FAS ligand
Encyclopedia
Fas ligand is a type-II transmembrane protein
that belongs to the tumor necrosis factor
(TNF) family. Its binding with its receptor induces apoptosis
. Fas ligand/receptor interactions play an important role in the regulation of the immune system
and the progression of cancer
.
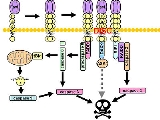
type II transmembrane protein. It signals through trimerization of FasR
, which spans the membrane of the "target" cell. This trimerization usually leads to apoptosis, or cell death.
Soluble Fas ligand is generated by cleaving membrane-bound FasL at a conserved cleavage site by the external matrix metalloproteinase
MMP-7.
(DISC) upon ligand binding. Membrane-anchored Fas ligand trimer on the surface of an adjacent cell causes trimerization of Fas receptor. This event is also mimicked by binding of an agonistic Fas antibody
, though some evidence suggests that the apoptotic signal induced by the antibody is unreliable in the study of Fas signaling. To this end, several clever ways of trimerizing the antibody for in vitro research have been employed.
Upon ensuing death domain (DD) aggregation, the receptor complex is internalized via the cellular endosomal machinery. This allows the adaptor molecule Fas-associated death domain (FADD) to bind the death domain of Fas through its own death domain. FADD also contains a death effector domain
(DED) near its amino terminus, which facilitates binding to the DED of FADD
-like ICE (FLICE), more commonly referred to as caspase-8. FLICE can then self-activate through proteolytic cleavage into p10 and p18 subunits, of which two form the active heterotetramer enzyme. Active caspase-8 is then released from the DISC into the cytosol, where it cleaves other effector caspases, eventually leading to DNA degradation, membrane blebbing, and other hallmarks of apoptosis.
 Some reports have suggested that the extrinsic Fas pathway is sufficient to induce complete apoptosis in certain cell types through DISC assembly and subsequent caspase-8 activation. These cells are dubbed Type 1 cells and are characterized by the inability of anti-apoptotic members of the Bcl-2
Some reports have suggested that the extrinsic Fas pathway is sufficient to induce complete apoptosis in certain cell types through DISC assembly and subsequent caspase-8 activation. These cells are dubbed Type 1 cells and are characterized by the inability of anti-apoptotic members of the Bcl-2
family (namely Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL
) to protect from Fas-mediated apoptosis. Characterized Type 1 cells include H9, CH1, SKW6.4, and SW480, all of which are lymphocyte lineages except the latter, which is of the colon adenocarcinoma lineage.
Evidence for crosstalk between the extrinsic and intrinsic pathways exists in the Fas signal cascade. In most cell types, caspase-8 catalyzes the cleavage of the pro-apoptotic BH3
-only protein Bid
into its truncated form, tBid. BH-3 only members of the Bcl-2 family engage exclusively anti-apoptotic members of the family (Bcl-2, Bcl-xL), allowing Bak
and Bax
to translocate to the outer mitochondrial membrane, thus permeabilizing it and facilitating release of pro-apoptotic proteins such as cytochrome c
and Smac/DIABLO
, an antagonist of inhibitors of apoptosis proteins (IAPs
).
Soluble FasL is less active than its membrane-bound counterpart and does not induce receptor trimerization and DISC
formation.
triggered by Fas-Fas ligand binding plays a fundamental role in the regulation of the immune system
. Its functions include:
(ALPS), a childhood disorder of apoptosis.
with FADD
, Grb2
, Caspase 8
, Fas receptor
, FYN
, EZR, PACSIN2
, FNBP1
and TNFRSF6B
.
Transmembrane protein
A transmembrane protein is a protein that goes from one side of a membrane through to the other side of the membrane. Many TPs function as gateways or "loading docks" to deny or permit the transport of specific substances across the biological membrane, to get into the cell, or out of the cell as...
that belongs to the tumor necrosis factor
Tumor necrosis factors
Tumor necrosis factors refers to a group of cytokines family that can cause cell death . The first two members of the family to be identified were:...
(TNF) family. Its binding with its receptor induces apoptosis
Apoptosis
Apoptosis is the process of programmed cell death that may occur in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, and chromosomal DNA fragmentation...
. Fas ligand/receptor interactions play an important role in the regulation of the immune system
Immune system
An immune system is a system of biological structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease by identifying and killing pathogens and tumor cells. It detects a wide variety of agents, from viruses to parasitic worms, and needs to distinguish them from the organism's own...
and the progression of cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
.
Structure
Fas ligand or FasL is a homotrimericHomotrimer
thumbnail|right|400px|Trimeric form of a TNF-α mutantA Homotrimer is a protein which is composed of three identical units of polypeptide....
type II transmembrane protein. It signals through trimerization of FasR
Fas receptor
The FAS receptor also known as apoptosis antigen 1 , cluster of differentiation 95 or tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNFRSF6 gene....
