Freeform surface modelling
Encyclopedia
Freeform surface modelling is the art of engineering Freeform Surfaces with a CAD
or CAID
system.
The technology has encompassed two main fields. Either creating aesthetic (Class A surfaces
) that also perform a function; for example, car bodies and consumer product outer forms, or technical surfaces for components such as gas turbine blades and other fluid dynamic engineering components.
CAD software packages use two basic methods for the creation of surfaces. The first begins with construction curves (splines) from which the 3D surface is then swept (section along guide rail) or meshed (lofted) through.
 The second method is direct creation of the surface with manipulation of the surface poles/control points.
The second method is direct creation of the surface with manipulation of the surface poles/control points.
 From these initially created surfaces, other surfaces are constructed using either derived methods such as offset or angled extensions from surfaces; or via bridging and blending between groups of surfaces.
From these initially created surfaces, other surfaces are constructed using either derived methods such as offset or angled extensions from surfaces; or via bridging and blending between groups of surfaces.
software to describe the skin of a 3D geometric element. Freeform surfaces do not have rigid radial dimensions, unlike regular surfaces such as plane
s, cylinder
s and conic surfaces. They are used to describe forms such as turbine
blades, car bodies and boat hull
s. Initially developed for the automotive and aerospace
industries, freeform surfacing is now widely used in all engineering
design disciplines from consumer goods products to ships. Most systems today use nonuniform rational B-spline
(NURBS) mathematics to describe the surface
forms; however, there are other methods such as Gorden surfaces or Coons surfaces .
The forms of freeform surfaces (and curves) are not stored or defined in CAD
software in terms of polynomial equations, but by their poles, degree
, and number of patches (segments with spline
curves). The degree of a surface determines its mathematical properties, and can be seen as representing the shape by a polynomial with variables to the power of the degree value. For example, a surface with a degree of 1 would be a flat cross section
surface. A surface with degree 2 would be curved in one direction, while a degree 3 surface could (but does not necessarily) change once from concave to convex curvature. Some CAD systems use the term order instead of degree. The order of a polynomial is one greater than the degree, and gives the number of coefficient
s rather than the greatest exponent.
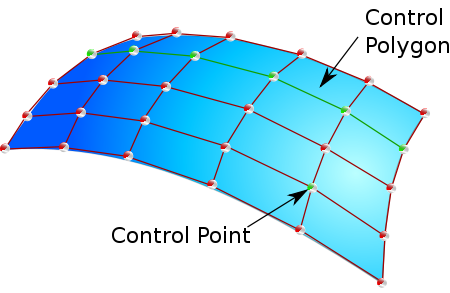 The poles (sometimes known as control points) of a surface define its shape. The natural surface edges are defined by the positions of the first and last poles. (Note that a surface can have trimmed boundaries.) The intermediate poles act like magnets drawing the surface in their direction. The surface does not, however, go through these points. The second and third poles as well as defining shape, respectively determine the start and tangent
The poles (sometimes known as control points) of a surface define its shape. The natural surface edges are defined by the positions of the first and last poles. (Note that a surface can have trimmed boundaries.) The intermediate poles act like magnets drawing the surface in their direction. The surface does not, however, go through these points. The second and third poles as well as defining shape, respectively determine the start and tangent
angles and the curvature
. In a single patch surface (Bézier surface
), there is one more pole than the degree values of the surface.
Surface patches can be merged into a single NURBS surface; at these points are knot lines. The number of knots will determine the influence of the poles on either side and how smooth the transition is. The smoothness between patches, known as continuity, is often referred to in terms of a C value:
Two more important aspects are the U and V parameters. These are values on the surface ranging from 0 to 1, used in the mathematical definition of the surface and for defining paths on the surface: for example, a trimmed boundary edge. Note that they are not proportionally spaced along the surface. A curve of constant U or constant V is known as an isoperimetric curve, or U (V) line. In CAD systems, surfaces are often displayed with their poles of constant U or constant V values connected together by lines; these are known as control polygons.
