains many fragrant terpenoid
Terpenoid
The terpenoids , sometimes called isoprenoids, are a large and diverse class of naturally occurring organic chemicals similar to terpenes, derived from five-carbon isoprene units assembled and modified in thousands of ways. Most are multicyclic structures that differ from one another not only in...
s which may synergize with the cannabinoids to produce their unique effects. THC is converted rapidly to 11-hydroxy-THC
11-Hydroxy-THC
11-Hydroxy-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, abbreviated as 11-OH-THC, is the main active metabolite of THC which is formed in the body after cannabis consumption. 11-Hydroxy-THC has been shown to be active in its own right, but the effects produced are not necessarily identical to those of THC...
, which is also pharmacologically active, so the drug effect outlasts measurable THC levels in blood.
THC and cannabidiol are also neuroprotective antioxidant
Antioxidant
An antioxidant is a molecule capable of inhibiting the oxidation of other molecules. Oxidation is a chemical reaction that transfers electrons or hydrogen from a substance to an oxidizing agent. Oxidation reactions can produce free radicals. In turn, these radicals can start chain reactions. When...
s. Research in rats has indicated that THC prevented hydroperoxide-induced oxidative damage as well as or better than other antioxidants in a chemical (Fenton reaction) system and neuron
Neuron
A neuron is an electrically excitable cell that processes and transmits information by electrical and chemical signaling. Chemical signaling occurs via synapses, specialized connections with other cells. Neurons connect to each other to form networks. Neurons are the core components of the nervous...
al cultures. Cannabidiol was significantly more protective than either vitamin E
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is used to refer to a group of fat-soluble compounds that include both tocopherols and tocotrienols. There are many different forms of vitamin E, of which γ-tocopherol is the most common in the North American diet. γ-Tocopherol can be found in corn oil, soybean oil, margarine and dressings...
or vitamin C
Vitamin C
Vitamin C or L-ascorbic acid or L-ascorbate is an essential nutrient for humans and certain other animal species. In living organisms ascorbate acts as an antioxidant by protecting the body against oxidative stress...
.
The cannabinoid receptor is a typical member of the largest known family of receptors called a G protein-coupled receptor
G protein-coupled receptor
G protein-coupled receptors , also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein-linked receptors , comprise a large protein family of transmembrane receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal...
. A signature of this type of receptor is the distinct pattern of how the receptor molecule spans the cell membrane
Cell membrane
The cell membrane or plasma membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. It basically protects the cell...
seven times. The location of cannabinoid receptors exists on the cell membrane, and both outside (extracellular
Extracellular
In cell biology, molecular biology and related fields, the word extracellular means "outside the cell". This space is usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid...
ly) and inside (intracellular
Intracellular
Not to be confused with intercellular, meaning "between cells".In cell biology, molecular biology and related fields, the word intracellular means "inside the cell".It is used in contrast to extracellular...
ly) the cell membrane. CB1 receptors, the bigger of the two, are extraordinarily abundant in the brain: 10 times more plentiful than μ-opioid receptor
Opioid receptor
Opioid receptors are a group of G protein-coupled receptors with opioids as ligands. The endogenous opioids are dynorphins, enkephalins, endorphins, endomorphins and nociceptin. The opioid receptors are ~40% identical to somatostatin receptors...
s, the receptors responsible for the effects of morphine
Morphine
Morphine is a potent opiate analgesic medication and is considered to be the prototypical opioid. It was first isolated in 1804 by Friedrich Sertürner, first distributed by same in 1817, and first commercially sold by Merck in 1827, which at the time was a single small chemists' shop. It was more...
. CB2 receptors are structurally different (the sequence similarity between the two subtypes of receptors is 44%), found only on cells of the immune system, and seems to function similarly to its CB1 counterpart. CB2 receptors are most commonly prevalent on B-cells, natural killer cells, and monocytes, but can also be found on polymorphonuclear neutrophil cells, T8 cells
Cytotoxic T cell
A cytotoxic T cell belongs to a sub-group of T lymphocytes that are capable of inducing the death of infected somatic or tumor cells; they kill cells that are infected with viruses , or are otherwise damaged or...
, and T4 cells
T helper cell
T helper cells are a sub-group of lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell, that play an important role in the immune system, particularly in the adaptive immune system. These cells have no cytotoxic or phagocytic activity; they cannot kill infected host cells or pathogens. Rather, they help other...
. In the tonsils the CB2 receptors appear to be restricted to B-lymphocyte-enriched areas.
THC and endogenous anandamide additionally interact with glycine receptor
Glycine receptor
The glycine receptor, or GlyR, is the receptor for the amino acid neurotransmitter glycine. GlyR is an ionotropic receptor that produces its effects through chloride current...
s.
Biochemical mechanisms in the brain
In 1990, the discovery of cannabinoid receptorCannabinoid receptor
The cannabinoid receptors are a class of cell membrane receptors under the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily. As is typical of G protein-coupled receptors, the cannabinoid receptors contain seven transmembrane spanning domains...
s located throughout the brain
Brain
The brain is the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few primitive invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, sea squirts and starfishes do not have one. It is located in the head, usually close to primary sensory apparatus such as vision, hearing,...
and body, along with endogenous
Endogenous
Endogenous substances are those that originate from within an organism, tissue, or cell. Endogenous retroviruses are caused by ancient infections of germ cells in humans, mammals and other vertebrates...
cannabinoid neurotransmitters like anandamide
Anandamide
Anandamide, also known as N-arachidonoylethanolamide or AEA, is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter. The name is taken from the Sanskrit word ananda, which means "bliss, delight", and amide. It is synthesized from N-arachidonoyl phosphatidylethanolamine by multiple pathways...
(a lipid
Lipid
Lipids constitute a broad group of naturally occurring molecules that include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins , monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, phospholipids, and others...
material derived ligand
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding between metal and ligand generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs. The nature of metal-ligand bonding can range from...
from arachidonic acid
Arachidonic acid
Arachidonic acid is a polyunsaturated omega-6 fatty acid 20:4.It is the counterpart to the saturated arachidic acid found in peanut oil, Arachidonic acid (AA, sometimes ARA) is a polyunsaturated omega-6 fatty acid 20:4(ω-6).It is the counterpart to the saturated arachidic acid found in peanut oil,...
), suggested that the use of cannabis affects the brain in the same manner as a naturally occurring brain chemical. Cannabinoids usually contain a 1,1'-di-methyl-pyrane ring, a variedly derivatized aromatic ring and a variedly unsaturated
Saturation (chemistry)
In chemistry, saturation has six different meanings, all based on reaching a maximum capacity...
cyclohexyl
Cyclohexane
Cyclohexane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula C6H12. Cyclohexane is used as a nonpolar solvent for the chemical industry, and also as a raw material for the industrial production of adipic acid and caprolactam, both of which being intermediates used in the production of nylon...
ring and their immediate chemical precursors, constituting a family of about 60 bi-cyclic and tri-cyclic compounds. Like most other neurological processes, the effects of cannabis on the brain follow the standard protocol of signal transduction
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a cell surface receptor. In turn, this receptor alters intracellular molecules creating a response...
