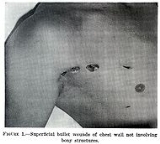
Wound
Encyclopedia
A wound is a type of injury
in which skin
is torn, cut or punctured (an open wound), or where blunt force trauma
causes a contusion
(a closed wound). In pathology
, it specifically refers to a sharp injury which damages the dermis
of the skin.
a wound, the body undertakes a series of actions collectively known as the wound healing
process.
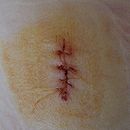 The treatment depends on the type, cause, and depth of the wound as well as whether other structure beyond the skin are involved. Treatment of recent lacerations involves examination, cleaning, and closing the wound. If the laceration occurred some time ago it may be allowed to heal by secondary intention due to the high rate of infection with immediate closure. Minor wounds like bruises will heal on their own with skin discoloration usually disappears in 1–2 weeks. Abrasions which are wounds with intact skin usually require no active treatment except keeping the area clean with soap and water. Puncture wounds may be prone to infection depending on the depth of penetration. The entry of puncture wound is left open to allow for bacteria or debris to be removed from inside.
The treatment depends on the type, cause, and depth of the wound as well as whether other structure beyond the skin are involved. Treatment of recent lacerations involves examination, cleaning, and closing the wound. If the laceration occurred some time ago it may be allowed to heal by secondary intention due to the high rate of infection with immediate closure. Minor wounds like bruises will heal on their own with skin discoloration usually disappears in 1–2 weeks. Abrasions which are wounds with intact skin usually require no active treatment except keeping the area clean with soap and water. Puncture wounds may be prone to infection depending on the depth of penetration. The entry of puncture wound is left open to allow for bacteria or debris to be removed from inside.
, sterile saline solution
, or antiseptic solution. Infection rates may be lower with the use of tap water in regions where water quality is high. Evidence for the effectiveness of any cleaning of simple wound however is limited.
If closure of a wound is decided upon a number of techniques can be used. These include bandage
s, a cyanoacrylate
glue, staples
, and sutures. Absorbable sutures have the benefit over non absorbable sutures of not requiring removal. They are often preferred in children. Buffering the pH
of lidocaine
makes the freezing less painful.
are positive. Excess use of antibiotics only leads to resistance and side effects. All open wounds should be cleaned at least twice a day with warm water and soap. Once the wound is cleaned, it should be covered with moist gauze
. This should be followed by application of dry gauze and then the wound covered with a bandage. The purpose of a wet to dry dressing allows the bandage to adhere to dead tissue performing a mechanical debridement when removed.This allows new healthy skin to grow and prevents debris from collecting.
When the wound is clean, it may be closed with a skin graft. No wound is ever closed if it is suspected to be infected.
of wound can impede the healing process and lead to life threatening complications. Scientists at Sheffield University have identified a way of using light to rapidly detect the presence of bacteria
. They are developing a portable kit in which specially designed molecules emit a light signal when bound to bacteria. Current laboratory-based detection of bacteria can take hours or even days.
Although diabetes can ravage the body in many ways, non-healing ulcers on the feet and lower legs are common outward manifestations of the disease. Also, diabetics often suffer from nerve damage in their feet and legs, allowing small wounds or irritations to develop without awareness. Given the abnormalities of the microvasculature and other side effects of diabetes, these wounds take a long time to heal and require a specialized treatment approach for proper healing.
As many as 25% of diabetic patients will eventually develop foot ulcers, and recurrence within five years is 70%. If not aggressively treated, these wounds can lead to amputations. It is estimated that every 30 seconds a lower limb is amputated somewhere in the world because of a diabetic wound. Amputation often triggers a downward spiral of declining quality of life, frequently leading to disability and death. In fact, only about one third of diabetic amputees will live more than five years, a survival rate equivalent to that of many cancers.
