
Wnt signaling pathway
Encyclopedia
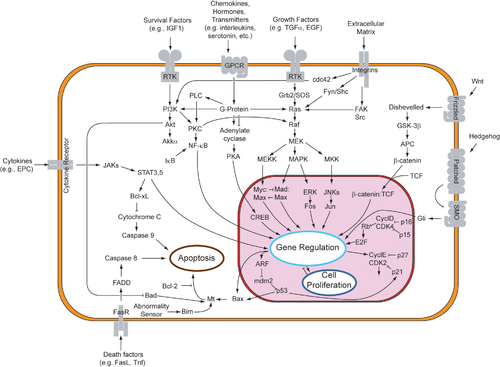
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a cell surface receptor. In turn, this receptor alters intracellular molecules creating a response...
is a network of protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s best known for their roles in embryogenesis
Embryogenesis
Embryogenesis is the process by which the embryo is formed and develops, until it develops into a fetus.Embryogenesis starts with the fertilization of the ovum by sperm. The fertilized ovum is referred to as a zygote...
and cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
, but also involved in normal physiological processes in adult animals.
Discovery
The first Wnt gene was discovered by Roeland Nusse and Harold Varmus in 1982 when they observed activation of Int1 (integration 1) in the breast tumors of mice infected with mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTVMouse mammary tumor virus
Mouse mammary tumor virus is a milk transmitted retrovirus like the HTL viruses, HI viruses and BLV. It belongs to the genus betaretroviruses. MMTV was formerly known as Bittner virus, and previously the 'milk factor' referring to the extra-chromosomal vertical transmission of murine breast cancer...
), in which Int was identified as a vertebrate gene near several integration sites of MMTV. The origin of the name Wnt comes from a hybrid of Int and Wg (wingless) in Drosophila, which is the best characterized Wnt gene. Although the wingless gene was originally identified as a recessive mutation affecting wing and haltere
Halteres
Halteres are small knobbed structures modified from the hind wings in some two-winged insects. They are flapped rapidly and function as gyroscopes, informing the insect about rotation of the body during flight....
development in Drosophila melanogaster
Drosophila melanogaster
Drosophila melanogaster is a species of Diptera, or the order of flies, in the family Drosophilidae. The species is known generally as the common fruit fly or vinegar fly. Starting from Charles W...
, wingless has been important towards understanding the Wnt signaling system in other organisms, and its function as a segment polarity gene was discovered by Christiane Nüsslein-Volhard
Christiane Nüsslein-Volhard
Christiane Nüsslein-Volhard is a German biologist who won the Albert Lasker Award for Basic Medical Research in 1991 and the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1995, together with Eric Wieschaus and Edward B...
and Eric Wieschaus through their work on Drosophila mutants with phenotypes related to mutations in the Wg signaling pathway. As a result of their work, they later went on to win the Nobel Prize
Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes are annual international awards bestowed by Scandinavian committees in recognition of cultural and scientific advances. The will of the Swedish chemist Alfred Nobel, the inventor of dynamite, established the prizes in 1895...
in Physiology and Medicine in 1995. It was not until 1987 that researchers found that Wg was the homologue to mammalian Int1 due to a common evolutionary origin evidenced by similar amino acid sequences of their encoded proteins.
Mutations of the wingless gene in the fruit fly were found in wingless flies, while tumors caused by MMTV were found to have copies of the virus integrated into the genome forcing overproduction of one of several Wnt genes. The ensuing effort to understand how similar genes produce such different effects has revealed that Wnt proteins are a major class of secreted morphogenic ligands
Ligand (biochemistry)
In biochemistry and pharmacology, a ligand is a substance that forms a complex with a biomolecule to serve a biological purpose. In a narrower sense, it is a signal triggering molecule, binding to a site on a target protein.The binding occurs by intermolecular forces, such as ionic bonds, hydrogen...
of profound importance in establishing the pattern of development in the bodies of all multicellular organisms studied.
Members
The following is a list of human genes that encode WNT signaling proteins:- WNT1WNT1Proto-oncogene protein Wnt-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WNT1 gene.-Further reading:...
