Geology of Yorkshire
Encyclopedia
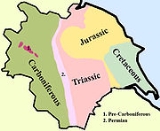
In Yorkshire there is a very close relationship between the major topographical areas and the geological period in which they were formed. The rocks of the Pennine chain of hills in the west are of Carboniferous origin whilst those of the central vale are Permo-Triassic. The North York Moors
in the north-east of the county are Jurassic in age while the Yorkshire Wolds
to the south east are Cretaceous chalk uplands. The plain of Holderness
and the Humberhead levels both owe their present form to the Quaternary ice ages.
The strata become gradually younger from west to east.
Much of Yorkshire presents heavily glaciated scenery as few places escaped the great ice sheets as they advanced during the last ice age.
to the north of the Craven Fault
. This Ingletonian group of folded and cleaved mudstones and sandstones is of disputed age but fossils equate them with the Lower Skiddaw Group of the Lake District
which are Ordovician
. These rocks were laid down when the area was part of the Avalonia
land mass and was positioned about 30° south of the equator.
By the end of the Ordovician period the Avalonian land mass had collided with Baltica
and this event caused a marine regression which was exacerbated by a world wide drop in sea level caused by a period of glaciation.
During the Silurian
period Avalonia and Baltica moved rapidly towards Laurentia
at a position about 20°south of the equator. The Iapetus Ocean
which lay between them was closed. Inliers of the Silurian rocks which were formed at this time occur at Cross Fell
, adjacent to the Pennine Fault, and at Horton in Ribblesdale
and Austwick
, north of the Craven Fault.
In the following Devonian
period the land area which is now Yorkshire was in a continental, inland, phase of deposition. There are no proven remaining Devonian deposits in the Yorkshire area and the Carboniferous rocks lie unconformably on the Silurian
.
 Carboniferous
Carboniferous
deposits were laid down on and between large pre-existing land blocks and intervening troughs.The blocks are known as the Askrigg and Alston blocks.These upstanding areas and the troughs between were actively subsiding into shallow seas which were the result of a global rise in sea levels. These seas contained high levels of calcium carbonate and calcium forming fossils. There are areas of reef deposition around the blocks where the seas were temporarily shallower. The land mass was by now astride the equator. The bordering seas began to be periodically invaded by delta
s formed by rivers flowing from the adjacent higher ground.The sand of the deltas became the Millstone Grit
s of the Yorkshire Pennines. The climate then became humid and the delta areas started to support swamp
s and tropical rain forests. These deltas changed size and shape frequently and were regularly innundated by the sea. They would eventually form the numerous coal seams of the Coal Measures
sandstones. The Variscan orogeny
occurred towards the end of the Carboniferous period as the former supercontinent
s of Gondwanaland and Euramerica
collided to form the single supercontinent of Pangea. The seas between the land masses were closed up and fold mountain ranges were formed along the closure line in many areas. The area of Britain was uplifted and fault lines developed.
and significant evaporite deposits as it dried up. This Zechstein Sea had completely evaporated by the end of the Permian. At the end of the Permian 95 per cent of animals and plants throughout the world became extinct. During the following Triassic period a hot and mainly arid climate continued but with flash floods from the south which deposited pebble beds in the mainly wind-deposited Sherwood sandstones. Another mass extinction at the end of this period saw 80 per cent of species disappear from earth.
At the end of the Triassic the Rhaetic
ocean spread its shallow waters over the deserts to start the Jurassic period.
The main area of Jurassic deposition in Yorkshire was the North York Moors.
Marine conditions continued into the Cretaceous period in the Yorkshire area.
, the British land mass drifted northwards from 40°N to its present latitude. It was also moved eastwards by the widening of the Atlantic Ocean and there was violent volcanic activity over north west Britain. It was in this period that the Cleveland
dyke was formed, originating from volcanic activity near the Scottish island of Mull
. The highlands and lowlands of Britain assumed their present relative positions by the late Tertiary period, about 2 million years ago.
Each cycle had a period of about 10,000 years and they became more pronounced in the last two million years. Seventeen cycles of cold and temperate
climate are recognised in Britain with three positive episodes of actual glaciation being confirmed. The latest glacial episode destroyed much of the evidence for former ones but traces do exist. On each occasion ice fields formed on the higher land and sent glaciers down the main valleys. There was scouring of material from the valley sides by the glaciers and this was deposited on lower ground as the ice retreated when the climate became warmer. In Yorkshire the higher land of the North York Moors stood proud of the glaciers, the Pennine valleys show classic glacial features and there was abundant deposition in the Vale of York and Holderness as the ice melted.
 The Pennines
The Pennines
form an anticline
which extends in a north-south direction, consisting of Millstone Grit
and the underlying Carboniferous
Limestone
. The limestone is exposed at the surface to the north of the range in the North Pennines
AONB. In the Yorkshire Dales
this limestone exposure has led to the formation of large underground cave systems and watercourses, known as "gills" and "pots". These potholes are more prevalent on the eastern side and are amongst the largest in England; notable examples are the chasms of Gaping Gill
, which is over 350 ft (107 m) deep and Rowten Pot
, which is 365 ft (111 m) deep. The presence of limestone has also led to some unusual geological formations in the region, such as the limestone pavement
s of the Yorkshire Pennines. Between the Northern and Southern areas of exposed limestone, between Skipton and the Peak, lies a narrow belt of gritstone country. Here the shales and sandstones of the Millstone Grit form high hills occupied by moors and peat-mosses with the higher ground being uncultivable and barely fit for pastures.
