
Brinell scale
Encyclopedia
Materials science
Materials science is an interdisciplinary field applying the properties of matter to various areas of science and engineering. This scientific field investigates the relationship between the structure of materials at atomic or molecular scales and their macroscopic properties. It incorporates...
.
Proposed by Swedish
Sweden
Sweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
engineer
Engineer
An engineer is a professional practitioner of engineering, concerned with applying scientific knowledge, mathematics and ingenuity to develop solutions for technical problems. Engineers design materials, structures, machines and systems while considering the limitations imposed by practicality,...
Johan August Brinell
Johan August Brinell
August Brinell was a Swedish Mechanical Engineer.Brinell is noted as the creator of a method for quantifying the surface hardness of materials, now known as the Brinell hardness test...
in 1900, it was the first widely used and standardised hardness test in engineering
Engineering
Engineering is the discipline, art, skill and profession of acquiring and applying scientific, mathematical, economic, social, and practical knowledge, in order to design and build structures, machines, devices, systems, materials and processes that safely realize improvements to the lives of...
and metallurgy
Metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their intermetallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are called alloys. It is also the technology of metals: the way in which science is applied to their practical use...
. The large size of indentation and possible damage to test-piece limits its usefulness.
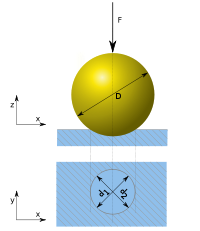
The typical test uses a 10 millimetre (0.393700787401575 in) diameter
Diameter
In geometry, a diameter of a circle is any straight line segment that passes through the center of the circle and whose endpoints are on the circle. The diameters are the longest chords of the circle...
steel
Steel
Steel is an alloy that consists mostly of iron and has a carbon content between 0.2% and 2.1% by weight, depending on the grade. Carbon is the most common alloying material for iron, but various other alloying elements are used, such as manganese, chromium, vanadium, and tungsten...
ball as an indenter with a 3000 kgf (29.4 kN; 6,613.9 lbf) force. For softer materials, a smaller force is used; for harder materials, a tungsten carbide
Tungsten carbide
Tungsten carbide is an inorganic chemical compound containing equal parts of tungsten and carbon atoms. Colloquially, tungsten carbide is often simply called carbide. In its most basic form, it is a fine gray powder, but it can be pressed and formed into shapes for use in industrial machinery,...
ball is substituted for the steel ball. The indentation is measured and hardness calculated as:

where:
- P = applied force (kgfKGFKGF may refer to:*Keratinocyte Growth Factor*King George's Fields A UK set of 471 memorial playing fields and recreation grounds*Kolar Gold Fields*The IATA code for Sary-Arka Airport, Karaganda, Kazakhstan...
) - D = diameter of indenter (mm)
- d = diameter of indentation (mm)
The BHN can be converted into the ultimate tensile strength (UTS), although the relationship is dependent on the material, and therefore determined empirically. The relationship is based on Meyer's index (n) from Meyer's law
Meyer's law
Meyer's law is an empirical relation between the size of a hardness test indentation and the load required to leave the indentation.- Equation :It take the form:P\,=\,kd^nwhere*P = pressure in megapascals*k = property of the material...
. If Meyer's index is less than 2.2 then the ratio of UTS to BHN is 0.36. If Meyer's index is greater than 2.2, then the ratio increases.
BHN is designated by the most commonly used test standards (ASTM E10-08 and ISO 6506-1:2005) as HBW (H from hardness, B from brinell and W from the material of the indenter, tungsten (wolfram) carbide). In former standards HB or HBS were used to refer to measurements made with steel indenters.
HBW is calculated in both standards using the SI units as

where:
- F = applied force (N)
- D = diameter of indenter (mm)
- d = diameter of indentation (mm)
Common values
When quoting a Brinell hardness number (BHN or more commonly HB), the conditions of the test used to obtain the number must be specified. The standard format for specifying tests can be seen in the example "HBW 10/3000". "HBW" means that a tungsten carbide (from the chemical symbol for tungsten) ball indenter was used, as opposed to "HBS", which means a hardened steel ball. The "10" is the ball diameter in millimeters. The "3000" is the force in kilograms force.The hardness may also be shown as XXX HB YYD^2. The XXX is the force to apply (in kgf) on a material of type YY (5 for aluminum alloys, 10 for copper alloys, 30 for steels). Thus a typical steel hardness could be written: 250 HB 30D^2. It could be a maximum or a minimum.
