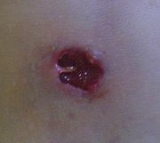
Abscess
Encyclopedia
An abscess is a collection of pus
(dead neutrophils) that has accumulated in a cavity formed by the tissue in which the pus resides due to an infectious
process (usually caused by bacteria
or parasites) or other foreign materials (e.g., splinters, bullet
wound
s, or injecting needles). It is a defensive reaction
of the tissue to prevent the spread of infectious materials to other parts of the body. One example of an abscess is a BCG-oma
, which is caused because of incorrect administration of the BCG
vaccine.
The organisms or foreign materials kill the local cells
, resulting in the release of cytokine
s. The cytokines trigger an inflammatory response
, which draws large numbers of white blood cell
s to the area and increases the regional blood
flow.
The final structure of the abscess is an abscess wall, or capsule, that is formed by the adjacent healthy cells in an attempt to keep the pus from infecting neighboring structures. However, such encapsulation tends to prevent immune cells from attacking bacteria in the pus, or from reaching the causative organism or foreign object.
Abscesses must be differentiated from empyema
s, which are accumulations of pus in a preexisting rather than a newly formed anatomical cavity.
s) or deep skin abscesses), in the lungs, brain
, teeth
, kidneys and tonsils. Major complications are spreading of the abscess material to adjacent or remote tissues and extensive regional tissue death (gangrene
). Abscesses in most parts of the body rarely heal themselves, so prompt medical attention is indicated at the first suspicion of an abscess.
An abscess could potentially be fatal (although this is rare) if it compresses vital structures such as the trachea
in the context of a deep neck abscess.
and curettage
(Ubi pus, ibi evacua. Hippocrates).
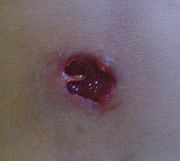 The abscess should be inspected to identify if foreign objects are a cause, which may require their removal. If foreign objects are not the cause, a doctor will incise and drain the abscess and prescribe painkillers and possibly antibiotics.
The abscess should be inspected to identify if foreign objects are a cause, which may require their removal. If foreign objects are not the cause, a doctor will incise and drain the abscess and prescribe painkillers and possibly antibiotics.
Surgical
drainage of the abscess (e.g., lancing
) is usually indicated once the abscess has developed from a harder serous inflammation to a softer pus
stage. This is expressed in the Latin
medical aphorism
: Ubi pus, ibi evacua
.
In critical areas where surgery presents a high risk, it may be delayed or used as a last resort. The drainage of a lung abscess may be performed by positioning the patient in a way that enables the contents to be discharged via the respiratory tract
. Warm compresses and elevation of the limb may be beneficial for a skin abscess.
and antibiotics or with curettage alone. However, another randomized controlled trial
found primary closure led to 35% failing to heal primarily and primary closure longer median number of days to closure (8.9 versus 7.8).
In anorectal abscesses, primary closure healed faster, but 25% of abscesses healed by secondary intention
and recurrence was higher.
bacteria
is a common cause, an anti-staphylococcus antibiotic such as flucloxacillin
or dicloxacillin
is used. With the emergence of community-acquired methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus MRSA, these traditional antibiotics may be ineffective; alternative antibiotics effective against community-acquired MRSA often include clindamycin
, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and doxycycline
. These antibiotics may also be prescribed to patients with a documented allergy to penicillin. (If the condition is thought to be cellulitis rather than abscess, consideration should be given to possibility of strep species as cause that are still sensitive to traditional anti-staphylococcus agents such as dicloxacillin or cephalexin in patients able to tolerate penicillin). It is important to note that antibiotic
therapy alone without surgical drainage of the abscess is seldom effective due to antibiotics often being unable to get into the abscess and their ineffectiveness at low pH
levels. Whilst most medical texts advocate surgical incision some medical doctors will treat small abscesses conservatively with antibiotics.
To prevent recurrent infections due to Staphylococcus
, consider the following measures:
(Epsom salt) paste. This works by drawing the infected pus to the surface of the skin before rupturing and leaking out. After this the body will usually repair the old infected cavity. Magnesium sulfate is therefore best applied at night with a sterile dressing covering it, the rupture itself is not painful but the drawing up may be uncomfortable. Magnesium sulfate paste is not necessarily an effective or accepted medical treatment.