, the electrochemical system of sending signals through neurons for a biological response. It is now understood that cannabinoid receptors appear in similar forms in most vertebrates and invertebrates and have a long evolutionary history of 500 million years. The binding of cannabinoids to cannabinoid receptors decrease adenylyl cyclase activity, inhibit calcium N channels
Ion channel
Ion channels are pore-forming proteins that help establish and control the small voltage gradient across the plasma membrane of cells by allowing the flow of ions down their electrochemical gradient. They are present in the membranes that surround all biological cells...
, and disinhibit K+A channels
Potassium channel
In the field of cell biology, potassium channels are the most widely distributed type of ion channel and are found in virtually all living organisms. They form potassium-selective pores that span cell membranes...
. There are two types of cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2).
The CB1 receptor is found primarily in the brain and mediates the psychological effects of THC. The CB2 receptor is most abundantly found on cells of the immune system
Immune system
An immune system is a system of biological structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease by identifying and killing pathogens and tumor cells. It detects a wide variety of agents, from viruses to parasitic worms, and needs to distinguish them from the organism's own...
. Cannabinoids act as immunomodulators at CB2 receptors, meaning they increase some immune responses and decrease others. For example, nonpsychotropic cannabinoids can be used as a very effective anti-inflammatory
Anti-inflammatory
Anti-inflammatory refers to the property of a substance or treatment that reduces inflammation. Anti-inflammatory drugs make up about half of analgesics, remedying pain by reducing inflammation as opposed to opioids, which affect the central nervous system....
. The affinity of cannabinoids to bind to either receptor is about the same, with only a slight increase observed with the plant-derived compound CBD binding to CB2 receptors more frequently. Cannabinoids likely have a role in the brain’s control of movement
Locomotor system
Locomotor system may mean:* Animal locomotion system* Human musculoskeletal system, also known simply as "the locomotor system"...
and memory
Memory
In psychology, memory is an organism's ability to store, retain, and recall information and experiences. Traditional studies of memory began in the fields of philosophy, including techniques of artificially enhancing memory....
, as well as natural pain modulation. It is clear that cannabinoids can affect pain transmission and, specifically, that cannabinoids interact with the brain's endogenous opioid
Opioid
An opioid is a psychoactive chemical that works by binding to opioid receptors, which are found principally in the central and peripheral nervous system and the gastrointestinal tract...
system and may affect dopamine transmission. This is an important physiological pathway for the medical treatment of pain.
Sustainability in the body
Most cannabinoidsCannabinoids
Cannabinoids are a class of chemical compounds that include the phytocannabinoids , and chemical compounds that mimic the actions of phytocannabinoids or have a similar structure...
are lipophilic
Lipophilic
Lipophilicity, , refers to the ability of a chemical compound to dissolve in fats, oils, lipids, and non-polar solvents such as hexane or toluene. These non-polar solvents are themselves lipophilic — the axiom that like dissolves like generally holds true...
(fat soluble) compounds that easily store in fat, thus yielding a long elimination half-life relative to other recreational drug
Recreational drug use
Recreational drug use is the use of a drug, usually psychoactive, with the intention of creating or enhancing recreational experience. Such use is controversial, however, often being considered to be also drug abuse, and it is often illegal...
s. The THC molecule, and related compounds, are usually detectable in drug tests from 3 days up to 10 days according to Redwood Laboratories, heavy users can produce positive tests for up to 3 months after ceasing cannabis use (see drug test
Drug test
A drug test is a technical analysis of a biological specimen – for example urine, hair, blood, sweat, or oral fluid / saliva – to determine the presence or absence of specified parent drugs or their metabolites...
).
Toxicity
THC has an extremely low toxicityToxicity
Toxicity is the degree to which a substance can damage a living or non-living organisms. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a substructure of the organism, such as a cell or an organ , such as the liver...
and the amount that can enter the body through the consumption of cannabis plants poses no threat of death. In lab animal tests, scientists have had much difficulty administering a dosage of THC that is high enough to be lethal. Accordingly, there is little reason to believe a human would self-administer such doses. Indeed, a 1988 ruling from the United States Department of Justice concluded that "In practical terms, marijuana cannot induce a lethal response as a result of drug-related toxicity."
According to the Merck Index
Merck Index
The Merck Index is an encyclopedia of chemicals, drugs and biologicals with over 10,000 monographs on single substances or groups of related compounds. It also includes an appendix with monographs on organic name reactions. It is published by the United States pharmaceutical company Merck & Co...
, the of THC (the dose which causes the death of 50% of individuals) is 1270 mg/kg for male rats and 730 mg/kg for female rats from oral consumption in sesame oil, and 42 mg/kg for rats from inhalation.
The ratio of cannabis material required to produce a fatal overdose to the amount required to saturate cannabinoid receptors and cause intoxication is approximately 40,000:1. It is extremely difficult to overdose by smoking marijuana; a typical marijuana "joint" contains less than 10 mg of THC, and one would have to smoke thousands of those in a short period of time to approach toxic levels. According to a 2006 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
government report, using cannabis is much less dangerous than tobacco, prescription drugs, and alcohol in social harms, physical harm, and addiction. It was found in 2007 that while tobacco and cannabis smoke are quite similar, cannabis smoke contained higher amounts of ammonia
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
, hydrogen cyanide, and nitrogen oxides, but lower levels of carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons , also known as poly-aromatic hydrocarbons or polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons, are potent atmospheric pollutants that consist of fused aromatic rings and do not contain heteroatoms or carry substituents. Naphthalene is the simplest example of a PAH...
s (PAHs). This study found that directly inhaled cannabis smoke contained as much as 20 times as much ammonia and 5 times as much hydrogen cyanide as tobacco smoke and compared the properties of both mainstream and sidestream (smoke emitted from a smouldering 'joint' or 'cone') smoke. Mainstream cannabis smoke was found to contain higher concentrations of selected polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) than sidestream tobacco smoke. However, other studies have found much lower disparities in ammonia and hydrogen cyanide between cannabis and tobacco, and that some other constituents (such as polonium-210, lead, arsenic, nicotine, and tobacco-specific nitrosamines) are either lower or non-existent in cannabis smoke.
Short-term effects
When smoked, the short-term effects of cannabis manifest within seconds and are fully apparent within a few minutes, typically lasting for 2–3 hours. The duration of noticeable effects has been observed to diminish due to prolonged, repeated use and the development of a tolerance to cannabinoids.Psychoactive effects
The psychoactive effects of cannabis, known as a "high", are subjective and can vary based on the individual and the method of use.Cannabis is often considered an atypical, unique and sometimes paradoxical psychotropic due to its vast and sometimes contradictory array of effects. The subjective experience induced by imbibing in cannabis use can be considered stimulatory
Stimulant
Stimulants are psychoactive drugs which induce temporary improvements in either mental or physical function or both. Examples of these kinds of effects may include enhanced alertness, wakefulness, and locomotion, among others...
and yet also sedative
Sedative
A sedative or tranquilizer is a substance that induces sedation by reducing irritability or excitement....
or depressant
Depressant
A depressant, or central depressant, is a drug or endogenous compound that depresses the function or activity of a specific part of the brain...
