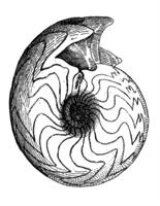
Goniatite
Encyclopedia
Goniatites are extinct ammonoids, shelled cephalopods related to squid
, octopus
, and belemnites, that form the order Goniatitida. The Gonatitida originated from within the more primitive anarcestine ammonoids in the Middle Devonian
some 390 million years ago. Surviving the Late Devonian extinction
, goniatitids flourished during the Carboniferous
and Permian
only to become extinct at the end of the Permian some 251.4 million years ago. They were survived by their cousins the ceratite ammonoids, indirect descendants of the Anarcestida.
, making the animal buoyant
in the water. The general structure of the goniatites would have been similar to that of their relatives the ammonites, being a free swimming animal possessing a head with two well developed eyes and arms (or tentacle
s).
 Goniatite shells are small to medium in size, almost always less than 15 centimeters (6 inches) in diameter and often smaller than 5 centimeters (2 inches) in diameter. The shell is always planispirally coiled, unlike those of Mesozoic
Goniatite shells are small to medium in size, almost always less than 15 centimeters (6 inches) in diameter and often smaller than 5 centimeters (2 inches) in diameter. The shell is always planispirally coiled, unlike those of Mesozoic
ammonites
in which some are trochoidal and even aberrant (called heteromorphs). Goniatitid shells vary in form from thinly discoidal to broadly globular and may be smooth or distinctly ornamented. Their shape suggests many were poor swimmers
The thin walls between the internal chambers of the shell are called the septa, and as the goniatite grew it would move its body forward in the shell secreting septa behind it, thereby adding new chambers to the shell. The sutures (or suture lines) are visible as a series of narrow, wavy lines on the surface of the shell. The sutures appear where each septa contacts the wall of the outer shell.
The typical goniatitid has a suture with smooth saddles and lobes, which gives the name "goniatitic" to this particular suture pattern. In some the sutures has a distinctive "zigzag" pattern Not all goniatitid ammonoides have goniatitic sutures. In some the sutures are ceratitic, in others, even ammonitic. Nor are goniatitic sutures limited to the Goniatidia.
The sutures of nautiloids are by comparison somewhat simpler, being either straight or slightly curved, whereas later ammonoids showed suture patterns of increasing complexity. One explanation for this increasing extravagancy in suture pattern is that it leads to a higher strength of the shell.
(also called epicontinental
or inland
) sea sediments than they are in rocks understood to represent open ocean sediments. Within these inland seas, goniatites' greatest abundance and diversity appears to have been achieved in offshore deep ramp and basinal
environments rather than in nearshore environments. Known nearshore (e.g., lagoon
al) occurrences have generally been ascribed to wash-in of shells from offshore waters.
Due to lack of strong evidence for any particular life mode (e.g., nekton
ic, plankton
ic, demersal, planktivorous
, piscivorous
), it remains unclear what resources goniatites were capitalizing on in these offshore environments. Only a few goniatites' full trophic apparatuses have ever been described, and reports of stomach contents in these creatures' fossils remain questionable at best. However, goniatites clearly lacked the calcified jaw apparatuses developed later in ammonoid history by the ammonites; this has been cited as evidence against a durophagous
(shell-crushing) diet for goniatites.
, Europe
, North Africa
and Australasia
. However, they seem to occur mostly in areas which at the time would have been tropical to subtropical. Almost any fossil-bearing limestone or shale from inland seas of the late Paleozoic tropics or subtropics is likely to yield some goniatites. In the USA, such rocks are found from Maine
, New York
, and Virginia
and in every state west to Nebraska
and south to Texas
and Alabama
; as well as in parts of almost every western state (with North Dakota
, Oregon
, Washington, and Hawai'i as the exceptions).
Notable goniatite occurrences include the following:
Certain limestone
s in western part of the Republic of Ireland
are packed with beautifully preserved goniatite fossil
s. They are also found in marine bands of the Carboniferous
coal measures in Europe
, and in marine rocks of the Pennsylvanian
period in Arkansas
. Large numbers of goniatites occur in rocks
from the Devonian period of Morocco
, and they are important zone, or index fossil
s used in dating the rocks of that period.
