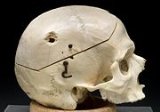
Ballistic trauma
Encyclopedia
The term ballistic trauma refers to a form of physical trauma
sustained from the discharge of arms
or munitions
. The most common forms of ballistic trauma stem from firearm
s used in armed conflicts, civilian sporting and recreational pursuits, and criminal activity.
is related to the size of the temporary versus permanent cavity
it creates as it passes through tissue. The extent of cavitation
, in turn, is related to the following characteristics of the projectile:
The immediate damaging effects of the bullet are typically bleeding, and with it the potential for hypovolemic shock
, an inadequate amount of blood in the circulatory system. More immediate effects can result when a bullet strikes a critical organ such as the heart
or damages a component of the central nervous system
such as the spine
or brain. Common causes of death following gunshot injury include exsanguination
, hypoxia
caused by pneumothorax
, heart failure and brain damage. Non-fatal gunshot wounds can result in serious disability.
Gunshot injuries can vary widely from case to case since the location of the injury can be in any part of the body, with wide variations in entry point. Also, the path and possible fragmentation of the bullet within the body is unpredictable. The study of the dynamics of bullets in gunshot injuries is called terminal ballistics
.
Non-fatal gunshot wounds frequently have severe and long-lasting effects, even after the victim has made a successful recovery. Typically, the consequences involve some form of major disfigurement
and/or permanent disability
. As a rule, all gunshot wounds are considered medical emergencies that require immediate hospital treatment.
Physical trauma
Trauma refers to "a body wound or shock produced by sudden physical injury, as from violence or accident." It can also be described as "a physical wound or injury, such as a fracture or blow." Major trauma can result in secondary complications such as circulatory shock, respiratory failure and death...
sustained from the discharge of arms
Weapon
A weapon, arm, or armament is a tool or instrument used with the aim of causing damage or harm to living beings or artificial structures or systems...
or munitions
Ammunition
Ammunition is a generic term derived from the French language la munition which embraced all material used for war , but which in time came to refer specifically to gunpowder and artillery. The collective term for all types of ammunition is munitions...
. The most common forms of ballistic trauma stem from firearm
Firearm
A firearm is a weapon that launches one, or many, projectile at high velocity through confined burning of a propellant. This subsonic burning process is technically known as deflagration, as opposed to supersonic combustion known as a detonation. In older firearms, the propellant was typically...
s used in armed conflicts, civilian sporting and recreational pursuits, and criminal activity.
Destructive effects
The degree of tissue disruption caused by a projectileProjectile
A projectile is any object projected into space by the exertion of a force. Although a thrown baseball is technically a projectile too, the term more commonly refers to a weapon....
is related to the size of the temporary versus permanent cavity
Permanent cavity
Permanent cavity refers to the hole left by the passage of a projectile. It is measured as the volume of tissue or ballistics gel that has been displaced by the passage of a bullet.- See also :* Terminal ballistics* Forensic ballistics* Stopping power...
it creates as it passes through tissue. The extent of cavitation
Cavitation
Cavitation is the formation and then immediate implosion of cavities in a liquidi.e. small liquid-free zones that are the consequence of forces acting upon the liquid...
, in turn, is related to the following characteristics of the projectile:
- Kinetic energyKinetic energyThe kinetic energy of an object is the energy which it possesses due to its motion.It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acceleration, the body maintains this kinetic energy unless its speed changes...
: KE = mv2/2 (where m is massMassMass can be defined as a quantitive measure of the resistance an object has to change in its velocity.In physics, mass commonly refers to any of the following three properties of matter, which have been shown experimentally to be equivalent:...
and v is velocityVelocityIn physics, velocity is speed in a given direction. Speed describes only how fast an object is moving, whereas velocity gives both the speed and direction of the object's motion. To have a constant velocity, an object must have a constant speed and motion in a constant direction. Constant ...
). This helps to explain why wounds produced by missiles of higher mass and/or higher velocity produce greater tissue disruption than missiles of lower mass and velocity. - Yaw
- Deformation
- FragmentationFragmentation (weaponry)Fragmentation is the process by which the casing of an artillery shell, bomb, grenade, etc. is shattered by the detonating high explosive filling. The correct technical terminology for these casing pieces is fragments , although shards or splinters can be used for non-preformed fragments...
The immediate damaging effects of the bullet are typically bleeding, and with it the potential for hypovolemic shock
Hypovolemia
In physiology and medicine, hypovolemia is a state of decreased blood volume; more specifically, decrease in volume of blood plasma...