The landscape of the Pennines is generally upland areas of high moorland
indented by the more fertile valleys of the region's various rivers.
which consist mainly of mudstone with beds of sandstone and many seams of coal
.The sandstones resist erosion so they form a recurring pattern of escarpments that stand out from the shallow mudstone floors of the valleys. The major rivers crossing the area have carved broad valleys which have been glaciated and are floored by fertile alluvial deposits.
deposits were laid down in an evaporating inland sea in the Permian period. They are made up of a lower layer of dolomite
and dolomitic limestone
, which form the dominant landscape feature, overlain by red mudstone with gypsum
. The upper layer is made of a similar sequence. There are numerous swallow holes caused by the underground dissolution of limestone and gypsum. The sequence can be seen clearly where it is cut by rivers in the Nidd
gorge at Knaresborough
, the Wharfe
valley at Wetherby
and the Don gorge near Doncaster
.
The York and Escrick glacial moraines swing north and merge north of Wetherby to cover the magnesian limestone with glacial deposits. In the Bedale
area and northwards thes deposits are so extensive as to mask the limestone topography. South of Wetherby there is only a thin layer of glacial deposits overlying the limestone. The soils here are from the limestone and clay deposits and are generally very fertile.
lie Triassic
sandstone and mudstone, and lower Jurassic
mudstone but these are completely masked by the surface deposits. These deposits include glacial till, sand and gravel and both terminal and recessional moraines left by receding ice sheets at the end of the last ice age. The Escrick moraine extends across the vale from west to east and the York moraine, 8 miles further north, forms a similar curving ridge from York eastwards to Sand Hutton. To the north of these ridges are deposits of clay, sand and gravel left by a glacial lake. There are also areas of river alluvium consisting of clay, silt and sand deposited by the main rivers and streams.
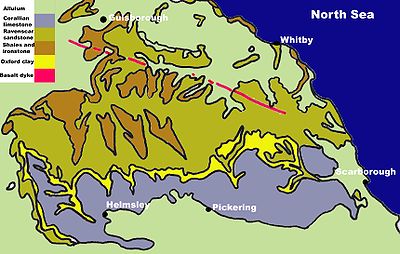 The geology of the North York Moors
The geology of the North York Moors
is dominated by rocks of the Jurassic
period. They were mostly laid down in tropical seas 205 to 142 million years ago. Fluctuations in sea level produced different rock types varying from shales to sandstones and limestones derived from coral. These marine and delta deposited rocks are superbly exposed on the Yorkshire coast from Staithes to Filey.
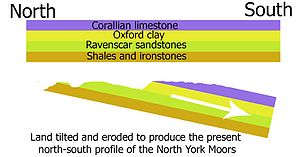 Subsequently, about 30 million years ago, the land was uplifted and tilted towards the south by earth movements. The upper layers of rock were eroded away and the older rocks were exposed in places. Because of the tilt the oldest rocks became exposed in the north. These are the bands of shales and ironstones on the northern scarp of the moors and Cleveland Hills. The middle layers form the sandstones of the high moors and the youngest layers of limestone form the tabular hills. In the dales where the rivers have cut through the younger rocks there are also exposures of older shales, ironstone and sandstone. Rosedale is an example of this.
Subsequently, about 30 million years ago, the land was uplifted and tilted towards the south by earth movements. The upper layers of rock were eroded away and the older rocks were exposed in places. Because of the tilt the oldest rocks became exposed in the north. These are the bands of shales and ironstones on the northern scarp of the moors and Cleveland Hills. The middle layers form the sandstones of the high moors and the youngest layers of limestone form the tabular hills. In the dales where the rivers have cut through the younger rocks there are also exposures of older shales, ironstone and sandstone. Rosedale is an example of this.
During the Quaternary
period, the last 2 million years, the area has experienced a sequence of glaciations. The most recent glaciation, the Devensian, ended about 10,000 years ago. The higher parts of the North York Moors were not covered by the ice sheets but glaciers flowed southwards on either side of the higher land mass.
As the climate became warmer at the end of the ice age the snowfields on the moors began to melt. The meltwater was unable to escape northwards, westwards or eastwards because it was blocked by ice. Huge torrents of water were forced southwards. Water from the Esk valley area flowed southwards gouging out the deep Newtondale valley as it went. Water from the moors formed a vast lake in the area of the Vale of Pickering. Eventually this lake filled its basin and then overflowed at the lowest point which was at Kirkham. Here it cut the steep sided Kirkham gorge. When the glacier finally retreated they left deep deposits of boulder clay and glacial alluvium behind. The boulder clay blocked the eastern end of the Vale of Pickering causing a permanent deviation in the course of the River Derwent. Alluvium from the glaciers covers many areas to the north of the moors and in the Esk valley
The Vale of Pickering
The site of the post glacial Lake Pickering
, the vale has a predominantly level topography covered by glacial drift deposits, with some rolling low ground on boulder clay and moraines in the far east. The underlying Jurassic sandstones and mudstones have little direct influence upon the landscape. There are minor outliers of Jurassic
limestone in places at the foot of the Howardian Hills
and the North York Moors, and there is some eroded chalk from the Wolds mixed with sands at the base of the Wolds in the southeast. There are springs associated with calcareous aquifers in places on the periphery of the vale.
The Yorkshire Wolds
The hills are formed from Cretaceous
chalk
, and make an arc from the Humber
estuary west of Kingston upon Hull
up to the North Sea
coast between Bridlington
and Scarborough. Here they rise up to form cliffs, most notably at Flamborough
, Bempton Cliffs and Filey
; Flamborough Headland is designated a Heritage Coast
. On the other side of the Humber, the chalk formations continue as the Lincolnshire Wolds
.
Most of the area takes the form of an elevated, gently rolling plateau, cut by numerous deep, steep-sided, flat-bottomed valleys of glacial origin. The chalk formation of the hills provides exceptionally good drainage, with the result that most of these valleys are dry; indeed, surface water is quite scarce throughout the Wolds. Typically the valleys are hard to see from above, creating the visual impression that the landscape is much flatter than is actually the case.
