.gif)
Fort Stanton (Washington, D.C.)
Encyclopedia
Fort Stanton was a Civil War
-era fortification constructed in the hills above Anacostia
in the District of Columbia and was intended to prevent Confederate artillery from threatening the Washington Navy Yard
. It also guarded the approach to the bridge that connected Anacostia (then known as Uniontown) with Washington. Built in 1861, the fort was expanded throughout the war and was joined by two subsidiary forts: Fort Ricketts and Fort Snyder. Following the surrender of the Army of Northern Virginia
, it was dismantled and the land returned to its original owner. It never saw combat. Abandoned after the war, the site of the fort was planned to be part of a grand "Fort Circle" park system encircling the city of Washington. Though this system of interconnected parks never was fully implemented, the site of the fort is today a park maintained by the National Park Service
, and a historical marker stands near the fort's original location.
and that state joining the Confederacy
, Federal troops marched from Washington into the Arlington region of northern Virginia. The move was intended to forestall any attempt by Virginia militia or Confederate soldiers to seize the capital city of the United States. Over the next seven weeks, forts were constructed along the banks of the Potomac River and at the approaches to each of the three major bridges (Chain Bridge, Long Bridge, and Aqueduct Bridge
) connecting Virginia to Washington and Georgetown
.
While the Potomac River forts were being built, planning and surveying was ordered for an enormous new ring of forts to protect the city. Unlike the fortifications under construction, the new forts would defend the city in all directions, not just the most direct route through Arlington. In mid-July, this work was interrupted by the First Battle of Bull Run
. As the Army of Northeastern Virginia
marched south to Manassas
, the soldiers previously assigned to construction duties marched instead to battle. In the days that followed the Union defeat at Bull Run, panicked efforts were made to defend Washington from what was perceived as an imminent Confederate attack. The makeshift trenches and earthworks that resulted were largely confined to Arlington and the direct approaches to Washington.
On July 26, 1861, five days after the battle, Maj. Gen. George B. McClellan
was named commander of the military district of Washington and the subsequently renamed Army of the Potomac
. Upon arriving in Washington, McClellan was appalled by the condition of the city's defenses. "In no quarter were the dispositions for defense such as to offer a vigorous resistance to a respectable body of the enemy, either in the position and numbers of the troops or the number and character of the defensive works... not a single defensive work had been commenced on the Maryland side. There was nothing to prevent the enemy shelling the city from heights within easy range, which could be occupied by a hostile column almost without resistance."
To remedy the situation, one of McClellan's first orders upon taking command was to greatly expand the defenses of Washington. At all points of the compass, forts and entrenchments would be constructed in sufficient strength to defeat any attack. One area of particular concern was the region of Maryland
south of the Anacostia River
. Confederate artillery floated across the Potomac in secret and mounted south of the river could threaten the Washington Navy Yard
and Washington Arsenal, both of which lay at the junction of the Potomac and Anacostia Rivers.
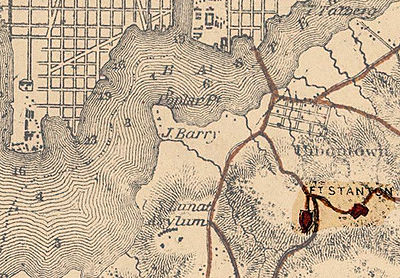 To prevent that threat from coming to pass, Brig. Gen. John G. Barnard
To prevent that threat from coming to pass, Brig. Gen. John G. Barnard
, chief engineer of the defenses of Washington, directed that a line of forts be constructed on the heights southeast of the Anacostia River. From Fort Greble
at the western end to Fort Mahan at the eastern end, the forts along the Eastern Branch River (as the Anacostia was then known) were not intended to constitute a continuous defensive line as was the Arlington Line
that defended the Virginia approaches to the city. Instead, they were merely intended to deny Confederate artillery the position and to provide warning of any sneak attack upon Washington from the southeast. General Barnard illustrated this in an October, 1862 report, saying, "As the enemy cannot enter the city from this direction, the object of the works is to prevent him seizing these heights, and occupying them long enough to shell the navy-yard and arsenal. For this, the works must be made secure against assault, and auxiliary to this object is the construction of roads by which succor can be readily thrown to any point menaced."