(such as Crohn's disease
) or diabetes. Often the abscess will start as an internal wound caused by ulceration, hard stool or penetrative objects with insufficient lubrication. This wound typically becomes infected as a result of the normal presence of feces in the rectal area, and then develops into an abscess. This often presents itself as a lump of tissue near the anus
which grows larger and more painful with time. Like other abscesses, perianal abscesses may require prompt medical treatment, such as an incision and debridement
or lancing.
Pus
Pus is a viscous exudate, typically whitish-yellow, yellow, or yellow-brown, formed at the site of inflammatory during infection. An accumulation of pus in an enclosed tissue space is known as an abscess, whereas a visible collection of pus within or beneath the epidermis is known as a pustule or...
(dead neutrophils) that has accumulated in a cavity formed by the tissue in which the pus resides due to an infectious
Infection
An infection is the colonization of a host organism by parasite species. Infecting parasites seek to use the host's resources to reproduce, often resulting in disease...
process (usually caused by bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
or parasites) or other foreign materials (e.g., splinters, bullet
Bullet
A bullet is a projectile propelled by a firearm, sling, or air gun. Bullets do not normally contain explosives, but damage the intended target by impact and penetration...
wound
Wound
A wound is a type of injury in which skin is torn, cut or punctured , or where blunt force trauma causes a contusion . In pathology, it specifically refers to a sharp injury which damages the dermis of the skin.-Open:...
s, or injecting needles). It is a defensive reaction
Immune system
An immune system is a system of biological structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease by identifying and killing pathogens and tumor cells. It detects a wide variety of agents, from viruses to parasitic worms, and needs to distinguish them from the organism's own...
of the tissue to prevent the spread of infectious materials to other parts of the body. One example of an abscess is a BCG-oma
BCG-oma
A BCG-oma is an abscess caused by the BCG strain of Mycobacterium bovis. It follows incorrect administration of BCG . It is treated as for any Mycobacterium bovis infection ....
, which is caused because of incorrect administration of the BCG
Bacillus Calmette-Guérin
Bacillus Calmette-Guérin is a vaccine against tuberculosis that is prepared from a strain of the attenuated live bovine tuberculosis bacillus, Mycobacterium bovis, that has lost its virulence in humans by being specially subcultured in an artificial medium for 13 years, and also prepared from...
vaccine.
The organisms or foreign materials kill the local cells
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
, resulting in the release of cytokine
Cytokine
Cytokines are small cell-signaling protein molecules that are secreted by the glial cells of the nervous system and by numerous cells of the immune system and are a category of signaling molecules used extensively in intercellular communication...
s. The cytokines trigger an inflammatory response
Inflammation
Inflammation is part of the complex biological response of vascular tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. Inflammation is a protective attempt by the organism to remove the injurious stimuli and to initiate the healing process...
, which draws large numbers of white blood cell
White blood cell
White blood cells, or leukocytes , are cells of the immune system involved in defending the body against both infectious disease and foreign materials. Five different and diverse types of leukocytes exist, but they are all produced and derived from a multipotent cell in the bone marrow known as a...
s to the area and increases the regional blood
Blood
Blood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells....
flow.
The final structure of the abscess is an abscess wall, or capsule, that is formed by the adjacent healthy cells in an attempt to keep the pus from infecting neighboring structures. However, such encapsulation tends to prevent immune cells from attacking bacteria in the pus, or from reaching the causative organism or foreign object.
Abscesses must be differentiated from empyema
Empyema
Pleural empyema is an accumulation of pus in the pleural cavity. Most pleural empyemas arise from an infection within the lung , often associated with parapneumonic effusions. There are three stages: exudative, fibrinopurulent and organizing. In the exudative stage, the pus accumulates...
s, which are accumulations of pus in a preexisting rather than a newly formed anatomical cavity.
