
DVD-Video
Encyclopedia
DVD-Video is a consumer video format used to store digital video on DVD
discs, and is currently the dominant consumer video format in Asia
, North America
, Europe
, and Australia
. Discs using the DVD-Video specification require a DVD drive and a MPEG-2
decoder (e.g., a DVD player, or a computer DVD drive with a software DVD player). Commercial DVD movies are encoded using a combination of MPEG-2 compressed video and audio of varying formats (often multi-channel formats as described below). Typically, the data rate for DVD movies ranges from 3 Mbit/s to 9.5 Mbit/s, and the bit rate
is usually adaptive. It was first available for retail around 1997.
The DVD-Video specification was created by DVD Forum
and can be obtained from DVD Format/Logo Licensing Corporation for a fee of $5,000. The specification is not publicly available, because every subscriber must sign a non-disclosure agreement
. Certain information in the DVD Book is proprietary and confidential.
compression at up to 9.8 Mbit/s (9,800 kbit/s) or MPEG-1
compression at up to 1.856 Mbit/s (1,856 kbit/s).
The following formats are allowed for MPEG-2 video:
The following formats are allowed for MPEG-1 video:
Video with 4:3 frame aspect ratio is supported in all video modes. Widescreen video is supported only in full D1 resolutions.
MPEG-1 formats do not support interlaced video; content must be progressive-scan only. MPEG-2 formats support both interlaced and progressive-scan content.
MPEG-2 also supports numerous video stream flags, used to note scan type, field order, and other effects. In particular, this allows the encoding of 23.976 frame per second video using pulldown. Because MPEG-1 video lacks these flags, it cannot be used to encode 23.976 frame/s content for DVD-Video.
MPEG-2 video flags also have numerous additional uses. A DVD player uses these flags to convert progressive content into interlaced video suitable for interlaced TV sets. These flags also help reproducing progressive content on progressive-scan television sets.
, DTS, MPEG-1 Audio Layer II
(MP2), or Dolby Digital
(AC-3) format. In countries using the PAL
system standard DVD-Video releases must contain at least one audio track using the PCM, MP2, or AC-3 format, and all standard PAL players must support all three of these formats. A similar standard exists in countries using the NTSC
system, though with no requirement mandating the use of or support for the MP2 format. DTS audio is optional for all players, as DTS was not part of the initial draft standard and was added later; thus, many early players are unable to play DTS audio tracks. The vast majority of commercial DVD-Video releases today employ AC-3
audio. The official allowed formats for the audio tracks on a DVD Video are:
DVDs can contain more than one channel of audio to go together with the video content, supporting a maximum of 8 simultaneous audio tracks per video. This is most commonly used for different audio formats—DTS 5.1, AC-3 2.0 etc.—as well as for commentary and audio tracks in different languages.
Professionally encoded videos average a bitrate of 4-5 Mbit/s with a maximum of 7–8 Mbit/s in high-action scenes. This is typically done to allow greater compatibility amongst players, and to help prevent buffer underrun
s in the case of dirty or scratched discs.
Columbia TriStar Home Entertainment
has created a line of DVDs (dubbed "Superbit
") aiming to maximize picture quality by eliminating multiple languages, angles, and audio tracks. This allows average bitrates closer to 6 Mbit/s.
and SVCD
. While VCD and CVD video is supported by the DVD standard, neither SVCD video nor VCD, CVD, or SVCD audio is compatible with the DVD standard.
Some hardware players will also play DVD-ROMs or CD-ROM
s containing "raw" MPEG video files; these are "unauthored" and lack the file
and header structure that defines DVD-Video. Standard DVD-Video files contain extra information (such as the number of video tracks, chapters and links to extra features) that DVD players use to navigate the disc.
The maximum chapters allowed per title is 99 and the maximum titles allowed per DVD is 99.
file systems.
The UDF bridge format provides backwards compatibility for operating systems that support only ISO 9660. Most (and new) DVD players read the UDF filesystem from a DVD-Video disc and ignore the ISO9660 filesystem.
IFO
files store control and playback information – e.g. information about chapters, subtitles and audio tracks. They do not store any video or audio data or subtitles.
BUP
files are only backups of the IFO files.
container format (Video Object). VOB is based on the MPEG program stream format, but with additional limitations and specifications in the private streams. The MPEG program stream has provisions for non-standard data (as AC-3, DTS, LPCM or subtitles used in VOB files) in the form of so-called private streams. VOB files are a very strict subset of the MPEG program stream standard. While all VOB files are MPEG program streams, not all MPEG program streams comply with the definition for a VOB file.
DVD recorder
s can use DVD-VR
or DVD+VR
format instead of DVD-Video. DVD-VR format store multiplexed audiovisual content in VRO containers. VRO file is an equivalent to a collection of DVD-Video VOB files. Fragmented VRO files are not widely supported by hardware or software players and video editing software. DVD+VR standard defines a logical format for DVD-Video compliant recording on optical discs and is commonly used on DVD+R/RW media.
or subpicture tracks. Subtitles are usually intended as a visual help for the deaf and hearing impaired and for translating dialogs.
Subtitles can serve other purposes as well. For example, in the DVD release of Thirteen Days
one of the subtitle tracks includes history notes, giving additional information timed to the events depicted in the film. In the release of For All Mankind
subtitles display names of the NASA missions and names of the people shown on the screen.
Subtitles are stored as bitmap
images and therefore can contain messages in any language. Subtitles are restricted to four colors, including transparent "color", and thus tend to look cruder than permanent subtitles on film. Transparency allows laying subtitles over the video during playback. The subtitle tracks are contained within the VOB
file of the DVD.
DVD Video may also contain closed captioning
material which can only be viewed on a television set with a decoder.
, and the scrolling text in the openings of the Star Wars
films). Multiple angles have found a niche in markets such as yoga
and erotica
.
features, commonly about the making of the main title; deleted scene
s; photo galleries; storyboards; isolated music scores
; trivia text commentary; simple games; film shorts; TV spots; radio spots; theatrical trailers which were used to promote the main title; and teaser trailer
s advertising related movies or DVDs.
Extra features often provide entertainment or add depth and understanding to the film. Games, bloopers, and galleries provide entertainment, especially for younger ages. Deleted scenes and alternative endings allow the audience to view additional content which was not included in a theatrical release. Directors cuts allow the audience to see how the director envisioned the main title without the constraints which are placed on a theatrical release.
Other extras that can be included on DVDs are motion menus, still pictures, up to 32 selectable subtitles, seamless branching
for multiple storylines, up to 9 camera angles, and DVD-ROM / data files that can be accessed on a computer.
Extra features require additional storage space, which often means encoding the main title with lower than possible data rate to fit both the main title and the extras on one disc. Lower data rate may decrease visual and sound quality, which manifests itself in various digital artifact
s. To maintain quality the main title and the extras may be released on several discs, or the extras may be omitted completely like in the "Superbit
" line of DVDs.
, Content Scramble System
(CSS), region codes
, and disabled user operations
(UOPs). There are also anti-ripping techniques intended to foil ripping software
.
, TotalMedia Theatre, PowerDVD
, VLC
or WinDVD
to be able to view the disc in a computer system.
CSS does not make it more difficult (anymore) to copy the digital content now that a decoder (DeCSS
) has been released, nor possible to distinguish between legal and illegal copies of a work, but it does restrict the playback software that may be used.
CSS has caused major problems for the inclusion of DVD players in any open source
operating systems, since open source player implementations are not officially given access to the decryption keys or license to the patent
s involved in CSS. Proprietary software
players were also difficult to find on some platforms. However, a successful effort has been made to write a decoder by reverse engineering
, resulting in DeCSS
. This has led to long-running legal battles and the arrest of some of those involved in creating or distributing the DeCSS code, through the use of the controversial U.S. Digital Millennium Copyright Act
(DMCA), on the grounds that such software could also be used to facilitate unauthorized copying of the data on the discs. The Videolan
team, however, went on to make the libdvdcss
library. Unlike DeCSS, libdvdcss can access a CSS-encypted DVD without the need of a cracked key, thus enabling playback of such discs on opensource players without legal restraints (although DVD rippers using this library may still be subject to restrictions).
