
BMP Development
Encyclopedia

Infantry fighting vehicle
An infantry fighting vehicle , also known as a mechanized infantry combat vehicle , is a type of armoured fighting vehicle used to carry infantry into battle and provide fire support for them...
s were the first production line IFVs. Included in the series are the mainline BMPs, the airborne variant BMDs, and licensed modified (i.e. MLI-84
MLI-84
The MLI-84 is a native-made Romanian infantry fighting vehicle currently in service with the Romanian Land Forces. It is basically a stock BMP-1 with a lengthened hull and a 12.7x108mm DShK 1938/46 heavy machine gun mounted on the roof of the troop compartment....
) and reverse engineered versions (i.e. Boragh
Boragh
The Boragh is an Iranian-made armoured personnel carrier. Boragh is believed to be a reverse engineered and upgraded model of the Chinese Type 86 . The upgrades include a reduction in weight, a higher road speed, and stronger armor...
, Type 86). BMP stands for Boyevaya Mashina Pekhoty , meaning "fighting vehicle of infantry"). They were initially developed in the 1960s in the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
.
Background

World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
began with the concepts of armored warfare relatively undeveloped, particularly the use of combined arms teams. Tank and infantry units were often organized as separate units, which led to problems of command and coordination.
As the war progressed the doctrine of combined arms
Combined arms
Combined arms is an approach to warfare which seeks to integrate different branches of a military to achieve mutually complementary effects...
became better refined, and the need for specialist vehicles to keep the infantry in close contact with the armor became increasingly important. Most of these vehicles were half-track
Half-track
A half-track is a civilian or military vehicle with regular wheels on the front for steering, and caterpillar tracks on the back to propel the vehicle and carry most of the load. The purpose of this combination is to produce a vehicle with the cross-country capabilities of a tank and the handling...
s, arguably the best known being the US M3
M3 Half-track
The Carrier, Personnel Half-track M3 was an armored vehicle used by the United States, the British Empire and the other Allies during World War II and the Cold War. Nearly 43,000 were produced, and supplied to the U.S...
. Other forces adopted expedient measures; the Red Army was famed for having their infantry ride on the top of tanks
Tank desant
Tank desant is a military combined arms tactic, where infantry soldiers ride into an attack on tanks, then dismount to fight on foot in the final phase of the assault...
, an extremely dangerous tactic, while the Canadians introduced a series of converted tanks known as Kangaroos
Kangaroo (armoured personnel carrier)
A Kangaroo was a World War II Commonwealth or British armoured personnel carrier , created by conversion of a tank chassis. Created as an expedient measure by the Canadian Army, the Kangaroos were so successful that they were soon being used by British forces as well...
. The Kangaroo pointed the way forward, offering much better armor than half-tracks and able to keep up with the tanks on any terrain.
In the post-war era most armies started introducing fully tracked vehicles in the dedicated armored personnel carrier role, including the Soviet BTR-50
BTR-50
The BTR-50 The BTR-50 The BTR-50 (BTR stands for Bronetransporter (БТР, Бронетранспортер, literally "armored transporter") is a Soviet amphibious armored personnel carrier (APC) based on the PT-76 light tank. The BTR-50 is tracked, unlike most in the BTR series, which are wheeled. The BTR-50...
, German Schützenpanzer Lang HS.30
Schützenpanzer Lang HS.30
The Schützenpanzer Lang HS.30 was a German infantry fighting vehicle developed during the 1950s. It was a Swiss Hispano-Suiza design, with a Rolls-Royce engine. After some early mechanical problems only some 2000 were built of the 10,000 planned...
, British FV432
FV432
The FV432 is the armoured personnel carrier variant of the British Army's FV430 series of armoured fighting vehicles. Since its introduction in the 1960s it has been the most common variant, being used for transporting infantry on the battlefield...
, and perhaps most notable, the US M113
M113 armored personnel carrier
The M113 is a fully tracked armored personnel carrier that has formed the backbone of the United States Army's mechanized infantry units from the time of its first fielding in Vietnam in April 1962. The M113 was the most widely used armored vehicle of the U.S...