Many of these lower extremity amputations can be prevented through an interdisciplinary approach to treatment involving a variety of advanced therapies and techniques, such as debridement, hyperbaric oxygen treatment therapy, dressing selection, special shoes, and patient education. When wounds persist, a specialized approach is required for healing.
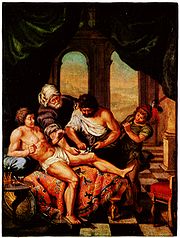 From the Classical Period
From the Classical Period
to the Medieval Period, the body and the soul were believed to be intimately connected, based on several theories put forth by the philosopher Plato
. Wounds on the body were believed to correlate with wounds to the soul and vice versa; wounds were seen as an outward sign of an inward illness. Thus, a man who was wounded physically in a serious way was said to be hindered not only physically but spiritually as well. If the soul was wounded, that wound may also eventually become physically manifest, revealing the true state of the soul. Wounds were also seen as writing on the "tablet" of the body. Wounds acquired in war, for example, told the story of a soldier in a form which all could see and understand, and the wounds of a martyr
told the story of their faith.
Injury
-By cause:*Traumatic injury, a body wound or shock produced by sudden physical injury, as from violence or accident*Other injuries from external physical causes, such as radiation injury, burn injury or frostbite*Injury from infection...
in which skin
Skin
-Dermis:The dermis is the layer of skin beneath the epidermis that consists of connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. The dermis is tightly connected to the epidermis by a basement membrane. It also harbors many Mechanoreceptors that provide the sense of touch and heat...
is torn, cut or punctured (an open wound), or where blunt force trauma
Physical trauma
Trauma refers to "a body wound or shock produced by sudden physical injury, as from violence or accident." It can also be described as "a physical wound or injury, such as a fracture or blow." Major trauma can result in secondary complications such as circulatory shock, respiratory failure and death...
causes a contusion
Bruise
A bruise, also called a contusion, is a type of relatively minor hematoma of tissue in which capillaries and sometimes venules are damaged by trauma, allowing blood to seep into the surrounding interstitial tissues. Bruises can involve capillaries at the level of skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscle,...
(a closed wound). In pathology
Pathology
Pathology is the precise study and diagnosis of disease. The word pathology is from Ancient Greek , pathos, "feeling, suffering"; and , -logia, "the study of". Pathologization, to pathologize, refers to the process of defining a condition or behavior as pathological, e.g. pathological gambling....
, it specifically refers to a sharp injury which damages the dermis
Dermis
The dermis is a layer of skin between the epidermis and subcutaneous tissues, and is composed of two layers, the papillary and reticular dermis...
of the skin.
Open
Open wounds can be classified according to the object that caused the wound. The types of open wound are:- Incisions or incised wounds, caused by a clean, sharp-edged object such as a knifeKnifeA knife is a cutting tool with an exposed cutting edge or blade, hand-held or otherwise, with or without a handle. Knives were used at least two-and-a-half million years ago, as evidenced by the Oldowan tools...
, a razorRazorA razor is a bladed tool primarily used in the removal of unwanted body hair through the act of shaving. Kinds of razors include straight razors, disposable razors and electric razors....
or a glass splinter. - Lacerations, irregular tear-like wounds caused by some blunt traumaBlunt traumaIn medical terminology, blunt trauma, blunt injury, non-penetrating trauma or blunt force trauma refers to a type of physical trauma caused to a body part, either by impact, injury or physical attack; the latter usually being referred to as blunt force trauma...
. Lacerations and incisions may appear linear (regular) or stellate (irregular). The term laceration is commonly misused in reference to incisions. - Abrasions (grazes), superficial wounds in which the topmost layer of the skinSkin-Dermis:The dermis is the layer of skin beneath the epidermis that consists of connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. The dermis is tightly connected to the epidermis by a basement membrane. It also harbors many Mechanoreceptors that provide the sense of touch and heat...