| Material | Hardness |
|---|---|
| Softwood Softwood The term softwood is used to describe wood from trees that are known as gymnosperms.Conifers are an example. It may also be used to describe trees, which tend to be evergreen, notable exceptions being bald cypress and the larches.... (e.g., pine Pine Pines are trees in the genus Pinus ,in the family Pinaceae. They make up the monotypic subfamily Pinoideae. There are about 115 species of pine, although different authorities accept between 105 and 125 species.-Etymology:... ) |
1.6 HBS 10/100 |
| Hardwood Hardwood Hardwood is wood from angiosperm trees . It may also be used for those trees themselves: these are usually broad-leaved; in temperate and boreal latitudes they are mostly deciduous, but in tropics and subtropics mostly evergreen.Hardwood contrasts with softwood... |
2.6–7.0 HBS 1.6 10/100 |
| Aluminium Aluminium Aluminium or aluminum is a silvery white member of the boron group of chemical elements. It has the symbol Al, and its atomic number is 13. It is not soluble in water under normal circumstances.... |
15 HB |
| Copper Copper Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish... |
35 HB |
| Mild steel | 120 HB |
| 18-8 (304) stainless steel Stainless steel In metallurgy, stainless steel, also known as inox steel or inox from French "inoxydable", is defined as a steel alloy with a minimum of 10.5 or 11% chromium content by mass.... annealed |
200 HB |
| Glass Glass Glass is an amorphous solid material. Glasses are typically brittle and optically transparent.The most familiar type of glass, used for centuries in windows and drinking vessels, is soda-lime glass, composed of about 75% silica plus Na2O, CaO, and several minor additives... |
1550 HB |
| Hardened tool steel Tool steel Tool steel refers to a variety of carbon and alloy steels that are particularly well-suited to be made into tools. Their suitability comes from their distinctive hardness, resistance to abrasion, their ability to hold a cutting edge, and/or their resistance to deformation at elevated temperatures... |
1500–1900 HB |
| Rhenium diboride Rhenium diboride Rhenium diboride is a synthetic superhard material. It was first synthesized in 1962 and re-emerged recently due to hopes of achieving high hardness comparable to that of diamond... |
4600 HB |
| Note: Standard test conditions unless otherwise stated | |
Standards
- International (ISOInternational Organization for StandardizationThe International Organization for Standardization , widely known as ISO, is an international standard-setting body composed of representatives from various national standards organizations. Founded on February 23, 1947, the organization promulgates worldwide proprietary, industrial and commercial...
) and European (CENEuropean Committee for StandardizationThe European Committee for Standardization or Comité Européen de Normalisation , is a non-profit organisation whose mission is to foster the European economy in global trading, the welfare of European citizens and the environment by providing an efficient infrastructure to interested parties for...
) Standard- EN ISO 6506-1:2005: Metallic materials - Brinell hardness test - Part 1: test method
- EN ISO 6506-2:2005: Metallic materials - Brinell hardness test - Part 2: verification and calibration of testing machine
- EN ISO 6506-3:2005: Metallic materials - Brinell hardness test - Part 3: calibration of reference blocks
- EN ISO 6506-4:2005: Metallic materials - Brinell hardness test - Part 4: Table of hardness values
- US standard (ASTM InternationalASTM InternationalASTM International, known until 2001 as the American Society for Testing and Materials , is an international standards organization that develops and publishes voluntary consensus technical standards for a wide range of materials, products, systems, and services...
)- ASTM E10-08: Standard method for Brinell hardness of metallic materials.
See also
- BrinellingBrinellingBrinelling is a material surface failure caused by contact stress that exceeds the material limit. This failure is caused by just one application of a load great enough to exceed the material limit. The result is a permanent dent or "brinell" mark. It is a common cause of roller bearing failures,...
- Hardness comparisonHardness comparisonThere are a large number of hardness testing methods available . Although it is impossible in many cases to give an exact conversion, it is possible to give an approximate material-specific comparison table e.g...
- Knoop hardness testKnoop hardness testThe Knoop hardness test is a microhardness test - a test for mechanical hardness used particularly for very brittle materials or thin sheets, where only a small indentation may be made for testing purposes...
- Leeb Rebound Hardness TestLeeb rebound hardness testThe Leeb rebound hardness test is one of the four most used method for testing metal hardness. This portable method is mainly used for testing sufficiently large workpieces .-History:...
- Rockwell scaleRockwell scaleThe Rockwell scale is a hardness scale based on the indentation hardness of a material. The Rockwell test determines the hardness by measuring the depth of penetration of an indenter under a large load compared to the penetration made by a preload. There are different scales, denoted by a single...
- Vickers hardness testVickers hardness testThe Vickers hardness test was developed in 1924 by Smith and Sandland at Vickers Ltd as an alternative to the Brinell method to measure the hardness of materials. The Vickers test is often easier to use than other hardness tests since the required calculations are independent of the size of the...
External links
- Rockwell to Brinell conversion chart (Brinell, Rockwell A,B,C)
- Struers hardness conversion table (Vickers, Brinell, Rockwell B,C,D)
- Brinell Hardness HB conversion chart (N/mm2, Brinell, Vickers, Rockwell C)