The DMCA currently affects only the United States
, however many other countries are signatories to the similar WIPO Treaty
. In some countries it is not illegal to use de-scrambling software to bypass the DVD restrictions. A number of software programs have since appeared on the Web to view DVDs on a number of different platforms.
Other measures such as anti-ripping, as well as U.S. and non-U.S. copyright
law, may be used to prevent making unauthorized copies of DVDs. CSS decrypting software, or ripping software, such as DVD Decrypter
, AnyDVD
, MacTheRipper
, and DVD Shrink
allows a disc to be copied to hard disk unscrambled. Some DeCSS applications also remove Macrovision
, region codes
, and disabled user operations (UOPs).
, Macrovision RipGuard, X-protect, ProtectDisc SecureBurn, Anaho, Fortium, and others. All of these methods have been circumvented (as might have been expected, since all standard DVD players naturally circumvent them to play and navigate the discs normally). Riplock
is a feature that reduces drive noise during playback but inadvertently reduces ripping speed.
players ignore UOPs and some DVD "re-authoring" software packages allow the user to produce a copy without these restrictions. The legality of these activities varies by jurisdiction and is the subject of debate. (See fair use
.)
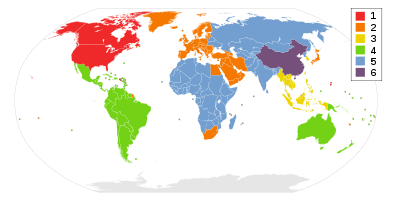 Each DVD-Video disc contains one or more region codes, denoting the area(s) of the world in which distribution and playback are intended. The commercial DVD player specification dictates that a player must only play discs that contain its region code. In theory, this allows the motion picture studios to control the various aspects of a release (including content, date and price) on a region-by-region basis, or ensure the success of "staggered" or delayed cinema releases from country to country. For example, the British movie 28 Days Later
Each DVD-Video disc contains one or more region codes, denoting the area(s) of the world in which distribution and playback are intended. The commercial DVD player specification dictates that a player must only play discs that contain its region code. In theory, this allows the motion picture studios to control the various aspects of a release (including content, date and price) on a region-by-region basis, or ensure the success of "staggered" or delayed cinema releases from country to country. For example, the British movie 28 Days Later
was released on DVD in Europe several months prior to the film's release in North American movie theaters. Regional coding kept the European DVD unplayable for most North American consumers, thereby ensuring that ticket sales would be relatively unaffected.
In practice, many DVD players allow playback of any disc, or can be modified to do so. Entirely independent of encryption, region coding pertains to regional lockout
, which originated in the video game industry.
From a worldwide perspective regional coding may be seen as a failure. A huge percentage of players outside of North America can be easily modified (and are even sold pre-modified by mainstream stores such as Amazon.co.uk) to ignore the regional codes on a disc. This, coupled with the fact that almost all televisions in Europe and Australasia
are capable of displaying NTSC video (at the very least, in black and white), means that consumers in these regions have a huge choice of discs. Contrary to popular belief, this practice is not illegal and in some countries that strongly support free trade it is encouraged.
A normal DVD player can only play region-coded discs designated for the player's own particular region. However, a code-free or region-free DVD player is capable of playing DVDs from any of the six regions around the world.
The CSS
license prohibits manufacturing of DVD players that are not set to a single region by default. While the same license prohibits manufacturers from including prominent interfaces to change the region setting it does not clearly prevent them from including "hidden" menus that enable the player's region to be changed; as such, many high-end models in the U.S. include password-protected or otherwise hidden methods to enable multi-region playback. Conversely in the UK and Ireland many cheap DVD players are multi-region while more expensive systems, including the majority of home cinema
systems, are preset to play only region 2 discs.
In China, DVD-Videos for television series are usually released in MPEG-1 video, with MP2 audio. By forgoing Dolby standards, manufacturers cut costs considerably; encoding in lower bit-rates also allows a TV series to be squeezed onto fewer discs. There are no region coding in such cases.
There are also two additional region codes, region 7, which is reserved, and region 8, which is used exclusively for passenger transport such as airlines and cruise ships.
implemented by the DVD player runs bytecode
contained on the DVD. This is used to control playback and display special effects on the menus. The instruction set
is called the Virtual Machine (VM) DVD command set. There are 16 general parameter registers (GPRM) to hold temporary values and 24 system parameters (SPRM). As a result of a moderately flexible programming interface, DVD players can be used to play games, such as the DVD re-release of Dragon's Lair
, along with more sophisticated and advanced games such as Scene It, all of which can be run on standard DVD players.
s often support additional formats, including DVD+/-R/RW, CD-R/RW, MP3
, WMA
, SVCD
, JPEG
, PNG, SVG
, KAR
and MPEG-4
(DivX
/Xvid
). Some also include USB
ports or flash memory
readers. Player prices range from as low as US$
20 (GB£
10) to as high as US$2,700 (GB£1,350).
DVD drives for computers usually come with one of two kinds of Regional Playback Control
(RPC), either RPC-1 or RPC-2. This is used to enforce the publisher's restrictions on what regions of the world the DVD can be played. (See Regional lockout
and DVD region code
s.) While Open source
software DVD players allow everything, commercial ones (both standalone models and software players) come further encumbered with restrictions forbidding the viewer from skipping (or in some cases fast-forwarding) certain content such as copyright warnings or advertisements. (See User operation prohibition
.)
Video game systems with DVD-Video playback functionality are PlayStation 2
, PlayStation 3
, Xbox
(additional remote required), Xbox 360
, Panasonic Q
, and Wii
(with an unsupported hack).
extension to DVD. However hDVD failed to gain much popularity.
On November 18, 2003, the Chinese news agency Xinhua
reported the final standard of the Chinese government-sponsored Enhanced Versatile Disc
(EVD) which is another extension of standard DVD. Shortly thereafter the development of the format was halted by a licensing dispute between Chinese companies and On2 Technologies
, but on December 6, 2006, 20 Chinese electronic firms unveiled 54 prototype EVD players and announced their intention for the format to completely replace DVDs in China by 2008. However, due to a lack of sales, support for EVD has recently been dropped by the Xinhua Bookstore in Wuhan
, which was a major supporter of the format.
and Blu-ray, were introduced in 2006. The HD DVD format, promoted by Toshiba, had the backing by the DVD Forum
, which voted to make it the official successor to DVD. Opposing HD DVD was the Blu-ray format, led by the Blu-ray Disc Association
, which shares many of the same members.
Despite HD DVD's slight market lead and earlier introduction to the retail market (March 2006 vs June 2006), both formats engaged in a brief format war
. Industry analysts likened the situation to the VHS/Betamax format war
of the 1980s. But this time, consumer awareness of either high-definition format was severely limited, with the end result that most consumers avoided both formats, already content with DVD. Toshiba capitulated in February 2008, citing low demand for HD DVD and the faster growth of Blu-ray, among other reasons. Toshiba ended production of their HD DVD players and discontinued promotion of the format, while the HD DVD movie release schedule concluded by June 2008.
As of February 2009, Blu-ray disc is the de facto high-definition optical disc format. However, sales figures suggest DVD is in no immediate danger of disappearing. Until households acquire high-definition-capable displays, they have no reason to switch to Blu-ray (other than more data capacity and less disc scratching), while households which are already equipped with HD-capable displays overwhelmingly have access to competing sources of HD video, from traditional subscription-based cable or satellite TV, to the fast growing market of Internet-hosted video-download services.
All standard DVDs will play on existing Blu-ray players, making the switch to Blu-ray much easier than the switch from VHS to DVD. In addition, a growing number of hardware vendors are enhancing their Blu-ray players with Internet connectivity for subscription-based video downloads.
. While the Blu-ray format is marketed internationally, CBHDs have sold significantly in the Chinese market.
DVD
A DVD is an optical disc storage media format, invented and developed by Philips, Sony, Toshiba, and Panasonic in 1995. DVDs offer higher storage capacity than Compact Discs while having the same dimensions....
discs, and is currently the dominant consumer video format in Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
, North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
, Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
, and Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
. Discs using the DVD-Video specification require a DVD drive and a MPEG-2
MPEG-2
MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission...
decoder (e.g., a DVD player, or a computer DVD drive with a software DVD player). Commercial DVD movies are encoded using a combination of MPEG-2 compressed video and audio of varying formats (often multi-channel formats as described below). Typically, the data rate for DVD movies ranges from 3 Mbit/s to 9.5 Mbit/s, and the bit rate
Bit rate
In telecommunications and computing, bit rate is the number of bits that are conveyed or processed per unit of time....
is usually adaptive. It was first available for retail around 1997.