One example of where surfacing excels is automotive body panels. Just blending two curved areas of the panel with different radii of curvature together, maintaining tangential continuity (meaning that the blended surface doesn't change direction suddenly, but smoothly) won't be enough. They need to have a continuous rate of curvature change between the two sections, or else their reflections will appear disconnected.
The continuity is defined using the terms
To achieve a high quality NURBS or Bezier surface, degrees of 5 or greater are generally used. Depending on the product and production process, different levels of accuracy are used but tolerances usually range from 0.02 mm to .001 mm (for example, in the fairing of BIW
concept surfaces to production surface). For ship building, this need not be so tight, but for precision gears and medical devices it is much finer.
The term spline also has nautical origins coming from East Anglian dialect word for a thin long strip of wood (probably from old English and Germanic word splint).
Computer-aided design
Computer-aided design , also known as computer-aided design and drafting , is the use of computer technology for the process of design and design-documentation. Computer Aided Drafting describes the process of drafting with a computer...
or CAID
Computer-aided industrial design
Computer-aided industrial design is a subset of computer-aided design that includes software that directly helps in product development....
system.
The technology has encompassed two main fields. Either creating aesthetic (Class A surfaces
Class A surfaces
Class A surfaces is a term used in automotive design to describe a set of freeform surfaces of high efficiency and quality. Although, strictly, it is nothing more than saying the surfaces have curvature and tangency alignment - to ideal aesthetical reflection quality, many people interpret class A...
) that also perform a function; for example, car bodies and consumer product outer forms, or technical surfaces for components such as gas turbine blades and other fluid dynamic engineering components.
CAD software packages use two basic methods for the creation of surfaces. The first begins with construction curves (splines) from which the 3D surface is then swept (section along guide rail) or meshed (lofted) through.



Surfaces
Freeform surface, or freeform surfacing, is used in CAD and other computer graphicsComputer graphics
Computer graphics are graphics created using computers and, more generally, the representation and manipulation of image data by a computer with help from specialized software and hardware....
software to describe the skin of a 3D geometric element. Freeform surfaces do not have rigid radial dimensions, unlike regular surfaces such as plane
Plane (mathematics)
In mathematics, a plane is a flat, two-dimensional surface. A plane is the two dimensional analogue of a point , a line and a space...
s, cylinder
Cylinder (geometry)
A cylinder is one of the most basic curvilinear geometric shapes, the surface formed by the points at a fixed distance from a given line segment, the axis of the cylinder. The solid enclosed by this surface and by two planes perpendicular to the axis is also called a cylinder...
s and conic surfaces. They are used to describe forms such as turbine
Turbine
A turbine is a rotary engine that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work.The simplest turbines have one moving part, a rotor assembly, which is a shaft or drum with blades attached. Moving fluid acts on the blades, or the blades react to the flow, so that they move and...
blades, car bodies and boat hull
Hull (watercraft)
A hull is the watertight body of a ship or boat. Above the hull is the superstructure and/or deckhouse, where present. The line where the hull meets the water surface is called the waterline.The structure of the hull varies depending on the vessel type...
s. Initially developed for the automotive and aerospace
Aerospace
Aerospace comprises the atmosphere of Earth and surrounding space. Typically the term is used to refer to the industry that researches, designs, manufactures, operates, and maintains vehicles moving through air and space...
industries, freeform surfacing is now widely used in all engineering
Engineering
Engineering is the discipline, art, skill and profession of acquiring and applying scientific, mathematical, economic, social, and practical knowledge, in order to design and build structures, machines, devices, systems, materials and processes that safely realize improvements to the lives of...
design disciplines from consumer goods products to ships. Most systems today use nonuniform rational B-spline
Nonuniform rational B-spline
Non-uniform rational basis spline is a mathematical model commonly used in computer graphics for generating and representing curves and surfaces which offers great flexibility and precision for handling both analytic and freeform shapes.- History :Development of NURBS began in the 1950s by...