Holderness
Geologically, Holderness is underlain by Cretaceous
Chalk but in most places it is so deeply buried beneath glacial deposits that it has no influence on the landscape. The landscape is dominated by deposits of till, boulder clays and glacial lake clays. These were deposited during the Devensian glaciation. The glacial deposits form a more or less continuous lowland plain which has some peat filled depressions (known locally as meres) which mark the presence of former lake beds. There are other glacial landscape features such as drumlin
mounds, ridges and kettle holes scattered throughout the area.
The well drained glacial deposits provide fertile soils that can support intensive arable cultivation. Fields are generally large and bounded by drainage ditches. There is very little woodland in the area and this leads to a landscape that is essentially rural but very flat and exposed. The coast is subject to rapid marine erosion.
.
The Humberhead Levels
During the last ice age, a glacier extended across this area almost to where Doncaster now is. The main glacial front was at Escrick where the Escrick moraine marks its position. This formed the northern limit of an extensive lake, Glacial Lake Humber, which was impounded by the blocking of the Humber Gap by another ice front. Later the lake was filled with clay sediments which are up to 20 metres thick in some places.These clay sediments are locally overlain by peat deposits forming raised mires. At the base of the peat layers can be found the remains of a buried forest.
North York Moors
The North York Moors is a national park in North Yorkshire, England. The moors are one of the largest expanses of heather moorland in the United Kingdom. It covers an area of , and it has a population of about 25,000...
in the north-east of the county are Jurassic in age while the Yorkshire Wolds
Yorkshire Wolds
The Yorkshire Wolds are low hills in the counties of East Riding of Yorkshire and North Yorkshire in northeastern England. The name also applies to the district in which the hills lie....
to the south east are Cretaceous chalk uplands. The plain of Holderness
Holderness
Holderness is an area of the East Riding of Yorkshire, on the east coast of England. An area of rich agricultural land, Holderness was marshland until it was drained in the Middle Ages. Topographically, Holderness has more in common with the Netherlands than other parts of Yorkshire...
and the Humberhead levels both owe their present form to the Quaternary ice ages.
The strata become gradually younger from west to east.
Much of Yorkshire presents heavily glaciated scenery as few places escaped the great ice sheets as they advanced during the last ice age.

Pre-Carboniferous
The oldest rocks in Yorkshire are represented by a number of small inliers of Palaeozoic areas along the southern margin of the Askrigg BlockAskrigg Block
The Askrigg Block is the name applied by geologists to the crustal block forming a part of The Pennines of northern England and which is essentially coincident with the Yorkshire Dales. It is defined by the Dent Fault to the west and the Craven Fault System to the south whilst to the north it is...
to the north of the Craven Fault
Craven Fault
The Craven Fault is the name applied by geologists to the group of crustal faults in the Pennines that form the south edge of the Askrigg Block. It is evident at the surface in the contrast of limestone with millstone grit. It is coincident with the south edge of the Yorkshire Dales National Park...
. This Ingletonian group of folded and cleaved mudstones and sandstones is of disputed age but fossils equate them with the Lower Skiddaw Group of the Lake District
Lake District
The Lake District, also commonly known as The Lakes or Lakeland, is a mountainous region in North West England. A popular holiday destination, it is famous not only for its lakes and its mountains but also for its associations with the early 19th century poetry and writings of William Wordsworth...
which are Ordovician
Ordovician
The Ordovician is a geologic period and system, the second of six of the Paleozoic Era, and covers the time between 488.3±1.7 to 443.7±1.5 million years ago . It follows the Cambrian Period and is followed by the Silurian Period...
. These rocks were laid down when the area was part of the Avalonia
Avalonia
Avalonia was a microcontinent in the Paleozoic era. Crustal fragments of this former microcontinent underlie south-west Great Britain, and the eastern coast of North America. It is the source of many of the older rocks of Western Europe, Atlantic Canada, and parts of the coastal United States...
land mass and was positioned about 30° south of the equator.
By the end of the Ordovician period the Avalonian land mass had collided with Baltica
Baltica
Baltica is a name applied by geologists to a late-Proterozoic, early-Palaeozoic continent that now includes the East European craton of northwestern Eurasia. Baltica was created as an entity not earlier than 1.8 billion years ago. Before this time, the three segments/continents that now comprise...
and this event caused a marine regression which was exacerbated by a world wide drop in sea level caused by a period of glaciation.
During the Silurian
Silurian
The Silurian is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Ordovician Period, about 443.7 ± 1.5 Mya , to the beginning of the Devonian Period, about 416.0 ± 2.8 Mya . As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the...
period Avalonia and Baltica moved rapidly towards Laurentia
Laurentia
Laurentia is a large area of continental craton, which forms the ancient geological core of the North American continent...
at a position about 20°south of the equator. The Iapetus Ocean
Iapetus Ocean
The Iapetus Ocean was an ocean that existed in the Neoproterozoic and Paleozoic eras of the geologic timescale . The Iapetus Ocean was situated in the southern hemisphere, between the paleocontinents of Laurentia, Baltica and Avalonia...
which lay between them was closed. Inliers of the Silurian rocks which were formed at this time occur at Cross Fell
Cross Fell
Cross Fell is the highest point in the Pennine Hills of northern England and the highest point in England outside of the Lake District.The summit, at , is a stony plateau, part of a long ridge running North West to South East, which also incorporates Little Dun Fell at and Great Dun Fell at...
