Zinc-copper couple
Encyclopedia
Zinc-copper couple is an alloy
of zinc
and copper
that is employed as a reagent in organic synthesis
. The “couple” was popularized after the report by Simmons and Smith in 1959 of its application as an activated source of zinc required for formation of an organozinc reagent
in the Simmons-Smith cyclopropanation
of alkene
s. The couple has been widely applied as a reagent in other reactions requiring activated zinc metal. Zinc-copper couple does not refer to a rigorously defined chemical structure or alloy composition. The couple may contain varying proportions of copper and zinc; the zinc content is typically greater than 90%, although an alloy containing similar proportions of zinc and copper is used in some cases. The couple is frequently prepared as a darkly-colored powder and is slurried in an ethereal solvent prior to being used in slight excess relative to the substrate. Activation of zinc by copper is essential to the couple’s utility, but the origin of this effect is poorly documented. It is speculated that copper enhances reactivity of zinc at the surface of the alloy.
An early method for the synthesis of zinc-copper couple entailed treatment of a mixture of zinc dust and copper(II) oxide
with hydrogen
gas at 500 °C. A more convenient and cheaper method proceeds by treatment of zinc powder with hydrochloric acid
and copper(II) sulfate. Treatment of zinc powder with copper(II) acetate monohydrate in hot acetic acid
is reportedly highly reproducible. The couple may also be generated in situ by reaction of one equivalent of zinc dust with one equivalent of copper(I) chloride
(or copper powder) in refluxing ether
.
The choice of method is dictated primarily by the application. The development of newer methods was motivated by the need for zinc-copper couple with reproducible behavior.
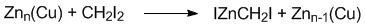
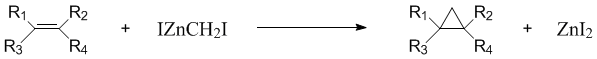
The couple has also been employed to generate alkyl zinc reagents for conjugate addition, as a dehalogenating reagent, as a promoter of reductive coupling of carbonyl compounds, and to reduce
electron-deficient alkenes and alkynes. Sonication
has been employed to enhance the rate of the zinc-copper couple-mediated cycloaddition
of α,α’-dibromo ketones to 1,3-dienes.
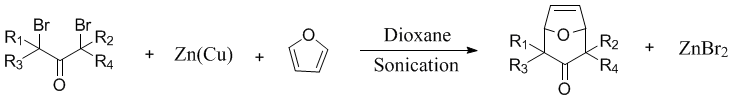
Alloy
An alloy is a mixture or metallic solid solution composed of two or more elements. Complete solid solution alloys give single solid phase microstructure, while partial solutions give two or more phases that may or may not be homogeneous in distribution, depending on thermal history...
of zinc
Zinc
Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2...
and copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
that is employed as a reagent in organic synthesis
Organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the construction of organic compounds via organic reactions. Organic molecules can often contain a higher level of complexity compared to purely inorganic compounds, so the synthesis of organic compounds has...
. The “couple” was popularized after the report by Simmons and Smith in 1959 of its application as an activated source of zinc required for formation of an organozinc reagent
Organozinc compound
Organozinc compounds in organic chemistry contain carbon to zinc chemical bonds. Organozinc chemistry is the science of organozinc compounds describing their physical properties, synthesis and reactions....
in the Simmons-Smith cyclopropanation
Simmons-Smith reaction
The Simmons–Smith reaction is an organic cheletropic reaction in which a carbenoid reacts with an alkene to form a cyclopropane. It is named after Howard Ensign Simmons, Jr. and R. D. Smith...
of alkene
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, olefin, or olefine is an unsaturated chemical compound containing at least one carbon-to-carbon double bond...
s. The couple has been widely applied as a reagent in other reactions requiring activated zinc metal. Zinc-copper couple does not refer to a rigorously defined chemical structure or alloy composition. The couple may contain varying proportions of copper and zinc; the zinc content is typically greater than 90%, although an alloy containing similar proportions of zinc and copper is used in some cases. The couple is frequently prepared as a darkly-colored powder and is slurried in an ethereal solvent prior to being used in slight excess relative to the substrate. Activation of zinc by copper is essential to the couple’s utility, but the origin of this effect is poorly documented. It is speculated that copper enhances reactivity of zinc at the surface of the alloy.
Synthesis
Zinc-copper couple has been prepared by numerous methods, which vary mainly with respect to the source of copper, but also by the ratio of copper to zinc, the physical state of the zinc (e.g. powder or granules), the use of protic acids and other additives, and temperature of the preparation. Most often the couple is generated and isolated prior to use, but routes have been described to storable forms of the alloy. Most methods involve reduction of an oxidized copper species with zinc, which is used in excess.An early method for the synthesis of zinc-copper couple entailed treatment of a mixture of zinc dust and copper(II) oxide
Copper(II) oxide
Copper oxide or cupric oxide is the higher oxide of copper. As a mineral, it is known as tenorite.-Chemistry:It is a black solid with an ionic structure which melts above 1200 °C with some loss of oxygen...
with hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
gas at 500 °C. A more convenient and cheaper method proceeds by treatment of zinc powder with hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid is a solution of hydrogen chloride in water, that is a highly corrosive, strong mineral acid with many industrial uses. It is found naturally in gastric acid....
and copper(II) sulfate. Treatment of zinc powder with copper(II) acetate monohydrate in hot acetic acid
Acetic acid
Acetic acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3CO2H . It is a colourless liquid that when undiluted is also called glacial acetic acid. Acetic acid is the main component of vinegar , and has a distinctive sour taste and pungent smell...
is reportedly highly reproducible. The couple may also be generated in situ by reaction of one equivalent of zinc dust with one equivalent of copper(I) chloride
Copper(I) chloride
Copper chloride, commonly called cuprous chloride, is the lower chloride of copper, with the formula CuCl. The substance is a white solid sparingly soluble in water, but very soluble in concentrated hydrochloric acid...
(or copper powder) in refluxing ether
Ether
Ethers are a class of organic compounds that contain an ether group — an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups — of general formula R–O–R'. A typical example is the solvent and anesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether"...
.
The choice of method is dictated primarily by the application. The development of newer methods was motivated by the need for zinc-copper couple with reproducible behavior.
Application
Zinc-copper couple has found widespread use in organic synthesis, especially in the Simmons-Smith cyclopropanation of alkenes. In this application, the couple (typically a slurry in an ethereal solvent) reacts with methylene iodide to generate iodomethylzinc iodide, which is the intermediate responsible for cyclopropanation.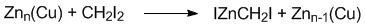
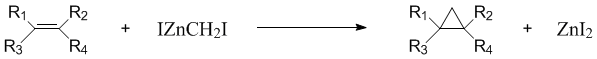
The couple has also been employed to generate alkyl zinc reagents for conjugate addition, as a dehalogenating reagent, as a promoter of reductive coupling of carbonyl compounds, and to reduce
Redox
Redox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed....
electron-deficient alkenes and alkynes. Sonication
Sonication
thumb|right|A sonicator at the [[Weizmann Institute of Science]] during sonicationSonication is the act of applying sound energy to agitate particles in a sample, for various purposes. In the laboratory, it is usually applied using an ultrasonic bath or an ultrasonic probe, colloquially known as...
has been employed to enhance the rate of the zinc-copper couple-mediated cycloaddition
Cycloaddition
A cycloaddition is a pericyclic chemical reaction, in which "two or more unsaturated molecules combine with the formation of a cyclic adduct in which there is a net reduction of the bond multiplicity." The resulting reaction is a cyclization reaction.Cycloadditions are usually described by the...
of α,α’-dibromo ketones to 1,3-dienes.