The DVD-Video specification was created by DVD Forum
DVD Forum
The DVD Forum is an international organization composed of hardware, software, media and content companies that use and develop the DVD and formerly HD DVD formats...
and can be obtained from DVD Format/Logo Licensing Corporation for a fee of $5,000. The specification is not publicly available, because every subscriber must sign a non-disclosure agreement
Non-disclosure agreement
A non-disclosure agreement , also known as a confidentiality agreement , confidential disclosure agreement , proprietary information agreement , or secrecy agreement, is a legal contract between at least two parties that outlines confidential material, knowledge, or information that the parties...
. Certain information in the DVD Book is proprietary and confidential.
Frame size and frame rate
To record moving pictures, DVD-Video uses either MPEG-2MPEG-2
MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission...
compression at up to 9.8 Mbit/s (9,800 kbit/s) or MPEG-1
MPEG-1
MPEG-1 is a standard for lossy compression of video and audio. It is designed to compress VHS-quality raw digital video and CD audio down to 1.5 Mbit/s without excessive quality loss, making video CDs, digital cable/satellite TV and digital audio broadcasting possible.Today, MPEG-1 has become...
compression at up to 1.856 Mbit/s (1,856 kbit/s).
The following formats are allowed for MPEG-2 video:
- At 25 frames per second (commonly used in regions with 50 Hz image scanning576i576i is a standard-definition video mode used in PAL and SECAM countries. In digital applications it is usually referred to as "576i", in analogue contexts it is often quoted as "625 lines"...
frequency):
- 720 × 576 pixels (same resolution as D-1)
- 704 × 576 pixels
- 352 × 576 pixels (same as the China Video Disc standard)
- 352 x 288 pixels
- At 29.97 frames per second (commonly used in regions with 60 Hz image scanning480i480i is the shorthand name for a video mode, namely the US NTSC television system or digital television systems with the same characteristics. The i, which is sometimes uppercase, stands for interlaced, the 480 for a vertical frame resolution of 480 lines containing picture information; while NTSC...
frequency):
- 720 × 480 pixels (same resolution as D-1)
- 704 × 480 pixels
- 352 × 480 pixels (same as the China Video Disc standard)
- 352 x 240 pixels
The following formats are allowed for MPEG-1 video:
- 352 × 288 pixels at 25 frame/s, progressiveProgressive scanProgressive scanning is a way of displaying, storing, or transmitting moving images in which all the lines of each frame are drawn in sequence...
(Same as the VCDVideo CDBefore the advent of DVD and Blu-ray, the Video CD became the first format for distributing films on standard 120 mm optical discs. The format is a standard digital format for storing video on a Compact Disc...
Standard) - 352 × 240 pixels at 29.97 frame/s, progressive (Same as the VCDVideo CDBefore the advent of DVD and Blu-ray, the Video CD became the first format for distributing films on standard 120 mm optical discs. The format is a standard digital format for storing video on a Compact Disc...
Standard)
Video with 4:3 frame aspect ratio is supported in all video modes. Widescreen video is supported only in full D1 resolutions.
MPEG-1 formats do not support interlaced video; content must be progressive-scan only. MPEG-2 formats support both interlaced and progressive-scan content.
MPEG-2 also supports numerous video stream flags, used to note scan type, field order, and other effects. In particular, this allows the encoding of 23.976 frame per second video using pulldown. Because MPEG-1 video lacks these flags, it cannot be used to encode 23.976 frame/s content for DVD-Video.
MPEG-2 video flags also have numerous additional uses. A DVD player uses these flags to convert progressive content into interlaced video suitable for interlaced TV sets. These flags also help reproducing progressive content on progressive-scan television sets.
Audio data
The audio data on a DVD movie can be PCMPulse-code modulation
Pulse-code modulation is a method used to digitally represent sampled analog signals. It is the standard form for digital audio in computers and various Blu-ray, Compact Disc and DVD formats, as well as other uses such as digital telephone systems...
, DTS, MPEG-1 Audio Layer II
MPEG-1 Audio Layer II
MPEG-1 Audio Layer II or MPEG-2 Audio Layer II is a lossy audio compression format defined by ISO/IEC 11172-3 alongside MPEG-1 Audio Layer I and MPEG-1 Audio Layer III...
(MP2), or Dolby Digital
Dolby Digital
Dolby Digital is the name for audio compression technologies developed by Dolby Laboratories. It was originally called Dolby Stereo Digital until 1994. Except for Dolby TrueHD, the audio compression is lossy. The first use of Dolby Digital was to provide digital sound in cinemas from 35mm film prints...
(AC-3) format. In countries using the PAL
PAL
PAL, short for Phase Alternating Line, is an analogue television colour encoding system used in broadcast television systems in many countries. Other common analogue television systems are NTSC and SECAM. This page primarily discusses the PAL colour encoding system...
system standard DVD-Video releases must contain at least one audio track using the PCM, MP2, or AC-3 format, and all standard PAL players must support all three of these formats. A similar standard exists in countries using the NTSC
NTSC
NTSC, named for the National Television System Committee, is the analog television system that is used in most of North America, most of South America , Burma, South Korea, Taiwan, Japan, the Philippines, and some Pacific island nations and territories .Most countries using the NTSC standard, as...
system, though with no requirement mandating the use of or support for the MP2 format. DTS audio is optional for all players, as DTS was not part of the initial draft standard and was added later; thus, many early players are unable to play DTS audio tracks. The vast majority of commercial DVD-Video releases today employ AC-3
Dolby Digital
Dolby Digital is the name for audio compression technologies developed by Dolby Laboratories. It was originally called Dolby Stereo Digital until 1994. Except for Dolby TrueHD, the audio compression is lossy. The first use of Dolby Digital was to provide digital sound in cinemas from 35mm film prints...
audio. The official allowed formats for the audio tracks on a DVD Video are:
- PCM: 48 kHz or 96 kHz sampling rate, 16 bit or 24 bit Linear PCM, 2 to 6 channels, up to 6,144 kbit/s. N.B. 16-bit 48 kHz 8 channel PCM is allowed by the DVD-Video specification but is not well-supported by authoring applications or players.
- AC-3: 48 kHz sampling rate, 1 to 5.1 (6) channels, up to 640 kbit/s
- DTS: 48 kHz or 96 kHz sampling rate, 2 to 6.1 channels, Half Rate (768 kbit/s) or Full Rate (1,536 kbit/s)
- MP2: 48 kHz sampling rate, 1 to 7.1 channelsMPEG MultichannelMPEG Multichannel is an extension to the MPEG-1 Layer II audio compression specification, as defined in the MPEG-2 Audio standard , which allows it provide up to 5.1-channels of audio...
, up to 912 kbit/s
DVDs can contain more than one channel of audio to go together with the video content, supporting a maximum of 8 simultaneous audio tracks per video. This is most commonly used for different audio formats—DTS 5.1, AC-3 2.0 etc.—as well as for commentary and audio tracks in different languages.
Data rate
DVD-Video discs have a raw bitrate of 11.08 Mbit/s, with a 1.0 Mbit/s overhead, leaving a payload bitrate of 10.08 Mbit/s. Of this, up to 3.36 Mbit/s can be used for subtitles and a maximum of 9.80 Mbit/s can be split amongst audio and video. In the case of multiple angles the data is stored interleaved, and so there's a bitrate penalty leading to a max bitrate of 8 Mbit/s per angle to compensate for additional seek time. This limit is not cumulative, so each additional angle can still have up to 8 Mbit/s of bitrate available.Professionally encoded videos average a bitrate of 4-5 Mbit/s with a maximum of 7–8 Mbit/s in high-action scenes. This is typically done to allow greater compatibility amongst players, and to help prevent buffer underrun
Buffer underrun
In computing, buffer underrun or buffer underflow is a state occurring when a buffer used to communicate between two devices or processes is fed with data at a lower speed than the data is being read from it. This requires the program or device reading from the buffer to pause its processing while...
s in the case of dirty or scratched discs.
