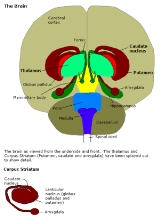
Amygdala
Overview
The are almond-shaped groups of nuclei
located deep within the medial temporal lobes of the brain
in complex vertebrates, including humans. Shown in research to perform a primary role in the processing and memory
of emotional reactions, the amygdalae are considered part of the limbic system
.
The regions described as amygdala nuclei
encompass several structures with distinct functional traits. Among these nuclei are the basolateral complex, the cortical nucleus, the medial nucleus, and the central nucleus.
Nucleus (neuroanatomy)
In neuroanatomy, a nucleus is a brain structure consisting of a relatively compact cluster of neurons. It is one of the two most common forms of nerve cell organization, the other being layered structures such as the cerebral cortex or cerebellar cortex. In anatomical sections, a nucleus shows up...
located deep within the medial temporal lobes of the brain
Brain
The brain is the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few primitive invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, sea squirts and starfishes do not have one. It is located in the head, usually close to primary sensory apparatus such as vision, hearing,...
in complex vertebrates, including humans. Shown in research to perform a primary role in the processing and memory
Memory
In psychology, memory is an organism's ability to store, retain, and recall information and experiences. Traditional studies of memory began in the fields of philosophy, including techniques of artificially enhancing memory....
of emotional reactions, the amygdalae are considered part of the limbic system
Limbic system
The limbic system is a set of brain structures including the hippocampus, amygdala, anterior thalamic nuclei, septum, limbic cortex and fornix, which seemingly support a variety of functions including emotion, behavior, long term memory, and olfaction. The term "limbic" comes from the Latin...
.
The regions described as amygdala nuclei
Nucleus (neuroanatomy)
In neuroanatomy, a nucleus is a brain structure consisting of a relatively compact cluster of neurons. It is one of the two most common forms of nerve cell organization, the other being layered structures such as the cerebral cortex or cerebellar cortex. In anatomical sections, a nucleus shows up...
encompass several structures with distinct functional traits. Among these nuclei are the basolateral complex, the cortical nucleus, the medial nucleus, and the central nucleus.
Unanswered Questions