, while also having markedly mild psychedelic
Psychedelic
The term psychedelic is derived from the Greek words ψυχή and δηλοῦν , translating to "soul-manifesting". A psychedelic experience is characterized by the striking perception of aspects of one's mind previously unknown, or by the creative exuberance of the mind liberated from its ostensibly...
and even dissociative characteristics.
Some effects may include a general alteration of conscious perception
Altered state of consciousness
An altered state of consciousness , also named altered state of mind, is any condition which is significantly different from a normal waking beta wave state. The expression was used as early as 1966 by Arnold M. Ludwig and brought into common usage from 1969 by Charles Tart: it describes induced...
, euphoria
Euphoria
Euphoria is an emotional and mental state defined as a sense of great elation and well being.Euphoria may also refer to:* Euphoria , a genus of scarab beetles* Euphoria, a genus name previously used for the longan and other trees...
, feelings of well-being, relaxation or stress reduction, increased appreciation of humor, music or the arts, joviality, metacognition
Metacognition
Metacognition is defined as "cognition about cognition", or "knowing about knowing." It can take many forms; it includes knowledge about when and how to use particular strategies for learning or for problem solving...
and introspection
Introspection
Introspection is the self-observation and reporting of conscious inner thoughts, desires and sensations. It is a conscious and purposive process relying on thinking, reasoning, and examining one's own thoughts, feelings, and, in more spiritual cases, one's soul...
, enhanced recollection (episodic memory
Episodic memory
Episodic memory is the memory of autobiographical events that can be explicitly stated. Semantic and episodic memory together make up the category of declarative memory, which is one of the two major divisions in memory...
), increased sensuality, increased awareness of sensation, increased libido
Libido
Libido refers to a person's sex drive or desire for sexual activity. The desire for sex is an aspect of a person's sexuality, but varies enormously from one person to another, and it also varies depending on circumstances at a particular time. A person who has extremely frequent or a suddenly...
, creative, abstract or philosophical thinking, disruption of linear memory and paranoia
Paranoia
Paranoia [] is a thought process believed to be heavily influenced by anxiety or fear, often to the point of irrationality and delusion. Paranoid thinking typically includes persecutory beliefs, or beliefs of conspiracy concerning a perceived threat towards oneself...
or anxiety
Anxiety
Anxiety is a psychological and physiological state characterized by somatic, emotional, cognitive, and behavioral components. The root meaning of the word anxiety is 'to vex or trouble'; in either presence or absence of psychological stress, anxiety can create feelings of fear, worry, uneasiness,...
. Anxiety
Anxiety
Anxiety is a psychological and physiological state characterized by somatic, emotional, cognitive, and behavioral components. The root meaning of the word anxiety is 'to vex or trouble'; in either presence or absence of psychological stress, anxiety can create feelings of fear, worry, uneasiness,...
is the most commonly reported side effect of smoking marijuana. Between 20 and 30 percent of recreational users experience intense anxiety and/or panic attacks after smoking cannabis.
Cannabis also produces many subjective
Subjectivity
Subjectivity refers to the subject and his or her perspective, feelings, beliefs, and desires. In philosophy, the term is usually contrasted with objectivity.-Qualia:...
and highly tangible effects, such as greater enjoyment of food taste and aroma (The Munchies), an enhanced enjoyment of music and comedy, and marked distortions in the perception of time and space (where experiencing a "rush" of ideas from the bank of long-term memory can create the subjective impression of long elapsed time, while a clock reveals that only a short time has passed). At higher doses, effects can include altered body image
Body image
Body image refers to a person's perception of the aesthetics and sexual attractiveness of their own body. The phrase body image was first coined by the Austrian neurologist and psychoanalyst Paul Schilder in his masterpiece The Image and Appearance of the Human Body...
, auditory and/or visual illusions, pseudo-hallucinatory or (rarely, at very high doses) fully hallucinatory experiences, and ataxia
Ataxia
Ataxia is a neurological sign and symptom that consists of gross lack of coordination of muscle movements. Ataxia is a non-specific clinical manifestation implying dysfunction of the parts of the nervous system that coordinate movement, such as the cerebellum...
from selective impairment of polysynaptic reflexes. In some cases, cannabis can lead to dissociative
Dissociation
Dissociation is an altered state of consciousness characterized by partial or complete disruption of the normal integration of a person’s normal conscious or psychological functioning. Dissociation is most commonly experienced as a subjective perception of one's consciousness being detached from...
states such as depersonalization
Depersonalization
Depersonalization is an anomaly of the mechanism by which an individual has self-awareness. It is a feeling of watching oneself act, while having no control over a situation. Sufferers feel they have changed, and the world has become less real, vague, dreamlike, or lacking in significance...
and derealization
Derealization
Derealization is an alteration in the perception or experience of the external world so that it seems unreal. Other symptoms include feeling as though one's environment is lacking in spontaneity, emotional coloring and depth. It is a dissociative symptom of many conditions, such as psychiatric and...
; such effects are most often considered desirable, but have the potential to induce panic attack and paranoia in some unaccustomed users.
Somatic effects
Some of the short-term physical effects of cannabis use include increased heart rateHeart rate
Heart rate is the number of heartbeats per unit of time, typically expressed as beats per minute . Heart rate can vary as the body's need to absorb oxygen and excrete carbon dioxide changes, such as during exercise or sleep....
, dry mouth
Xerostomia
Xerostomia is the medical term for the subjective complaint of dry mouth due to a lack of saliva. Xerostomia is sometimes colloquially called pasties, cottonmouth, drooth, or doughmouth. Several diseases, treatments, and medications can cause xerostomia. It can also be exacerbated by smoking or...
(cotton mouth), reddening of the eyes
Human eye
The human eye is an organ which reacts to light for several purposes. As a conscious sense organ, the eye allows vision. Rod and cone cells in the retina allow conscious light perception and vision including color differentiation and the perception of depth...
(congestion of the conjunctiva
Conjunctiva
The conjunctiva covers the sclera and lines the inside of the eyelids. It is composed of rare stratified columnar epithelium.-Function:...
l blood vessel
Blood vessel
The blood vessels are the part of the circulatory system that transports blood throughout the body. There are three major types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the capillaries, which enable the actual exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and...
s), a reduction in intra-ocular pressure, muscle relaxation and a sensation of cold or hot hands and feet.