(the epidermis) is scraped off. Abrasions are often caused by a sliding fall onto a rough surface. - Puncture wounds, caused by an object puncturing the skinSkin-Dermis:The dermis is the layer of skin beneath the epidermis that consists of connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. The dermis is tightly connected to the epidermis by a basement membrane. It also harbors many Mechanoreceptors that provide the sense of touch and heat...
, such as a nail or needleHypodermic needleA hypodermic needle is a hollow needle commonly used with a syringe to inject substances into the body or extract fluids from it...
. - Penetration woundPenetrating traumaPenetrating trauma is an injury that occurs when an object pierces the skin and enters a tissue of the body, creating an open wound. In blunt, or non-penetrating trauma, there may be an impact, but the skin is not necessarily broken. The penetrating object may remain in the tissues, come back out...
s, caused by an object such as a knife entering and coming out from the skin . - Gunshot woundsBallistic traumaThe term ballistic trauma refers to a form of physical trauma sustained from the discharge of arms or munitions. The most common forms of ballistic trauma stem from firearms used in armed conflicts, civilian sporting and recreational pursuits, and criminal activity.-Destructive effects:The degree...
, caused by a bulletBulletA bullet is a projectile propelled by a firearm, sling, or air gun. Bullets do not normally contain explosives, but damage the intended target by impact and penetration...
or similar projectile driving into or through the body. There may be two wounds, one at the site of entry and one at the site of exit, generally referred to as a "through-and-through."
Closed
Closed wounds have fewer categories, but are just as dangerous as open wounds. The types of closed wounds are:- Contusions, more commonly known as bruiseBruiseA bruise, also called a contusion, is a type of relatively minor hematoma of tissue in which capillaries and sometimes venules are damaged by trauma, allowing blood to seep into the surrounding interstitial tissues. Bruises can involve capillaries at the level of skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscle,...
s, caused by a blunt force trauma that damages tissueBiological tissueTissue is a cellular organizational level intermediate between cells and a complete organism. A tissue is an ensemble of cells, not necessarily identical, but from the same origin, that together carry out a specific function. These are called tissues because of their identical functioning...
under the skin. - HematomaHematomaA hematoma, or haematoma, is a localized collection of blood outside the blood vessels, usually in liquid form within the tissue. This distinguishes it from an ecchymosis, which is the spread of blood under the skin in a thin layer, commonly called a bruise...
s, also called a blood tumor, caused by damage to a blood vesselBlood vesselThe blood vessels are the part of the circulatory system that transports blood throughout the body. There are three major types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the capillaries, which enable the actual exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and...
that in turn causes bloodBloodBlood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells....
to collect under the skinSkin-Dermis:The dermis is the layer of skin beneath the epidermis that consists of connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. The dermis is tightly connected to the epidermis by a basement membrane. It also harbors many Mechanoreceptors that provide the sense of touch and heat...
. - Crush injury, caused by a great or extreme amount of force applied over a long period of time.
Pathophysiology
To healHealing
Physiological healing is the restoration of damaged living tissue, organs and biological system to normal function. It is the process by which the cells in the body regenerate and repair to reduce the size of a damaged or necrotic area....
a wound, the body undertakes a series of actions collectively known as the wound healing
Wound healing
Wound healing, or cicatrisation, is an intricate process in which the skin repairs itself after injury. In normal skin, the epidermis and dermis exists in a steady-state equilibrium, forming a protective barrier against the external environment...
process.
Management

Cleaning
For simple lacerations cleaning can be accomplished using a number of different solutions including tap waterTap water
Tap water is a principal component of "indoor plumbing", which became available in urban areas of the developed world during the last quarter of the 19th century, and common during the mid-20th century...
, sterile saline solution
Saline (medicine)
In medicine, saline is a general term referring to a sterile solution of sodium chloride in water but is only sterile when it is to be placed intravenously, otherwise, a saline solution is a salt water solution...
, or antiseptic solution. Infection rates may be lower with the use of tap water in regions where water quality is high. Evidence for the effectiveness of any cleaning of simple wound however is limited.