(NURBS) mathematics to describe the surface
Surface
In mathematics, specifically in topology, a surface is a two-dimensional topological manifold. The most familiar examples are those that arise as the boundaries of solid objects in ordinary three-dimensional Euclidean space R3 — for example, the surface of a ball...
forms; however, there are other methods such as Gorden surfaces or Coons surfaces .
The forms of freeform surfaces (and curves) are not stored or defined in CAD
Computer-aided design
Computer-aided design , also known as computer-aided design and drafting , is the use of computer technology for the process of design and design-documentation. Computer Aided Drafting describes the process of drafting with a computer...
software in terms of polynomial equations, but by their poles, degree
Degree (mathematics)
In mathematics, there are several meanings of degree depending on the subject.- Unit of angle :A degree , usually denoted by ° , is a measurement of a plane angle, representing 1⁄360 of a turn...
, and number of patches (segments with spline
Spline
Spline can refer to:* Spline , a mating feature for rotating elements* Spline , a mathematical function used for interpolation or smoothing* Smoothing spline, a method of smoothing using a spline function...
curves). The degree of a surface determines its mathematical properties, and can be seen as representing the shape by a polynomial with variables to the power of the degree value. For example, a surface with a degree of 1 would be a flat cross section
Cross section (geometry)
In geometry, a cross-section is the intersection of a figure in 2-dimensional space with a line, or of a body in 3-dimensional space with a plane, etc...
surface. A surface with degree 2 would be curved in one direction, while a degree 3 surface could (but does not necessarily) change once from concave to convex curvature. Some CAD systems use the term order instead of degree. The order of a polynomial is one greater than the degree, and gives the number of coefficient
Coefficient
In mathematics, a coefficient is a multiplicative factor in some term of an expression ; it is usually a number, but in any case does not involve any variables of the expression...
s rather than the greatest exponent.

Tangent
In geometry, the tangent line to a plane curve at a given point is the straight line that "just touches" the curve at that point. More precisely, a straight line is said to be a tangent of a curve at a point on the curve if the line passes through the point on the curve and has slope where f...
angles and the curvature
Curvature
In mathematics, curvature refers to any of a number of loosely related concepts in different areas of geometry. Intuitively, curvature is the amount by which a geometric object deviates from being flat, or straight in the case of a line, but this is defined in different ways depending on the context...
. In a single patch surface (Bézier surface
Bézier surface
Bézier surfaces are a species of mathematical spline used in computer graphics, computer-aided design, and finite element modeling.As with the Bézier curve, a Bézier surface is defined by a set of control points...
), there is one more pole than the degree values of the surface.
Surface patches can be merged into a single NURBS surface; at these points are knot lines. The number of knots will determine the influence of the poles on either side and how smooth the transition is. The smoothness between patches, known as continuity, is often referred to in terms of a C value:
- C0: just touching, could have a nick
- C1: tangent, but could have sudden change in curvature
- C2: the patches are curvature continuous to one another
Two more important aspects are the U and V parameters. These are values on the surface ranging from 0 to 1, used in the mathematical definition of the surface and for defining paths on the surface: for example, a trimmed boundary edge. Note that they are not proportionally spaced along the surface. A curve of constant U or constant V is known as an isoperimetric curve, or U (V) line. In CAD systems, surfaces are often displayed with their poles of constant U or constant V values connected together by lines; these are known as control polygons.
Modelling
When defining a form, an important factor is the continuity between surfaces - how smoothly they connect to one another.One example of where surfacing excels is automotive body panels. Just blending two curved areas of the panel with different radii of curvature together, maintaining tangential continuity (meaning that the blended surface doesn't change direction suddenly, but smoothly) won't be enough. They need to have a continuous rate of curvature change between the two sections, or else their reflections will appear disconnected.