Columbia TriStar Home Entertainment
Sony Pictures Home Entertainment
Sony Pictures Home Entertainment is the home video distribution arm of Sony Pictures Entertainment, a subsidiary of Sony Corporation. It was established in November 1979 as Columbia Pictures Home Entertainment, releasing 20 titles: The Anderson Tapes, Bell, Book and Candle, Born Free, Breakout,...
has created a line of DVDs (dubbed "Superbit
Superbit
Superbit was a brand of premium DVD-Video versions of motion pictures from Columbia TriStar Home Video, a division of Sony Pictures Entertainment. Superbit DVDs aimed to improve picture quality over a standard DVD edition of a feature by increasing the bit rate of the encoded video...
") aiming to maximize picture quality by eliminating multiple languages, angles, and audio tracks. This allows average bitrates closer to 6 Mbit/s.
Other features
Some DVD hardware or software players may play discs whose MPEG files do not conform to the above standards; commonly this is used to support discs authored with formats such as VCDVideo CD
Before the advent of DVD and Blu-ray, the Video CD became the first format for distributing films on standard 120 mm optical discs. The format is a standard digital format for storing video on a Compact Disc...
and SVCD
Super Video CD
Super Video CD is a digital format for storing video on standard compact discs. SVCD was intended as a successor to Video CD and an alternative to DVD-Video, and falls somewhere between both in terms of technical capability and picture quality...
. While VCD and CVD video is supported by the DVD standard, neither SVCD video nor VCD, CVD, or SVCD audio is compatible with the DVD standard.
Some hardware players will also play DVD-ROMs or CD-ROM
CD-ROM
A CD-ROM is a pre-pressed compact disc that contains data accessible to, but not writable by, a computer for data storage and music playback. The 1985 “Yellow Book” standard developed by Sony and Philips adapted the format to hold any form of binary data....
s containing "raw" MPEG video files; these are "unauthored" and lack the file
Computer file
A computer file is a block of arbitrary information, or resource for storing information, which is available to a computer program and is usually based on some kind of durable storage. A file is durable in the sense that it remains available for programs to use after the current program has finished...
and header structure that defines DVD-Video. Standard DVD-Video files contain extra information (such as the number of video tracks, chapters and links to extra features) that DVD players use to navigate the disc.
The maximum chapters allowed per title is 99 and the maximum titles allowed per DVD is 99.
Filesystem
Almost all DVD-Video discs use the UDF bridge format, which is a combination of the DVD MicroUDF (a subset of UDF 1.02) and ISO 9660ISO 9660
ISO 9660, also referred to as CDFS by some hardware and software providers, is a file system standard published by the International Organization for Standardization for optical disc media....
file systems.
The UDF bridge format provides backwards compatibility for operating systems that support only ISO 9660. Most (and new) DVD players read the UDF filesystem from a DVD-Video disc and ignore the ISO9660 filesystem.
Directory and file structure
A DVD volume for the DVD-Video format has the following structure of directories and files:- AUDIO_TS directory: empty or not present on DVD-Video discs; contains files only on DVD Audio discs; a.k.a. Audio Title Sets directory; included on DVD-Video discs for compatibility reasons
- VIDEO_TS directory: stores all data for the DVD-Video; a.k.a. Video Title Sets directory. This directory is required to be present on a DVD-compliant disc.
- Video Manager (VMG) files:
- VIDEO_TS.IFO file: the Video Manager (VMG) information file – stores control and playback information for the entire DVD – e.g. the First Play PGC (Program Chain), locations of all Video Title Sets (VTS), table of titles, number of volumes, domains for multiple languages and regional and parental control settings, information about subtitles, audio tracks, etc. This file is required to be present on a DVD-compliant disc.
- VIDEO_TS.BUP file: the backup copy of the VIDEO_TS.IFO file. It is part of Video Manager (VMG).
- VIDEO_TS.VOB file: the first-play Video Object of the DVD-Video disc, usually a copyright notice or a menu. It is part of Video Manager (VMG). This file is not required to be present on a DVD-compliant disc.
- Video Title Set (VTS) files:
- VTS_01_0.IFO file: stores control and playback information for the Video Title Set 01 – e.g. information about chapters, subtitles and audio tracks. A "VTS_zz_0.IFO" file (where "zz" is from 01 to 99) is required to be present on each VTS.
- VTS_01_0.BUP file: a backup copy of the VTS_01_0.IFO file. This file is required to be present on a DVD-compliant disc. It is part of Video Title Set (VTS).
- VTS_01_0.VOB file: Video Title Set 01, Video Object 0, contains the menu for this title. This file is not required to be present on a DVD-compliant disc.
- VTS_01_1.VOB file: Video Title Set 01, Video Object 1, contains the video for this title. At least one file "VTS_zz_1.VOB" is required in the VTS and each "VTS_zz_x". DVD-Video can contain up to 99 (1–99) titles with max 10 (0–9) VOB files each. The last possible VOB file is VTS_99_9.VOB.
- ... etc.
IFO
IFO
IFO is a type of DVD-Video file that stores information about chapters, subtitles and audio tracks.An IFO file is one of three types of files that are used on DVDs. It contains important navigational information, such as where a video chapter begins, and where audio and subtitle streams exist...
files store control and playback information – e.g. information about chapters, subtitles and audio tracks. They do not store any video or audio data or subtitles.
BUP
BUP
A BUP file is a backup of the IFO file on a DVD, which contains the information about the organization of tracks, menus, chapters, subtitles on the disc. BUP files are used in the event that the corresponding IFO file is unreadable, perhaps due to a scratch on the surface of the disc.Other DVD...
files are only backups of the IFO files.
Domains
Data structures recorded on a DVD-compliant disc are components of one of the four data groups called domains:- First-play (FP) – First Play PGC located in the VIDEO_TS.IFO file
- Video Manager (VMG) – contains VIDEO_TS.IFO, VIDEO_TS.BUP and VIDEO_TS.VOB
- Video Title Set (VTS) – contains "VTS_zz_x.IFO", "VTS_zz_x.BUP" and "VTS_zz_x.VOB" files (where "x" is from 1 to 9)
- Video Title Set Menu (VTSM) – uses "VTS_zz_0.VOB" files
Container
Video, audio, subtitle and navigation streams are multiplexed and stored on a DVD-Video disc in the VOBVOB
A VOB file is a container format in DVD-Video media. VOB can contain video, audio, subtitle, menu and navigation contents multiplexed together into a stream form. VOB is based on the MPEG program stream format, but with additional limitations and specifications in the private streams...
container format (Video Object). VOB is based on the MPEG program stream format, but with additional limitations and specifications in the private streams. The MPEG program stream has provisions for non-standard data (as AC-3, DTS, LPCM or subtitles used in VOB files) in the form of so-called private streams. VOB files are a very strict subset of the MPEG program stream standard. While all VOB files are MPEG program streams, not all MPEG program streams comply with the definition for a VOB file.
DVD recorder
DVD recorder
A DVD recorder , is an optical disc recorder that uses Optical disc recording technologies to digitally record analog signal or digital signals onto blank writable DVD media...
s can use DVD-VR
DVD-VR
The DVD-VR standard defines a logical format for video recording on DVD-R, DVD-RW, and DVD-RAM style media, including the dual layer versions of these media. As opposed to media recorded with the DVD+VR recording standard, the resulting media are not DVD-Video compliant, and will not play back in...
or DVD+VR
DVD+VR
The DVD+VR standard defines a logical format for DVD-Video compliant recording on optical discs. It is intended to be used on DVD+R and DVD+RW media. Most DVD video recorders in the market that support these two types of media also use the DVD+VR format for recording video on them. It is possible...
format instead of DVD-Video. DVD-VR format store multiplexed audiovisual content in VRO containers. VRO file is an equivalent to a collection of DVD-Video VOB files. Fragmented VRO files are not widely supported by hardware or software players and video editing software. DVD+VR standard defines a logical format for DVD-Video compliant recording on optical discs and is commonly used on DVD+R/RW media.