Closure
If a person presents within 6 hours of a laceration they are typically closed immediately. After this point in time however there is a theoretical concern of increased risks of infection if closed immediately. Thus some may delay closure while other may close immediately up till 24 hours. A single study has found that using clean non sterile gloves is equivalent to using sterile gloves during wound closure.If closure of a wound is decided upon a number of techniques can be used. These include bandage
Bandage
A bandage is a piece of material used either to support a medical device such as a dressing or splint, or on its own to provide support to the body; they can also be used to restrict a part of the body. During heavy bleeding or following a poisonous bite it is important to slow the flow of blood,...
s, a cyanoacrylate
Cyanoacrylate
Cyanoacrylate is the generic name for cyanoacrylate based fast-acting adhesives such as methyl 2-cyanoacrylate, ethyl-2-cyanoacrylate , and n-butyl cyanoacrylate...
glue, staples
Surgical staple
Surgical staples are specialized staples used in surgery in place of sutures to close skin wounds, connect or remove parts of the bowels or lungs. A more recent development, from the 1990s, uses clips instead of staples for some applications; this does not require the staple to penetrate.Stapling...
, and sutures. Absorbable sutures have the benefit over non absorbable sutures of not requiring removal. They are often preferred in children. Buffering the pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
of lidocaine
Lidocaine
Lidocaine , Xylocaine, or lignocaine is a common local anesthetic and antiarrhythmic drug. Lidocaine is used topically to relieve itching, burning and pain from skin inflammations, injected as a dental anesthetic or as a local anesthetic for minor surgery.- History :Lidocaine, the first amino...
makes the freezing less painful.
Dressings
The effectiveness of dressings and creams containing silver to prevent infection or improve healing is not currently supported by evidence.Antibiotics
Most clean open wounds do not require any antibiotics unless the wound is contaminated or the bacterial culturesMicrobiological culture
A microbiological culture, or microbial culture, is a method of multiplying microbial organisms by letting them reproduce in predetermined culture media under controlled laboratory conditions. Microbial cultures are used to determine the type of organism, its abundance in the sample being tested,...
are positive. Excess use of antibiotics only leads to resistance and side effects. All open wounds should be cleaned at least twice a day with warm water and soap. Once the wound is cleaned, it should be covered with moist gauze
Gauze
Gauze is a thin, translucent fabric with a loose open weave.-Uses and types:Gauze was originally made of silk and was used for clothing. It is now used for many different things, including gauze sponges for medical purposes. When used as a medical dressing, gauze is generally made of cotton...
. This should be followed by application of dry gauze and then the wound covered with a bandage. The purpose of a wet to dry dressing allows the bandage to adhere to dead tissue performing a mechanical debridement when removed.This allows new healthy skin to grow and prevents debris from collecting.
When the wound is clean, it may be closed with a skin graft. No wound is ever closed if it is suspected to be infected.
Complications
Bacterial infectionInfection
An infection is the colonization of a host organism by parasite species. Infecting parasites seek to use the host's resources to reproduce, often resulting in disease...
of wound can impede the healing process and lead to life threatening complications. Scientists at Sheffield University have identified a way of using light to rapidly detect the presence of bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
. They are developing a portable kit in which specially designed molecules emit a light signal when bound to bacteria. Current laboratory-based detection of bacteria can take hours or even days.