, which spans the membrane of the "target" cell. This trimerization usually leads to apoptosis, or cell death.
Soluble Fas ligand is generated by cleaving membrane-bound FasL at a conserved cleavage site by the external matrix metalloproteinase
Matrix metalloproteinase
Matrix metalloproteinases are zinc-dependent endopeptidases; other family members are adamalysins, serralysins, and astacins. The MMPs belong to a larger family of proteases known as the metzincin superfamily....
MMP-7.
Receptors
- FasR: The Fas receptorFas receptorThe FAS receptor also known as apoptosis antigen 1 , cluster of differentiation 95 or tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNFRSF6 gene....
(FasR), or CD95, is the most intensely studied member of the death receptor family. The gene is situated on chromosome 10Chromosome 10 (human)125px|rightChromosome 10 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 10 spans about 135 million base pairs and represents between 4 and 4.5 percent of the total DNA in cells.Identifying genes on each chromosome is an active area...
in humans and 19 in mice. Previous reports have identified as many as eight splice variants, which are translated into seven isoformsProtein isoformA protein isoform is any of several different forms of the same protein. Different forms of a protein may be produced from related genes, or may arise from the same gene by alternative splicing. A large number of isoforms are caused by single-nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs, small genetic...
of the protein. Many of these isoforms are rare haplotypes that are usually associated with a state of disease. Apoptosis-inducing Fas receptor is dubbed isoform 1 and is a type 1 transmembrane proteinTransmembrane proteinA transmembrane protein is a protein that goes from one side of a membrane through to the other side of the membrane. Many TPs function as gateways or "loading docks" to deny or permit the transport of specific substances across the biological membrane, to get into the cell, or out of the cell as...
. It consists of three cysteineCysteineCysteine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2SH. It is a non-essential amino acid, which means that it is biosynthesized in humans. Its codons are UGU and UGC. The side chain on cysteine is thiol, which is polar and thus cysteine is usually classified as a hydrophilic amino acid...
-rich pseudorepeats, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular death domain.
- DcR3: Decoy receptor 3 (DcR3) is a recently discovered decoy receptor of the tumor necrosis factorTumor necrosis factorsTumor necrosis factors refers to a group of cytokines family that can cause cell death . The first two members of the family to be identified were:...
superfamily that binds to FasL, LIGHTLightLight or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light has wavelength in a range from about 380 nanometres to about 740 nm, with a frequency range of about 405 THz to 790 THz...
, and TLA1. DcR3 is a soluble receptor that has no signal transductionSignal transductionSignal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a cell surface receptor. In turn, this receptor alters intracellular molecules creating a response...
capabilities (hence a "decoy") and functions to prevent FasR-FasL interactions by competitively binding to membrane-bound Fas ligand and rendering them inactive.
Cell signaling
Fas forms the Death-Inducing Signaling ComplexDeath-inducing signaling complex
The death-inducing signaling complex or DISC is a multi-protein complex formed by members of the "death receptor" family of apoptosis-inducing cellular receptors. A typical example is FasR, which forms the DISC upon trimerization as a result of its ligand binding. Dogma states that the DISC is...
(DISC) upon ligand binding. Membrane-anchored Fas ligand trimer on the surface of an adjacent cell causes trimerization of Fas receptor. This event is also mimicked by binding of an agonistic Fas antibody
Antibody
An antibody, also known as an immunoglobulin, is a large Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique part of the foreign target, termed an antigen...
, though some evidence suggests that the apoptotic signal induced by the antibody is unreliable in the study of Fas signaling. To this end, several clever ways of trimerizing the antibody for in vitro research have been employed.
Upon ensuing death domain (DD) aggregation, the receptor complex is internalized via the cellular endosomal machinery. This allows the adaptor molecule Fas-associated death domain (FADD) to bind the death domain of Fas through its own death domain. FADD also contains a death effector domain
Death effector domain
The death-effector domain is a protein interaction domain found to regulate a variety of cellular signalling pathways. The DED domain is found in inactive procaspases and proteins that regulate caspase activation in the apoptosis cascade such as FAS-associating death domain-containing protein...
(DED) near its amino terminus, which facilitates binding to the DED of FADD
FADD
Fas-Associated protein with Death Domain is an adaptor molecule that bridges the Fas-receptor, and other death receptors, to caspase-8 through its death domain to form the death-inducing signaling complex during apoptosis. -Signalling:...
-like ICE (FLICE), more commonly referred to as caspase-8. FLICE can then self-activate through proteolytic cleavage into p10 and p18 subunits, of which two form the active heterotetramer enzyme. Active caspase-8 is then released from the DISC into the cytosol, where it cleaves other effector caspases, eventually leading to DNA degradation, membrane blebbing, and other hallmarks of apoptosis.