. These vehicles generally suffered in terms of range and speed, and many forces also adopted wheeled vehicles in addition to, or completely replacing the tracked versions. Examples include the British Saracen
Alvis Saracen
The FV603 Saracen is a six-wheeled armoured personnel carrier built by Alvis and used by the British army. It became a recognisable vehicle as a result of its part in the policing of Northern Ireland.-History:...
and most of the Soviet BTR series, which were far more numerous than the tracked BTR-50. In general, these vehicles offered limited protection and were not expected to join in the actual fighting; they would keep the infantry in close proximity with the armor during movement, but upon enemy contact they would unload their infantry before retreating to safer areas. In US service they were derided as "battlefield taxis".
During the 1950s this mode of combat was increasingly questioned. Unloading the infantry onto a battlefield that was assumed to be littered with chemical and nuclear poisons did not seem like a good idea. Further, while the APCs moved to and from combat the infantry section in the back had nothing to do, a claustrophobic environment where the men could not add to the fight. Military theorists turned to the concept of the infantry fighting vehicle
Infantry fighting vehicle
An infantry fighting vehicle , also known as a mechanized infantry combat vehicle , is a type of armoured fighting vehicle used to carry infantry into battle and provide fire support for them...
(IFV), similar to the APC but with the expectation that the infantry section would be able to stay in the vehicle fight effectively, while also improving the vehicles own armament. The Soviets were the first to adapt to this new style of combat, issuing requirements and then introducing the BMP
BMP-1
The BMP-1 is a Soviet amphibious tracked infantry fighting vehicle. BMP stands for Boyevaya Mashina Pekhoty 1 , meaning "infantry fighting vehicle". The BMP-1 was the world's first mass-produced infantry fighting vehicle...
in the late 1960s, followed soon after by the German Marder
Marder (IFV)
The Marder is a German infantry fighting vehicle operated by the German Army as the main weapon of the Panzergrenadiere from the 1970s through the present day. Developed as part of the rebuilding of Germany's armoured fighting vehicle industry, the Marder has proven to be a successful and solid...
.
Requirements
The requirement for the BMPBMP-1
The BMP-1 is a Soviet amphibious tracked infantry fighting vehicle. BMP stands for Boyevaya Mashina Pekhoty 1 , meaning "infantry fighting vehicle". The BMP-1 was the world's first mass-produced infantry fighting vehicle...
was first drawn up in the late 1950s. The requirement stressed speed, good armament, and the ability for all squad members to fire from within the vehicle. The armament had to provide direct support for dismounted infantry in the attack and defense and to be able to destroy comparable light armored vehicles such as the American M-59
M59 (APC)
The M59 was a U.S. armored personnel carrier that entered service in spring of 1954 replacing the M75. It had three key advantages over the M75: it was amphibious, had a lower profile, and was considerably cheaper to produce. Approximately 6,300 were built before production ended in 1960. The M84...
or the West German HS.30
Schützenpanzer Lang HS.30
The Schützenpanzer Lang HS.30 was a German infantry fighting vehicle developed during the 1950s. It was a Swiss Hispano-Suiza design, with a Rolls-Royce engine. After some early mechanical problems only some 2000 were built of the 10,000 planned...
APCs.
The armor was required to protect the crew and passengers from light shell fragments as well as .50 cal armor-piercing bullets and 20–23 mm caliber autocannons across the frontal arc at distances between 500 m and 800 m (the distance of infantrymen dismounting onto the battlefield during an attack). Side armor should be capable of withstanding 7.62 mm armor-piercing bullets from a distance of 75 m. The requirements also included an NBC protection system, observation devices similar to those used in MBTs and a radio capable of communicating with unit commanders and tanks.
The original specification called for the vehicle to be armed with a 23 millimetre (0.905511811023622 in) autocannon, however an innovative combination of the 73 mm 2A28 Grom
2A28 Grom
The 2A28 Grom is the main armament of the BMP-1 infantry fighting vehicle. It is a 73 mm low pressure smoothbore semi-automatic gun with wedge breechblock.-Description:...
low pressure smoothbore semi-automatic gun firing rocket-assisted projectiles and the newly developed 9S428 anti tank wire guided missile (ATGM) launcher for the selected 9M14 "Malyutka"
AT-3
AT-3 may be:* AT III, a protein in the coagulation system that is activated by Heparin* AT-3 of the Republic of China Air Force * AT-3 plane, Very Light Aircraft* AT-3 Sagger, Soviet anti-tank missile...