Squid
Squid are cephalopods of the order Teuthida, which comprises around 300 species. Like all other cephalopods, squid have a distinct head, bilateral symmetry, a mantle, and arms. Squid, like cuttlefish, have eight arms arranged in pairs and two, usually longer, tentacles...
, octopus
Octopus
The octopus is a cephalopod mollusc of the order Octopoda. Octopuses have two eyes and four pairs of arms, and like other cephalopods they are bilaterally symmetric. An octopus has a hard beak, with its mouth at the center point of the arms...
, and belemnites, that form the order Goniatitida. The Gonatitida originated from within the more primitive anarcestine ammonoids in the Middle Devonian
Devonian
The Devonian is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic Era spanning from the end of the Silurian Period, about 416.0 ± 2.8 Mya , to the beginning of the Carboniferous Period, about 359.2 ± 2.5 Mya...
some 390 million years ago. Surviving the Late Devonian extinction
Late Devonian extinction
The Late Devonian extinction was one of five major extinction events in the history of the Earth's biota. A major extinction, the Kellwasser Event, occurred at the boundary that marks the beginning of the last phase of the Devonian period, the Famennian faunal stage, , about 374 million years ago...
, goniatitids flourished during the Carboniferous
Carboniferous
The Carboniferous is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Devonian Period, about 359.2 ± 2.5 Mya , to the beginning of the Permian Period, about 299.0 ± 0.8 Mya . The name is derived from the Latin word for coal, carbo. Carboniferous means "coal-bearing"...
and Permian
Permian
The PermianThe term "Permian" was introduced into geology in 1841 by Sir Sir R. I. Murchison, president of the Geological Society of London, who identified typical strata in extensive Russian explorations undertaken with Edouard de Verneuil; Murchison asserted in 1841 that he named his "Permian...
only to become extinct at the end of the Permian some 251.4 million years ago. They were survived by their cousins the ceratite ammonoids, indirect descendants of the Anarcestida.
Morphology
The goniatites all possessed an external shell, which is divided internally into chambers. The animal lived in the largest of the external chambers, and the internal chambers would have been filled with gasGas
Gas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons...
, making the animal buoyant
Buoyancy
In physics, buoyancy is a force exerted by a fluid that opposes an object's weight. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus a column of fluid, or an object submerged in the fluid, experiences greater pressure at the bottom of the...
in the water. The general structure of the goniatites would have been similar to that of their relatives the ammonites, being a free swimming animal possessing a head with two well developed eyes and arms (or tentacle
Tentacle
A tentacle or bothrium is one of usually two or more elongated flexible organs present in animals, especially invertebrates. The term may also refer to the hairs of the leaves of some insectivorous plants. Usually, tentacles are used for feeding, feeling and grasping. Anatomically, they work like...
s).

Mesozoic
The Mesozoic era is an interval of geological time from about 250 million years ago to about 65 million years ago. It is often referred to as the age of reptiles because reptiles, namely dinosaurs, were the dominant terrestrial and marine vertebrates of the time...
ammonites
Ammonitida
The Ammonitida is an order of more highly evolved ammonoid cephalopods from the Jurassic and Cretaceous time periods, commonly with intricate ammonitic sutures....
in which some are trochoidal and even aberrant (called heteromorphs). Goniatitid shells vary in form from thinly discoidal to broadly globular and may be smooth or distinctly ornamented. Their shape suggests many were poor swimmers
The thin walls between the internal chambers of the shell are called the septa, and as the goniatite grew it would move its body forward in the shell secreting septa behind it, thereby adding new chambers to the shell. The sutures (or suture lines) are visible as a series of narrow, wavy lines on the surface of the shell. The sutures appear where each septa contacts the wall of the outer shell.
The typical goniatitid has a suture with smooth saddles and lobes, which gives the name "goniatitic" to this particular suture pattern. In some the sutures has a distinctive "zigzag" pattern Not all goniatitid ammonoides have goniatitic sutures. In some the sutures are ceratitic, in others, even ammonitic. Nor are goniatitic sutures limited to the Goniatidia.