, adjacent to the Pennine Fault, and at Horton in Ribblesdale
Horton in Ribblesdale
Horton in Ribblesdale is a small village and civil parish in the Craven district of North Yorkshire, England. It is situated in Ribblesdale on the Settle–Carlisle Railway to the west of Pen-y-ghent....
and Austwick
Austwick
Austwick is a village and civil parish in the Craven district of North Yorkshire, England, about north west of Settle. The village is on the edge of the Yorkshire Dales National Park....
, north of the Craven Fault.
In the following Devonian
Devonian
The Devonian is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic Era spanning from the end of the Silurian Period, about 416.0 ± 2.8 Mya , to the beginning of the Carboniferous Period, about 359.2 ± 2.5 Mya...
period the land area which is now Yorkshire was in a continental, inland, phase of deposition. There are no proven remaining Devonian deposits in the Yorkshire area and the Carboniferous rocks lie unconformably on the Silurian
Silurian
The Silurian is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Ordovician Period, about 443.7 ± 1.5 Mya , to the beginning of the Devonian Period, about 416.0 ± 2.8 Mya . As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the...
.
Carboniferous

Carboniferous
The Carboniferous is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Devonian Period, about 359.2 ± 2.5 Mya , to the beginning of the Permian Period, about 299.0 ± 0.8 Mya . The name is derived from the Latin word for coal, carbo. Carboniferous means "coal-bearing"...
deposits were laid down on and between large pre-existing land blocks and intervening troughs.The blocks are known as the Askrigg and Alston blocks.These upstanding areas and the troughs between were actively subsiding into shallow seas which were the result of a global rise in sea levels. These seas contained high levels of calcium carbonate and calcium forming fossils. There are areas of reef deposition around the blocks where the seas were temporarily shallower. The land mass was by now astride the equator. The bordering seas began to be periodically invaded by delta
River delta
A delta is a landform that is formed at the mouth of a river where that river flows into an ocean, sea, estuary, lake, reservoir, flat arid area, or another river. Deltas are formed from the deposition of the sediment carried by the river as the flow leaves the mouth of the river...
s formed by rivers flowing from the adjacent higher ground.The sand of the deltas became the Millstone Grit
Millstone Grit
Millstone Grit is the name given to any of a number of coarse-grained sandstones of Carboniferous age which occur in the Northern England. The name derives from its use in earlier times as a source of millstones for use principally in watermills...
s of the Yorkshire Pennines. The climate then became humid and the delta areas started to support swamp
Swamp
A swamp is a wetland with some flooding of large areas of land by shallow bodies of water. A swamp generally has a large number of hammocks, or dry-land protrusions, covered by aquatic vegetation, or vegetation that tolerates periodical inundation. The two main types of swamp are "true" or swamp...
s and tropical rain forests. These deltas changed size and shape frequently and were regularly innundated by the sea. They would eventually form the numerous coal seams of the Coal Measures
Coal Measures
The Coal Measures is a lithostratigraphical term for the coal-bearing part of the Upper Carboniferous System. It represents the remains of fluvio-deltaic sediment, and consists mainly of clastic rocks interstratified with the beds of coal...
sandstones. The Variscan orogeny
Orogeny
Orogeny refers to forces and events leading to a severe structural deformation of the Earth's crust due to the engagement of tectonic plates. Response to such engagement results in the formation of long tracts of highly deformed rock called orogens or orogenic belts...
occurred towards the end of the Carboniferous period as the former supercontinent
Supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is a landmass comprising more than one continental core, or craton. The assembly of cratons and accreted terranes that form Eurasia qualifies as a supercontinent today.-History:...
s of Gondwanaland and Euramerica
Euramerica
Euramerica was a minor supercontinent created in the Devonian as the result of a collision between the Laurentian, Baltica, and Avalonia cratons .300 million years ago in the Late Carboniferous tropical rainforests lay over the equator of Euramerica...
collided to form the single supercontinent of Pangea. The seas between the land masses were closed up and fold mountain ranges were formed along the closure line in many areas. The area of Britain was uplifted and fault lines developed.
Permo-Triassic
Yorkshire lay in the arid hinterland of Pangea, between 20° and 30° north of the equator. The rocks of this period are dominated by red desert sandstones. The area which is now beneath the North Sea was a dry area of subsidence which was filled with a great thickness of wind-blown sands. Later a marine transgression from the north established a shallow saline sea which produced a thickness of dolomitic limestoneDolostone
Dolostone or dolomite rock is a sedimentary carbonate rock that contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite. In old U.S.G.S. publications it was referred to as magnesian limestone. Most dolostone formed as a magnesium replacement of limestone or lime mud prior to lithification. It is...
and significant evaporite deposits as it dried up. This Zechstein Sea had completely evaporated by the end of the Permian. At the end of the Permian 95 per cent of animals and plants throughout the world became extinct. During the following Triassic period a hot and mainly arid climate continued but with flash floods from the south which deposited pebble beds in the mainly wind-deposited Sherwood sandstones. Another mass extinction at the end of this period saw 80 per cent of species disappear from earth.
At the end of the Triassic the Rhaetic
Rhaetian
The Rhaetian is in geochronology the latest age of the Triassic period or in chronostratigraphy the uppermost stage of the Triassic system. It lasted from 203.6 ± 1.5 to 199.6 ± 0.6 million years ago...
ocean spread its shallow waters over the deserts to start the Jurassic period.
Jurassic
A shallow epicontinental sea, normally less than 100m deep, spread over the British area during this period. Britain at this time lay between 30° and 40° north of the equator. However, the Pennines, along with parts of Wales and Scotland were probably above sea level for most of the time. During the early and middle Jurassic an area of uplift around Market Weighton affected the way that sediments were deposited causing thinner bands of Jurassic rocks to be formed immediately north and south of the uplifted block.The main area of Jurassic deposition in Yorkshire was the North York Moors.