(AT-3A Sagger A) ATGMs. The gun was intended to engage enemy armored vehicles and firing points
Firing points
A firing point is a prepared fighting position from which infantry can defend territory with minimal exposure to return fire. Construction ranges from simple sandbag walls to sophisticated, permanent fortifications...
at a range of up to 1300 metres (1,421.7 yd), while the missile launcher was intended to be used against targets that were 500 metres (546.8 yd) to 3000 metres (3,280.8 yd) away. The smoothbore gun and the ATGM launching system were to be mounted in a compact one-man turret from the Tula Instrument Engineering Design Bureau (KBP)
KBP Instrument Design Bureau
KBP Instrument Design Bureau is a Russian developer and manufacturer of high-precision weapons. It was established in 1927 in Tula, USSR. Arkady Shipunov has been the Designer General since 1962...
.
Prototypes
The requirements were issued to the various design bureaus between 1959 and 1960. There was a question as to whether the BMP should be tracked or wheeled, so a number of experimental configurations were explored including hybrid wheeled/tracked designs. The prototypes (designated as "objects" according to Soviet classification) were:- Ob'yekt 1200 from BryanskBryanskBryansk is a city and the administrative center of Bryansk Oblast, Russia, located southwest of Moscow. Population: -History:The first written mention of Bryansk was in 1146, in the Hypatian Codex, as Debryansk...
Automobile Works (BAZ), 1964 - an 8 wheeled design, similar to the BTR-60PBBTR-60The BTR-60 is the first vehicle in a series of Soviet eight-wheeled armoured personnel carriers. It was developed in the late 1950s as a replacement for the BTR-152 and was seen first time in public in 1961...
APC. Like the said APC, the Ob'yekt 1200 prototype had a rear engine design which counted against it. It was eliminated because its cross-country ability (especially in snow and deep mud) was similarly mediocre to the said APC due to the overweight of the 8 x 8 chassis. - Ob'yekt 911 from the VolgogradVolgogradVolgograd , formerly called Tsaritsyn and Stalingrad is an important industrial city and the administrative center of Volgograd Oblast, Russia. It is long, north to south, situated on the western bank of the Volga River...
Tractor Works (VTZ), chief designer I. V. Gavalov, 1964 - was a hybrid tracked design, with 4 additional retractable wheels for high speed road travel. The complex design was felt to offer no advantages. - Ob'yekt 914 from the Volgograd Tractor Works (VTZ), chief designer I. V. Gavalov, 1964 - was a tracked design and a variant of Ob'yekt 911. Based on the PT-76PT-76The PT-76 is a Soviet amphibious light tank which was introduced in the early 1950s and soon became the standard reconnaissance tank of the Soviet Army and the other Warsaw Pact armed forces. It was widely exported to other friendly states, like India, Iraq, North Korea and North Vietnam. Overall,...
amphibious light tank chassis with a similar armament to other BMP prototypes (except the Ob'yekt 914 was also armed with two 7.62 mm PKT machine guns mounted in the hull on both sides of the driver). It weighed 14.4 tonnes, had a crew of two and could transport up to eight fully equipped soldiers (two of whom operated the PKT machine guns). The rear engine design counted against it, forcing infantry to mount and dismount through the single door in the rear of the right hand side of the vehicle and roof hatches. It was also felt that the Ob'yekt 764 had a better layout. Work on the experimental Ob'yekt 914 helped a lot in the following layout development of the BMD-1BMD-1The BMD-1 is a Soviet airborne amphibious tracked infantry fighting vehicle, which was introduced in 1969 and first seen by the West in 1970. BMD stands for Boyevaya Mashina Desanta . It can be dropped by parachute and although it resembles the BMP-1 it is in fact much smaller...
(Ob'yekt 915) airborne infantry fighting vehicle. - Ob'yekt 19 from the Altai Tractor Works in RubtsovskRubtsovskRubtsovsk is a city in Altai Krai, Russia, located on the Aley River southwest of Barnaul. Population: 167,000 ; 111,000 ; 38,000 ....