Fort Stanton, located in the Garfield Heights, was the first fort of this line to begin construction. Begun in September 1861, the fort was located almost directly south of the Washington Navy Yard and the Navy Yard Bridge that crossed the Anacostia River and connected Uniontown, a suburb of Washington, with the city itself. Work progressed rapidly, and by Christmas
, a report by General Barnard indicated the fort was "completed and armed."
Despite that speed, not everything went in the engineers' favor. Barnard's report indicates "the sites of Fort... Stanton and others were entirely wooded, which, in conjunction with the broken character of the ground, has made the selection of sites frequently very embarrassing and the labor of preparing them very great." The experience of surveying and preparing the site of Fort Stanton would serve the engineers well in the construction of future forts around Washington and in service to the Army of the Potomac. Clearing brush and forest away from the site of Fort Stanton allowed for clear fields of fire for the fort's cannon for several hundred yards in each direction, a technique that would be applied (and later used) to great effect at Fort Stevens
.
The commission had been ordered by Secretary of War
Edwin M. Stanton
to inspect each of the forts surrounding Washington in late 1862 and make a report on the deficiencies of each. In addition to examining Fort Stanton, the commission analyzed two smaller works that supported Fort Stanton. Fort Ricketts was identified in the report as "a battery intended to see the ravine in front of Fort Stanton, which it does but imperfectly," while Fort Snyder "may be regarded as an outwork to Fort Stanton, guarding the head of one branch of the ravine just mentioned. Except additional platforms for field guns, and a ditch in front of the gorge stockade, and blockhouses, nothing further seems necessary."
To support Fort Stanton and its two subsidiary positions, a military road was constructed from Uniontown to the fort. Tributary roads led from Fort Stanton to the other forts in the Eastern Branch line. These roads were eventually widened into a large ring road that circled most of the 37-mile perimeter of Washington, a fact that can be noted in the 1865 map of the city's defenses. In fall 1862, however, the commission examining the defenses noted that "the work on roads about Washington requires ten regiments for twenty days ... or an equivalent of labor in some other shape."
An 1864 inspection by Brig. Gen. Albion P. Howe
, Inspector-General of Artillery, found Fort Stanton to be well-equipped, but the garrison poorly trained. The fort was armed with six 32-pounder barbettes, three 24-pounder field howitzers, four 8-inch siege howitzers, one Coehorn mortar, and one 4-inch rifled mortar. The ammunition was listed as "complete and servicible," but the 131 men of a single company of the Heavy Massachusetts Volunteer Artillery that comprised the garrison at the time were "not drilled in artillery; some in infantry."
Following the Confederate raid on Washington that resulted in the Battle of Fort Stevens
, new assessments were made of weak spots in Washington's defenses. In the three years between the construction of Fort Stanton and the attack on Fort Stevens, Fort Stanton's perimeter had been greatly increased with the addition of two subsidiary forts and additional rifle pits and trenches, as well as the completion of the military ring road. A report by Maj. Gen. Christopher C. Augur
of the U.S. Volunteers recommended Fort Stanton receive one 32-pounder howitzer, two 4½-inch rifled guns, four 12-pounder howitzers, and two 12-pounder Napoleons to bolster its defenses and control its position at the center of the Eastern Branch defenses.
In August 1864, Gen. Barnard was replaced in his capacity as chief engineer of the defenses of Washington by Lt. Col.
Barton S. Alexander
. With the war winding down, Alexander's duties consisted primarily of maintaining and expanding the already-existing defenses, rather than building new forts as Barnard had done. An October 1864 report from Col. Alexander to Brig. Gen. Richard Delafield
, head of the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, lists a series of improvements to Fort Stanton's already-impressive defenses. "Constructing three bastions, two new magazines, bomb-proofs, traverses, platforms, embrasure
s, grading glacis
, and renewing abatis
," the report reads.