The sutures of nautiloids are by comparison somewhat simpler, being either straight or slightly curved, whereas later ammonoids showed suture patterns of increasing complexity. One explanation for this increasing extravagancy in suture pattern is that it leads to a higher strength of the shell.
Ecology
Ecologically, goniatites were limited to environments of normal-marine salinity—as appears to be the case for all cephalopods throughout their history. Goniatites are much more abundant and speciose in rocks understood to represent cratonicEpeiric Sea
An epeiric sea is a shallow sea that extends over part of a continent.Epeiric seas are usually associated with the marine transgressions of the geologic past, which have variously been due to either global eustatic sea level changes, local tectonic deformation, or both, and are occasionally...
(also called epicontinental
Epeiric Sea
An epeiric sea is a shallow sea that extends over part of a continent.Epeiric seas are usually associated with the marine transgressions of the geologic past, which have variously been due to either global eustatic sea level changes, local tectonic deformation, or both, and are occasionally...
or inland
Epeiric Sea
An epeiric sea is a shallow sea that extends over part of a continent.Epeiric seas are usually associated with the marine transgressions of the geologic past, which have variously been due to either global eustatic sea level changes, local tectonic deformation, or both, and are occasionally...
) sea sediments than they are in rocks understood to represent open ocean sediments. Within these inland seas, goniatites' greatest abundance and diversity appears to have been achieved in offshore deep ramp and basinal
Oceanic basin
Hydrologically, an oceanic basin may be anywhere on Earth that is covered by seawater, but geologically ocean basins are large geologic basins that are below sea level...
environments rather than in nearshore environments. Known nearshore (e.g., lagoon
Lagoon
A lagoon is a body of shallow sea water or brackish water separated from the sea by some form of barrier. The EU's habitat directive defines lagoons as "expanses of shallow coastal salt water, of varying salinity or water volume, wholly or partially separated from the sea by sand banks or shingle,...
al) occurrences have generally been ascribed to wash-in of shells from offshore waters.
Due to lack of strong evidence for any particular life mode (e.g., nekton
Nekton
Nekton refers to the aggregate of actively swimming aquatic organisms in a body of water able to move independently of water currents....
ic, plankton
Plankton
Plankton are any drifting organisms that inhabit the pelagic zone of oceans, seas, or bodies of fresh water. That is, plankton are defined by their ecological niche rather than phylogenetic or taxonomic classification...
ic, demersal, planktivorous
Plankton
Plankton are any drifting organisms that inhabit the pelagic zone of oceans, seas, or bodies of fresh water. That is, plankton are defined by their ecological niche rather than phylogenetic or taxonomic classification...
, piscivorous
Fish
Fish are a paraphyletic group of organisms that consist of all gill-bearing aquatic vertebrate animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as various extinct related groups...
), it remains unclear what resources goniatites were capitalizing on in these offshore environments. Only a few goniatites' full trophic apparatuses have ever been described, and reports of stomach contents in these creatures' fossils remain questionable at best. However, goniatites clearly lacked the calcified jaw apparatuses developed later in ammonoid history by the ammonites; this has been cited as evidence against a durophagous
Durophagy
Durophagy is the term for describing the eating behavior of animals that consume hard-shelled or exoskeleton bearing organisms, such as corals, shelled mollusks, or crabs....
(shell-crushing) diet for goniatites.
Distribution
Goniatites are found in North AmericaNorth America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
, Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
, North Africa
North Africa
North Africa or Northern Africa is the northernmost region of the African continent, linked by the Sahara to Sub-Saharan Africa. Geopolitically, the United Nations definition of Northern Africa includes eight countries or territories; Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, South Sudan, Sudan, Tunisia, and...
and Australasia
Australasia
Australasia is a region of Oceania comprising Australia, New Zealand, the island of New Guinea, and neighbouring islands in the Pacific Ocean. The term was coined by Charles de Brosses in Histoire des navigations aux terres australes...