, 1965 - was a 4 x 4 wheeled design with retractable tracks between the wheel axles which were intended for crossing rough ground. Once again the very complicated hybrid design was felt to offer no clear advantage over a tracked design. - Ob'yekt 764 from the Chelyabinsk Tractor Works (ChTZ)Chelyabinsk Tractor PlantChelyabinsk Tractor Plant also known as CTZ-Uraltrak is a tractor plant in the Russian city of Chelyabinsk.-History:The plant was founded in 1933; the first product was a 60 hp tracked tractor С-60 fueled by petroleum ether . In 1937 the factory produced its first diesel-powered vehicle C-65...
; chief designer P. P. Isakov, 1964-1965 - the main prototype of the BMP was equipped with a waterjet for swimming (the waterjet was later removed to save interior space). After it passed the trials, it was improved and became the BMP-1 (Ob'yekt 765).
During this time, the United States had successfully introduced the M113
M113 armored personnel carrier
The M113 is a fully tracked armored personnel carrier that has formed the backbone of the United States Army's mechanized infantry units from the time of its first fielding in Vietnam in April 1962. The M113 was the most widely used armored vehicle of the U.S...
armored personnel carrier in the Vietnam War
Vietnam War
The Vietnam War was a Cold War-era military conflict that occurred in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. This war followed the First Indochina War and was fought between North Vietnam, supported by its communist allies, and the government of...
in 1962. Though not designed as a combat vehicle, its light armor and mobility was effective against most small arms employed by the Viet Cong forces. It had been adapted into an infantry fighting vehicle with the fitting of an open turret and gun shields. Unlike the BMP, it lacked the firepower and armor to defeat and survive against other armored combat vehicles. After the appearance of the BMP, the US responded with a series of infantry fighting vehicle designs, starting with the MICV-65
MICV-65
MICV-65, short for Mechanized Infantry Combat Vehicle, 1965, was a US Army project that studied a number of armored fighting vehicles that would replace the M113 and M114 as well as take on a variety of new roles. A number of designs were studied as part of the MICV project, but none of the entered...
, although nothing entered service until the M-2 Bradley appeared during the early 1980s.
Ob'yekt 765
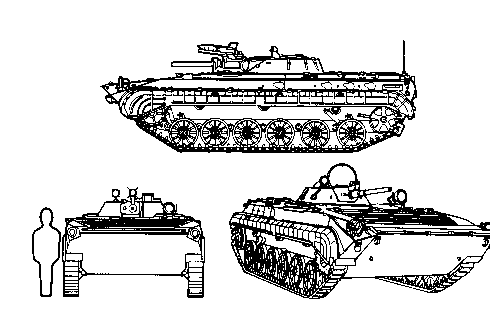
The tracked Ob'yekt 764 was chosen, after a few improvements, because its front engine design provided a convenient and fast way of mounting and dismounting through two rear doors. As a result of its rather weak armor, the BMP was relatively light and required little preparation for amphibious operations.
The original production prototype, which was built in 1965, was designated BMP. Small scale production began in 1966 at Chelyabinsk
Chelyabinsk
Chelyabinsk is a city and the administrative center of Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, located in the northwestern side of the oblast, south of Yekaterinburg, just to the east of the Ural Mountains, on the Miass River. Population: -History:...
to permit field trials, although the Kurgan Machine Building Plant (KMZ) was converted to BMP production as Chelyabinsk was committed to tank production. A number of defects were corrected between 1966 and 1970 resulting in four slightly different production design variants of the first models. (Ob'yekt 765Sp1 and Ob'yekt 765Sp2). The key changes made to the design were:
- The suspension was strengthened to cope with high speeds.
- A new chemical filter system was fitted on the left hand side of the turret in addition to the already existing radiological protection system.
- The openly mounted air filtration system was moved from the left hand side of the hull to a separate compartment inside the vehicle behind the commander's station.
- The fume extractors for the firing ports were moved to eject the fumes to the rear of the vehicle.
- The trim board was modified.
- The new air intake was fitted with a low snorkel to prevent water flooding the vehicle while swimming.
- The fender profile was modified.
- The detachable hatch cover over the engine compartment was replaced with a hinged cover.
- The Commander's hatch was fitted with a torsion bar, the troop hatches were fitted with key locks.
- The tool stowage boxes on the fenders were removed.
- Firing ports (one on each side) were provided for the squad's PKMPK machine gunThe PK is a 7.62 mm general-purpose machine gun designed in the Soviet Union and currently in production in Russia. The PK machine gun was introduced in the 1960s and replaced the SGM and RPD machine guns in Soviet service...
general purpose machine gun. - The 9S428 ATGM launcher was improved to fire 9M14M 'Malyutka-M' (AT-3B Sagger B) ATGMs.