Subtitles
DVD Video may also include up to 32 subtitleSubtitle (captioning)
Subtitles are textual versions of the dialog in films and television programs, usually displayed at the bottom of the screen. They can either be a form of written translation of a dialog in a foreign language, or a written rendering of the dialog in the same language, with or without added...
or subpicture tracks. Subtitles are usually intended as a visual help for the deaf and hearing impaired and for translating dialogs.
Subtitles can serve other purposes as well. For example, in the DVD release of Thirteen Days
Thirteen Days (film)
Thirteen Days is a 2000 docudrama directed by Roger Donaldson about the Cuban Missile Crisis of 1962, seen from the perspective of the US political leadership. Kevin Costner stars, with Bruce Greenwood featured as John F. Kennedy....
one of the subtitle tracks includes history notes, giving additional information timed to the events depicted in the film. In the release of For All Mankind
For All Mankind
For All Mankind is a 1989 documentary film documenting the Apollo missions of NASA. It was directed by Al Reinert.Music for the film was originally composed in 1983 by Brian Eno and released as an album entitled Apollo: Atmospheres and Soundtracks...
subtitles display names of the NASA missions and names of the people shown on the screen.
Subtitles are stored as bitmap
Bitmap
In computer graphics, a bitmap or pixmap is a type of memory organization or image file format used to store digital images. The term bitmap comes from the computer programming terminology, meaning just a map of bits, a spatially mapped array of bits. Now, along with pixmap, it commonly refers to...
images and therefore can contain messages in any language. Subtitles are restricted to four colors, including transparent "color", and thus tend to look cruder than permanent subtitles on film. Transparency allows laying subtitles over the video during playback. The subtitle tracks are contained within the VOB
VOB
A VOB file is a container format in DVD-Video media. VOB can contain video, audio, subtitle, menu and navigation contents multiplexed together into a stream form. VOB is based on the MPEG program stream format, but with additional limitations and specifications in the private streams...
file of the DVD.
DVD Video may also contain closed captioning
Closed captioning
Closed captioning is the process of displaying text on a television, video screen or other visual display to provide additional or interpretive information to individuals who wish to access it...
material which can only be viewed on a television set with a decoder.
Chapters and angles
DVD Video may contain chapters for easy navigation (and continuation of a partially watched film). If space permits, it is also possible to include several versions (called "angles") of certain scenes, though today this feature is mostly used—if at all—not to show different angles of the action, but as part of internationalization to, for example, show different language versions of images containing written text, if subtitles will not do (e.g., the Queen's spell book in Snow WhiteSnow White and the Seven Dwarfs (1937 film)
Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs is a 1937 American animated film based on Snow White, a German fairy tale by the Brothers Grimm. It was the first full-length cel-animated feature in motion picture history, as well as the first animated feature film produced in America, the first produced in full...
, and the scrolling text in the openings of the Star Wars
Star Wars
Star Wars is an American epic space opera film series created by George Lucas. The first film in the series was originally released on May 25, 1977, under the title Star Wars, by 20th Century Fox, and became a worldwide pop culture phenomenon, followed by two sequels, released at three-year...
films). Multiple angles have found a niche in markets such as yoga
Yoga
Yoga is a physical, mental, and spiritual discipline, originating in ancient India. The goal of yoga, or of the person practicing yoga, is the attainment of a state of perfect spiritual insight and tranquility while meditating on Supersoul...
and erotica
Erotica
Erotica are works of art, including literature, photography, film, sculpture and painting, that deal substantively with erotically stimulating or sexually arousing descriptions...
.
Extra features
A significant selling point of DVD Video is that the storage capacity allows for a wide variety of extra, or bonus, features in addition to the feature film. These extra features can include audio commentary; documentaryDocumentary film
Documentary films constitute a broad category of nonfictional motion pictures intended to document some aspect of reality, primarily for the purposes of instruction or maintaining a historical record...
features, commonly about the making of the main title; deleted scene
Deleted scene
In Entertainment, especially the film and television industry, Deleted scenes are parts of a film removed or censored from or replaced by another scene in the final "cut", or version, of a film...
s; photo galleries; storyboards; isolated music scores
Film score
A film score is original music written specifically to accompany a film, forming part of the film's soundtrack, which also usually includes dialogue and sound effects...
; trivia text commentary; simple games; film shorts; TV spots; radio spots; theatrical trailers which were used to promote the main title; and teaser trailer
Teaser trailer
A teaser campaign is an advertising campaign which typically consists of a series of small, cryptic, challenging advertisements that anticipate a larger, full-blown campaign for a product launch or otherwise important event. These advertisements are called "teasers" or "teaser ads"...
s advertising related movies or DVDs.
Extra features often provide entertainment or add depth and understanding to the film. Games, bloopers, and galleries provide entertainment, especially for younger ages. Deleted scenes and alternative endings allow the audience to view additional content which was not included in a theatrical release. Directors cuts allow the audience to see how the director envisioned the main title without the constraints which are placed on a theatrical release.
Other extras that can be included on DVDs are motion menus, still pictures, up to 32 selectable subtitles, seamless branching
Seamless branching
Seamless branching is a mechanism used on DVDs and Blu-ray Discs to allow the player to jump to a different scene after finishing one. The most common purpose is to have several versions of a scene within one film, without having to store the entire film on the disc several times.A popular example...
for multiple storylines, up to 9 camera angles, and DVD-ROM / data files that can be accessed on a computer.
Extra features require additional storage space, which often means encoding the main title with lower than possible data rate to fit both the main title and the extras on one disc. Lower data rate may decrease visual and sound quality, which manifests itself in various digital artifact
Digital artifact
A digital artifact is any undesired alteration in data introduced in a digital process by an involved technique and/or technology.-Possible causes:...
s. To maintain quality the main title and the extras may be released on several discs, or the extras may be omitted completely like in the "Superbit
Superbit
Superbit was a brand of premium DVD-Video versions of motion pictures from Columbia TriStar Home Video, a division of Sony Pictures Entertainment. Superbit DVDs aimed to improve picture quality over a standard DVD edition of a feature by increasing the bit rate of the encoded video...
" line of DVDs.
Restrictions
DVD-Video has four complementary systems designed to restrict the DVD user in various ways: MacrovisionMacrovision
Rovi Corporation is a globally operating, US-based company that provides guidance technology, entertainment data, copy protection, industry standard networking and media management technology for digital entertainment devices and services...
, Content Scramble System
Content Scramble System
Content Scramble System is a Digital Rights Management and encryption system employed on almost all commercially produced DVD-Video discs. CSS utilizes a proprietary 40-bit stream cipher algorithm...
(CSS), region codes
Regional lockout
Regional lockout is the programming practice, code, chip, or physical barrier used to prevent the playing of media designed for a device from the country where it is marketed on the version of the same device marketed in another country.-Video games:...
, and disabled user operations
User operation prohibition
The user operation prohibition is a form of use restriction used on video DVD discs and Blu-ray discs. Most DVD players and Blu-ray players prohibit the viewer from performing a large majority of actions during sections of a DVD that are protected or restricted by this feature, and will display...
(UOPs). There are also anti-ripping techniques intended to foil ripping software
DVD ripper
A DVD ripper is a software program that facilitates copying the content of a DVD to a hard disk drive. They are mainly used to transfer video on DVDs to different formats, to edit or back up DVD content, and to convert DVD video for playback on media players and mobile devices...
.
Content Scramble System
Many DVD-Video titles use Content Scramble System (CSS) encryption, which is intended to discourage people from copying the disc. Usually, users need to install software provided on the DVD or downloaded from the Internet such as MPlayerMPlayer
MPlayer is a free and open source media player. The program is available for all major operating systems, including Linux and other Unix-like systems, Microsoft Windows and Mac OS X. Versions for OS/2, Syllable, AmigaOS and MorphOS are also available. The Windows version works, with some minor...
, TotalMedia Theatre, PowerDVD
PowerDVD
CyberLink PowerDVD is a media player for Microsoft Windows. Several editions of the software are sold including "Ultra", "Deluxe" and "Standard". All editions support the viewing of DVD and the Ultra edition supports Blu-ray playback, including the playback of Blu-ray 3D content.The product is...