Electroencephalography
Electroencephalography
Electroencephalography is the recording of electrical activity along the scalp. EEG measures voltage fluctuations resulting from ionic current flows within the neurons of the brain...
or EEG shows somewhat more persistent alpha wave
Alpha wave
Alpha waves are neural oscillations in the frequency range of 8–12 Hz arising from synchronous and coherent electrical activity of thalamic pacemaker cells in humans...
s of slightly lower frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
than usual. Cannabinoids produce a "marked depression of motor activity" via activation of neuronal cannabinoid receptors belonging to the CB1
Cannabinoid receptor type 1
The cannabinoid receptor type 1, often abbreviated to CB1, is a G protein-coupled cannabinoid receptor located in the brain. It is activated by endocannabinoid neurotransmitters including anandamide and by the compound THC, found in the psychoactive drug cannabis.-Expression:The CB1 receptor is...
subtype.
Duration
Effects of cannabis generally range from 30 minutes to 8 hours, depending on the potency of the dose, and method of ingestion.Smoked
The total short-term duration of cannabis use when smoked is based on the potency and how much is smoked. Effects can typically last two to three hours.A study of ten healthy, robust, male volunteers who resided in a residential research facility sought to examine both acute and residual subjective, physiologic, and performance effects of smoking marijuana cigarettes. On three separate days, subjects smoked one NIDA
National Institute on Drug Abuse
The National Institute on Drug Abuse is a United States federal-government research institute whose mission is to "lead the Nation in bringing the power of science to bear on drug abuse and addiction."-History:...
marijuana cigarette containing either 0%, 1.8%, or 3.6% THC, documenting subjective, physiologic, and performance measures prior to smoking, five times following smoking on that day, and three times on the following morning. Subjects reported robust subjective effects following both active doses of marijuana, which returned to baseline levels within 3.5 hours. Heart rate increased and the pupillary light reflex decreased following active dose administration with return to baseline on that day. Additionally, marijuana smoking acutely produced decrements in smooth pursuit eye tracking. Although robust acute effects of marijuana were found on subjective and physiological measures, no effects were evident the day following administration, indicating that the residual effects of smoking a single marijuana cigarette are minimal.
A Dutch double blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, cross-over study examining male volunteers aged 18–45 years with a self-reported history of regular cannabis use concluded that smoking of cannabis with very high THC levels (marijuana with 9–23% THC), as currently sold in coffee shops in the Netherlands, may lead to higher THC blood-serum concentrations. This is reflected by an increase of the occurrence of impaired psychomotor skills, particularly among younger or inexperienced cannabis smokers, who do not always adapt their smoking-style to the higher THC content. High THC concentrations in cannabis were associated with a dose-related increase of physical effects (such as increase of heart rate, and decrease of blood pressure) and psychomotor effects (such as reacting more slowly, being less concentrated, making more mistakes during performance testing, having less motor control, and experiencing drowsiness). It was also observed during the study that the effects from a single joint
Joint (cannabis)
Joint is a slang term for a cigarette rolled using cannabis. Rolling papers are the most common rolling medium among industrialized countries, however brown paper, cigarettes with the tobacco removed, and newspaper are commonly used in developing countries. Modern papers are now made from a wide...
lasted for more than eight hours. Reaction times remained impaired five hours after smoking, when the THC serum concentrations were significantly reduced, but still present. However, it is important to note that the subjects (without knowing the potency) were told to finish their (unshared) joints rather than titrate their doses, leading in many cases to significantly higher doses than they would normally take. Also, when subjects smoke on several occasions per day, accumulation of THC in blood-serum may occur.
Oral
When taken orally, the psychoactive effects take longer to manifest and generally last longer, typically lasting for 4–10 hours after consumption. Very high doses may last even longer. Also, oral use eliminates the need to inhale toxic combustion products created by smoking, which eliminates much of the respiratory and cardiovascular harm associated with cannabis smoking.Neurological effects
The areas of the brain where cannabinoid receptors are most prevalently located are consistent with the behavioralHuman behavior
Human behavior refers to the range of behaviors exhibited by humans and which are influenced by culture, attitudes, emotions, values, ethics, authority, rapport, hypnosis, persuasion, coercion and/or genetics....
effects produced by cannabinoids. Brain regions in which cannabinoid receptors are very abundant are the basal ganglia
Basal ganglia
The basal ganglia are a group of nuclei of varied origin in the brains of vertebrates that act as a cohesive functional unit. They are situated at the base of the forebrain and are strongly connected with the cerebral cortex, thalamus and other brain areas...
, associated with movement control; the cerebellum
Cerebellum
The cerebellum is a region of the brain that plays an important role in motor control. It may also be involved in some cognitive functions such as attention and language, and in regulating fear and pleasure responses, but its movement-related functions are the most solidly established...
, associated with body movement coordination; the hippocampus
Hippocampus
The hippocampus is a major component of the brains of humans and other vertebrates. It belongs to the limbic system and plays important roles in the consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory and spatial navigation. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in...
, associated with learning
Learning
Learning is acquiring new or modifying existing knowledge, behaviors, skills, values, or preferences and may involve synthesizing different types of information. The ability to learn is possessed by humans, animals and some machines. Progress over time tends to follow learning curves.Human learning...
, memory, and stress
Stress (medicine)
Stress is a term in psychology and biology, borrowed from physics and engineering and first used in the biological context in the 1930s, which has in more recent decades become commonly used in popular parlance...
control; the cerebral cortex
Cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex is a sheet of neural tissue that is outermost to the cerebrum of the mammalian brain. It plays a key role in memory, attention, perceptual awareness, thought, language, and consciousness. It is constituted of up to six horizontal layers, each of which has a different...
, associated with higher cognitive functions; and the nucleus accumbens
Nucleus accumbens
The nucleus accumbens , also known as the accumbens nucleus or as the nucleus accumbens septi , is a collection of neurons and forms the main part of the ventral striatum...
, regarded as the reward center of the brain. Other regions where cannabinoid receptors are moderately concentrated are the hypothalamus
Hypothalamus
The Hypothalamus is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions...
, which regulates homeostatic functions; the amygdala
Amygdala
The ' are almond-shaped groups of nuclei located deep within the medial temporal lobes of the brain in complex vertebrates, including humans. Shown in research to perform a primary role in the processing and memory of emotional reactions, the amygdalae are considered part of the limbic system.-...
, associated with emotional responses and fear
Fear
Fear is a distressing negative sensation induced by a perceived threat. It is a basic survival mechanism occurring in response to a specific stimulus, such as pain or the threat of danger...
s; the spinal cord
Spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissue and support cells that extends from the brain . The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system...
, associated with peripheral sensations like pain; the brain stem
Brain stem
In vertebrate anatomy the brainstem is the posterior part of the brain, adjoining and structurally continuous with the spinal cord. The brain stem provides the main motor and sensory innervation to the face and neck via the cranial nerves...
, associated with sleep
Sleep
Sleep is a naturally recurring state characterized by reduced or absent consciousness, relatively suspended sensory activity, and inactivity of nearly all voluntary muscles. It is distinguished from quiet wakefulness by a decreased ability to react to stimuli, and is more easily reversible than...
, arousal
Arousal
Arousal is a physiological and psychological state of being awake or reactive to stimuli. It involves the activation of the reticular activating system in the brain stem, the autonomic nervous system and the endocrine system, leading to increased heart rate and blood pressure and a condition of...