Work up
Individuals who have wounds that are not healing should be investigated to find the causes. Many microbiological agents can be responsible for this. The basic work up includes evaluating the wound, its extent and severity. Cultures are usually obtained both from the wound site and blood. X rays are obtained and a tetanus shot may be administered if there is any doubt about prior vaccinationChronic
Non-healing wounds of the diabetic foot are considered one of the most significant complications of diabetes, representing a major worldwide medical, social, and economic burden that greatly affects patient quality of life. Almost 24 million Americans—one in every 12—are diabetic and the disease is causing widespread disability and death at an epidemic pace, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Of those with diabetes, 6.5 million are estimated to suffer with chronic or non-healing wounds. Associated with inadequate circulation, poorly functioning veins, and immobility, non-healing wounds occur most frequently in the elderly and in people with diabetes—populations that are sharply rising as the nation ages and chronic diseases increase.Although diabetes can ravage the body in many ways, non-healing ulcers on the feet and lower legs are common outward manifestations of the disease. Also, diabetics often suffer from nerve damage in their feet and legs, allowing small wounds or irritations to develop without awareness. Given the abnormalities of the microvasculature and other side effects of diabetes, these wounds take a long time to heal and require a specialized treatment approach for proper healing.
As many as 25% of diabetic patients will eventually develop foot ulcers, and recurrence within five years is 70%. If not aggressively treated, these wounds can lead to amputations. It is estimated that every 30 seconds a lower limb is amputated somewhere in the world because of a diabetic wound. Amputation often triggers a downward spiral of declining quality of life, frequently leading to disability and death. In fact, only about one third of diabetic amputees will live more than five years, a survival rate equivalent to that of many cancers.
Many of these lower extremity amputations can be prevented through an interdisciplinary approach to treatment involving a variety of advanced therapies and techniques, such as debridement, hyperbaric oxygen treatment therapy, dressing selection, special shoes, and patient education. When wounds persist, a specialized approach is required for healing.
History

Classical antiquity
Classical antiquity is a broad term for a long period of cultural history centered on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ancient Greece and ancient Rome, collectively known as the Greco-Roman world...
to the Medieval Period, the body and the soul were believed to be intimately connected, based on several theories put forth by the philosopher Plato
Plato
Plato , was a Classical Greek philosopher, mathematician, student of Socrates, writer of philosophical dialogues, and founder of the Academy in Athens, the first institution of higher learning in the Western world. Along with his mentor, Socrates, and his student, Aristotle, Plato helped to lay the...
. Wounds on the body were believed to correlate with wounds to the soul and vice versa; wounds were seen as an outward sign of an inward illness. Thus, a man who was wounded physically in a serious way was said to be hindered not only physically but spiritually as well. If the soul was wounded, that wound may also eventually become physically manifest, revealing the true state of the soul. Wounds were also seen as writing on the "tablet" of the body. Wounds acquired in war, for example, told the story of a soldier in a form which all could see and understand, and the wounds of a martyr
Martyr
A martyr is somebody who suffers persecution and death for refusing to renounce, or accept, a belief or cause, usually religious.-Meaning:...
told the story of their faith.
See also
- International Red Cross Wound Classification SystemInternational Red Cross Wound Classification SystemThe International Red Cross wound classification system is a system whereby certain features of a wound are scored: the size of the skin wound; whether there is a cavity, fracture or vital structure injured; the presence or absence of metallic foreign bodies. A numerical value is given to each...
- European Wound Management AssociationEuropean Wound Management AssociationThe European Wound Management Association was founded in 1991.The association works to promote the advancement of education and research into native epidemiology, pathology, diagnosis, prevention and management of wounds of all aetiologies....
External links
- WOUNDS, open-access, print and online, peer-reviewedPeer reviewPeer review is a process of self-regulation by a profession or a process of evaluation involving qualified individuals within the relevant field. Peer review methods are employed to maintain standards, improve performance and provide credibility...
journal featuring articles about wound care and related research. - Ostomy Wound Management, open-access, print and online, peer-reviewed journal featuring articles about wound care, ostomy care, incontinence care, and nutrition
- Today's Wound Clinic, the leading journal decision makers read in US wound care clinics.
- Journal of Burns and Wounds, online open-access journal featuring articles about wound care and related research
- Journal of Wound Care, the leading monthly journal for nurses, medics and researchers working in wound care
- US based wound healing society
- Association for the Advancement of Wound Care AAWC
- European Wound Management Association - EWMA works to promote the advancement of education and research.

