
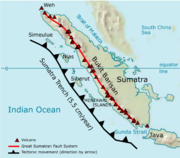
Barisan Mountains
Encyclopedia
Mountain range
A mountain range is a single, large mass consisting of a succession of mountains or narrowly spaced mountain ridges, with or without peaks, closely related in position, direction, formation, and age; a component part of a mountain system or of a mountain chain...
on the western side of Sumatra
Sumatra
Sumatra is an island in western Indonesia, westernmost of the Sunda Islands. It is the largest island entirely in Indonesia , and the sixth largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 with a population of 50,365,538...
, Indonesia
Indonesia
Indonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an...
, covering nearly 1,700 km (1,050 mi) from the north to the south of the island. The Bukit Barisan range consists primarily of volcano
Volcano
2. Bedrock3. Conduit 4. Base5. Sill6. Dike7. Layers of ash emitted by the volcano8. Flank| 9. Layers of lava emitted by the volcano10. Throat11. Parasitic cone12. Lava flow13. Vent14. Crater15...
es shrouded in dense jungle cover, including Sumatran tropical pine forests
Sumatran tropical pine forests
The Sumatran tropical pine forests is a subtropical coniferous forest ecoregion on the island of Sumatra in Indonesia.-Location and description:...
on the higher slopes. The highest peak of the range is Mount Kerinci
Mount Kerinci
Mount Kerinci is the highest volcano in Indonesia, and the highest peak on the island of Sumatra...
at 3,800 metres (12,467 ft). The Bukit Barisan Selatan National Park
Bukit Barisan Selatan National Park
Bukit Barisan Selatan National Park is a national park in Sumatra, Indonesia. The park has a total area of 3,568 km², and spans three provinces: Lampung, Bengkulu, and South Sumatra...
is situated towards the southern end of the range.
The name Bukit Barisan actually means "row of hills" or "hills that make a row" in Indonesian
Indonesian language
Indonesian is the official language of Indonesia. Indonesian is a normative form of the Riau Islands dialect of Malay, an Austronesian language which has been used as a lingua franca in the Indonesian archipelago for centuries....
and Malay
Malay language
Malay is a major language of the Austronesian family. It is the official language of Malaysia , Indonesia , Brunei and Singapore...
, for the range stretches end to end along the island of Sumatra.
There are 35 active volcanos in Bukit Barisan. The largest volcano is the supervolcano
Supervolcano
A supervolcano is a volcano capable of producing a volcanic eruption with an ejecta volume greater than 1,000 cubic kilometers . This is thousands of times larger than most historic volcanic eruptions. Supervolcanoes can occur when magma in the Earth rises into the crust from a hotspot but is...
Toba
Lake Toba
Lake Toba is a lake and supervolcano. The lake is 100 kilometres long and 30 kilometres wide, and 505 metres at its deepest point. Located in the middle of the northern part of the Indonesian island of Sumatra with a surface elevation of about , the lake stretches from to...
within the 100 km (62 miles) × 30 km (19 miles) Lake Toba, which was created after a caldera collapse
Caldera
A caldera is a cauldron-like volcanic feature usually formed by the collapse of land following a volcanic eruption, such as the one at Yellowstone National Park in the US. They are sometimes confused with volcanic craters...
(est. in 74,000 Before Present
Before Present
Before Present years is a time scale used in archaeology, geology, and other scientific disciplines to specify when events in the past occurred. Because the "present" time changes, standard practice is to use AD 1950 as the origin of the age scale, reflecting the fact that radiocarbon...
). The eruption is estimated to have been at level eight on the VEI
Volcanic Explosivity Index
The Volcanic Explosivity Index was devised by Chris Newhall of the U.S. Geological Survey and Stephen Self at the University of Hawaii in 1982 to provide a relative measure of the explosiveness of volcanic eruptions....
scale, the largest possible for a volcanic eruption. The highest peak of the mountain range is Mount Kerinci
Mount Kerinci
Mount Kerinci is the highest volcano in Indonesia, and the highest peak on the island of Sumatra...