, and motor control; and the nucleus of the solitary tract
Solitary nucleus
The solitary tract and nucleus are structures in the brainstem that carry and receive visceral sensation and taste from the facial , glossopharyngeal and vagus cranial nerves.-Anatomy:...
, associated with visceral sensations like nausea
Nausea
Nausea , is a sensation of unease and discomfort in the upper stomach with an involuntary urge to vomit. It often, but not always, precedes vomiting...
and vomiting
Vomiting
Vomiting is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose...
.
Most notably, the two areas of motor control and memory are where the effects of cannabis are directly and irrefutably evident. Cannabinoids, depending on the dose, inhibit the transmission of neural signals through the basal ganglia and cerebellum. At lower doses, cannabinoids seem to stimulate locomotion while greater doses inhibit it, most commonly manifested by lack of steadiness (body sway and hand steadiness) in motor tasks that require a lot of attention. Other brain regions, like the cortex, the cerebellum, and the neural pathway from cortex to striatum
Striatum
The striatum, also known as the neostriatum or striate nucleus, is a subcortical part of the forebrain. It is the major input station of the basal ganglia system. The striatum, in turn, gets input from the cerebral cortex...
, are also involved in the control of movement and contain abundant cannabinoid receptors, indicating their possible involvement as well.
Experiments on animal and human tissue have demonstrated a disruption of short-term memory
Short-term memory
Short-term memory is the capacity for holding a small amount of information in mind in an active, readily available state for a short period of time. The duration of short-term memory is believed to be in the order of seconds. A commonly cited capacity is 7 ± 2 elements...
formation, which is consistent with the abundance of CB1 receptors on the hippocampus, the region of the brain most closely associated with memory. Cannabinoids inhibit the release of several neurotransmitters in the hippocampus, like acetylcholine
Acetylcholine
The chemical compound acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter in both the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system in many organisms including humans...
, norepinephrine
Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine is the US name for noradrenaline , a catecholamine with multiple roles including as a hormone and a neurotransmitter...
, and glutamate, resulting in a major decrease in neuronal activity in that region. This decrease in activity resembles a "temporary hippocampal lesion." In the end, this procedure could lead to the blocking of cellular processes that are associated with memory formation.
In in-vitro experiments THC at extremely high concentrations, which could not be reached with commonly consumed doses, caused competitive inhibition
Competitive inhibition
Competitive inhibition is a form of enzyme inhibition where binding of the inhibitor to the active site on the enzyme prevents binding of the substrate and vice versa.-Mechanism:...
of the AChE
Ache
Ache may refer to:* Ache, a chronic, painful sensation* Ache , a You've Got Foetus on Your Breath album* "Ache" , a song by No Doubt* Ache Records, a Vancouver-based record label* The American College of Healthcare Executives...
enzyme and inhibition of β-amyloid
Amyloid beta
Amyloid beta is a peptide of 36–43 amino acids that is processed from the Amyloid precursor protein. While it is most commonly known in association with Alzheimer's disease, it does not exist specifically to cause disease...
peptide aggregation, the cause of Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease also known in medical literature as Alzheimer disease is the most common form of dementia. There is no cure for the disease, which worsens as it progresses, and eventually leads to death...
. Compared to currently approved drugs prescribed for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, THC is a considerably superior inhibitor of A aggregation, and this study provides a previously unrecognized molecular mechanism through which cannabinoid molecules may directly impact the progression of this debilitating disease.
Effects on driving
A 2001 study by the United Kingdom Transit Research Laboratory (TRL) specifically focuses on the effects of cannabis use on driving, and is one of the most recent and commonly quoted studies on the subject. The report summarizes current knowledge about the effects of cannabis on driving and accident risk based on a review of available literature published since 1994 and the effects of cannabis on laboratory based tasks.The study identified young males, amongst whom cannabis consumption is frequent and increasing, and in whom alcohol consumption is also common, as a risk group for traffic accidents. This is due to driving inexperience and factors associated with youth relating to risk
Risk
Risk is the potential that a chosen action or activity will lead to a loss . The notion implies that a choice having an influence on the outcome exists . Potential losses themselves may also be called "risks"...
taking, delinquency
Juvenile delinquency
Juvenile delinquency is participation in illegal behavior by minors who fall under a statutory age limit. Most legal systems prescribe specific procedures for dealing with juveniles, such as juvenile detention centers. There are a multitude of different theories on the causes of crime, most if not...
and motivation
Motivation
Motivation is the driving force by which humans achieve their goals. Motivation is said to be intrinsic or extrinsic. The term is generally used for humans but it can also be used to describe the causes for animal behavior as well. This article refers to human motivation...
. These demographic and psychosocial variables may relate to both drug use and accident risk, thereby presenting an artificial relationship between use of drugs and accident involvement.
The effects of cannabis on laboratory-based tasks show clear impairment with respect to tracking ability, attention
Attention
Attention is the cognitive process of paying attention to one aspect of the environment while ignoring others. Attention is one of the most intensely studied topics within psychology and cognitive neuroscience....
, and other tasks depending on the dose administered. Both simulation and road trials generally find that driving behavior shortly after consumption of larger doses of cannabis results in:
- increased variability in lane position (such as taking a curve too tightly or too loosely).
- longer decision times, leading to slower responses to driving situations
Kelly, Darke and Ross show similar results, with laboratory studies examining the effects of cannabis on skills utilised while driving showing impairments in tracking, attention, reaction time, short-term memory, hand-eye coordination, vigilance, time and distance perception, and decision making and concentration. An EMCDDA review concluded that "the acute effect of moderate or higher doses of cannabis impairs the skills related to safe driving and injury risk", specifically "attention, tracking and psychomotor skills".
In their review of driving simulator studies, Kelly et al. conclude that there is evidence of dose-dependent impairments in cannabis-affected drivers' ability to control a vehicle in the areas of steering, headway control, speed variability, car following, reaction time and lane positioning. The researchers note that "even in those who learn to compensate for a drug's impairing effects, substantial impairment in performance can still be observed under conditions of general task performance (i.e. when no contingencies are present to maintain compensated performance)."
Vascular effects
Cannabis arteritis is a very rare peripheral vascular disease similar to Buerger's diseaseBuerger's disease
Thromboangiitis obliterans is a recurring progressive inflammation and thrombosis of small and medium arteries and veins of the hands and feet...
. There were about 50 confirmed cases from 1960 to 2008, all of which occurred in Europe. However, all of the cases also involved tobacco (a known cause of Buerger's disease) in one way or another, and nearly all of the cannabis use was quite heavy. In Europe, cannabis is typically mixed with tobacco, in contrast to North America.
A 2008 study by the National Institutes of Health
National Institutes of Health
The National Institutes of Health are an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services and are the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and health-related research. Its science and engineering counterpart is the National Science Foundation...