- The nose section of the hull was modified and extended by 250 mm to shift the center of gravity to prevent the nose section from being too heavy, it could often cause "submarining" when swimming. The height of the hull was slightly increased for the same purpose.
Further improvements included a new 1PN22M2 sight, turn signals, and many smaller details, (for example, mounting the trim vane on six hinges instead of two, improved hermetic sealing of the commander's hatch, new construction of the gunner's seat, etc.). All those changes resulted in the combat weight increasing from 13.0 tonnes to 13.2 tonnes. Series production of the final production model, the Ob'yekt 765Sp3 (NATO: BMP-1 Model 1970), began at the Kurgan Engineering Works in 1973.
Models
A large number of variants of the BMP-1 were produced. The most notable IFV variants based on the BMP-1 were: BMP-2BMP-2
The BMP-2 is a second-generation, amphibious infantry fighting vehicle introduced in the 1980s in the Soviet Union, following the BMP-1 of the 1960s....
, MLI-84
MLI-84
The MLI-84 is a native-made Romanian infantry fighting vehicle currently in service with the Romanian Land Forces. It is basically a stock BMP-1 with a lengthened hull and a 12.7x108mm DShK 1938/46 heavy machine gun mounted on the roof of the troop compartment....
and Boragh
Boragh
The Boragh is an Iranian-made armoured personnel carrier. Boragh is believed to be a reverse engineered and upgraded model of the Chinese Type 86 . The upgrades include a reduction in weight, a higher road speed, and stronger armor...
.
Table of models
| BMP-1 (ob'yekt 765Sp1) | BMP-1 (ob'yekt 765Sp2) | BMP-1 (ob'yekt 765Sp3) |
BMP-1P (ob'yekt 765Sp4/5) | BMP-1D | BMP-2 BMP-2 The BMP-2 is a second-generation, amphibious infantry fighting vehicle introduced in the 1980s in the Soviet Union, following the BMP-1 of the 1960s.... |
BMP-3 BMP-3 The BMP-3 is a Russian amphibious infantry fighting vehicle, successor to the BMP-1 and BMP-2. BMP stands for Boyevaya Mashina Pekhoty .- Production history :... |
|
| Weight (tonnes) |
12.6 | 13.0 | 13.2 | 13.4 | 14.5 | 14.0 | 18.7 |
| Crew | 3+8 | 3+7 | |||||
| Main gun | 73 mm 2A28 "Grom" low pressure smoothbore semi-automatic gun | 30 mm 2A42 30 mm automatic cannon 2A42 The 30 mm automatic cannon 2A42, also known as the Shipunov 2A42, is a Soviet/Russian 30 mm automatic cannon. It is built by the Tulamashzavod Joint Stock Company.-Design:... autocannon |
100 mm 2A70 rifled automatic gun/missile-launcher 30 mm 2A72 autocannon |
||||
| Machine gun(s) | 7.62 mm PKT coaxial | 3 × 7.62 mm PKT (1 coaxial, 2 bow mounted) | |||||
| ATGM (NATO designation) | 9M14 "Malyutka" (AT-3 Sagger) and variants |
9M113 "Konkurs" (AT-5 Spandrel) or 9M111 "Fagot" (AT-4 Spigot) and variants |
9M14 "Malyutka" or 9M113 "Konkurs" or removed (on most vehicles) |
9M113 "Konkurs" (AT-5 Spandrel) or 9M111 "Fagot" (AT-4 Spigot) and variants |
9M117 "Bastion" 9M117 Bastion The 9M117 Bastion is a Russian laser beam-riding anti-tank missile. It is used in a number of separate weapon systems including the 9K116-1 Bastion missile system , 9K118 Sheksna , Kastet and the 3UBK12 fired from the BMP-3... (AT-10 Stabber) |
||
| Engine | UTD-20 6-cylinder 4-stroke V-shaped airless-injection water cooled diesel developing 300 hp (224 kW) at 2,600 rpm |
UTD-20S1 diesel developing 300 hp (224 kW) at 2,600 rpm |
UTD-29M 10-cylinder diesel developing 500 hp (375 kW) at 2,600 rpm |
||||
| Power-to-weight ratio hp/tonne (kW/tonne) |
23.8 (17.8) |
23.1 (17.2) |
22.7 (17.0) |
22.4 (16.7) | 20.7 (15.5) |
21.4 (16.0) | 26.7 (20.0) |
BMP-2
Although the BMP-1BMP-1
The BMP-1 is a Soviet amphibious tracked infantry fighting vehicle. BMP stands for Boyevaya Mashina Pekhoty 1 , meaning "infantry fighting vehicle". The BMP-1 was the world's first mass-produced infantry fighting vehicle...