's Army of Northern Virginia
on April 9, 1865, the primary reason for manned defenses protecting Washington ceased to exist. Initial recommendations by Col. Alexander, chief engineer of the Washington defenses, were to divide the defenses into three classes: those that should be kept active (first-class), those that should be mothballed and kept in a reserve state (second-class), and those that should be abandoned entirely (third-class). Fort Stanton fell into the first-class category, as it was thought that the fort would be needed to defend the Washington Navy Yard.
Thanks to its status as a first-class fortification, Fort Stanton continued to receive regular maintenance and was continually garrisoned even after the final armistice. Work was even done to strengthen the defenses, as a stockade
was added in the summer of 1865, and the parapets of the fort were re-sodded with fresh grass for better traction and to improve the look of the fortification.
In 1873, journalist George Alfred Townsend
published Washington, Outside and Inside. A Picture and A Narrative of the Origin, Growth, Excellences, Abuses, Beauties, and Personages of Our Governing City, a work that covered the history of Washington from its inception to the then-present day. The Civil War defenses of Washington figure prominently in the later portions of the book, and he uses the state of Fort Stanton as an example of what had become of the forts a decade after they had been built.
and Senate
.
Despite that failure, in 1925 a similar bill passed both the House and Senate, which allowed for the creation of the National Capital Parks Commission (NCPC) to oversee the construction of a Fort Circle of parks similar to that proposed in 1919. The NCPC was authorized to begin purchasing land occupied by the old forts, much of which had been turned over to private ownership following the war. Records indicate that the site of Fort Stanton was purchased for a total of $56,000 in 1926. The duty of purchasing land and constructing the fort parks changed hands several times throughout the 1920s and 1930s, eventually culminating with the Department of the Interior and the National Park Service taking control of the project in the 1940s.
During the Great Depression
, crews from the Civilian Conservation Corps
embarked on projects to improve and maintain the parks, which were still under the control of District authority at that time. At Fort Stanton, CCC members trimmed trees and cleared brush, as well as maintaining and constructing park buildings. Various non-park buildings were also discussed for the land. The City Department of Education proposed building a school on park land, while authorities from the local water utility suggested the construction of a water tower would be suitable for the tall hills of the park. The Second World War interrupted these plans, and post-war budget cuts instituted by President Harry S. Truman
postponed the construction of the Fort Drive once more. Though land for the parks had mostly been purchased, construction of the ring road connecting them was pushed back again and again. Other projects managed to find funding, however. In 1949, President Truman approved a supplemental appropriation request of $175,000 to construct "a swimming pool and associated facilities" at Fort Stanton Park.
By 1963, when President John F. Kennedy
began pushing Congress to finally build the Fort Circle Drive, many in Washington and the National Park Service were openly questioning whether the plan had outgrown its usefulness. After all, by this time, Washington had grown past the ring of forts that had protected it a century earlier, and city surface roads already connected the parks, albeit not in as linear a route as envisioned. The plan to link Fort Stanton Park with other fort parks via a grand drive was quietly dropped in the years that followed.
, a Smithsonian Institution
facility devoted to the history of African-Americans.
American Civil War
The American Civil War was a civil war fought in the United States of America. In response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ; the other 25...
-era fortification constructed in the hills above Anacostia
Anacostia
Anacostia is a historic neighborhood in Washington, D.C. Its historic downtown is located at the intersection of Good Hope Road and Martin Luther King, Jr. Avenue It is the most famous neighborhood in the Southeast quadrant of Washington, located east of the Anacostia River, after which the...
in the District of Columbia and was intended to prevent Confederate artillery from threatening the Washington Navy Yard
Washington Navy Yard
The Washington Navy Yard is the former shipyard and ordnance plant of the United States Navy in Southeast Washington, D.C. It is the oldest shore establishment of the U.S. Navy...
. It also guarded the approach to the bridge that connected Anacostia (then known as Uniontown) with Washington. Built in 1861, the fort was expanded throughout the war and was joined by two subsidiary forts: Fort Ricketts and Fort Snyder. Following the surrender of the Army of Northern Virginia
Army of Northern Virginia
The Army of Northern Virginia was the primary military force of the Confederate States of America in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War, as well as the primary command structure of the Department of Northern Virginia. It was most often arrayed against the Union Army of the Potomac...