Biomedical Research Centre in Baltimore found that heavy, chronic smoking of marijuana (138 joints per week) changed blood proteins
Blood proteins
Blood proteins, also termed serum proteins or plasma proteins, are proteins found in blood plasma. Serum total protein in blood is 7g/dl...
associated with heart disease
Heart disease
Heart disease, cardiac disease or cardiopathy is an umbrella term for a variety of diseases affecting the heart. , it is the leading cause of death in the United States, England, Canada and Wales, accounting for 25.4% of the total deaths in the United States.-Types:-Coronary heart disease:Coronary...
and stroke
Stroke
A stroke, previously known medically as a cerebrovascular accident , is the rapidly developing loss of brain function due to disturbance in the blood supply to the brain. This can be due to ischemia caused by blockage , or a hemorrhage...
. This is a result of raised carboxyhemoglobin levels from carbon monoxide. A similar increase in heart disease and ischemic strokes is observed in tobacco smokers, which suggests that the harmful effects come from combustion products, not marijuana.
A 2005 article in the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry reported on a 36-year-old man who suffered a stroke on three separate occasions after smoking a large amount of marijuana, despite having no known risk factors for the disorder, suggesting that a rare side effect of marijuana use may be an increase in the incidence of strokes among young smokers. A 2000 study by researchers at Boston's Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston, Massachusetts is a major flagship teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School. It was formed out of the 1996 merger of Beth Israel Hospital and New England Deaconess Hospital...
, Massachusetts General Hospital
Massachusetts General Hospital
Massachusetts General Hospital is a teaching hospital and biomedical research facility in the West End neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts...
and Harvard School of Public Health
Harvard School of Public Health
The Harvard School of Public Health is one of the professional graduate schools of Harvard University, located in the Longwood Area of the Boston, Massachusetts neighborhood of Mission Hill, which is next to Harvard Medical School. HSPH is considered a significant school focusing on health in the...
also found that a middle-age person's risk of heart attack rises nearly fivefold in the first hour after smoking marijuana, about the same elevated risk as vigorous exercise or sexual intercourse.
Adulterated cannabis
Contaminants may be found in hashishHashish
Hashish is a cannabis preparation composed of compressed stalked resin glands, called trichomes, collected from the unfertilized buds of the cannabis plant. It contains the same active ingredients but in higher concentrations than unsifted buds or leaves...
obtained from "soap bar"-type sources. The dried flowers of the plant may be contaminated by the plant taking up heavy metals and other toxins from its growing environment, or by the addition of lead or glass beads, used to increase the weight or to make the cannabis appear as if it has more crystal-looking trichomes indicating a higher THC content. Users who burn hot or mix cannabis with tobacco are at risk of failing to detect deviations from appropriate cannabis taste.
Despite cannabis being generally perceived as a natural or "chemical-free"
Chemical free
Chemical free or chemical-free is a term used in marketing to imply that a product is safe, healthy or environmentally friendly because it only contains natural ingredients. The term is a misnomer, as nothing that physically exists is free of chemicals...
product, in a recent Australian survey one in four Australians consider cannabis grown indoors under hydroponic conditions to be a greater health risk due to increased contamination, added to the plant during cultivation to enhance the plant growth and quality.
Combination with other drugs
The most obvious confounding factor in cannabis research is the prevalent usage of other recreational drugs, especially alcoholAlcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
and nicotine. Such complications demonstrate the need for studies on cannabis that have stronger controls, and investigations into alleged symptoms of cannabis use that may also be caused by tobacco. Some critics question whether agencies doing the research make an honest effort to present an accurate, unbiased summary of the evidence, or whether they "cherry-pick
Confirmation bias
Confirmation bias is a tendency for people to favor information that confirms their preconceptions or hypotheses regardless of whether the information is true.David Perkins, a geneticist, coined the term "myside bias" referring to a preference for "my" side of an issue...
" their data to please funding sources which may include the tobacco industry or governments dependent on cigarette tax revenue; others caution that the raw data, and not the final conclusions, are what should be examined.
Cannabis also has been shown to have a synergistic cytotoxic effect on lung cancer cell cultures in vitro with the food additive butylated hydroxyanisole
Butylated hydroxyanisole
Butylated hydroxyanisole is an antioxidant consisting of a mixture of two isomeric organic compounds, 2-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyanisole and 3-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyanisole. It is prepared from 4-methoxyphenol and isobutylene. It is a waxy solid used as a food additive with the E number E320...
(BHA) and possibly the related compound butylated hydroxytoluene
Butylated hydroxytoluene
Butylated hydroxytoluene , also known as butylhydroxytoluene, is a lipophilic organic compound that is primarily used as an antioxidant food additive as well as an antioxidant additive in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, jet fuels, rubber, petroleum products, electrical transformer oil, and embalming...
(BHT). The study concluded, "Exposure to marijuana smoke in conjunction with BHA, a common food additive, may promote deleterious health effects in the lung." BHA & BHT are human-made fat preservatives, and are found in many packaged foods including: plastics in boxed cereal, Jello, Slim Jims, and more.
The Australian National Household Survey of 2001 showed that cannabis use in Australia is rarely used without other drugs. 95% of cannabis users also drank alcohol; 26% took amphetamines; 19% took ecstasy and only 2.7% reported not having used any other drug with cannabis. While research has been undertaken on the combined effects of alcohol and cannabis on performing certain tasks, little research has been conducted on the reasons why this combination is so popular. Evidence from a controlled experimental study undertaken by Lukas and Orozco suggests that alcohol causes THC to be absorbed more rapidly into the blood plasma of the user. Data from the Australian National Survey of Mental Health and Wellbeing found that three-quarters of recent cannabis users reported using alcohol when cannabis was not available.
Memory and learning
Studies on cannabis and memory are hindered by small sample sizes, confounding drug use, and other factors. The strongest evidence regarding cannabis and memory focuses on its short-term negative effects on short-term and working memory.A 2008 review of the evidence surrounding the acute impact on memory concluded that cannabinoids impair all aspects of short-term memory, especially short-term episodic and working memory. One small study found that no learning occurred during the 2 hour period in which the subjects (infrequent users) were "stoned".
Appetite
The feeling of increased appetite following the use of cannabisCannabis
Cannabis is a genus of flowering plants that includes three putative species, Cannabis sativa, Cannabis indica, and Cannabis ruderalis. These three taxa are indigenous to Central Asia, and South Asia. Cannabis has long been used for fibre , for seed and seed oils, for medicinal purposes, and as a...
has been documented for hundreds of years, and is commonly known as "the munchies" in popular culture. Clinical studies and survey data have found that cannabis increases food enjoyment and interest in food. Scientists have claimed to be able to explain what causes the increase in appetite, concluding that "endocannabinoids in the hypothalamus activate cannabinoid receptors that are responsible for maintaining food intake".
Endogenous cannabinoids have recently been discovered in foods such as chocolate and bovine milk.
It is widely accepted that the neonatal survival of many species "is largely dependent upon their suckling behavior, or appetite for breast milk" and recent research has identified the endogenous cannabinoid system to be the first neural system to display complete control over milk ingestion and neonatal survival. It is possible that "cannabinoid receptors in our body interact with the cannabinoids in milk to stimulate a suckling response in newborns so as to prevent growth failure".