- Lower Jurassic At the beginning of the Jurassic period shales, clays and thin limestones and sandstones were deposited in a shallow sea. These deposits are many metres thick and include layers of ironstone of various thicknesses and the rocks from which alum is extracted.
- Middle Jurassic A period of gradual uplift happened when mudstone and sandstone were deposited on a low lying coastal plain crossed by large rivers. Occasionally this land area was inundated by the sea and at these times calcareous rocks containing marine fossils were deposited. These are the Ravenscar Group of rocks. The Oxford ClayOxford ClayThe Oxford Clay Formation is a Jurassic marine sedimentary rock formation underlying much of southeast England, from as far west as Dorset and as far north as Yorkshire. The Oxford Clay is of middle Callovian to lower Oxfordian age and comprises 2 main facies. The lower facies comprises the...
was deposited at the end of this era. - Upper Jurassic Towards the end of the Jurassic period the land again sank beneath the sea. At first the sea was shallow and calcareous sandstones and limestones were deposited. These are the Corallian rocksCorallian LimestoneCorallian Limestone is a coralliferous sedimentary rock, laid down in Jurassic times. It is a hard variety of "coral rag". Building stones from this geological structure tend to be irregular in shape. It is often found close to seams of Portland Limestone...
of the Tabular HillsTabular HillsThe Tabular Hills are an east west line of distinct hills on the southern boundary of the North Yorkshire Moors, running from Scarborough in the east all the way to Black Hambleton in the west. The name refers to their flat tabular shaped summits composed of hard Corallian limestone known...
towards the south of the area. Overlying the Corallian rocks is the Kimmeridge ClayKimmeridge ClayThe Kimmeridge Clay Formation is a sedimentary deposit of fossiliferous marine clay which is of Jurassic age. It occurs in Europe.Kimmeridge Clay is arguably the most economically important unit of rocks in the whole of Europe, being the major source rock for oil fields in the North Sea hydrocarbon...
which underlies the Vale of PickeringVale of PickeringThe Vale of Pickering is a low-lying flat area of land in North Yorkshire, England. It is drained by the River Derwent. The landscape is rural with scattered villages and small market towns. It has been inhabited continuously from the Mesolithic period...
but this is not exposed on the surface.
Marine conditions continued into the Cretaceous period in the Yorkshire area.
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous period lasted for 80 million years. It was during this time that the North Atlantic was formed as North America and Europe drifted apart.To the north of the Market Weighton block only small amounts of deposit were laid down in the early part of the Cretaceous.These were the Speeton clays which are 100m thick and lie directly on the Jurassic deposits at Filey Bay. Above this clay is a 14m thick layer of red chalk coloured by impurities washing from the land. Later in the Cretaceous seawater covered the whole of southern Britain and deposited a layer of chalk up to 550m thick forming a great swathe from Flamborough Head to the Channel coast. At the end of the Cretaceous period there was another mass extinction of life with 75 per cent of all life becoming extinct, including the dinosaurs.Tertiary
During the TertiaryTertiary
The Tertiary is a deprecated term for a geologic period 65 million to 2.6 million years ago. The Tertiary covered the time span between the superseded Secondary period and the Quaternary...
, the British land mass drifted northwards from 40°N to its present latitude. It was also moved eastwards by the widening of the Atlantic Ocean and there was violent volcanic activity over north west Britain. It was in this period that the Cleveland
Cleveland, England
Cleveland is an area in the north east of England. Its name means literally "cliff-land", referring to its hilly southern areas, which rise to nearly...
dyke was formed, originating from volcanic activity near the Scottish island of Mull
Isle of Mull
The Isle of Mull or simply Mull is the second largest island of the Inner Hebrides, off the west coast of Scotland in the council area of Argyll and Bute....
. The highlands and lowlands of Britain assumed their present relative positions by the late Tertiary period, about 2 million years ago.
Quaternary
Towards the end of the Tertiary period there were repeated cycles of warmer and cooler climate.Each cycle had a period of about 10,000 years and they became more pronounced in the last two million years. Seventeen cycles of cold and temperate
Temperate
In geography, temperate or tepid latitudes of the globe lie between the tropics and the polar circles. The changes in these regions between summer and winter are generally relatively moderate, rather than extreme hot or cold...
climate are recognised in Britain with three positive episodes of actual glaciation being confirmed. The latest glacial episode destroyed much of the evidence for former ones but traces do exist. On each occasion ice fields formed on the higher land and sent glaciers down the main valleys. There was scouring of material from the valley sides by the glaciers and this was deposited on lower ground as the ice retreated when the climate became warmer. In Yorkshire the higher land of the North York Moors stood proud of the glaciers, the Pennine valleys show classic glacial features and there was abundant deposition in the Vale of York and Holderness as the ice melted.
The Pennines

Pennines
The Pennines are a low-rising mountain range, separating the North West of England from Yorkshire and the North East.Often described as the "backbone of England", they form a more-or-less continuous range stretching from the Peak District in Derbyshire, around the northern and eastern edges of...
form an anticline
Anticline
In structural geology, an anticline is a fold that is convex up and has its oldest beds at its core. The term is not to be confused with antiform, which is a purely descriptive term for any fold that is convex up. Therefore if age relationships In structural geology, an anticline is a fold that is...
which extends in a north-south direction, consisting of Millstone Grit
Millstone Grit
Millstone Grit is the name given to any of a number of coarse-grained sandstones of Carboniferous age which occur in the Northern England. The name derives from its use in earlier times as a source of millstones for use principally in watermills...
and the underlying Carboniferous
Carboniferous
The Carboniferous is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Devonian Period, about 359.2 ± 2.5 Mya , to the beginning of the Permian Period, about 299.0 ± 0.8 Mya . The name is derived from the Latin word for coal, carbo. Carboniferous means "coal-bearing"...