, it was dismantled and the land returned to its original owner. It never saw combat. Abandoned after the war, the site of the fort was planned to be part of a grand "Fort Circle" park system encircling the city of Washington. Though this system of interconnected parks never was fully implemented, the site of the fort is today a park maintained by the National Park Service
National Park Service
The National Park Service is the U.S. federal agency that manages all national parks, many national monuments, and other conservation and historical properties with various title designations...
, and a historical marker stands near the fort's original location.
Planning and construction
Following the secession of VirginiaVirginia
The Commonwealth of Virginia , is a U.S. state on the Atlantic Coast of the Southern United States. Virginia is nicknamed the "Old Dominion" and sometimes the "Mother of Presidents" after the eight U.S. presidents born there...
and that state joining the Confederacy
Confederate States of America
The Confederate States of America was a government set up from 1861 to 1865 by 11 Southern slave states of the United States of America that had declared their secession from the U.S...
, Federal troops marched from Washington into the Arlington region of northern Virginia. The move was intended to forestall any attempt by Virginia militia or Confederate soldiers to seize the capital city of the United States. Over the next seven weeks, forts were constructed along the banks of the Potomac River and at the approaches to each of the three major bridges (Chain Bridge, Long Bridge, and Aqueduct Bridge
Potomac Aqueduct Bridge
The Aqueduct Bridge was a bridge between Georgetown, Washington, D.C., and Rosslyn, Virginia, in Arlington County. It was built to transport cargo-carrying boats on the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal in Georgetown across the Potomac River to the Alexandria Canal...
) connecting Virginia to Washington and Georgetown
Georgetown, Maryland
Georgetown is an unincorporated community in Kent County, Maryland, United States. The former Georgetown located in Montgomery County, Maryland, was incorporated into the District of Columbia when it was created in 1790.-References:...
.
While the Potomac River forts were being built, planning and surveying was ordered for an enormous new ring of forts to protect the city. Unlike the fortifications under construction, the new forts would defend the city in all directions, not just the most direct route through Arlington. In mid-July, this work was interrupted by the First Battle of Bull Run
First Battle of Bull Run
First Battle of Bull Run, also known as First Manassas , was fought on July 21, 1861, in Prince William County, Virginia, near the City of Manassas...
. As the Army of Northeastern Virginia
Army of the Potomac
The Army of the Potomac was the major Union Army in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War.-History:The Army of the Potomac was created in 1861, but was then only the size of a corps . Its nucleus was called the Army of Northeastern Virginia, under Brig. Gen...
marched south to Manassas
Manassas, Virginia
The City of Manassas is an independent city surrounded by Prince William County and the independent city of Manassas Park in the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. Its population was 37,821 as of 2010. Manassas also surrounds the county seat for Prince William County but that county...
, the soldiers previously assigned to construction duties marched instead to battle. In the days that followed the Union defeat at Bull Run, panicked efforts were made to defend Washington from what was perceived as an imminent Confederate attack. The makeshift trenches and earthworks that resulted were largely confined to Arlington and the direct approaches to Washington.
On July 26, 1861, five days after the battle, Maj. Gen. George B. McClellan
George B. McClellan
George Brinton McClellan was a major general during the American Civil War. He organized the famous Army of the Potomac and served briefly as the general-in-chief of the Union Army. Early in the war, McClellan played an important role in raising a well-trained and organized army for the Union...
was named commander of the military district of Washington and the subsequently renamed Army of the Potomac
Army of the Potomac
The Army of the Potomac was the major Union Army in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War.-History:The Army of the Potomac was created in 1861, but was then only the size of a corps . Its nucleus was called the Army of Northeastern Virginia, under Brig. Gen...
. Upon arriving in Washington, McClellan was appalled by the condition of the city's defenses. "In no quarter were the dispositions for defense such as to offer a vigorous resistance to a respectable body of the enemy, either in the position and numbers of the troops or the number and character of the defensive works... not a single defensive work had been commenced on the Maryland side. There was nothing to prevent the enemy shelling the city from heights within easy range, which could be occupied by a hostile column almost without resistance."