was a revolutionary design, its main armament, the 2A28 Grom
2A28 Grom
The 2A28 Grom is the main armament of the BMP-1 infantry fighting vehicle. It is a 73 mm low pressure smoothbore semi-automatic gun with wedge breechblock.-Description:...
and the 9S428 ATGM launcher capable of firing the 9M14 Malyutka (NATO: AT-3A Sagger A) and the 9M14M Malyutka-M (NATO: AT-3B Sagger B) ATGMs, quickly became obsolete. Therefore the Soviet Union decided to produce an updated and improved version of the BMP-1. The main emphasis was put on improving the main armament. In 1972 work got underway to develop an improved version of the BMP-1. An experimental prototype, the Ob'yekt 680 was produced. Ob'yekt 680 had a new two-man turret armed with a Shipunov 2A42 30 mm autocannon and a secondary 7.62 mm machine gun mounted in a barbette similar to the Marder.
The BMP-1 was to be tested in combat in the October 1973 Yom Kippur War
Yom Kippur War
The Yom Kippur War, Ramadan War or October War , also known as the 1973 Arab-Israeli War and the Fourth Arab-Israeli War, was fought from October 6 to 25, 1973, between Israel and a coalition of Arab states led by Egypt and Syria...
. Egypt
Egypt
Egypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world...
received 230 BMP-1s in 1973. Syria
Syria
Syria , officially the Syrian Arab Republic , is a country in Western Asia, bordering Lebanon and the Mediterranean Sea to the West, Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east, Jordan to the south, and Israel to the southwest....
had received between 150 and 170 by the start of the war, of which about 100 were committed to the front line. Israeli forces captured or destroyed 40 to 60 Egyptian BMPs and 50 to 60 Syrian BMPs, mechanical problems accounting for a large number of the Syrian losses.
The BMP proved vulnerable to .50 caliber machinegun fire in the sides and rear, and to infantry-based 106 mm recoilless rifle
Recoilless rifle
A recoilless rifle or recoilless gun is a lightweight weapon that fires a heavier projectile than would be practical to fire from a recoiling weapon of comparable size. Technically, only devices that use a rifled barrel are recoilless rifles. Smoothbore variants are recoilless guns...
s. The need to keep some of the roof hatches open to prevent the vehicle from overheating meant that the vehicle could be disabled by machinegun fire from infantry on higher ground shooting into open hatches. The 73 mm gun
2A28 Grom
The 2A28 Grom is the main armament of the BMP-1 infantry fighting vehicle. It is a 73 mm low pressure smoothbore semi-automatic gun with wedge breechblock.-Description:...
proved inaccurate beyond 500 meters, and the AT-3 Sagger
AT-3 Sagger
The 9K11 Malyutka is a Manual Command to Line-of-Sight wire-guided anti-tank guided missile developed in the Soviet Union. It was the first man-portable anti-tank guided missile of the Soviet Union and is probably the most widely produced ATGM of all time—with Soviet production peaking at...
missile could not be guided effectively from the confines of the turret. The BMP-1's low profile means that it was difficult for the BMP to fire over the heads of the advancing infantry it was supporting.
On the positive side, the vehicle was praised for being fast and agile. Its low ground pressure enabled it to navigate the northern Kantara salt marshes where other vehicles would have bogged down. Its ability to swim proved useful: it was used in the first wave of canal crossings by the Egyptians.
Several Soviet technical teams were sent to Syria in the wake of the war to gather information. These lessons combined with observations of western AFV developments resulting in a replacement program for the original BMP in 1974.