. However, they seem to occur mostly in areas which at the time would have been tropical to subtropical. Almost any fossil-bearing limestone or shale from inland seas of the late Paleozoic tropics or subtropics is likely to yield some goniatites. In the USA, such rocks are found from Maine
Maine
Maine is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the east and south, New Hampshire to the west, and the Canadian provinces of Quebec to the northwest and New Brunswick to the northeast. Maine is both the northernmost and easternmost...
, New York
New York
New York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east...
, and Virginia
Virginia
The Commonwealth of Virginia , is a U.S. state on the Atlantic Coast of the Southern United States. Virginia is nicknamed the "Old Dominion" and sometimes the "Mother of Presidents" after the eight U.S. presidents born there...
and in every state west to Nebraska
Nebraska
Nebraska is a state on the Great Plains of the Midwestern United States. The state's capital is Lincoln and its largest city is Omaha, on the Missouri River....
and south to Texas
Texas
Texas is the second largest U.S. state by both area and population, and the largest state by area in the contiguous United States.The name, based on the Caddo word "Tejas" meaning "friends" or "allies", was applied by the Spanish to the Caddo themselves and to the region of their settlement in...
and Alabama
Alabama
Alabama is a state located in the southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Tennessee to the north, Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gulf of Mexico to the south, and Mississippi to the west. Alabama ranks 30th in total land area and ranks second in the size of its inland...
; as well as in parts of almost every western state (with North Dakota
North Dakota
North Dakota is a state located in the Midwestern region of the United States of America, along the Canadian border. The state is bordered by Canada to the north, Minnesota to the east, South Dakota to the south and Montana to the west. North Dakota is the 19th-largest state by area in the U.S....
, Oregon
Oregon
Oregon is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is located on the Pacific coast, with Washington to the north, California to the south, Nevada on the southeast and Idaho to the east. The Columbia and Snake rivers delineate much of Oregon's northern and eastern...
, Washington, and Hawai'i as the exceptions).
Notable goniatite occurrences include the following:
Certain limestone
Limestone
Limestone is a sedimentary rock composed largely of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Many limestones are composed from skeletal fragments of marine organisms such as coral or foraminifera....
s in western part of the Republic of Ireland
Republic of Ireland
Ireland , described as the Republic of Ireland , is a sovereign state in Europe occupying approximately five-sixths of the island of the same name. Its capital is Dublin. Ireland, which had a population of 4.58 million in 2011, is a constitutional republic governed as a parliamentary democracy,...
are packed with beautifully preserved goniatite fossil
Fossil
Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of animals , plants, and other organisms from the remote past...
s. They are also found in marine bands of the Carboniferous
Carboniferous
The Carboniferous is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Devonian Period, about 359.2 ± 2.5 Mya , to the beginning of the Permian Period, about 299.0 ± 0.8 Mya . The name is derived from the Latin word for coal, carbo. Carboniferous means "coal-bearing"...
coal measures in Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
, and in marine rocks of the Pennsylvanian
Pennsylvanian
The Pennsylvanian is, in the ICS geologic timescale, the younger of two subperiods of the Carboniferous Period. It lasted from roughly . As with most other geochronologic units, the rock beds that define the Pennsylvanian are well identified, but the exact date of the start and end are uncertain...
period in Arkansas
Arkansas
Arkansas is a state located in the southern region of the United States. Its name is an Algonquian name of the Quapaw Indians. Arkansas shares borders with six states , and its eastern border is largely defined by the Mississippi River...
. Large numbers of goniatites occur in rocks
Rock (geology)
In geology, rock or stone is a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals and/or mineraloids.The Earth's outer solid layer, the lithosphere, is made of rock. In general rocks are of three types, namely, igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic...
from the Devonian period of Morocco
Morocco
Morocco , officially the Kingdom of Morocco , is a country located in North Africa. It has a population of more than 32 million and an area of 710,850 km², and also primarily administers the disputed region of the Western Sahara...
, and they are important zone, or index fossil
Index fossil
Index fossils are fossils used to define and identify geologic periods . They work on the premise that, although different sediments may look different depending on the conditions under which they were laid down, they may include the remains of the same species of fossil...
s used in dating the rocks of that period.