To remedy the situation, one of McClellan's first orders upon taking command was to greatly expand the defenses of Washington. At all points of the compass, forts and entrenchments would be constructed in sufficient strength to defeat any attack. One area of particular concern was the region of Maryland
Maryland
Maryland is a U.S. state located in the Mid Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware to its east...
south of the Anacostia River
Anacostia River
The Anacostia River is a river in the Mid Atlantic region of the United States. It flows from Prince George's County in Maryland into Washington, D.C., where it joins with the Washington Channel to empty into the Potomac River at Buzzard Point. It is approximately long...
. Confederate artillery floated across the Potomac in secret and mounted south of the river could threaten the Washington Navy Yard
Washington Navy Yard
The Washington Navy Yard is the former shipyard and ordnance plant of the United States Navy in Southeast Washington, D.C. It is the oldest shore establishment of the U.S. Navy...
and Washington Arsenal, both of which lay at the junction of the Potomac and Anacostia Rivers.

John G. Barnard
John Gross Barnard was a career engineering officer in the U.S. Army, serving in the Mexican-American War, as the Superintendent of the United States Military Academy and as a general in the Union Army during the American Civil War...
, chief engineer of the defenses of Washington, directed that a line of forts be constructed on the heights southeast of the Anacostia River. From Fort Greble
Fort Greble
Fort Greble was an American Civil War-era Union fortification constructed as part of the defenses of Washington, D.C. during that war. Named after 1st Lt. John T. Greble, the first West Point graduate killed in the U.S...
at the western end to Fort Mahan at the eastern end, the forts along the Eastern Branch River (as the Anacostia was then known) were not intended to constitute a continuous defensive line as was the Arlington Line
Arlington Line
The Arlington Line was a series of fortifications erected in present-day Arlington County, Virginia, to protect the City of Washington during the American Civil War....
that defended the Virginia approaches to the city. Instead, they were merely intended to deny Confederate artillery the position and to provide warning of any sneak attack upon Washington from the southeast. General Barnard illustrated this in an October, 1862 report, saying, "As the enemy cannot enter the city from this direction, the object of the works is to prevent him seizing these heights, and occupying them long enough to shell the navy-yard and arsenal. For this, the works must be made secure against assault, and auxiliary to this object is the construction of roads by which succor can be readily thrown to any point menaced."
Fort Stanton, located in the Garfield Heights, was the first fort of this line to begin construction. Begun in September 1861, the fort was located almost directly south of the Washington Navy Yard and the Navy Yard Bridge that crossed the Anacostia River and connected Uniontown, a suburb of Washington, with the city itself. Work progressed rapidly, and by Christmas
Christmas
Christmas or Christmas Day is an annual holiday generally celebrated on December 25 by billions of people around the world. It is a Christian feast that commemorates the birth of Jesus Christ, liturgically closing the Advent season and initiating the season of Christmastide, which lasts twelve days...
, a report by General Barnard indicated the fort was "completed and armed."
Despite that speed, not everything went in the engineers' favor. Barnard's report indicates "the sites of Fort... Stanton and others were entirely wooded, which, in conjunction with the broken character of the ground, has made the selection of sites frequently very embarrassing and the labor of preparing them very great." The experience of surveying and preparing the site of Fort Stanton would serve the engineers well in the construction of future forts around Washington and in service to the Army of the Potomac. Clearing brush and forest away from the site of Fort Stanton allowed for clear fields of fire for the fort's cannon for several hundred yards in each direction, a technique that would be applied (and later used) to great effect at Fort Stevens
Fort Stevens
Fort Stevens may refer to one of two decommissioned American military forts:*Fort Stevens , a fort in Oregon that guarded the mouth of the Columbia River...
.
Wartime operation
By the summer of 1862, the fort was already being heavily used. A garrison had been assigned in the winter, and the 1862 report of the Commission to Study the Defenses of Washington describes Fort Stanton as "a work of considerable dimensions, well built, and tolerably well armed. Casemates for reversed fires are recommended in northwest and southwest counterscarp angles, and platforms for two or three rifled guns on the east front. The deep ravine which flanks this work on two sides requires some additional precaution, and further study of it is recommended."The commission had been ordered by Secretary of War
United States Secretary of War
The Secretary of War was a member of the United States President's Cabinet, beginning with George Washington's administration. A similar position, called either "Secretary at War" or "Secretary of War," was appointed to serve the Congress of the Confederation under the Articles of Confederation...