The continuity is defined using the terms
- G0 – position (touching)
- G1 – tangent (angle)
- G2 – curvature (radius)
- G3 – acceleration (rate of change of curvature)
To achieve a high quality NURBS or Bezier surface, degrees of 5 or greater are generally used. Depending on the product and production process, different levels of accuracy are used but tolerances usually range from 0.02 mm to .001 mm (for example, in the fairing of BIW
Body in White
Body in white or BIW refers to the stage in automotive design or automobile manufacturing in which a car body's sheet metal components have been welded together — but before moving parts the motor, chassis sub-assemblies, or trim have been added and before painting.The name...
concept surfaces to production surface). For ship building, this need not be so tight, but for precision gears and medical devices it is much finer.
History of Terms
The term lofting originally came from the shipbuilding industry where loftsmen worked on "barn loft" type structures to create the keel and bulkhead forms out of wood. This was then passed on to the aircraft then automotive industries who also required streamline shapes.The term spline also has nautical origins coming from East Anglian dialect word for a thin long strip of wood (probably from old English and Germanic word splint).
Freeform Surface Modelling Software
- CATIACATIACATIA is a multi-platform CAD/CAM/CAE commercial software suite developed by the French company Dassault Systemes...
- CobaltCobalt (CAD program)Cobalt is a parametric-based computer-aided design and 3D modeling program that runs on both Macintosh and Microsoft Windows operating systems...
(Ashlar-Vellum) - form•ZForm-Zform·Z is a computer-aided design tool developed by AutoDesSys for all design fields that deal with the articulation of 3D spaces and forms and which is used for 3D modeling, drafting, animation and rendering.-Overview:...
(http:www.formz.com) - SolidworksSolidWorksSolidWorks is a 3D mechanical CAD program that runs on Microsoft Windows and is being developed by Dassault Systèmes SolidWorks Corp., a subsidiary of Dassault Systèmes, S. A. . SolidWorks is currently used by over 1.3 million engineers and designers at more than 130,000 companies worldwide...
- ICEM Surf
- Imageware
- ProEngineer ISDX (http://www.ptc.com/products/creo/interactive-surface-design-extension)
- NX (Unigraphics)NX (Unigraphics)NX, also known as NX Unigraphics or usually just U-G, is an advanced CAD/CAM/CAE software package developed by Siemens PLM Software.It is used, among other tasks, for:* Design...
- ProEngineer
- Rhinoceros 3DRhinoceros 3DRhinoceros is a stand-alone, commercial NURBS-based 3-D modeling tool, developed by Robert McNeel & Associates. The software is commonly used for industrial design, architecture, marine design, jewelry design, automotive design, CAD / CAM, rapid prototyping, reverse engineering as well as the...
- FreeForm Modeling Plus from SensAble Technologies (Sensable.com)
- Autodesk InventorAutodesk InventorAutodesk Inventor, developed by U.S.-based software company Autodesk, is 3D mechanical solid modeling design software for creating 3D digital prototypes used in the design, visualization and simulation of products...
- Alias StudioToolsStudioToolsAutodesk Alias is a family of computer-aided industrial design products starting with Alias Design as the entry-level conceptual design system, progressing to Alias Surface, and then to Alias Automotive as the top-of-the-line product with all of the options.Tools for sketching, modeling and...
- FreeSHIP (FreeSHIP)
- GenesisIOD (GenesisIOD)
- OmniCAD (OmniCAD)
- Thinkdesign (Thinkdesign)
- MicroStation (Bentley Systems Inc)
- Shark FX (Punch!)
- Moi Moment of Inspiration 3D modeling for designers and artists (Moi3d)
See also
- Solid modelling
- Computer representation of surfacesComputer representation of surfacesIn technical applications of 3D computer graphics such as computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing, surfaces are one way of representing objects. The other ways are wireframe and solids...
- Steven Anson CoonsSteven Anson CoonsSteven Anson Coons was an early pioneer in the field of computer graphical methods. He was a professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in the Mechanical Engineering Department...
- NURBS
- Parametric surfaceParametric surfaceA parametric surface is a surface in the Euclidean space R3 which is defined by a parametric equation with two parameters. Parametric representation is the most general way to specify a surface. Surfaces that occur in two of the main theorems of vector calculus, Stokes' theorem and the divergence...