Long-term effects
Though the long-term effects of cannabis have been studied, there remains much to be concluded; debated topics include the drug's addictiveness, its potential as a "gateway drug", its effects on intelligence and memory, and its contributions to mental disorders such as schizophrenia and depression. On some such topics, such as the drug's effects on the lungs, relatively little research has been conducted, leading to division as to the severity of its impact.Higher rates of testicular cancer in western nations have been linked to use of cannabis. A study conducted by the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center
Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center
The Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, is one of the world’s leading cancer research institutes...
and funded by the National Institutes of Health
National Institutes of Health
The National Institutes of Health are an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services and are the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and health-related research. Its science and engineering counterpart is the National Science Foundation...
, published in the journal Cancer
Cancer (journal)
Cancer is a peer-reviewed academic journal published by John Wiley & Sons for the American Cancer Society as their official journal. The journal started publication in 1948. Since 1997 one volume per year has the section title Cancer Cytopathology, with volume numbers integrated into those of...
March 15, 2009, linked long term use of cannabis to an increased risk of 70 percent for testicular cancer
Testicular cancer
Testicular cancer is cancer that develops in the testicles, a part of the male reproductive system.In the United States, between 7,500 and 8,000 diagnoses of testicular cancer are made each year. In the UK, approximately 2,000 men are diagnosed each year. Over his lifetime, a man's risk of...
with the scientists concluding that cannabis is harmful to the human endocrine and reproductive system.
More research is no guarantee of greater consensus in the field of cannabis studies, however; both advocates and opponents of the drug are able to call upon multiple scientific studies supporting their respective positions. Cannabis has been correlated with the development of various mental disorders in multiple studies, for example a recent 10 year study on 1923 individuals from the general population in Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
, aged 14–24, concluded that cannabis use is a risk factor for the development of incident psychotic symptoms. Continued cannabis use might increase the risk for psychotic disorder.
Other studies differ widely as to whether cannabis use is the cause of the mental problems, whether the mental problems encourage cannabis use, or whether both the cannabis use and the mental problems are the effects of some other cause. Still other studies even encourage the use of cannabis in treating schizophrenia. Similarly, efforts to prove the "gateway drug" hypothesis that cannabis and alcohol makes users more inclined to become addicted to "harder" drugs like cocaine and heroin have produced mixed results, with different studies finding varying degrees of correlation between the use of cannabis and other drugs, and some finding none. Some, however, believe the "gateway effect," currently being pinned on the use of marijuana, should not be attributed to the drug itself but rather the illegality of the drug in most countries. Supporters of this theory believe that the grouping of marijuana and harder drugs in law is, in fact, the cause of users of marijuana to move on to those harder drugs.
Pathogens and microtoxins
Most microorganismMicroorganism
A microorganism or microbe is a microscopic organism that comprises either a single cell , cell clusters, or no cell at all...
s found in cannabis only affect plants and not humans, but some microorganisms, especially those that proliferate when the herb is not correctly dried and stored, can be harmful to humans. Some users may store marijuana in an airtight bag or jar in a refrigerator
Refrigerator
A refrigerator is a common household appliance that consists of a thermally insulated compartment and a heat pump that transfers heat from the inside of the fridge to its external environment so that the inside of the fridge is cooled to a temperature below the ambient temperature of the room...
to prevent fungi and bacterial growth.
Fungi

Aspergillus flavus
Aspergillus flavus is a fungus. It is a common mold in the environment, and can cause storage problems in stored grains. It can also be a human pathogen, associated with aspergillosis of the lungs and sometimes causing corneal, otomycotic, and nasoorbital infections. Many strains produce...
, Aspergillus fumigatus
Aspergillus fumigatus
Aspergillus fumigatus is a fungus of the genus Aspergillus, and is one of the most common Aspergillus species to cause disease in individuals with an immunodeficiency....
, Aspergillus niger
Aspergillus niger
Aspergillus niger is a fungus and one of the most common species of the genus Aspergillus. It causes a disease called black mold on certain fruits and vegetables such as grapes, onions, and peanuts, and is a common contaminant of food...
, Aspergillus parasiticus
Aspergillus parasiticus
Aspergillus parasiticus is a mold known to produce aflatoxin, although strains of it that do not produce this carcinogen exist. It is sometimes found on black olives....
, Aspergillus tamarii, Aspergillus sulphureus, Aspergillus repens, Mucor hiemalis
Mucor hiemalis
Mucor hiemalis is a fungal plant pathogen.Morphology and cell structure: M. hiemalis grows in expanding gray colonies. It grows branched sporangiophores that yielding yellow to dark brown sporangia which can mate to form black-brown, spiny zygospores.Physiology: M. hiemalis is nitrate positive and...
(not a human pathogen), Penicillium chrysogenum
Penicillium chrysogenum
Penicillium chrysogenum is common in temperate and subtropical regions and can be found on salted food products, but it is mostly found in indoor environments, especially in damp or waterdamaged buildings. It was previously known as Penicillium notatum. It has rarely been reported as a cause of...
, Penicillium italicum
Penicillium italicum
Penicillium italicum is a plant pathogen.- External links :* *...
and Rhizopus nigrans have been found in moldy cannabis. Aspergillus
Aspergillus
Aspergillus is a genus consisting of several hundred mold species found in various climates worldwide. Aspergillus was first catalogued in 1729 by the Italian priest and biologist Pier Antonio Micheli...
mold species can infect the lungs via smoking or handling of infected cannabis and cause opportunistic and sometimes deadly aspergillosis
Aspergillosis
Aspergillosis is the name given to a wide variety of diseases caused by fungi of the genus Aspergillus. The most common forms are allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, pulmonary aspergilloma and invasive aspergillosis. Most humans inhale Aspergillus spores every day...
. Some of the microorganisms found create aflatoxin
Aflatoxin
Aflatoxins are naturally occurring mycotoxins that are produced by many species of Aspergillus, a fungus, the most notable ones being Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus. Aflatoxins are toxic and among the most carcinogenic substances known...
s, which are toxic and carcinogenic. Researchers suggest that moldy cannabis thus be discarded.
Mold is also found in smoke from mold infected cannabis, and the lungs and nasal passages are a major means of contracting fungal infections. Levitz and Diamond (1991) suggested baking marijuana in home ovens at 150 °C [302 °F], for five minutes before smoking. Oven treatment killed conidia of A. fumigatus, A. flavus and A. niger, and did not degrade the active component of marijuana, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)."
Bacteria
Cannabis contaminated with Salmonella muenchen was positively correlatedCorrelation
In statistics, dependence refers to any statistical relationship between two random variables or two sets of data. Correlation refers to any of a broad class of statistical relationships involving dependence....
with dozens of cases of salmonellosis
Salmonellosis
Salmonellosis is an infection with Salmonella bacteria. Most people infected with Salmonella develop diarrhea, fever, vomiting, and abdominal cramps 12 to 72 hours after infection. In most cases, the illness lasts four to seven days, and most people recover without treatment...
in 1981. "Thermophilic actinomycetes" were also found in cannabis.
