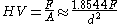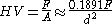Vickers hardness test
Encyclopedia

Brinell scale
The Brinell scale characterizes the indentation hardness of materials through the scale of penetration of an indenter, loaded on a material test-piece. It is one of several definitions of hardness in materials science....
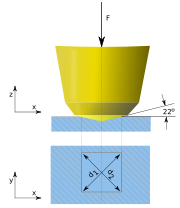
method to measure the hardness of materials. The Vickers test is often easier to use than other hardness tests since the required calculations are independent of the size of the indenter, and the indenter can be used for all materials irrespective of hardness. The basic principle, as with all common measures of hardness, is to observe the questioned material's ability to resist plastic deformation from a standard source. The Vickers test can be used for all metal
Metal
A metal , is an element, compound, or alloy that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat. Metals are usually malleable and shiny, that is they reflect most of incident light...
s and has one of the widest scales among hardness tests. The unit of hardness given by the test is known as the Vickers Pyramid Number (HV) or Diamond Pyramid Hardness (DPH). The hardness number can be converted into units of pascals
Pascal (unit)
The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre...
, but should not be confused with a pressure, which also has units of pascals. The hardness number is determined by the load over the surface area of the indentation and not the area normal to the force, and is therefore not a pressure.
The hardness number is not really a true property of the material and is an empirical value that should be seen in conjunction with the experimental methods and hardness scale used.
Implementation

which can be approximated by evaluating the sine term to give
where d is the average length of the diagonal left by the indenter in millimeters. Hence,
where F is in kgf and d is in millimeters.
The corresponding units of HV are then kilograms-force per square millimeter (kgf/mm²). To calculate Vickers hardness number using SI units one needs to convert the force applied from kilogram-force
Kilogram-force
A kilogram-force , or kilopond , is a gravitational metric unit of force. It is equal to the magnitude of the force exerted by one kilogram of mass in a gravitational field...
to newtons by multiplying by 9.806 65 (standard gravity
Standard gravity
Standard gravity, or standard acceleration due to free fall, usually denoted by g0 or gn, is the nominal acceleration of an object in a vacuum near the surface of the Earth. It is defined as precisely , or about...
) and convert mm to m. To do the calculation directly, the following equation can be used:
where F is newtons and d is millimeters.
Vickers hardness numbers are reported as xxxHVyy, e.g. 440HV30, or xxxHVyy/zz if duration of force differs from 10 s to 15 s, e.g. 440Hv30/20, where:
- 440 is the hardness number,
- HV gives the hardness scale (Vickers),
- 30 indicates the load used in kg.
- 20 indicates the loading time if it differs from 10 s to 15 s
Vickers values are generally independent of the test force: they will come out the same for 500 gf and 50 kgf, as long as the force is at least 200 gf.
| Material | Value |
|---|---|
| 316L stainless steel | 140HV30 |
| 347L stainless steel | 180HV30 |
| Carbon steel | 55–120HV5 |
| Iron | 30–80HV5 |
Precautions
When doing the hardness tests the minimum distance between indentations and the distance from the indentation to the edge of the specimen must be taken into account to avoid interaction between the work-hardened regions and effects of the edge. This minimum distances are different for ISO 6507-1 and ASTM E384 standards.| Standard | Distance between indentations | Distance from the center of the indentation to the edge of the specimen |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 6507-1 | > 3·d for steel and copper alloys and > 6·d for light metals | 2.5·d for steel and copper alloys and > 3·d for light metals |
| ASTM E384 | 2.5·d | 2.5·d |
Estimating tensile strength
If HV is expressed in SI units the Yield Stress of the material can be approximated as: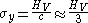
where c is a constant determined by geometrical factors usually ranging between 2 and 4.
Example of use
The finVertical stabilizer
The vertical stabilizers, vertical stabilisers, or fins, of aircraft, missiles or bombs are typically found on the aft end of the fuselage or body, and are intended to reduce aerodynamic side slip. It is analogical to a skeg on boats and ships.On aircraft, vertical stabilizers generally point upwards...
attachment pins and sleeves in the Convair 580 airliner were specified by the aircraft manufacturer to be hardened to a Vickers Hardness specification of 390HV5, the '5' meaning five kiloponds
Kilogram-force
A kilogram-force , or kilopond , is a gravitational metric unit of force. It is equal to the magnitude of the force exerted by one kilogram of mass in a gravitational field...
. However on the aircraft flying Partnair Flight 394
Partnair Flight 394
Partnair Flight 394 was a chartered flight which crashed on 8 September 1989 off the coast of Denmark 18 km north of Hirtshals. All 50 passengers and 5 crew members on board the aircraft perished, making it the deadliest civilian aviation accident involving an all-Norwegian airline company. It...
the pins were later found to have been replaced with sub-standard parts, leading to rapid wear and finally loss of the aircraft. On examination, accident investigators found that the sub-standard pins had a hardness value of only some 200-230HV5.
See also
- Indentation hardnessIndentation hardnessIndentation hardness tests are used to determine the hardness of a material to deformation. Several such tests exist, wherein the examined material is indented until an impression is formed; these tests can be performed on a macroscopic or microscopic scale....
- Leeb Rebound Hardness TestLeeb rebound hardness testThe Leeb rebound hardness test is one of the four most used method for testing metal hardness. This portable method is mainly used for testing sufficiently large workpieces .-History:...
- Hardness comparisonHardness comparisonThere are a large number of hardness testing methods available . Although it is impossible in many cases to give an exact conversion, it is possible to give an approximate material-specific comparison table e.g...
- Knoop hardness testKnoop hardness testThe Knoop hardness test is a microhardness test - a test for mechanical hardness used particularly for very brittle materials or thin sheets, where only a small indentation may be made for testing purposes...
- Meyer hardness testMeyer hardness testThe Meyer hardness test is a rarely used hardness test based upon projected area of an impression. This is a more fundamental measurement of hardness than other hardness tests which are based on the surface area of an indentation. The principle behind the test is that the mean pressure required to...
- Rockwell scaleRockwell scaleThe Rockwell scale is a hardness scale based on the indentation hardness of a material. The Rockwell test determines the hardness by measuring the depth of penetration of an indenter under a large load compared to the penetration made by a preload. There are different scales, denoted by a single...
- Vickers toughness test of ceramics
Further reading
- ASTM E92: Standard method for Vickers hardness of metallic materials (Withdrawn and replaced by E384-10e2)
- ASTM E384: Standard Test Method for Knoop and Vickers Hardness of Materials
- ISO 6507-1: Metallic materials - Vickers hardness test - Part 1: Test method
- ISO 6507-2: Metallic materials - Vickers hardness test - Part 2: Verification and calibration of testing machines
- ISO 6507-3: Metallic materials - Vickers hardness test - Part 3: Calibration of reference blocks
- ISO 6507-4: Metallic materials - Vickers hardness test - Part 4: Tables of hardness values
External links
- Vickers hardness test
- Conversion table - Vickers, Brinell, and Rockwell scales