, VLC
VLC media player
VLC media player is a free and open source media player and multimedia framework written by the VideoLAN project.VLC is a portable multimedia player, encoder, and streamer supporting many audio and video codecs and file formats as well as DVDs, VCDs, and various streaming protocols. It is able to...
or WinDVD
WinDVD
WinDVD is a commercial video player and music player software for Microsoft Windows. It enables the viewing of DVD-Video movies on the user's PC. DVD-Video backups stored on hard disk can also be played...
to be able to view the disc in a computer system.
CSS does not make it more difficult (anymore) to copy the digital content now that a decoder (DeCSS
DeCSS
DeCSS is a computer program capable of decrypting content on a commercially produced DVD video disc. Before the release of DeCSS, there was no way for computers running a Linux-based operating system to play video DVDs....
) has been released, nor possible to distinguish between legal and illegal copies of a work, but it does restrict the playback software that may be used.
CSS has caused major problems for the inclusion of DVD players in any open source
Open source
The term open source describes practices in production and development that promote access to the end product's source materials. Some consider open source a philosophy, others consider it a pragmatic methodology...
operating systems, since open source player implementations are not officially given access to the decryption keys or license to the patent
Patent
A patent is a form of intellectual property. It consists of a set of exclusive rights granted by a sovereign state to an inventor or their assignee for a limited period of time in exchange for the public disclosure of an invention....
s involved in CSS. Proprietary software
Proprietary software
Proprietary software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder. The licensee is given the right to use the software under certain conditions, while restricted from other uses, such as modification, further distribution, or reverse engineering.Complementary...
players were also difficult to find on some platforms. However, a successful effort has been made to write a decoder by reverse engineering
Reverse engineering
Reverse engineering is the process of discovering the technological principles of a device, object, or system through analysis of its structure, function, and operation...
, resulting in DeCSS
DeCSS
DeCSS is a computer program capable of decrypting content on a commercially produced DVD video disc. Before the release of DeCSS, there was no way for computers running a Linux-based operating system to play video DVDs....
. This has led to long-running legal battles and the arrest of some of those involved in creating or distributing the DeCSS code, through the use of the controversial U.S. Digital Millennium Copyright Act
Digital Millennium Copyright Act
The Digital Millennium Copyright Act is a United States copyright law that implements two 1996 treaties of the World Intellectual Property Organization . It criminalizes production and dissemination of technology, devices, or services intended to circumvent measures that control access to...
(DMCA), on the grounds that such software could also be used to facilitate unauthorized copying of the data on the discs. The Videolan
VideoLAN
VideoLAN is a project that develops software for playing video and other media formats across a local area network . It originally developed two programs for media streaming, VideoLAN Client and VideoLAN Server , but most of the features of VLS have been incorporated into VLC, with the result...
team, however, went on to make the libdvdcss
Libdvdcss
libdvdcss is a free software library for accessing and unscrambling DVDs encrypted with the Content Scramble System...
library. Unlike DeCSS, libdvdcss can access a CSS-encypted DVD without the need of a cracked key, thus enabling playback of such discs on opensource players without legal restraints (although DVD rippers using this library may still be subject to restrictions).
The DMCA currently affects only the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, however many other countries are signatories to the similar WIPO Treaty
World Intellectual Property Organization Copyright Treaty
The World Intellectual Property Organization Copyright Treaty, abbreviated as the WIPO Copyright Treaty, is an international treaty on copyright law adopted by the member states of the World Intellectual Property Organization in 1996...
. In some countries it is not illegal to use de-scrambling software to bypass the DVD restrictions. A number of software programs have since appeared on the Web to view DVDs on a number of different platforms.
Other measures such as anti-ripping, as well as U.S. and non-U.S. copyright
Copyright
Copyright is a legal concept, enacted by most governments, giving the creator of an original work exclusive rights to it, usually for a limited time...
law, may be used to prevent making unauthorized copies of DVDs. CSS decrypting software, or ripping software, such as DVD Decrypter
DVD Decrypter
DVD Decrypter is a software application for Microsoft Windows that can create backup disk images of the DVD-Video structure of DVDs. It can be used to image any DVD, but controversially it is especially useful for decrypting copy protected movies. The program can also record images to disc...
, AnyDVD
AnyDVD
AnyDVD is a Microsoft Windows driver allowing decryption of DVDs on-the-fly, as well as targeted removal of copy preventions and user operation prohibitions . With an upgrade, it will also do the same for HD DVD and Blu-ray. The AnyDVD program runs in the background, making discs unrestricted and...
, MacTheRipper
MacTheRipper
MacTheRipper is a Mac OS X application that enables users to create a playable copy of the contents of a Video DVD by defeating the Content Scramble System. During this process it may optionally modify or disable the DVD region code or the User operation prohibition features of the copied data...
, and DVD Shrink
DVD Shrink
DVD Shrink is a freeware DVD transcoder program for Microsoft Windows that uses a DVD ripper to back up DVD movies. The final versions are 3.2.0.15 and 3.2.0.16 ; all other versions, such as DVD Shrink 2010, are scams...
allows a disc to be copied to hard disk unscrambled. Some DeCSS applications also remove Macrovision
Macrovision
Rovi Corporation is a globally operating, US-based company that provides guidance technology, entertainment data, copy protection, industry standard networking and media management technology for digital entertainment devices and services...
, region codes
Regional lockout
Regional lockout is the programming practice, code, chip, or physical barrier used to prevent the playing of media designed for a device from the country where it is marketed on the version of the same device marketed in another country.-Video games:...
, and disabled user operations (UOPs).
Anti-ripping
After DeCSS ripping software became available, companies developed techniques to introduce errors in DVD-Video discs that do not normally affect playback and navigation of a disc, but can cause problems in software that attempts to copy the entire disc. These approaches, which are not part of the official DVD-Video specification, include Sony ARccOS ProtectionARccOS Protection
ARccOS is a copy-protection system made by Sony that is used on some DVDs. Designed as an additional layer to be used in conjunction with Content Scramble System , the system deliberately creates corrupted sectors on the DVD, which cause copying software to produce errors .Despite being promoted...
, Macrovision RipGuard, X-protect, ProtectDisc SecureBurn, Anaho, Fortium, and others. All of these methods have been circumvented (as might have been expected, since all standard DVD players naturally circumvent them to play and navigate the discs normally). Riplock
Riplock
Riplock is a characteristic of newer computer DVD-ROM drives that slows the drive transfer rate when reading DVD-Video data, typically to 2x-4x on drives that otherwise could read at 8x or 16x...
is a feature that reduces drive noise during playback but inadvertently reduces ripping speed.
Disabled user operations
DVD-Video allows the disc to specify whether or not the user may perform any operation, such as selecting a menu, skipping chapters, forwarding or rewinding—essentially any function on the remote control. This is known as User Operation Prohibitions, or Prohibited User Operations (UOPs or PUOs). Most DVD players respect these commands (e.g., by preventing skipping or fast-forwarding through a copyright message or an advertisement at the beginning of a disc). However, grey marketGrey market
A grey market or gray market also known as parallel market is the trade of a commodity through distribution channels which, while legal, are unofficial, unauthorized, or unintended by the original manufacturer...
players ignore UOPs and some DVD "re-authoring" software packages allow the user to produce a copy without these restrictions. The legality of these activities varies by jurisdiction and is the subject of debate. (See fair use
Fair use
Fair use is a limitation and exception to the exclusive right granted by copyright law to the author of a creative work. In United States copyright law, fair use is a doctrine that permits limited use of copyrighted material without acquiring permission from the rights holders...
.)
Region codes

28 Days Later
28 Days Later is an acclaimed 2002 British horror film directed by Danny Boyle. The screenplay was written by Alex Garland, and the film stars Cillian Murphy, Naomie Harris, Brendan Gleeson, Megan Burns, and Christopher Eccleston...
was released on DVD in Europe several months prior to the film's release in North American movie theaters. Regional coding kept the European DVD unplayable for most North American consumers, thereby ensuring that ticket sales would be relatively unaffected.
In practice, many DVD players allow playback of any disc, or can be modified to do so. Entirely independent of encryption, region coding pertains to regional lockout
Regional lockout
Regional lockout is the programming practice, code, chip, or physical barrier used to prevent the playing of media designed for a device from the country where it is marketed on the version of the same device marketed in another country.-Video games:...
, which originated in the video game industry.