Signs and symptoms
The cardinal symptoms and signs of any kind of inflammatory process are redness, heat, swelling, pain and loss of function. Abscesses may occur in any kind of solid tissue but most frequently on skin surface (where they may be superficial pustules (boilBoil
A boil, also called a furuncle, is a deep folliculitis, infection of the hair follicle. It is always caused by infection by the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus, resulting in a painful swollen area on the skin caused by an accumulation of pus and dead tissue...
s) or deep skin abscesses), in the lungs, brain
Brain abscess
Brain abscess is an abscess caused by inflammation and collection of infected material, coming from local or remote infectious sources, within the brain tissue...
, teeth
Tooth abscess
A tooth abscess or root abscess is pus enclosed in the tissues of the jaw bone at the apex of an infected tooth's root. Usually the abscess originates from a bacterial infection that has accumulated in the soft, often dead, pulp of the tooth. This can be caused by untreated tooth decay, cracked...
, kidneys and tonsils. Major complications are spreading of the abscess material to adjacent or remote tissues and extensive regional tissue death (gangrene
Gangrene
Gangrene is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that arises when a considerable mass of body tissue dies . This may occur after an injury or infection, or in people suffering from any chronic health problem affecting blood circulation. The primary cause of gangrene is reduced blood...
). Abscesses in most parts of the body rarely heal themselves, so prompt medical attention is indicated at the first suspicion of an abscess.
An abscess could potentially be fatal (although this is rare) if it compresses vital structures such as the trachea
Vertebrate trachea
In tetrapod anatomy the trachea, or windpipe, is a tube that connects the pharynx or larynx to the lungs, allowing the passage of air. It is lined with pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium cells with goblet cells that produce mucus...
in the context of a deep neck abscess.
Treatment
Wound abscesses cannot be treated with antibiotics. They require surgical intervention, debridementDebridement
Debridement is the medical removal of a patient's dead, damaged, or infected tissue to improve the healing potential of the remaining healthy tissue...
and curettage
Curettage
Curettage, in medical procedures, is the use of a curette to remove tissue by scraping or scooping.Curettages are also a declining method of abortion. It has been replaced by vacuum aspiration over the last decade....
(Ubi pus, ibi evacua. Hippocrates).
Incision and drainage

Surgical
Surgery
Surgery is an ancient medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a patient to investigate and/or treat a pathological condition such as disease or injury, or to help improve bodily function or appearance.An act of performing surgery may be called a surgical...
drainage of the abscess (e.g., lancing
Incision and drainage
Incision and drainage and clinical lancing are minor surgical procedures to release pus or pressure built up under the skin, such as from an abscess, boil, or infected paranasal sinus...
) is usually indicated once the abscess has developed from a harder serous inflammation to a softer pus
Pus
Pus is a viscous exudate, typically whitish-yellow, yellow, or yellow-brown, formed at the site of inflammatory during infection. An accumulation of pus in an enclosed tissue space is known as an abscess, whereas a visible collection of pus within or beneath the epidermis is known as a pustule or...
stage. This is expressed in the Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
medical aphorism
Aphorism
An aphorism is an original thought, spoken or written in a laconic and memorable form.The term was first used in the Aphorisms of Hippocrates...
: Ubi pus, ibi evacua
Ubi pus, ibi evacua
Ubi pus, ibi evacua is a Latin aphorism or adage, often cited in medicine, meaning "where [there is] pus, there evacuate [it]". It refers to what clinicians should do when there is a collection of pus in the body; that is, to create an opening for it to evacuate...
.
In critical areas where surgery presents a high risk, it may be delayed or used as a last resort. The drainage of a lung abscess may be performed by positioning the patient in a way that enables the contents to be discharged via the respiratory tract
Respiratory tract
In humans the respiratory tract is the part of the anatomy involved with the process of respiration.The respiratory tract is divided into 3 segments:*Upper respiratory tract: nose and nasal passages, paranasal sinuses, and throat or pharynx...
. Warm compresses and elevation of the limb may be beneficial for a skin abscess.