The first product of this program was the BMP-1P upgrade intended as a stopgap to address the most serious problems with the existing design. Smoke grenade launchers were added to the rear of the turret and the manually guided
MCLOS
MCLOS is a first-generation method for guiding guided missiles.With an MCLOS missile, the operator must track the missile and the target simultaneously and guide the missile to the target. Typically the missile is steered with a joystick, and its path is observed through a periscope-type...
AT-3 Sagger
AT-3 Sagger
The 9K11 Malyutka is a Manual Command to Line-of-Sight wire-guided anti-tank guided missile developed in the Soviet Union. It was the first man-portable anti-tank guided missile of the Soviet Union and is probably the most widely produced ATGM of all time—with Soviet production peaking at...
missile system was replaced with the semi-automatically
SACLOS
SACLOS is an acronym for Semi-Automatic Command to Line of Sight, a second-generation method of missile guidance. In SACLOS, the operator has to continually point a sighting device at the target while the missile is in flight...
guided AT-4 Spigot
AT-4 Spigot
The 9K111 Fagot is a SACLOS wire-guided anti-tank missile system of the Soviet Union. "9M111" is the GRAU designation of the missile. Its NATO reporting name is AT-4 Spigot.-Development:...
and AT-5 Spandrel
AT-5 Spandrel
The 9M113 Konkurs SACLOS wire-guided Anti-tank missile of the Soviet Union. "9M113" is the GRAU designation of the missile. Its NATO reporting name is AT-5 Spandrel.-Development:...
system. The new missiles were somewhat difficult to use since the gunner had to actually stand out on the roof to use the weapons, exposing himself to hostile fire. The BMP-1P was in production by the late 1970s and existing BMP-1s were gradually upgraded to the standard during the 1980s.
A development program to completely address the shortcomings of the BMP was started at the same time resulting in four prototypes, all of which had two man turrets.
- Ob'yekt 675 from KurganKurganKurgan is the Turkic term for a tumulus; mound of earth and stones raised over a grave or graves, originating with its use in Soviet archaeology, now widely used for tumuli in the context of Eastern European and Central Asian archaeology....
- BMP-1 hull, armed with a 2A42 30 mm autocannon. This eventually became the BMP-2. - Ob'yekt 681 from KurganKurganKurgan is the Turkic term for a tumulus; mound of earth and stones raised over a grave or graves, originating with its use in Soviet archaeology, now widely used for tumuli in the context of Eastern European and Central Asian archaeology....
- BMP-1 hull, armed with a lengthened 73 mm gun. - Ob'yekt 768 from ChelyabinskChelyabinskChelyabinsk is a city and the administrative center of Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, located in the northwestern side of the oblast, south of Yekaterinburg, just to the east of the Ural Mountains, on the Miass River. Population: -History:...
- Lengthened hull with 7 road wheels and armed with a lengthened 73 mm gun. - Ob'yekt 769 from ChelyabinskChelyabinskChelyabinsk is a city and the administrative center of Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, located in the northwestern side of the oblast, south of Yekaterinburg, just to the east of the Ural Mountains, on the Miass River. Population: -History:...
- Lengthened hull with 7 road wheels and armed with a 2A42 30 mm autocannon.
The commander was moved inside the turret on all of the prototypes because of the dead zone created by the infra-red searchlight when he was seated in the hull, additionally the commanders view to the rear was blocked by the turret. The new two man turret took up much more space in the hull than the original one man turret resulting in a smaller crew area. A lengthened version of the original 73 mm gun was considered, but after some debate the 30 mm gun was selected for the following reasons:
- It offered higher maximum elevation - a critical factor in AfghanistanAfghanistanAfghanistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in the centre of Asia, forming South Asia, Central Asia and the Middle East. With a population of about 29 million, it has an area of , making it the 42nd most populous and 41st largest nation in the world...
, where the limited elevation of the gun2A28 GromThe 2A28 Grom is the main armament of the BMP-1 infantry fighting vehicle. It is a 73 mm low pressure smoothbore semi-automatic gun with wedge breechblock.-Description:...
caused problems. - The high velocity gun had better maximum range (2000 – 4000 meters) that would allow the BMPs to support the tanks spearheading any assault.
- It also offered a useful anti-helicopter capability.