with an elevation of 3,800 m (12,467 ft). The list are below,
| Name | |Elevation | VEI Volcanic Explosivity Index The Volcanic Explosivity Index was devised by Chris Newhall of the U.S. Geological Survey and Stephen Self at the University of Hawaii in 1982 to provide a relative measure of the explosiveness of volcanic eruptions.... ) | Weh Weh Island Weh Island or Pulau Weh or Pulo Weh is a small active volcanic island to the northwest of Sumatra. It was originally connected to the Sumatran mainland and became separated by sea after the volcano's last eruption in the Pleistocene era. The island is situated in the Andaman Sea... | stratovolcano Stratovolcano A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a tall, conical volcano built up by many layers of hardened lava, tephra, pumice, and volcanic ash. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile and periodic, explosive eruptions... |
sortable=on 617 | Pleistocene Pleistocene The Pleistocene is the epoch from 2,588,000 to 11,700 years BP that spans the world's recent period of repeated glaciations. The name pleistocene is derived from the Greek and .... |
5.82°N 95.28°E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seulawah Agam Seulawah Agam Seulawah Agam is an extensive forested stratovolcano located at the northwestern tip of Sumatra. Several names have been given to the mountain: Seulawaih Agam, Seulawain Agam, Solawa Agam, Solawaik Agam, Selawadjanten and Goldberg.The volcano was constructed during the Pleistocene-Holocene age. The... |
stratovolcano Stratovolcano A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a tall, conical volcano built up by many layers of hardened lava, tephra, pumice, and volcanic ash. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile and periodic, explosive eruptions... |
sortable=on 1,810 | (2) | 5.448°N 95.658°E | |||
| Peuet Sague Peuet Sague Peuet Sague is a volcanic complex in the northwest of Sumatra, Indonesia. The name peuet in Acehnese language means square in English. The location of the volcanic complex is isolated that needs several journeys on foot from the nearest village to reach the mountain. There are four summits in the... |
complex volcano Complex volcano A complex volcano, also called a compound volcano, is a volcano with more than one feature. They form because changes of their eruptive characteristics or the location of multiple vents in an area... |
sortable=on 2,801 | (2) | 4.914°N 96.329°E | |||
| Geureudong Geureudong Geureudong or Bur ni Geureudong or Bur ni Telong is a stratovolcanic complex in the northern of Sumatra, Indonesia. The official name of the whole complex is confusing between the two adjacent volcanoes: Bur ni Geureudong and Bur ni Telong. Two other volcanic cones are Salah Nama and Pepanji, and... |
stratovolcano Stratovolcano A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a tall, conical volcano built up by many layers of hardened lava, tephra, pumice, and volcanic ash. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile and periodic, explosive eruptions... |
sortable=on 2,885 | 4.813°N 96.82°E | ||||
| Kembar Mount Kembar Mount Kembar is a Pleistocene volcano, located in the northern Sumatra island, Indonesia. It contains a fumarole field, named Gayolesten. The volcanic complex is located in the junction of two geological fault systems and it is a shield volcano.... |
shield volcano Shield volcano A shield volcano is a type of volcano usually built almost entirely of fluid lava flows. They are named for their large size and low profile, resembling a warrior's shield. This is caused by the highly fluid lava they erupt, which travels farther than lava erupted from more explosive volcanoes... |
sortable=on 2,245 | Pleistocene Pleistocene The Pleistocene is the epoch from 2,588,000 to 11,700 years BP that spans the world's recent period of repeated glaciations. The name pleistocene is derived from the Greek and .... |
3.850°N 97.664°E |
|-
| Sibayak
Sibayak
Mt. Sibayak is a small stratovolcano overlooking the town of Berastagi in northern Sumatra, Indonesia. Although its last eruption was more than a century ago, geothermal activity in the form of steam vents and hot springs remains high on and around the volcano. The vents produce crystalline...
|| stratovolcano
Stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a tall, conical volcano built up by many layers of hardened lava, tephra, pumice, and volcanic ash. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile and periodic, explosive eruptions...
|| align="right"|sortable=on 2,212 || || 3.23°N 98.52°E
|-
| Sinabung
Sinabung
Mount Sinabung is a Pleistocene-to-Holocene stratovolcano of andesite and dacite in the Karo plateau of Karo Regency, North Sumatra, Indonesia, 25 miles from Lake Toba supervolcano. Many old lava flows are on its flanks and the last known eruption, before recent times, occurred in the year 1600...
|| stratovolcano
Stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a tall, conical volcano built up by many layers of hardened lava, tephra, pumice, and volcanic ash. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile and periodic, explosive eruptions...