Packing
In North America, after drainage, an abscess cavity is often packed. However, there is no evidence to support this practice and it may in fact delay healing. To try to answer this question more definitely, a randomized double-blind study was started in September 2008 and was completed in March 2010. Interim analysis of data from this study suggests that "wound packing may significantly increase the failure rates." A small pilot study has found no benefit from packing of simple cutaneous abscesses.Primary closure
Primary closure has been successful when combined with curettageCurettage
Curettage, in medical procedures, is the use of a curette to remove tissue by scraping or scooping.Curettages are also a declining method of abortion. It has been replaced by vacuum aspiration over the last decade....
and antibiotics or with curettage alone. However, another randomized controlled trial
Randomized controlled trial
A randomized controlled trial is a type of scientific experiment - a form of clinical trial - most commonly used in testing the safety and efficacy or effectiveness of healthcare services or health technologies A randomized controlled trial (RCT) is a type of scientific experiment - a form of...
found primary closure led to 35% failing to heal primarily and primary closure longer median number of days to closure (8.9 versus 7.8).
In anorectal abscesses, primary closure healed faster, but 25% of abscesses healed by secondary intention
Wound healing
Wound healing, or cicatrisation, is an intricate process in which the skin repairs itself after injury. In normal skin, the epidermis and dermis exists in a steady-state equilibrium, forming a protective barrier against the external environment...
and recurrence was higher.
Antibiotics
As Staphylococcus aureusStaphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus aureus is a facultative anaerobic Gram-positive coccal bacterium. It is frequently found as part of the normal skin flora on the skin and nasal passages. It is estimated that 20% of the human population are long-term carriers of S. aureus. S. aureus is the most common species of...
bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
is a common cause, an anti-staphylococcus antibiotic such as flucloxacillin
Flucloxacillin
Flucloxacillin or floxacillin is a narrow-spectrum beta-lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class. It is used to treat infections caused by susceptible Gram-positive bacteria. Unlike other penicillins, flucloxacillin has activity against beta-lactamase-producing organisms such as Staphylococcus...
or dicloxacillin
Dicloxacillin
Dicloxacillin is a narrow-spectrum beta-lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class. It is used to treat infections caused by susceptible Gram-positive bacteria. It is active against beta-lactamase-producing organisms such as Staphylococcus aureus, which would otherwise be resistant to most...
is used. With the emergence of community-acquired methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus MRSA, these traditional antibiotics may be ineffective; alternative antibiotics effective against community-acquired MRSA often include clindamycin
Clindamycin
Clindamycin rINN is a lincosamide antibiotic. It is usually used to treat infections with anaerobic bacteria but can also be used to treat some protozoal diseases, such as malaria...
, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and doxycycline
Doxycycline
Doxycycline INN is a member of the tetracycline antibiotics group, and is commonly used to treat a variety of infections. Doxycycline is a semisynthetic tetracycline invented and clinically developed in the early 1960s by Pfizer Inc. and marketed under the brand name Vibramycin. Vibramycin...
. These antibiotics may also be prescribed to patients with a documented allergy to penicillin. (If the condition is thought to be cellulitis rather than abscess, consideration should be given to possibility of strep species as cause that are still sensitive to traditional anti-staphylococcus agents such as dicloxacillin or cephalexin in patients able to tolerate penicillin). It is important to note that antibiotic
Antibiotic
An antibacterial is a compound or substance that kills or slows down the growth of bacteria.The term is often used synonymously with the term antibiotic; today, however, with increased knowledge of the causative agents of various infectious diseases, antibiotic has come to denote a broader range of...
therapy alone without surgical drainage of the abscess is seldom effective due to antibiotics often being unable to get into the abscess and their ineffectiveness at low pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
levels. Whilst most medical texts advocate surgical incision some medical doctors will treat small abscesses conservatively with antibiotics.
Recurrent infections
Recurrent abscesses are often caused by community-acquired MRSA. While resistant to most beta lactam antibiotics commonly used for skin infections, it remains sensitive to alternative antibiotics, e.g., clindamycin (Cleocin), trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim), and doxycycline (unlike hospital-acquired MRSA that may only be sensitive to vancomycin IV).To prevent recurrent infections due to Staphylococcus
Staphylococcus
Staphylococcus is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria. Under the microscope they appear round , and form in grape-like clusters....