Edwin M. Stanton
Edwin M. Stanton
Edwin McMasters Stanton was an American lawyer and politician who served as Secretary of War under the Lincoln Administration during the American Civil War from 1862–1865...
to inspect each of the forts surrounding Washington in late 1862 and make a report on the deficiencies of each. In addition to examining Fort Stanton, the commission analyzed two smaller works that supported Fort Stanton. Fort Ricketts was identified in the report as "a battery intended to see the ravine in front of Fort Stanton, which it does but imperfectly," while Fort Snyder "may be regarded as an outwork to Fort Stanton, guarding the head of one branch of the ravine just mentioned. Except additional platforms for field guns, and a ditch in front of the gorge stockade, and blockhouses, nothing further seems necessary."
To support Fort Stanton and its two subsidiary positions, a military road was constructed from Uniontown to the fort. Tributary roads led from Fort Stanton to the other forts in the Eastern Branch line. These roads were eventually widened into a large ring road that circled most of the 37-mile perimeter of Washington, a fact that can be noted in the 1865 map of the city's defenses. In fall 1862, however, the commission examining the defenses noted that "the work on roads about Washington requires ten regiments for twenty days ... or an equivalent of labor in some other shape."
An 1864 inspection by Brig. Gen. Albion P. Howe
Albion P. Howe
Albion Parris Howe was a Union Army general in the American Civil War. Howe's contentious relationships with superior officers in the Army of the Potomac eventually led to his being deprived of division command....
, Inspector-General of Artillery, found Fort Stanton to be well-equipped, but the garrison poorly trained. The fort was armed with six 32-pounder barbettes, three 24-pounder field howitzers, four 8-inch siege howitzers, one Coehorn mortar, and one 4-inch rifled mortar. The ammunition was listed as "complete and servicible," but the 131 men of a single company of the Heavy Massachusetts Volunteer Artillery that comprised the garrison at the time were "not drilled in artillery; some in infantry."
Following the Confederate raid on Washington that resulted in the Battle of Fort Stevens
Battle of Fort Stevens
The Battle of Fort Stevens was an American Civil War battle fought July 11–12, 1864, in Northwest Washington, D.C., as part of the Valley Campaigns of 1864 between forces under Confederate Lt. Gen. Jubal A. Early and Union Maj. Gen. Alexander McD. McCook. Although Early caused consternation...
, new assessments were made of weak spots in Washington's defenses. In the three years between the construction of Fort Stanton and the attack on Fort Stevens, Fort Stanton's perimeter had been greatly increased with the addition of two subsidiary forts and additional rifle pits and trenches, as well as the completion of the military ring road. A report by Maj. Gen. Christopher C. Augur
Christopher C. Augur
Christopher Columbus Augur was an American military officer, most noted for his role in the American Civil War. Although less well known than other Union commanders, he was nonetheless considered an able battlefield commander.-Early life:Augur was born in Kendall, New York. He moved with his...
of the U.S. Volunteers recommended Fort Stanton receive one 32-pounder howitzer, two 4½-inch rifled guns, four 12-pounder howitzers, and two 12-pounder Napoleons to bolster its defenses and control its position at the center of the Eastern Branch defenses.
In August 1864, Gen. Barnard was replaced in his capacity as chief engineer of the defenses of Washington by Lt. Col.
Lieutenant Colonel (United States)
In the United States Army, United States Air Force, and United States Marine Corps, a lieutenant colonel is a field grade military officer rank just above the rank of major and just below the rank of colonel. It is equivalent to the naval rank of commander in the other uniformed services.The pay...
Barton S. Alexander
Barton S. Alexander
Barton Stone Alexander was an American engineer commander during the American Civil War who rose to the brevet rank of brigadier general in the regular army. He was a graduate of the U.S...