|| align="right"|sortable=on 2,460 || || 3.17°N 98.392°E
|-
| Toba
Lake Toba
Lake Toba is a lake and supervolcano. The lake is 100 kilometres long and 30 kilometres wide, and 505 metres at its deepest point. Located in the middle of the northern part of the Indonesian island of Sumatra with a surface elevation of about , the lake stretches from to...
|| supervolcano
Supervolcano
A supervolcano is a volcano capable of producing a volcanic eruption with an ejecta volume greater than 1,000 cubic kilometers . This is thousands of times larger than most historic volcanic eruptions. Supervolcanoes can occur when magma in the Earth rises into the crust from a hotspot but is...
|| align="right"|sortable=on 2,157 || unknown || 2.58°N 98.83°E
|-
| Helatoba-Tarutung
Helatoba-Tarutung
Helatoba-Tarutung is a group of sulfurous hot springs in the south of Lake Toba. It stretches 40 km long of the Renun-Toru geological fault zone. The last eruption was taken place during the Pleistocene age....
|| fumarole
Fumarole
A fumarole is an opening in a planet's crust, often in the neighborhood of volcanoes, which emits steam and gases such as carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, hydrochloric acid, and hydrogen sulfide. The steam is created when superheated water turns to steam as its pressure drops when it emerges from...
field || align="right"|sortable=on 1,100 || Pleistocene
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene is the epoch from 2,588,000 to 11,700 years BP that spans the world's recent period of repeated glaciations. The name pleistocene is derived from the Greek and ....
|| 2.03°N 98.93°E
|-
| Imun
Imun
Imun is a small dacitic and rhyolitic cone in the south of Lake Toba. Due to its closeness with the much larger caldera of the Lake Toba, there is not much of information about this small volcano....
|| unknown || align="right"|sortable=on 1,505 || unknown || 2.158°N 98.93°E
|-
| Sibualbuali
Sibualbuali
Sibualbuali is a stratovolcano in the northern Sumatra, Indonesia. It has two solfatara fields on the eastern flank. There is a rhyolitic-dacitic lava dome, erupted from the Toru-Asik fault....
|| stratovolcano
Stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a tall, conical volcano built up by many layers of hardened lava, tephra, pumice, and volcanic ash. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile and periodic, explosive eruptions...
|| align="right"|sortable=on 1,819 || unknown || 1.556°N 99.255°E
|-
| Lubukraya
Lubukraya
Lubukraya is an andesitic stratovolcano on Sumatra island, Indonesia. It has a broad crater breached to the south and a lava dome at the southern foot of the volcano....
|| stratovolcano
Stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a tall, conical volcano built up by many layers of hardened lava, tephra, pumice, and volcanic ash. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile and periodic, explosive eruptions...
|| align="right"|sortable=on 1,862 || unknown || 1.478°N 99.209°E
|-
| Sorikmarapi
Sorikmarapi
Sorikmarapi is highly vegetated stratovolcano on Sumatra island, Indonesia. It has 600 m wide of crater lake at the summit and some sulfur deposits. Small parasitic crater, called Danau Merah, is found at the upper southeast flank of the mountain and several solfatara fields at the eastern...
|| stratovolcano
Stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a tall, conical volcano built up by many layers of hardened lava, tephra, pumice, and volcanic ash. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile and periodic, explosive eruptions...
|| align="right"|sortable=on 2,145 || (1) || 0.686°N 99.539°E
|-
| Talakmau || complex volcano
Complex volcano
A complex volcano, also called a compound volcano, is a volcano with more than one feature. They form because changes of their eruptive characteristics or the location of multiple vents in an area...
|| align="right"|sortable=on 2,919 || unknown || 0.079°N 99.98°E
|-
| Sarik-Gajah
Sarik-Gajah
Sarik-Gajah are two pyroclastic cones right at the equator line on Sumatra island, Indonesia. The first cone is Sarik, an andesitic/basaltic vegetated cone. The other is andesic-dacitic Gajah cone, 10 km southwest of the first one and it contains lava flow. No eruptive history ever recorded...
|| volcanic cone
Volcanic cone
Volcanic cones are among the simplest volcanic formations. They are built by ejecta from a volcanic vent, piling up around the vent in the shape of a cone with a central crater. Volcanic cones are of different types, depending upon the nature and size of the fragments ejected during the eruption...