- The 73 mm gun had been mounted on the older BMP-1 to retain anti-tank capability as a basic doctrineMilitary doctrineMilitary doctrine is the concise expression of how military forces contribute to campaigns, major operations, battles, and engagements.It is a guide to action, not hard and fast rules. Doctrine provides a common frame of reference across the military...
design specificationDesign specificationA design specification provides explicit information about the requirements for a product and how the product is to be put together. It is the most traditional kind of specification, having been used historically in public contracting for buildings, highways, and other public works, and represents...
. With the introduction of Chobham armourChobham armourChobham armour is the name informally given to a composite armour developed in the 1960s at the British tank research centre on Chobham Common, Surrey, England...
on NATO tanks, the 73 mm gun became ineffectual and obsolete, and given a lack of a suitable gun design as a replacement in this role at the time, a 30 mm gun was introduced as a replacement, notably with an anti-helicopter role as a new threat emergent since the Vietnam War. (Perrett 1987:77) The anti-tank capability was however retained in the BMP-2 with the continued use of anti-tank guided missileAnti-tank guided missileAn anti-tank missile , anti-tank guided missile , anti-tank guided weapon or anti-armor guided weapon is a guided missile primarily designed to hit and destroy heavily-armored military vehicles....
s. The new vehicles now allowed the gunner to fire 9K111 Fagot (AT-4) and 9M113 Konkurs (AT-5) missiles from within the protection of the turretTurretIn architecture, a turret is a small tower that projects vertically from the wall of a building such as a medieval castle. Turrets were used to provide a projecting defensive position allowing covering fire to the adjacent wall in the days of military fortification...
.
Eventually the Ob'yekt 675 was selected to become the BMP-2, probably because a new hull design would have required extensive retooling at BMP production plants.
BMP-3
The design of the BMP-3 or Obyekt 688M can be traced back to the Obyekt 685 light tank prototype with 100 mm gun 2A48-1 from 1975. This vehicle did not enter series production, but the chassis, with a new engine, was used for the next-generation infantry combat vehicle Obyekt 688 from A. Blagonravov's design bureau. The Ob. 688 weapons configuration—an externally-mounted 30 mm gun and twin Konkurs ATGM launcher—was rejected; instead the new 2K23 armament system was selected. The resulting BMP-3 was developed in the early 1980s and entered service with the Soviet army officially in 1987.See also
- Infantry fighting vehicleInfantry fighting vehicleAn infantry fighting vehicle , also known as a mechanized infantry combat vehicle , is a type of armoured fighting vehicle used to carry infantry into battle and provide fire support for them...
- Armored personnel carrier
- M113 armored personnel carrierM113 armored personnel carrierThe M113 is a fully tracked armored personnel carrier that has formed the backbone of the United States Army's mechanized infantry units from the time of its first fielding in Vietnam in April 1962. The M113 was the most widely used armored vehicle of the U.S...
- M3 Halftrack
- Mechanized infantryMechanized infantryMechanized infantry are infantry equipped with armored personnel carriers , or infantry fighting vehicles for transport and combat ....
- MICV-65MICV-65MICV-65, short for Mechanized Infantry Combat Vehicle, 1965, was a US Army project that studied a number of armored fighting vehicles that would replace the M113 and M114 as well as take on a variety of new roles. A number of designs were studied as part of the MICV project, but none of the entered...
- BMP-23BMP-23The BMP-23 is a Bulgarian infantry fighting vehicle which was first introduced in the early 1980s. Despite its name, the BMP-23 is very different from the BMP-1 and more similar to BMP-2. The hull is based around that of the Soviet 2S1 Gvozdika, but with thicker armour and a more powerful diesel...
- M2 BradleyM2 BradleyThe Bradley Fighting Vehicle is an American fighting vehicle platform manufactured by BAE Systems Land and Armaments, formerly United Defense.As with other infantry fighting vehicles, the Bradley is designed to transport infantry with armor protection while providing covering fire to suppress enemy...
- BTR-50BTR-50The BTR-50 The BTR-50 The BTR-50 (BTR stands for Bronetransporter (БТР, Бронетранспортер, literally "armored transporter") is a Soviet amphibious armored personnel carrier (APC) based on the PT-76 light tank. The BTR-50 is tracked, unlike most in the BTR series, which are wheeled. The BTR-50...
- BTR-60BTR-60The BTR-60 is the first vehicle in a series of Soviet eight-wheeled armoured personnel carriers. It was developed in the late 1950s as a replacement for the BTR-152 and was seen first time in public in 1961...