Constraints on open research

Legal issues of cannabis
The legality of cannabis has been the subject of debate and controversy for decades. Cannabis is illegal to consume, use, possess, cultivate, transfer or trade in most countries...
. Thus, cannabis as a drug is often hard to fit into the structural confines of medical research because appropriate, research-grade samples are difficult to obtain for research purposes, unless granted under authority of national governments.
United States
This issue was highlighted in the United StatesUnited States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
by the clash between Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies
Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies
The Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies is a membership-based 501 non-profit research and educational organization working to develop psychedelics and marijuana into legal prescription drugs...
(MAPS), an independent research group, and the National Institute on Drug Abuse
National Institute on Drug Abuse
The National Institute on Drug Abuse is a United States federal-government research institute whose mission is to "lead the Nation in bringing the power of science to bear on drug abuse and addiction."-History:...
(NIDA), a federal agency
Federal government of the United States
The federal government of the United States is the national government of the constitutional republic of fifty states that is the United States of America. The federal government comprises three distinct branches of government: a legislative, an executive and a judiciary. These branches and...
charged with the application of science to the study of drug abuse. The NIDA largely operates under the general control of the Office of National Drug Control Policy
Office of National Drug Control Policy
The White House Office of National Drug Control Policy , a former cabinet level component of the Executive Office of the President of the United States, was established in 1989 by the Anti-Drug Abuse Act of 1988...
(ONDCP), a White House office
Executive Office of the President of the United States
The Executive Office of the President consists of the immediate staff of the President of the United States, as well as multiple levels of support staff reporting to the President. The EOP is headed by the White House Chief of Staff, currently William M. Daley...
responsible for the direct coordination of all legal, legislative, scientific, social and political aspects of federal drug control policy.
The cannabis that is available for research studies in the United States is grown at the University of Mississippi
University of Mississippi
The University of Mississippi, also known as Ole Miss, is a public, coeducational research university located in Oxford, Mississippi. Founded in 1844, the school is composed of the main campus in Oxford, four branch campuses located in Booneville, Grenada, Tupelo, and Southaven as well as the...
and solely controlled by the NIDA, which has veto power over the Food and Drug Administration
Food and Drug Administration
The Food and Drug Administration is an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, one of the United States federal executive departments...
(FDA) to define accepted protocols. Since 1942, when cannabis was removed from the U.S. Pharmacopoeia and its medical use was prohibited, there have been no legal (under federal law) privately funded cannabis production projects. This has resulted in a limited amount of research being done and possibly in NIDA producing cannabis which has been alleged to be of very low potency and inferior quality.
MAPS, in conjunction with Professor Lyle Craker
Lyle Craker
Lyle E. Craker is a Professor in the Department of Plant, Soil and Insect Sciences at the University of Massachusetts. Since 2005, Craker has been trying to obtain a permit from the United States Drug Enforcement Administration to grow marijuana for research purposes.-Education:In 1963, Craker...
, PhD, the director of the Medicinal Plant Program at the University of Massachusetts Amherst
University of Massachusetts Amherst
The University of Massachusetts Amherst is a public research and land-grant university in Amherst, Massachusetts, United States and the flagship of the University of Massachusetts system...
, sought to provide independently grown cannabis of more appropriate research quality for FDA-approved research studies, and encountered opposition by NIDA, the ONDCP, and the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration
Drug Enforcement Administration
The Drug Enforcement Administration is a federal law enforcement agency under the United States Department of Justice, tasked with combating drug smuggling and use within the United States...
(DEA).
United Kingdom
In countries such as the United Kingdom a license for growing cannabis is required if it is to be used for botanical or scientific reasons. It is referred to as a "controlled drug". In such countries a greater depth and variety of scientific research has been performed. Recently several habitual smokers were invited to partake in various tests by British medical companies in order for the UK government to ascertain the influence of cannabis on operating a motor vehicle, with the conclusion that marijuana strongly impairs the ability to drive a motor vehicle. A different UK study confirmed that while motor reflexes can be impaired by cannabis, the resulting impairment is far less of a threat than the motor impairment brought on through alcohol intake. The Transport Research Library of Berkshire concluded that in most cases, cannabis intake made subjects drive slower on the road.See also
- Contact highContact highContact high is a phenomenon that sometimes occurs in otherwise sober people and animals who come into contact with someone who is under the influence of drugs...
- Harm reductionHarm reductionHarm reduction refers to a range of public health policies designed to reduce the harmful consequences associated with recreational drug use and other high risk activities...
- Medical cannabisMedical cannabisMedical cannabis refers to the use of parts of the herb cannabis as a physician-recommended form of medicine or herbal therapy, or to synthetic forms of specific cannabinoids such as THC as a physician-recommended form of medicine...
- National Cannabis Prevention and Information CentreNational Cannabis Prevention and Information CentreThe National Cannabis Prevention and Information Centre or NCPIC, is an Australian centre funded by the Commonwealth Department of Health and Ageing....
- Psychoactive drugPsychoactive drugA psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, or psychotropic is a chemical substance that crosses the blood–brain barrier and acts primarily upon the central nervous system where it affects brain function, resulting in changes in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition, and behavior...
- Responsible drug useResponsible drug useResponsible drug use is a harm reduction strategy based on a belief that illegal recreational drug use can be responsible in terms of reduced or eliminated risk of negative impact on the lives of both the user and others....
External links
- Cannabis Use and Psychosis from National Drug and Alcohol Research Centre, Australia
- The key research on cannabis use and mental illness at BBC News
- Provision of Marijuana and Other Compounds For Scientific Research recommendations of The National Institute on Drug Abuse National Advisory Council
- Scientific American Magazine (December 2004 Issue) The Brain's Own Marijuana
- Ramström, J. (2003), Adverse Health Consequences of Cannabis Use, A Survey of Scientific Studies Published up to and including the Autumn of 2003, National institute of public health, Sweden, Stockholm.
- Hall, W., Solowij, N., Lemon, J., The Health and Psychological Consequences of Cannabis Use. Canberra: Australian Government Publishing Service; 1994.
- World Health Organisation, PROGRAMME ON SUBSTANCE ABUSE, Cannabis: a health perspective and research agenda;1997.
- Cannabis and mental health factsheet
- Bibliography of scholarly histories on cannabis and hashish. (Updated to include article abstracts.)
- Marijuana and Immunity
- The National Cannabis Prevention and Information Centre (Australia)
- EU Research paper on the potency of Cannabis (2004)(.pdf)
- Driving under the influence of cannabis: a brief review of the literature
- Cannabis Contamination Research Brief
- Cannabinoids and appetite
- NCPIC e-zine December 2007/ January 2008 Commentary on cannabis toxicity research and Moir report
- Cannabis use and reproduction
- Evidence-based answers to cannabis questions
- NCPIC Cannabis and alcohol factsheet
- Fast Facts on Mental Health + Cannabis National Cannabis Prevention and Information Centre (Australia)
- Cannabis and Mental Health information leaflet from mental health charity The Royal College of Psychiatrists