|| align="right"|unknown || unknown || 0.008°N 100.20°E
|-
| Marapi || complex volcano
Complex volcano
A complex volcano, also called a compound volcano, is a volcano with more than one feature. They form because changes of their eruptive characteristics or the location of multiple vents in an area...
|| align="right"|sortable=on 2,891 || (2) || 0.381°S 100.473°E
|-
| Tandikat || stratovolcano
Stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a tall, conical volcano built up by many layers of hardened lava, tephra, pumice, and volcanic ash. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile and periodic, explosive eruptions...
|| align="right"|sortable=on 2,438 || (1) || 0.433°S 100.317°E
|-
| Talang
Mount Talang
Mount Talang is an active stratovolcano in West Sumatra, Indonesia. Talang has two crater lakes on its flanks, the largest of which is 1 x 2 km wide and is called Lake Talang....
|| stratovolcano
Stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a tall, conical volcano built up by many layers of hardened lava, tephra, pumice, and volcanic ash. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile and periodic, explosive eruptions...
|| align="right"|sortable=on 2,597 || (2) || 0.978°S 100.679°E
|-
| Kerinci
Mount Kerinci
Mount Kerinci is the highest volcano in Indonesia, and the highest peak on the island of Sumatra...
|| stratovolcano
Stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a tall, conical volcano built up by many layers of hardened lava, tephra, pumice, and volcanic ash. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile and periodic, explosive eruptions...
|| align="right"|sortable=on 3,800 || (2) || 1.697°S 101.264°E
|-
| Hutapanjang
Mount Hutapanjang
Hutapanjang is a stratovolcano on Sumatra, Indonesia. Little is known about this volcano. However, recent research shows an uncomonly high amount of nuclear radiation being emitted from the area....
|| stratovolcano
Stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a tall, conical volcano built up by many layers of hardened lava, tephra, pumice, and volcanic ash. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile and periodic, explosive eruptions...
|| align="right"|sortable=on 2,021 || unknown || 2.33°S 101.60°E
|-
| Sumbing
Mount Sumbing (Sumatra)
Mount Sumbing is a stratovolcano in the central region of Sumatra, Indonesia. The volcano has a complicated summit region with several craters and a 180 m long crater lake.-Eruptions:...
|| stratovolcano
Stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a tall, conical volcano built up by many layers of hardened lava, tephra, pumice, and volcanic ash. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile and periodic, explosive eruptions...
|| align="right"|sortable=on 2,507 || (2) || 2.414°S 101.728°E
|-
| Kunyit
Mount Kunyit
Mount Kunyit is a fumarolic stratovolcano on Sumatra, Indonesia. The summit contains two craters; the uppermost is a crater lake....
|| stratovolcano
Stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a tall, conical volcano built up by many layers of hardened lava, tephra, pumice, and volcanic ash. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile and periodic, explosive eruptions...
|| align="right"|sortable=on 2,151 || unknown || 2.592°S 101.63°E
|-
| Pendan
Mount Pendan
Mount Pendan is an active volcano on Sumatra, Indonesia. There is little known about the volcano....
|| unknown || align="right"|unknown || unknown || 2.82°S 102.02°E
|-
| Belirang-Beriti
Belirang-Beriti
Belirang-Beriti is a volcanic complex that rises above the Semalako Plain in the southwest of Sumatra, Indonesia. It contains a 1.2 km-wide volcanic crater....
|| compound || align="right"|sortable=on 1,958 || unknown || 2.82°S 102.18°E
|-
| Bukit Daun
Bukit Daun
Bukit Daun is a stratovolcano, located in a sparsely populated region in Sumatra, Indonesia. A 600 m wide of crater lake is located at the summit. A smaller crater lake, Tologo Kecil, is found in the southwest flank....
|| stratovolcano
Stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a tall, conical volcano built up by many layers of hardened lava, tephra, pumice, and volcanic ash. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile and periodic, explosive eruptions...
|| align="right"|sortable=on 2,467 || unknown || 3.38°S 102.37°E
|-
| Kaba || stratovolcano
Stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a tall, conical volcano built up by many layers of hardened lava, tephra, pumice, and volcanic ash. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile and periodic, explosive eruptions...