From a worldwide perspective regional coding may be seen as a failure. A huge percentage of players outside of North America can be easily modified (and are even sold pre-modified by mainstream stores such as Amazon.co.uk) to ignore the regional codes on a disc. This, coupled with the fact that almost all televisions in Europe and Australasia
Australasia
Australasia is a region of Oceania comprising Australia, New Zealand, the island of New Guinea, and neighbouring islands in the Pacific Ocean. The term was coined by Charles de Brosses in Histoire des navigations aux terres australes...
are capable of displaying NTSC video (at the very least, in black and white), means that consumers in these regions have a huge choice of discs. Contrary to popular belief, this practice is not illegal and in some countries that strongly support free trade it is encouraged.
A normal DVD player can only play region-coded discs designated for the player's own particular region. However, a code-free or region-free DVD player is capable of playing DVDs from any of the six regions around the world.
The CSS
Content Scramble System
Content Scramble System is a Digital Rights Management and encryption system employed on almost all commercially produced DVD-Video discs. CSS utilizes a proprietary 40-bit stream cipher algorithm...
license prohibits manufacturing of DVD players that are not set to a single region by default. While the same license prohibits manufacturers from including prominent interfaces to change the region setting it does not clearly prevent them from including "hidden" menus that enable the player's region to be changed; as such, many high-end models in the U.S. include password-protected or otherwise hidden methods to enable multi-region playback. Conversely in the UK and Ireland many cheap DVD players are multi-region while more expensive systems, including the majority of home cinema
Home cinema
Home cinema, also commonly called home theater, are home entertainment set-ups that seek to reproduce a movie theater experience and mood with the help of video and audio equipment in a private home....
systems, are preset to play only region 2 discs.
In China, DVD-Videos for television series are usually released in MPEG-1 video, with MP2 audio. By forgoing Dolby standards, manufacturers cut costs considerably; encoding in lower bit-rates also allows a TV series to be squeezed onto fewer discs. There are no region coding in such cases.
There are also two additional region codes, region 7, which is reserved, and region 8, which is used exclusively for passenger transport such as airlines and cruise ships.
Programming interface
A virtual machineVirtual machine
A virtual machine is a "completely isolated guest operating system installation within a normal host operating system". Modern virtual machines are implemented with either software emulation or hardware virtualization or both together.-VM Definitions:A virtual machine is a software...
implemented by the DVD player runs bytecode
Bytecode
Bytecode, also known as p-code , is a term which has been used to denote various forms of instruction sets designed for efficient execution by a software interpreter as well as being suitable for further compilation into machine code...
contained on the DVD. This is used to control playback and display special effects on the menus. The instruction set
Instruction set
An instruction set, or instruction set architecture , is the part of the computer architecture related to programming, including the native data types, instructions, registers, addressing modes, memory architecture, interrupt and exception handling, and external I/O...
is called the Virtual Machine (VM) DVD command set. There are 16 general parameter registers (GPRM) to hold temporary values and 24 system parameters (SPRM). As a result of a moderately flexible programming interface, DVD players can be used to play games, such as the DVD re-release of Dragon's Lair
Dragon's Lair
Dragon's Lair is a laserdisc video game published by Cinematronics in 1983. It featured animation created by ex-Disney animator Don Bluth....
, along with more sophisticated and advanced games such as Scene It, all of which can be run on standard DVD players.
Players and recorders
Modern DVD recorderDVD recorder
A DVD recorder , is an optical disc recorder that uses Optical disc recording technologies to digitally record analog signal or digital signals onto blank writable DVD media...
s often support additional formats, including DVD+/-R/RW, CD-R/RW, MP3
MP3
MPEG-1 or MPEG-2 Audio Layer III, more commonly referred to as MP3, is a patented digital audio encoding format using a form of lossy data compression...
, WMA
Windows Media Audio
Windows Media Audio is an audio data compression technology developed by Microsoft. The name can be used to refer to its audio file format or its audio codecs. It is a proprietary technology that forms part of the Windows Media framework. WMA consists of four distinct codecs...
, SVCD
Super Video CD
Super Video CD is a digital format for storing video on standard compact discs. SVCD was intended as a successor to Video CD and an alternative to DVD-Video, and falls somewhere between both in terms of technical capability and picture quality...
, JPEG
JPEG
In computing, JPEG . The degree of compression can be adjusted, allowing a selectable tradeoff between storage size and image quality. JPEG typically achieves 10:1 compression with little perceptible loss in image quality....
, PNG, SVG
Scalable Vector Graphics
Scalable Vector Graphics is a family of specifications of an XML-based file format for describing two-dimensional vector graphics, both static and dynamic . The SVG specification is an open standard that has been under development by the World Wide Web Consortium since 1999.SVG images and their...
, KAR
Karaoke
is a form of interactive entertainment or video game in which amateur singers sing along with recorded music using a microphone and public address system. The music is typically a well-known pop song minus the lead vocal. Lyrics are usually displayed on a video screen, along with a moving symbol,...
and MPEG-4
MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
(DivX
DivX
DivX is a brand name of products created by DivX, Inc. , including the DivX Codec which has become popular due to its ability to compress lengthy video segments into small sizes while maintaining relatively high visual quality.There are two DivX codecs; the regular MPEG-4 Part 2 DivX codec and the...
/Xvid
XviD
Xvid is a video codec library following the MPEG-4 standard, specifically MPEG-4 Part 2 Advanced Simple Profile . It uses ASP features such as b-frames, global and quarter pixel motion compensation, lumi masking, trellis quantization, and H.263, MPEG and custom quantization matrices.Xvid is a...
). Some also include USB
Universal Serial Bus
USB is an industry standard developed in the mid-1990s that defines the cables, connectors and protocols used in a bus for connection, communication and power supply between computers and electronic devices....
ports or flash memory
Flash memory
Flash memory is a non-volatile computer storage chip that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. It was developed from EEPROM and must be erased in fairly large blocks before these can be rewritten with new data...
readers. Player prices range from as low as US$
United States dollar
The United States dollar , also referred to as the American dollar, is the official currency of the United States of America. It is divided into 100 smaller units called cents or pennies....
20 (GB£
Pound sterling
The pound sterling , commonly called the pound, is the official currency of the United Kingdom, its Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands, British Antarctic Territory and Tristan da Cunha. It is subdivided into 100 pence...
10) to as high as US$2,700 (GB£1,350).
DVD drives for computers usually come with one of two kinds of Regional Playback Control
Regional Playback Control
RPC-1 and RPC-2 are designations applied to firmware for DVD drives. Older DVD drives use RPC-1 firmware, which allows DVDs from any region to play. Newer drives use RPC-2 firmware, which enforces DVD region coding at the hardware level...
(RPC), either RPC-1 or RPC-2. This is used to enforce the publisher's restrictions on what regions of the world the DVD can be played. (See Regional lockout
Regional lockout
Regional lockout is the programming practice, code, chip, or physical barrier used to prevent the playing of media designed for a device from the country where it is marketed on the version of the same device marketed in another country.-Video games:...
and DVD region code
DVD region code
DVD region codes are a digital-rights management technique designed to allow film distributors to control aspects of a release, including content, release date, and price, according to the region...
s.) While Open source
Open source
The term open source describes practices in production and development that promote access to the end product's source materials. Some consider open source a philosophy, others consider it a pragmatic methodology...
software DVD players allow everything, commercial ones (both standalone models and software players) come further encumbered with restrictions forbidding the viewer from skipping (or in some cases fast-forwarding) certain content such as copyright warnings or advertisements. (See User operation prohibition
User operation prohibition
The user operation prohibition is a form of use restriction used on video DVD discs and Blu-ray discs. Most DVD players and Blu-ray players prohibit the viewer from performing a large majority of actions during sections of a DVD that are protected or restricted by this feature, and will display...
.)
Video game systems with DVD-Video playback functionality are PlayStation 2
PlayStation 2
The PlayStation 2 is a sixth-generation video game console manufactured by Sony as part of the PlayStation series. Its development was announced in March 1999 and it was first released on March 4, 2000, in Japan...
, PlayStation 3
PlayStation 3
The is the third home video game console produced by Sony Computer Entertainment and the successor to the PlayStation 2 as part of the PlayStation series. The PlayStation 3 competes with Microsoft's Xbox 360 and Nintendo's Wii as part of the seventh generation of video game consoles...