Limestone
Limestone
Limestone is a sedimentary rock composed largely of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Many limestones are composed from skeletal fragments of marine organisms such as coral or foraminifera....
. The limestone is exposed at the surface to the north of the range in the North Pennines
North Pennines
The North Pennines is the northernmost section of the Pennine range of hills which runs north-south through northern England. It lies between Carlisle to the west and Darlington to the east...
AONB. In the Yorkshire Dales
Yorkshire Dales
The Yorkshire Dales is the name given to an upland area in Northern England.The area lies within the historic county boundaries of Yorkshire, though it spans the ceremonial counties of North Yorkshire, West Yorkshire and Cumbria...
this limestone exposure has led to the formation of large underground cave systems and watercourses, known as "gills" and "pots". These potholes are more prevalent on the eastern side and are amongst the largest in England; notable examples are the chasms of Gaping Gill
Gaping Gill
Gaping Gill is a natural cave in North Yorkshire, England. It is one of the unmistakable landmarks on the southern slopes of Ingleborough – a deep pothole with the stream Fell Beck flowing into it...
, which is over 350 ft (107 m) deep and Rowten Pot
Rowten Pot
Rowten Pot is one of several hill top entrances into the West Kingsdale System in North Yorkshire, England. It connects into the Kingsdale Master Cave through a sump which is possible, though not recommended, to free-dive....
, which is 365 ft (111 m) deep. The presence of limestone has also led to some unusual geological formations in the region, such as the limestone pavement
Limestone pavement
A limestone pavement is a natural karst landform consisting of a flat, incised surface of exposed limestone that resembles an artificial pavement. The term is mainly used in the UK where many of these landforms have developed distinctive surface patterning resembling block of paving...
s of the Yorkshire Pennines. Between the Northern and Southern areas of exposed limestone, between Skipton and the Peak, lies a narrow belt of gritstone country. Here the shales and sandstones of the Millstone Grit form high hills occupied by moors and peat-mosses with the higher ground being uncultivable and barely fit for pastures.
The landscape of the Pennines is generally upland areas of high moorland
Moorland
Moorland or moor is a type of habitat, in the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome, found in upland areas, characterised by low-growing vegetation on acidic soils and heavy fog...
indented by the more fertile valleys of the region's various rivers.
The Yorkshire Coalfield
The coalfield area is underlain by Coal MeasuresCoal Measures
The Coal Measures is a lithostratigraphical term for the coal-bearing part of the Upper Carboniferous System. It represents the remains of fluvio-deltaic sediment, and consists mainly of clastic rocks interstratified with the beds of coal...
which consist mainly of mudstone with beds of sandstone and many seams of coal
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure...
.The sandstones resist erosion so they form a recurring pattern of escarpments that stand out from the shallow mudstone floors of the valleys. The major rivers crossing the area have carved broad valleys which have been glaciated and are floored by fertile alluvial deposits.
The Magnesian Limestone Belt
The Magnesian Limestone belt forms a narrow north- south oriented strip of undulating land on the eastern edge of the Pennines overlooking the Vale of York.The magnesian limestoneDolostone
Dolostone or dolomite rock is a sedimentary carbonate rock that contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite. In old U.S.G.S. publications it was referred to as magnesian limestone. Most dolostone formed as a magnesium replacement of limestone or lime mud prior to lithification. It is...
deposits were laid down in an evaporating inland sea in the Permian period. They are made up of a lower layer of dolomite
Dolomite
Dolomite is a carbonate mineral composed of calcium magnesium carbonate CaMg2. The term is also used to describe the sedimentary carbonate rock dolostone....
and dolomitic limestone
Dolostone
Dolostone or dolomite rock is a sedimentary carbonate rock that contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite. In old U.S.G.S. publications it was referred to as magnesian limestone. Most dolostone formed as a magnesium replacement of limestone or lime mud prior to lithification. It is...
, which form the dominant landscape feature, overlain by red mudstone with gypsum
Gypsum
Gypsum is a very soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula CaSO4·2H2O. It is found in alabaster, a decorative stone used in Ancient Egypt. It is the second softest mineral on the Mohs Hardness Scale...
. The upper layer is made of a similar sequence. There are numerous swallow holes caused by the underground dissolution of limestone and gypsum. The sequence can be seen clearly where it is cut by rivers in the Nidd
River Nidd
The River Nidd is a tributary of the River Ouse in the English county of North Yorkshire. In its first few miles it is dammed three times to create Angram Reservoir, Scar House Reservoir and Gouthwaite Reservoir which attract around 150,000 visitors a year...
gorge at Knaresborough
Knaresborough
Knaresborough is an old and historic market town, spa town and civil parish in the Borough of Harrogate, North Yorkshire, England, located on the River Nidd, four miles east of the centre of Harrogate.-History:...
, the Wharfe
River Wharfe
The River Wharfe is a river in Yorkshire, England. For much of its length it is the county boundary between West Yorkshire and North Yorkshire. The name Wharfe is Celtic and means "twisting, winding".The valley of the River Wharfe is known as Wharfedale...
valley at Wetherby
Wetherby
Wetherby is a market town and civil parish within the metropolitan borough of the City of Leeds, in West Yorkshire, England. It stands on the River Wharfe, and has been for centuries a crossing place and staging post on the Great North Road, being mid-way between London and Edinburgh...
and the Don gorge near Doncaster
Doncaster
Doncaster is a town in South Yorkshire, England, and the principal settlement of the Metropolitan Borough of Doncaster. The town is about from Sheffield and is popularly referred to as "Donny"...
.