|| align="right"|sortable=on 1,952 || (1) || 3.52°S 102.62°E
|-
| Dempo
Mount Dempo
Mount Dempo is a high stratovolcano that rises above Pasumah Plain in the province of South Sumatra in Sumatra, Indonesia. Seven craters are found around the summit. A 400 m wide lake is found at the northwest end of the crater complex....
|| stratovolcano
Stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a tall, conical volcano built up by many layers of hardened lava, tephra, pumice, and volcanic ash. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile and periodic, explosive eruptions...
|| align="right"|sortable=on 3,173 || (1) || 4.03°S 103.13°E
|-
| Patah
Mount Patah
Mount Patah is a heavily forested quaternary age volcano west of Mount Dempo on Sumatra island, Indonesia. On 1 May 1989, a fumarole activity was observed by a pilot near the summit. The exact location of the crater, the date of its formation and its geologic relationship is uncertain....
|| unknown || align="right"|sortable=on 2,817 || unknown || 4.27°S 103.30°E
|-
| Bukit Lumut Balai
Bukit Lumut Balai
Bukit Lumut Balai is a heavily eroded stratovolcano on Sumatra island, Indonesia. It consist of three eruption centers, two on the Bukit Lumut and one one the northeast side of the Bukit Balai. A large lava flow occurs on the north side of Bukit Balai. Active fumarole fields are found in two...
|| stratovolcano
Stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a tall, conical volcano built up by many layers of hardened lava, tephra, pumice, and volcanic ash. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile and periodic, explosive eruptions...
|| align="right"|sortable=on 2,055 || unknown || 4.23°S 103.62°E
|-
| Besar
Mount Besar
Mount Besar is a stratovolcano in the southeast of Sumatra, Indonesia. A minor sulfur deposit can be found in the crater. A big solfatara field called Marga Bayur is located along its north-southwest flanks or the Semangko fault system....
|| stratovolcano
Stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a tall, conical volcano built up by many layers of hardened lava, tephra, pumice, and volcanic ash. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile and periodic, explosive eruptions...
|| align="right"|sortable=on 1,899 || (1) || 4.43°S 103.67°E
|-
| Ranau
Lake Ranau
Lake Ranau is a lake in Lampung, Indonesia. It is located at ....
|| caldera
Caldera
A caldera is a cauldron-like volcanic feature usually formed by the collapse of land following a volcanic eruption, such as the one at Yellowstone National Park in the US. They are sometimes confused with volcanic craters...
|| align="right"|sortable=on 1,881 || unknown || 4.83°S 103.92°E
|-
| Sekincau Belirang
Sekincau Belirang
Sekincau is a volcano with two calderas, Belirang and Balak , located in the south of Sumatra, Indonesia. A 300 m wide of crater is found at the summit. Fumarole activities are found at the foot of calderas....
|| caldera
Caldera
A caldera is a cauldron-like volcanic feature usually formed by the collapse of land following a volcanic eruption, such as the one at Yellowstone National Park in the US. They are sometimes confused with volcanic craters...
|| align="right"|sortable=on 1,719 || unknown || 5.12°S 104.32°E
|-
| Suoh || caldera
Caldera
A caldera is a cauldron-like volcanic feature usually formed by the collapse of land following a volcanic eruption, such as the one at Yellowstone National Park in the US. They are sometimes confused with volcanic craters...
|| align="right"|sortable=on 1,000 || (4) || 5.25°S 104.27°E
|-
| Hulubelu
Hulubelu
Hulubelu is an elliptical, 4-km-long caldera the floor of which is about 700 m above sea level and is surrounded by steep walls in South-Eastern Sumatra...
|| caldera
Caldera
A caldera is a cauldron-like volcanic feature usually formed by the collapse of land following a volcanic eruption, such as the one at Yellowstone National Park in the US. They are sometimes confused with volcanic craters...
|| align="right"|sortable=on 1,040 || || 5.35°S 104.60°E
|-
| Rajabasa
Rajabasa
Rajabasa is an isolated 1281-m-high conical volcano along the Sunda Strait located at the most South-Eastern point of Sumatra.It has a well-preserved 500 x 700 m summit crater with a swampy floor, the volcano is covered with vegetation...
|| stratovolcano
Stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a tall, conical volcano built up by many layers of hardened lava, tephra, pumice, and volcanic ash. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile and periodic, explosive eruptions...
|| align="right"|sortable=on 1,281 || || 5.78°S 105.625°E
|}