Bcl-2
Bcl-2 is the founding member of the Bcl-2 family of apoptosis regulator proteins encoded by the BCL2 gene. Bcl-2 derives its name from B-cell lymphoma 2, as it is the second member of a range of proteins initially described in chromosomal translocations involving chromosomes 14 and 18 in...
family (namely Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL
Bcl-xL
B-cell lymphoma-extra large is a transmembrane molecule in the mitochondria. It is involved in the signal transduction pathway of the FAS-L. It is one of several anti-apoptotic proteins which are members of the Bcl-2 family of proteins. It has been implicated in the survival of cancer cells. Other...
) to protect from Fas-mediated apoptosis. Characterized Type 1 cells include H9, CH1, SKW6.4, and SW480, all of which are lymphocyte lineages except the latter, which is of the colon adenocarcinoma lineage.
Evidence for crosstalk between the extrinsic and intrinsic pathways exists in the Fas signal cascade. In most cell types, caspase-8 catalyzes the cleavage of the pro-apoptotic BH3
Bcl-2
Bcl-2 is the founding member of the Bcl-2 family of apoptosis regulator proteins encoded by the BCL2 gene. Bcl-2 derives its name from B-cell lymphoma 2, as it is the second member of a range of proteins initially described in chromosomal translocations involving chromosomes 14 and 18 in...
-only protein Bid
BH3 interacting domain death agonist
The BH3 interacting-domain death agonist, or BID, gene is a pro-apoptotic member of the Bcl-2 protein family. Bcl-2 family members share one or more of the four characteristic domains of homology entitled the Bcl-2 homology domains , and can form hetero- or homodimers...
into its truncated form, tBid. BH-3 only members of the Bcl-2 family engage exclusively anti-apoptotic members of the family (Bcl-2, Bcl-xL), allowing Bak
Bcl-2 homologous antagonist killer
Bcl-2 homologous antagonist/killer is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BAK1 gene. BAK1 orthologs have been identified in most mammals for which complete genome data are available....
and Bax
Bcl-2-associated X protein
The Bcl-2–associated X protein, or Bax is a protein of the Bcl-2 gene family. It promotes apoptosis by competing with Bcl-2 proper.The BAX gene was the first identified pro-apoptotic member of the Bcl-2 protein family....
to translocate to the outer mitochondrial membrane, thus permeabilizing it and facilitating release of pro-apoptotic proteins such as cytochrome c
Cytochrome c
The Cytochrome complex, or cyt c is a small heme protein found loosely associated with the inner membrane of the mitochondrion. It belongs to the cytochrome c family of proteins. Cytochrome c is a highly soluble protein, unlike other cytochromes, with a solubility of about 100 g/L and is an...
and Smac/DIABLO
Diablo homolog
Diablo homolog, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DIABLO gene . DIABLO is also referred to as second mitochondria-derived activator of caspases or SMAC.- Function :...
, an antagonist of inhibitors of apoptosis proteins (IAPs
Inhibitor of apoptosis
The Inhibitors of Apoptosis are a family of functionally- and structurally-related proteins, which serve as endogenous inhibitors of programmed cell death . A common feature of all IAPs is the presence of a BIR in one to three copies...
).
Soluble FasL is less active than its membrane-bound counterpart and does not induce receptor trimerization and DISC
Death-inducing signaling complex
The death-inducing signaling complex or DISC is a multi-protein complex formed by members of the "death receptor" family of apoptosis-inducing cellular receptors. A typical example is FasR, which forms the DISC upon trimerization as a result of its ligand binding. Dogma states that the DISC is...
formation.
Functions
ApoptosisApoptosis
Apoptosis is the process of programmed cell death that may occur in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, and chromosomal DNA fragmentation...
triggered by Fas-Fas ligand binding plays a fundamental role in the regulation of the immune system
Immune system
An immune system is a system of biological structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease by identifying and killing pathogens and tumor cells. It detects a wide variety of agents, from viruses to parasitic worms, and needs to distinguish them from the organism's own...
. Its functions include:
- T-cell homeostasisHomeostasisHomeostasis is the property of a system that regulates its internal environment and tends to maintain a stable, constant condition of properties like temperature or pH...
: the activation of T-cells leads to their expression of the Fas ligand. T cells are initially resistant to Fas-mediated apoptosis during clonal expansion, but become progressively more sensitive the longer they are activated, ultimately resulting in activation-induced cell death (AICD). This process is needed to prevent an excessive immune response and eliminate autoreactive T-cells. Humans and mice with deleterious mutations of Fas or Fas ligand develop an accumulation of aberrant T-cells, leading to lymphadenopathyLymphadenopathyLymphadenopathy is a term meaning "disease of the lymph nodes." It is, however, almost synonymously used with "swollen/enlarged lymph nodes". It could be due to infection, auto-immune disease, or malignancy....