. With the war winding down, Alexander's duties consisted primarily of maintaining and expanding the already-existing defenses, rather than building new forts as Barnard had done. An October 1864 report from Col. Alexander to Brig. Gen. Richard Delafield
Richard Delafield
Richard Delafield served as superintendent of the United States Military Academy, was Chief of Engineers, and was a major general in the Union Army during the American Civil War.-Biography:...
, head of the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, lists a series of improvements to Fort Stanton's already-impressive defenses. "Constructing three bastions, two new magazines, bomb-proofs, traverses, platforms, embrasure
Embrasure
In military architecture, an embrasure is the opening in a crenellation or battlement between the two raised solid portions or merlons, sometimes called a crenel or crenelle...
s, grading glacis
Glacis
A glacis in military engineering is an artificial slope of earth used in late European fortresses so constructed as to keep any potential assailant under the fire of the defenders until the last possible moment...
, and renewing abatis
Abatis
Abatis, abattis, or abbattis is a term in field fortification for an obstacle formed of the branches of trees laid in a row, with the sharpened tops directed outwards, towards the enemy. The trees are usually interlaced or tied with wire...
," the report reads.
Post-war use
After the surrender of Robert E. LeeRobert E. Lee
Robert Edward Lee was a career military officer who is best known for having commanded the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia in the American Civil War....
's Army of Northern Virginia
Army of Northern Virginia
The Army of Northern Virginia was the primary military force of the Confederate States of America in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War, as well as the primary command structure of the Department of Northern Virginia. It was most often arrayed against the Union Army of the Potomac...
on April 9, 1865, the primary reason for manned defenses protecting Washington ceased to exist. Initial recommendations by Col. Alexander, chief engineer of the Washington defenses, were to divide the defenses into three classes: those that should be kept active (first-class), those that should be mothballed and kept in a reserve state (second-class), and those that should be abandoned entirely (third-class). Fort Stanton fell into the first-class category, as it was thought that the fort would be needed to defend the Washington Navy Yard.
Thanks to its status as a first-class fortification, Fort Stanton continued to receive regular maintenance and was continually garrisoned even after the final armistice. Work was even done to strengthen the defenses, as a stockade
Stockade
A stockade is an enclosure of palisades and tall walls made of logs placed side by side vertically with the tops sharpened to provide security.-Stockade as a security fence:...
was added in the summer of 1865, and the parapets of the fort were re-sodded with fresh grass for better traction and to improve the look of the fortification.
Abandonment
With the conclusion of the fighting, however, military budgets were slashed, and even the forts that were designated for second- and first-class status were deemed surplus. The guns were removed, surplus equipment sold, and the land returned to its original owners. Fort Stanton itself was officially closed on March 20, 1866. Following the closure, the fort was abandoned to the elements, and the woods of Anacostia rapidly reclaimed the land.In 1873, journalist George Alfred Townsend
George Alfred Townsend
George Alfred Townsend , was a noted war correspondent during the American Civil War, and a later novelist. Townsend wrote under the pen name "Gath", which was derived by adding an "H" to his initials, and inspired by the biblical passage II Samuel 1:20, "Tell it not in Gath, publish it not in the...
published Washington, Outside and Inside. A Picture and A Narrative of the Origin, Growth, Excellences, Abuses, Beauties, and Personages of Our Governing City, a work that covered the history of Washington from its inception to the then-present day. The Civil War defenses of Washington figure prominently in the later portions of the book, and he uses the state of Fort Stanton as an example of what had become of the forts a decade after they had been built.
The Fort Circle Parks
The fort remained in a constantly deteriorating condition until 1919, when the Commissioners of the District of Columbia pushed Congress to pass a bill that would consolidate the aging forts into a "Fort Circle" system of parks that would ring the growing city of Washington. As envisioned by the Commissioners, the Fort Circle would be a green ring of parks outside the city, owned by the government, and connected by a "Fort Drive" road in order to allow Washington's citizens to easily escape the confines of the capital. However, the bill allowing for the purchase of the former forts, which had been turned back over to private ownership after the war, failed to pass both the House of RepresentativesUnited States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives is one of the two Houses of the United States Congress, the bicameral legislature which also includes the Senate.The composition and powers of the House are established in Article One of the Constitution...
and Senate
United States Senate
The United States Senate is the upper house of the bicameral legislature of the United States, and together with the United States House of Representatives comprises the United States Congress. The composition and powers of the Senate are established in Article One of the U.S. Constitution. Each...