, consider the following measures:
- Topical mupirocinMupirocinMupirocin is an antibiotic originally isolated from Pseudomonas fluorescens NCIMB 10586, developed by Beecham....
applied to the nares. In this randomized controlled trialRandomized controlled trialA randomized controlled trial is a type of scientific experiment - a form of clinical trial - most commonly used in testing the safety and efficacy or effectiveness of healthcare services or health technologies A randomized controlled trial (RCT) is a type of scientific experiment - a form of...
, patients used nasal mupirocin twice daily 5 days a month for 1 year. - Chlorhexidine baths, In a randomized controlled trialRandomized controlled trialA randomized controlled trial is a type of scientific experiment - a form of clinical trial - most commonly used in testing the safety and efficacy or effectiveness of healthcare services or health technologies A randomized controlled trial (RCT) is a type of scientific experiment - a form of...
, nasal recolonization with S. aureus occurred at 12 weeks in 24% of nursing home residents receiving mupirocin ointment alone (6/25) and in 15% of residents receiving mupirocin ointment plus chlorhexidine baths daily for the first three days of mupirocin treatment (4/27). Although these results did not reach statistical significanceStatistical significanceIn statistics, a result is called statistically significant if it is unlikely to have occurred by chance. The phrase test of significance was coined by Ronald Fisher....
, the baths are an easy treatment.
Magnesium sulfate paste
Historically abscesses as well as boils and many other collections of pus have been treated via application of magnesium sulfateMagnesium sulfate
Magnesium sulfate is a chemical compound containing magnesium, sulfur and oxygen, with the formula MgSO4. It is often encountered as the heptahydrate epsomite , commonly called Epsom salt, from the town of Epsom in Surrey, England, where the salt was distilled from the springs that arise where the...
(Epsom salt) paste. This works by drawing the infected pus to the surface of the skin before rupturing and leaking out. After this the body will usually repair the old infected cavity. Magnesium sulfate is therefore best applied at night with a sterile dressing covering it, the rupture itself is not painful but the drawing up may be uncomfortable. Magnesium sulfate paste is not necessarily an effective or accepted medical treatment.
Perianal abscess
Perianal abscesses can be seen in patients with for example inflammatory bowel diseaseInflammatory bowel disease
In medicine, inflammatory bowel disease is a group of inflammatory conditions of the colon and small intestine. The major types of IBD are Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.-Classification:...
(such as Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease, also known as regional enteritis, is a type of inflammatory bowel disease that may affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract from mouth to anus, causing a wide variety of symptoms...
) or diabetes. Often the abscess will start as an internal wound caused by ulceration, hard stool or penetrative objects with insufficient lubrication. This wound typically becomes infected as a result of the normal presence of feces in the rectal area, and then develops into an abscess. This often presents itself as a lump of tissue near the anus
Anus
The anus is an opening at the opposite end of an animal's digestive tract from the mouth. Its function is to control the expulsion of feces, unwanted semi-solid matter produced during digestion, which, depending on the type of animal, may be one or more of: matter which the animal cannot digest,...
which grows larger and more painful with time. Like other abscesses, perianal abscesses may require prompt medical treatment, such as an incision and debridement
Debridement
Debridement is the medical removal of a patient's dead, damaged, or infected tissue to improve the healing potential of the remaining healthy tissue...
or lancing.
See also
- Tooth abscessTooth abscessA tooth abscess or root abscess is pus enclosed in the tissues of the jaw bone at the apex of an infected tooth's root. Usually the abscess originates from a bacterial infection that has accumulated in the soft, often dead, pulp of the tooth. This can be caused by untreated tooth decay, cracked...
- Brain abscessBrain abscessBrain abscess is an abscess caused by inflammation and collection of infected material, coming from local or remote infectious sources, within the brain tissue...
- Hidradenitis suppurativaHidradenitis suppurativaHidradenitis suppurativa is a skin disease that most commonly affects areas bearing apocrine sweat glands or sebaceous glands, such as the underarms, breasts, inner thighs, groin and buttocks.-Overview:...
- Caseous lymphadenitisCaseous lymphadenitisCaseous lymphadenitis is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis found mostly in goats and sheep that at present has no cure. It manifests itself predominantly in the form of large, pus-filled cysts on the neck, sides and udders of goats and sheep...
in sheep and goats