, splenomegalySplenomegalySplenomegaly is an enlargement of the spleen. The spleen usually lies in the left upper quadrant of the human abdomen. It is one of the four cardinal signs of hypersplenism, some reduction in the number of circulating blood cells affecting granulocytes, erythrocytes or platelets in any...
, and lupus erythematosusLupus erythematosusLupus erythematosus is a category for a collection of diseases with similar underlying problems with immunity . Symptoms of these diseases can affect many different body systems, including joints, skin, kidneys, blood cells, heart, and lungs...
. - Cytotoxic T-cell activity: Fas-induced apoptosisApoptosisApoptosis is the process of programmed cell death that may occur in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, and chromosomal DNA fragmentation...
and the perforinPerforinPerforin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PRF1 gene.- Function :Perforin is a cytolytic protein found in the granules of CD8 T-cells and NK cells. Upon degranulation, perforin inserts itself into the target cell's plasma membrane, forming a pore. The lytic membrane-inserting part...
pathway are the two main mechanisms by which cytotoxic T lymphocytes induce cell death in cells expressing foreign antigens. - Immune privilegeImmune privilegeImmune privilege is a term used to describe certain sites in the body which are able to tolerate the introduction of antigen without eliciting an inflammatory immune response. Tissue grafts are normally recognised as foreign antigen by the body and attacked by the immune system...
: Cells in immune privileged areas such as the corneaCorneaThe cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Together with the lens, the cornea refracts light, with the cornea accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical power. In humans, the refractive power of the cornea is...
or testes express Fas ligand and induce the apoptosis of infiltrating lymphocytes. It is one of many mechanisms the body employs in the establishment and maintenance of immune privilege. - Maternal tolerance: Fas ligand may be instrumental in the prevention of leukocyte trafficking between the mother and the fetus, although no pregnancy defects have yet been attributed to a faulty Fas-Fas ligand system.
- Tumor counterattack: Tumors may over-express Fas ligand and induce the apoptosisApoptosisApoptosis is the process of programmed cell death that may occur in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, and chromosomal DNA fragmentation...
of infiltrating lymphocytes, allowing the tumor to escape the effects of an immune response. The up-regulation of Fas ligand often occurs following chemotherapyChemotherapyChemotherapy is the treatment of cancer with an antineoplastic drug or with a combination of such drugs into a standardized treatment regimen....
, from which the tumor cells have attained apoptosisApoptosisApoptosis is the process of programmed cell death that may occur in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, and chromosomal DNA fragmentation...
resistance.
Role in disease
Defective Fas-mediated apoptosis may lead to oncogenesis as well as drug resistance in existing tumors. Germline mutation of Fas is associated with autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndromeAutoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome
Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome is a form of lymphoproliferative disorder. It affects lymphocyte apoptosis. It is a RASopathy.-Introduction:...
(ALPS), a childhood disorder of apoptosis.
Interactions
Fas ligand has been shown to interactProtein-protein interaction
Protein–protein interactions occur when two or more proteins bind together, often to carry out their biological function. Many of the most important molecular processes in the cell such as DNA replication are carried out by large molecular machines that are built from a large number of protein...
with FADD
FADD
Fas-Associated protein with Death Domain is an adaptor molecule that bridges the Fas-receptor, and other death receptors, to caspase-8 through its death domain to form the death-inducing signaling complex during apoptosis. -Signalling:...
, Grb2
Grb2
Growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 also known as Grb2 is an adaptor protein involved in signal transduction/cell communication. In humans, the GRB2 protein is encoded by the GRB2 gene....
, Caspase 8
Caspase 8
Caspase 8 is a caspase protein, encoded by the CASP8 gene. It most likely acts upon caspase 3.CASP8 orthologs have been identified in numerous mammals for which complete genome data are available...
, Fas receptor
Fas receptor
The FAS receptor also known as apoptosis antigen 1 , cluster of differentiation 95 or tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNFRSF6 gene....
, FYN
FYN
Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the FYN gene.This gene is a member of the protein-tyrosine kinase oncogene family. It encodes a membrane-associated tyrosine kinase that has been implicated in the control of cell growth...
, EZR, PACSIN2
PACSIN2
Protein kinase C and casein kinase substrate in neurons protein 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PACSIN2 gene.-Interactions:PACSIN2 has been shown to interact with PACSIN1, PACSIN3 and Fas ligand.-Further reading:...
, FNBP1
FNBP1
Formin-binding protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FNBP1 gene.-Interactions:FNBP1 has been shown to interact with SNX2, DNM1, TNKS, Fas ligand and AKAP9.-Further reading:...
and TNFRSF6B
TNFRSF6B
Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 6B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNFRSF6B gene.-Interactions:TNFRSF6B has been shown to interact with TNFSF14 and Fas ligand.-External links:*...
.