.
Despite that failure, in 1925 a similar bill passed both the House and Senate, which allowed for the creation of the National Capital Parks Commission (NCPC) to oversee the construction of a Fort Circle of parks similar to that proposed in 1919. The NCPC was authorized to begin purchasing land occupied by the old forts, much of which had been turned over to private ownership following the war. Records indicate that the site of Fort Stanton was purchased for a total of $56,000 in 1926. The duty of purchasing land and constructing the fort parks changed hands several times throughout the 1920s and 1930s, eventually culminating with the Department of the Interior and the National Park Service taking control of the project in the 1940s.
During the Great Depression
Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe worldwide economic depression in the decade preceding World War II. The timing of the Great Depression varied across nations, but in most countries it started in about 1929 and lasted until the late 1930s or early 1940s...
, crews from the Civilian Conservation Corps
Civilian Conservation Corps
The Civilian Conservation Corps was a public work relief program that operated from 1933 to 1942 in the United States for unemployed, unmarried men from relief families, ages 18–25. A part of the New Deal of President Franklin D...
embarked on projects to improve and maintain the parks, which were still under the control of District authority at that time. At Fort Stanton, CCC members trimmed trees and cleared brush, as well as maintaining and constructing park buildings. Various non-park buildings were also discussed for the land. The City Department of Education proposed building a school on park land, while authorities from the local water utility suggested the construction of a water tower would be suitable for the tall hills of the park. The Second World War interrupted these plans, and post-war budget cuts instituted by President Harry S. Truman
Harry S. Truman
Harry S. Truman was the 33rd President of the United States . As President Franklin D. Roosevelt's third vice president and the 34th Vice President of the United States , he succeeded to the presidency on April 12, 1945, when President Roosevelt died less than three months after beginning his...
postponed the construction of the Fort Drive once more. Though land for the parks had mostly been purchased, construction of the ring road connecting them was pushed back again and again. Other projects managed to find funding, however. In 1949, President Truman approved a supplemental appropriation request of $175,000 to construct "a swimming pool and associated facilities" at Fort Stanton Park.
By 1963, when President John F. Kennedy
John F. Kennedy
John Fitzgerald "Jack" Kennedy , often referred to by his initials JFK, was the 35th President of the United States, serving from 1961 until his assassination in 1963....
began pushing Congress to finally build the Fort Circle Drive, many in Washington and the National Park Service were openly questioning whether the plan had outgrown its usefulness. After all, by this time, Washington had grown past the ring of forts that had protected it a century earlier, and city surface roads already connected the parks, albeit not in as linear a route as envisioned. The plan to link Fort Stanton Park with other fort parks via a grand drive was quietly dropped in the years that followed.
Continuing use
Not all the land that made up the site of Fort Stanton was converted to public park land. In 1920, local African-American Catholics constructed Our Lady of Perpetual Help church on land formerly owned by Dr. J.C. Norwood, a local physician. After the remaining grounds of the fort were purchased in 1925, nearby residents reportedly "walked family cows to Fort Stanton Park to graze before the school bell rang." Today, the church still stands adjacent to the grounds of the park. The Washington D.C. Department of Parks and National Parks Service jointly manage the 67 acres of park land that stand on the site of the fort today. D.C. authorities manage approximately 11 acres that contain a recreation center and ball fields, while the National Parks Service manages the remaining acreage, which is mostly wooded and contains the remains of forts Stanton and Ricketts. The area also is site to the Anacostia MuseumAnacostia Museum
The Anacostia Community Museum is a Smithsonian Institution museum in the Anacostia neighborhood of Washington, D.C., United States, opened in 1967...
, a Smithsonian Institution
Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution is an educational and research institute and associated museum complex, administered and funded by the government of the United States and by funds from its endowment, contributions, and profits from its retail operations, concessions, licensing activities, and magazines...
facility devoted to the history of African-Americans.