, an inadequate amount of blood in the circulatory system. More immediate effects can result when a bullet strikes a critical organ such as the heart
Heart
The heart is a myogenic muscular organ found in all animals with a circulatory system , that is responsible for pumping blood throughout the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions...
or damages a component of the central nervous system
Central nervous system
The central nervous system is the part of the nervous system that integrates the information that it receives from, and coordinates the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterian animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish...
such as the spine
Vertebral column
In human anatomy, the vertebral column is a column usually consisting of 24 articulating vertebrae, and 9 fused vertebrae in the sacrum and the coccyx. It is situated in the dorsal aspect of the torso, separated by intervertebral discs...
or brain. Common causes of death following gunshot injury include exsanguination
Exsanguination
Exsanguination is the fatal process of hypovolemia , to a degree sufficient enough to cause death. One does not have to lose literally all of one's blood to cause death...
, hypoxia
Hypoxia (medical)
Hypoxia, or hypoxiation, is a pathological condition in which the body as a whole or a region of the body is deprived of adequate oxygen supply. Variations in arterial oxygen concentrations can be part of the normal physiology, for example, during strenuous physical exercise...
caused by pneumothorax
Pneumothorax
Pneumothorax is a collection of air or gas in the pleural cavity of the chest between the lung and the chest wall. It may occur spontaneously in people without chronic lung conditions as well as in those with lung disease , and many pneumothoraces occur after physical trauma to the chest, blast...
, heart failure and brain damage. Non-fatal gunshot wounds can result in serious disability.
Gunshot injuries can vary widely from case to case since the location of the injury can be in any part of the body, with wide variations in entry point. Also, the path and possible fragmentation of the bullet within the body is unpredictable. The study of the dynamics of bullets in gunshot injuries is called terminal ballistics
Terminal ballistics
Terminal ballistics, a sub-field of ballistics, is the study of the behavior of a projectile when it hits its target. It is often referred to as stopping power when dealing with human or other living targets. Terminal ballistics is relevant both for small caliber projectiles as well as for large...
.
Non-fatal gunshot wounds frequently have severe and long-lasting effects, even after the victim has made a successful recovery. Typically, the consequences involve some form of major disfigurement
Disfigurement
Disfigurement is the state of having one's appearance deeply and persistently harmed medically, as from a disease, birth defect, or wound.Disfigurement, whether caused by a benign or malignant condition, often leads to severe psychosocial problems such as negative body image; depression;...
and/or permanent disability
Disability
A disability may be physical, cognitive, mental, sensory, emotional, developmental or some combination of these.Many people would rather be referred to as a person with a disability instead of handicapped...
. As a rule, all gunshot wounds are considered medical emergencies that require immediate hospital treatment.
See also
- Battlefield medicineBattlefield medicineBattlefield medicine, also called field surgery and later combat casualty care, is the treatment of wounded soldiers in or near an area of combat. Civilian medicine has been greatly advanced by procedures that were first developed to treat the wounds inflicted during combat...
- Emergency medicineEmergency medicineEmergency medicine is a medical specialty in which physicians care for patients with acute illnesses or injuries which require immediate medical attention. While not usually providing long-term or continuing care, emergency medicine physicians diagnose a variety of illnesses and undertake acute...
- Hydrostatic shockHydrostatic shockHydrostatic shock or hydraulic shock describes the observation that a penetrating projectile can produce remote wounding and incapacitating effects in living targets through a hydraulic effect in their liquid-filled tissues, in addition to local effects in tissue caused by direct impact...
- Multiple gunshot suicideMultiple gunshot suicideMultiple gunshot suicide occurs when a person commits suicide by inflicting multiple gunshots on himself or herself before becoming incapacitated. It excludes suicides where the firearms are operated by other people, such as suicide by cop....
- Penetrating traumaPenetrating traumaPenetrating trauma is an injury that occurs when an object pierces the skin and enters a tissue of the body, creating an open wound. In blunt, or non-penetrating trauma, there may be an impact, but the skin is not necessarily broken. The penetrating object may remain in the tissues, come back out...
- Stopping powerStopping powerStopping power is a colloquial term used to describe the ability of a firearm or other weapon to cause a penetrating ballistic injury to a target, human or animal, sufficient to incapacitate the target where it stands....
- Vincent Di MaioVincent Di MaioDr. Vincent J. M. Di Maio is an American pathologist and a nationally renowned expert on the subject of gunshot wounds. Di Maio is a board-certified anatomical, clinical and forensic pathologist, and a private forensic pathology consultant. He attended St...
External links
- Virtual Autopsy – CT scans of fatal gunshot wounds
- http://www.patient.co.uk/showdoc/40001334/