The York and Escrick glacial moraines swing north and merge north of Wetherby to cover the magnesian limestone with glacial deposits. In the Bedale
Bedale
Bedale is a market town and civil parish in the district of Hambleton, North Yorkshire, England. It lies north of Leeds, southwest of Middlesbrough, and south west of the county town of Northallerton...
area and northwards thes deposits are so extensive as to mask the limestone topography. South of Wetherby there is only a thin layer of glacial deposits overlying the limestone. The soils here are from the limestone and clay deposits and are generally very fertile.
The Vales of Mowbray and York
Beneath the drift deposits of the Vale of YorkVale of York
The Vale of York is an area of flat land in the north-east of England. The vale is a major agricultural area and serves as the main north-south transport corridor for northern England....
lie Triassic
Triassic
The Triassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about 250 to 200 Mya . As the first period of the Mesozoic Era, the Triassic follows the Permian and is followed by the Jurassic. Both the start and end of the Triassic are marked by major extinction events...
sandstone and mudstone, and lower Jurassic
Jurassic
The Jurassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about Mya to Mya, that is, from the end of the Triassic to the beginning of the Cretaceous. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic era, also known as the age of reptiles. The start of the period is marked by...
mudstone but these are completely masked by the surface deposits. These deposits include glacial till, sand and gravel and both terminal and recessional moraines left by receding ice sheets at the end of the last ice age. The Escrick moraine extends across the vale from west to east and the York moraine, 8 miles further north, forms a similar curving ridge from York eastwards to Sand Hutton. To the north of these ridges are deposits of clay, sand and gravel left by a glacial lake. There are also areas of river alluvium consisting of clay, silt and sand deposited by the main rivers and streams.
The North York Moors

North York Moors
The North York Moors is a national park in North Yorkshire, England. The moors are one of the largest expanses of heather moorland in the United Kingdom. It covers an area of , and it has a population of about 25,000...
is dominated by rocks of the Jurassic
Jurassic
The Jurassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about Mya to Mya, that is, from the end of the Triassic to the beginning of the Cretaceous. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic era, also known as the age of reptiles. The start of the period is marked by...
period. They were mostly laid down in tropical seas 205 to 142 million years ago. Fluctuations in sea level produced different rock types varying from shales to sandstones and limestones derived from coral. These marine and delta deposited rocks are superbly exposed on the Yorkshire coast from Staithes to Filey.

During the Quaternary
Quaternary
The Quaternary Period is the most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the ICS. It follows the Neogene Period, spanning 2.588 ± 0.005 million years ago to the present...
period, the last 2 million years, the area has experienced a sequence of glaciations. The most recent glaciation, the Devensian, ended about 10,000 years ago. The higher parts of the North York Moors were not covered by the ice sheets but glaciers flowed southwards on either side of the higher land mass.
As the climate became warmer at the end of the ice age the snowfields on the moors began to melt. The meltwater was unable to escape northwards, westwards or eastwards because it was blocked by ice. Huge torrents of water were forced southwards. Water from the Esk valley area flowed southwards gouging out the deep Newtondale valley as it went. Water from the moors formed a vast lake in the area of the Vale of Pickering. Eventually this lake filled its basin and then overflowed at the lowest point which was at Kirkham. Here it cut the steep sided Kirkham gorge. When the glacier finally retreated they left deep deposits of boulder clay and glacial alluvium behind. The boulder clay blocked the eastern end of the Vale of Pickering causing a permanent deviation in the course of the River Derwent. Alluvium from the glaciers covers many areas to the north of the moors and in the Esk valley
The Vale of PickeringVale of PickeringThe Vale of Pickering is a low-lying flat area of land in North Yorkshire, England. It is drained by the River Derwent. The landscape is rural with scattered villages and small market towns. It has been inhabited continuously from the Mesolithic period...
The site of the post glacial Lake PickeringLake Pickering
Lake Pickering was an extensive proglacial lake of the Devensian glacial. It filled the Vale of Pickering between the North York Moors and the Yorkshire Wolds, when the ice blocked the drainage, which had hitherto flowed north-eastwards past the site of Filey towards the Northern North Sea basin...
, the vale has a predominantly level topography covered by glacial drift deposits, with some rolling low ground on boulder clay and moraines in the far east. The underlying Jurassic sandstones and mudstones have little direct influence upon the landscape. There are minor outliers of Jurassic
Jurassic
The Jurassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about Mya to Mya, that is, from the end of the Triassic to the beginning of the Cretaceous. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic era, also known as the age of reptiles. The start of the period is marked by...
limestone in places at the foot of the Howardian Hills
Howardian Hills
The Howardian Hills form an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty in North Yorkshire, England. located between the Yorkshire Wolds, the North York Moors National Park and the Vale of York. The AONB includes farmland, wooded rolling countryside, villages and historic houses with parkland...
and the North York Moors, and there is some eroded chalk from the Wolds mixed with sands at the base of the Wolds in the southeast. There are springs associated with calcareous aquifers in places on the periphery of the vale.
The Yorkshire WoldsYorkshire WoldsThe Yorkshire Wolds are low hills in the counties of East Riding of Yorkshire and North Yorkshire in northeastern England. The name also applies to the district in which the hills lie....
The hills are formed from CretaceousCretaceous
The Cretaceous , derived from the Latin "creta" , usually abbreviated K for its German translation Kreide , is a geologic period and system from circa to million years ago. In the geologic timescale, the Cretaceous follows the Jurassic period and is followed by the Paleogene period of the...
chalk
Chalk
Chalk is a soft, white, porous sedimentary rock, a form of limestone composed of the mineral calcite. Calcite is calcium carbonate or CaCO3. It forms under reasonably deep marine conditions from the gradual accumulation of minute calcite plates shed from micro-organisms called coccolithophores....