, Xbox
Xbox
The Xbox is a sixth-generation video game console manufactured by Microsoft. It was released on November 15, 2001 in North America, February 22, 2002 in Japan, and March 14, 2002 in Australia and Europe and is the predecessor to the Xbox 360. It was Microsoft's first foray into the gaming console...
(additional remote required), Xbox 360
Xbox 360
The Xbox 360 is the second video game console produced by Microsoft and the successor to the Xbox. The Xbox 360 competes with Sony's PlayStation 3 and Nintendo's Wii as part of the seventh generation of video game consoles...
, Panasonic Q
Panasonic Q
The Q is a hybrid version of the Nintendo GameCube with a DVD player manufactured by Panasonic in cooperation with Nintendo. The system was only officially released in Japan. Since the GameCube lacked DVD playback functionality, a feature its competitors had, the system was licensed by Nintendo...
, and Wii
Wii
The Wii is a home video game console released by Nintendo on November 19, 2006. As a seventh-generation console, the Wii primarily competes with Microsoft's Xbox 360 and Sony's PlayStation 3. Nintendo states that its console targets a broader demographic than that of the two others...
(with an unsupported hack).
Competitors and successors
In April 2000, Sonic Solutions and Ravisent announced hDVD, a high-definitionHigh-definition video
High-definition video or HD video refers to any video system of higher resolution than standard-definition video, and most commonly involves display resolutions of 1,280×720 pixels or 1,920×1,080 pixels...
extension to DVD. However hDVD failed to gain much popularity.
On November 18, 2003, the Chinese news agency Xinhua
Xinhua News Agency
The Xinhua News Agency is the official press agency of the government of the People's Republic of China and the biggest center for collecting information and press conferences in the PRC. It is the largest news agency in the PRC, ahead of the China News Service...
reported the final standard of the Chinese government-sponsored Enhanced Versatile Disc
Enhanced Versatile Disc
The Enhanced Versatile Disc is an optical medium-based digital audio/video format, developed to provide a means for playing HDTV content using existing optical media. It was announced on November 18, 2003, by the People's Republic of China's Xinhua News Agency as a response to the popular...
(EVD) which is another extension of standard DVD. Shortly thereafter the development of the format was halted by a licensing dispute between Chinese companies and On2 Technologies
On2 Technologies
On2 Technologies , formerly known as The Duck Corporation, was a small publicly-traded company , headquartered in Clifton Park, New York, that designs video codec technology. They created a series of video codecs called TrueMotion...
, but on December 6, 2006, 20 Chinese electronic firms unveiled 54 prototype EVD players and announced their intention for the format to completely replace DVDs in China by 2008. However, due to a lack of sales, support for EVD has recently been dropped by the Xinhua Bookstore in Wuhan
Wuhan
Wuhan is the capital of Hubei province, People's Republic of China, and is the most populous city in Central China. It lies at the east of the Jianghan Plain, and the intersection of the middle reaches of the Yangtze and Han rivers...
, which was a major supporter of the format.
Blu-ray Disc and HD DVD
Two competing high-definition (HD) optical-disc formats, HD DVDHD DVD
HD DVD is a discontinued high-density optical disc format for storing data and high-definition video.Supported principally by Toshiba, HD DVD was envisioned to be the successor to the standard DVD format...
and Blu-ray, were introduced in 2006. The HD DVD format, promoted by Toshiba, had the backing by the DVD Forum
DVD Forum
The DVD Forum is an international organization composed of hardware, software, media and content companies that use and develop the DVD and formerly HD DVD formats...
, which voted to make it the official successor to DVD. Opposing HD DVD was the Blu-ray format, led by the Blu-ray Disc Association
Blu-ray Disc Association
The Blu-ray Disc Association is the industry consortium that develops and licenses Blu-ray Disc technology and is responsible for establishing format standards and promoting business opportunities for Blu-ray Disc...
, which shares many of the same members.
Despite HD DVD's slight market lead and earlier introduction to the retail market (March 2006 vs June 2006), both formats engaged in a brief format war
Format war
A format war describes competition between mutually incompatible proprietary formats that compete for the same market, typically for data storage devices and recording formats for electronic media. It is often characterized by political and financial influence on content publishers by the...
. Industry analysts likened the situation to the VHS/Betamax format war
Videotape format war
The videotape format war was a period of intense competition or "format war" of incompatible models of consumer-level analog video videocassette and video cassette recorders in the late 1970s and the 1980s.- Overview :...
of the 1980s. But this time, consumer awareness of either high-definition format was severely limited, with the end result that most consumers avoided both formats, already content with DVD. Toshiba capitulated in February 2008, citing low demand for HD DVD and the faster growth of Blu-ray, among other reasons. Toshiba ended production of their HD DVD players and discontinued promotion of the format, while the HD DVD movie release schedule concluded by June 2008.
As of February 2009, Blu-ray disc is the de facto high-definition optical disc format. However, sales figures suggest DVD is in no immediate danger of disappearing. Until households acquire high-definition-capable displays, they have no reason to switch to Blu-ray (other than more data capacity and less disc scratching), while households which are already equipped with HD-capable displays overwhelmingly have access to competing sources of HD video, from traditional subscription-based cable or satellite TV, to the fast growing market of Internet-hosted video-download services.
All standard DVDs will play on existing Blu-ray players, making the switch to Blu-ray much easier than the switch from VHS to DVD. In addition, a growing number of hardware vendors are enhancing their Blu-ray players with Internet connectivity for subscription-based video downloads.
CBHD
China Blue High-definition Disc (CBHD) was introduced in September 2007. This format is based on HD DVDHD DVD
HD DVD is a discontinued high-density optical disc format for storing data and high-definition video.Supported principally by Toshiba, HD DVD was envisioned to be the successor to the standard DVD format...
. While the Blu-ray format is marketed internationally, CBHDs have sold significantly in the Chinese market.
See also
- Blu-ray DiscBlu-ray DiscBlu-ray Disc is an optical disc storage medium designed to supersede the DVD format. The plastic disc is 120 mm in diameter and 1.2 mm thick, the same size as DVDs and CDs. Blu-ray Discs contain 25 GB per layer, with dual layer discs being the norm for feature-length video discs...
- CBHD
- DVD Video Recording ModeVR modeVR mode or Video Recording mode is a feature on stand-alone consumer and computer DVD recorders that allows video recording and editing on a DVD rewritable disc.In VR mode, users can create and rename titles for the scenes...
, DVD-VRDVD-VRThe DVD-VR standard defines a logical format for video recording on DVD-R, DVD-RW, and DVD-RAM style media, including the dual layer versions of these media. As opposed to media recorded with the DVD+VR recording standard, the resulting media are not DVD-Video compliant, and will not play back in...
, DVD+VRDVD+VRThe DVD+VR standard defines a logical format for DVD-Video compliant recording on optical discs. It is intended to be used on DVD+R and DVD+RW media. Most DVD video recorders in the market that support these two types of media also use the DVD+VR format for recording video on them. It is possible... - Format warFormat warA format war describes competition between mutually incompatible proprietary formats that compete for the same market, typically for data storage devices and recording formats for electronic media. It is often characterized by political and financial influence on content publishers by the...
- HD DVDHD DVDHD DVD is a discontinued high-density optical disc format for storing data and high-definition video.Supported principally by Toshiba, HD DVD was envisioned to be the successor to the standard DVD format...
- List of video players (software)
- Jon Lech JohansenJon Lech JohansenJon Lech Johansen , also known as DVD Jon, is a Norwegian programmer famous for his work on reverse engineering data formats....
, author of DeCSSDeCSSDeCSS is a computer program capable of decrypting content on a commercially produced DVD video disc. Before the release of DeCSS, there was no way for computers running a Linux-based operating system to play video DVDs.... - SuperbitSuperbitSuperbit was a brand of premium DVD-Video versions of motion pictures from Columbia TriStar Home Video, a division of Sony Pictures Entertainment. Superbit DVDs aimed to improve picture quality over a standard DVD edition of a feature by increasing the bit rate of the encoded video...
- Video Object
External links
- DVD-Video information including virtual machine instruction set information.