, and make an arc from the Humber
Humber
The Humber is a large tidal estuary on the east coast of Northern England. It is formed at Trent Falls, Faxfleet, by the confluence of the tidal River Ouse and the tidal River Trent. From here to the North Sea, it forms part of the boundary between the East Riding of Yorkshire on the north bank...
estuary west of Kingston upon Hull
Kingston upon Hull
Kingston upon Hull , usually referred to as Hull, is a city and unitary authority area in the ceremonial county of the East Riding of Yorkshire, England. It stands on the River Hull at its junction with the Humber estuary, 25 miles inland from the North Sea. Hull has a resident population of...
up to the North Sea
North Sea
In the southwest, beyond the Straits of Dover, the North Sea becomes the English Channel connecting to the Atlantic Ocean. In the east, it connects to the Baltic Sea via the Skagerrak and Kattegat, narrow straits that separate Denmark from Norway and Sweden respectively...
coast between Bridlington
Bridlington
Bridlington is a seaside resort, minor sea fishing port and civil parish on the Holderness Coast of the North Sea, in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England. It has a static population of over 33,000, which rises considerably during the tourist season...
and Scarborough. Here they rise up to form cliffs, most notably at Flamborough
Flamborough Head
Flamborough Head is a promontory of on the Yorkshire coast of England, between the Filey and Bridlington bays of the North Sea. It is a chalk headland, and the resistance it offers to coastal erosion may be contrasted with the low coast of Holderness to the south...
, Bempton Cliffs and Filey
Filey
Filey is a small town and civil parish in North Yorkshire, England. It forms part of the borough of Scarborough and is located between Scarborough and Bridlington on the North Sea coast. Although it started out as a fishing village, it has a large beach and is a popular tourist resort...
; Flamborough Headland is designated a Heritage Coast
Heritage Coast
A Heritage Coast is a strip of UK coastline designated by the Countryside Agency in England and the Countryside Council for Wales as having notable natural beauty or scientific significance.- Designated coastline :...
. On the other side of the Humber, the chalk formations continue as the Lincolnshire Wolds
Lincolnshire Wolds
The Lincolnshire Wolds is a range of hills in the county of Lincolnshire, England. It is a designated Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty , and the highest area of land in eastern England between Yorkshire and Kent...
.
Most of the area takes the form of an elevated, gently rolling plateau, cut by numerous deep, steep-sided, flat-bottomed valleys of glacial origin. The chalk formation of the hills provides exceptionally good drainage, with the result that most of these valleys are dry; indeed, surface water is quite scarce throughout the Wolds. Typically the valleys are hard to see from above, creating the visual impression that the landscape is much flatter than is actually the case.
HoldernessHoldernessHolderness is an area of the East Riding of Yorkshire, on the east coast of England. An area of rich agricultural land, Holderness was marshland until it was drained in the Middle Ages. Topographically, Holderness has more in common with the Netherlands than other parts of Yorkshire...
Geologically, Holderness is underlain by CretaceousCretaceous
The Cretaceous , derived from the Latin "creta" , usually abbreviated K for its German translation Kreide , is a geologic period and system from circa to million years ago. In the geologic timescale, the Cretaceous follows the Jurassic period and is followed by the Paleogene period of the...
Chalk but in most places it is so deeply buried beneath glacial deposits that it has no influence on the landscape. The landscape is dominated by deposits of till, boulder clays and glacial lake clays. These were deposited during the Devensian glaciation. The glacial deposits form a more or less continuous lowland plain which has some peat filled depressions (known locally as meres) which mark the presence of former lake beds. There are other glacial landscape features such as drumlin
Drumlin
A drumlin, from the Irish word droimnín , first recorded in 1833, is an elongated whale-shaped hill formed by glacial ice acting on underlying unconsolidated till or ground moraine.-Drumlin formation:...
mounds, ridges and kettle holes scattered throughout the area.
The well drained glacial deposits provide fertile soils that can support intensive arable cultivation. Fields are generally large and bounded by drainage ditches. There is very little woodland in the area and this leads to a landscape that is essentially rural but very flat and exposed. The coast is subject to rapid marine erosion.
.
The Humberhead LevelsHumberhead LevelsThe Humberhead Levels cover a large expanse of very flat, low lying land towards the eastern end of the Humber estuary in northern England. The Levels occupies the area of the former Glacial Lake Humber...
During the last ice age, a glacier extended across this area almost to where Doncaster now is. The main glacial front was at Escrick where the Escrick moraine marks its position. This formed the northern limit of an extensive lake, Glacial Lake Humber, which was impounded by the blocking of the Humber Gap by another ice front. Later the lake was filled with clay sediments which are up to 20 metres thick in some places.These clay sediments are locally overlain by peat deposits forming raised mires. At the base of the peat layers can be found the remains of a buried forest.Geological SSSI's in Yorkshire
| Site name | UK Grid reference | Geological feature |
|---|---|---|
| Millington Wood and Pastures | SE850545 | Dry chalk valleys |
| Rifle Butts Quarry | SE898426 | Cretaceous red Chalk |
| Withow Gap, Skipsea | TA183546 | Glacial lake deposits |
| Flamborough Head | TA170570 | Upper Cretaceous chalk cliffs |
| Malham - Arncliffe | SD920672 | Carboniferous limestone weathering |
| Robin Hoods Bay | NZ941082 | Jurassic strata |
| Newtondale | SE820915 | Glacial overflow channel |
| Micklefield Quarry | SE446325 | Magnesian limestone Dolostone Dolostone or dolomite rock is a sedimentary carbonate rock that contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite. In old U.S.G.S. publications it was referred to as magnesian limestone. Most dolostone formed as a magnesium replacement of limestone or lime mud prior to lithification. It is... |
| South Elmsall Quarry | SE484116 | Magnesian limestone |