- WNT2WNT2Wingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 2, also known as WNT2, is a human gene.This gene is a member of the WNT gene family. The WNT gene family consists of structurally related genes that encode secreted signaling proteins involved in the Wnt signaling pathway...
, WNT2BWNT2BProtein Wnt-2b is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WNT2B gene.-Further reading:... - WNT3WNT3Proto-oncogene protein Wnt-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WNT3 gene.-External links:* -Further reading:...
, WNT3AWNT3AProtein Wnt-3a is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WNT3A gene.-Further reading:... - WNT4WNT4Protein Wnt-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WNT4 gene.WNT4 is a secreted protein involved in female fetal genital development.- Function :...
- WNT5AWNT5AProtein Wnt-5a is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WNT5A gene.-Further reading:...
, WNT5BWNT5BProtein Wnt-5b is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WNT5B gene.-Further reading:... - WNT6WNT6Wingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 6, also known as WNT6, is a human gene.The WNT gene family consists of structurally related genes that encode secreted signaling proteins. These proteins have been implicated in oncogenesis and in several developmental processes, including...
- WNT7AWNT7AProtein Wnt-7a is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WNT7A gene.-Further reading:...
, WNT7BWNT7BProtein Wnt-7b is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WNT7B gene.-Further reading:... - WNT8A, WNT8BWNT8BProtein Wnt-8b is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WNT8B gene.-Further reading:...
- WNT9AWNT9AProtein Wnt-9a is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WNT9A gene.-Further reading:...
, WNT9B - WNT10AWNT10AWnt-10a is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WNT10A gene.- Function :The WNT gene family consists of structurally related genes which encode secreted signaling proteins. These proteins have been implicated in oncogenesis and in several developmental processes, including regulation of cell...
- WNT10BWNT10BProtein Wnt-10b is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WNT10B gene.-Further reading:...
, WNT11WNT11Protein Wnt-11 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WNT11 gene.-Further reading:... - WNT16WNT16Protein Wnt-16 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WNT16 gene.-Further reading:...
The following is a list of receptors that are acted upon by various WNT signalling proteins:
- FZD1FZD1Frizzled-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FZD1 gene.-Further reading:...
- FZD2FZD2Frizzled-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FZD2 gene.-Further reading:...
- FZD3FZD3Frizzled-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FZD3 gene.-Further reading:...
- FZD4FZD4Frizzled-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FZD4 gene. FZD4 has also been designated as CD344 .-External links:]*...
- FZD5FZD5Frizzled-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FZD5 gene.-Further reading:...
- FZD6FZD6Frizzled-6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FZD6 gene.Members of the 'frizzled' gene family encode 7-transmembrane domain proteins that are receptors for Wnt signaling proteins. The FZD6 protein contains a signal peptide, a cysteine-rich domain in the N-terminal extracellular region,...
- FZD7FZD7Frizzled-7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FZD7 gene.-Further reading:...
- FZD8FZD8Frizzled-8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FZD8 gene.-Further reading:...
- FZD9FZD9Frizzled-9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FZD9 gene. FZD9 has also been designated as CD349 .-External links:...
- FZD10FZD10Frizzled-10 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FZD10 gene. FZD10 has also been designated as CD350 .-External links:...
Wnt signaling proteins
The Wnt proteins are a group of secreted lipid-modified (palmitoylationPalmitoylation
S-Palmitoylation is the covalent attachment of fatty acids, such as palmitic acid, to cysteine residues of membrane proteins. The precise function of palmitoylation depends on the particular protein being considered. Palmitoylation enhances the hydrophobicity of proteins and contributes to their...
) signaling proteins of 350-400 amino acids in length. Following the signal sequence
Signal sequence
Signal sequence can refer to:*Protein targeting*Signal peptide*DNA uptake signal sequence...
, they carry a conserved pattern of 23-24 cysteine residues, on which palmitoylation occurs on a cysteine residue. These proteins activate various pathways in the cell that can be categorized into the canonical and noncanonical Wnt pathways. Through these signaling pathways, Wnt proteins play a variety of important roles in embryonic development, cell differentiation, and cell polarity
Cell polarity
Cell Polarity refers to spatial differences in the shape, structure, and function of cells. Almost all cell types exhibit some sort of polarity, which enables them to carry out specialized functions...
generation.
Mechanism
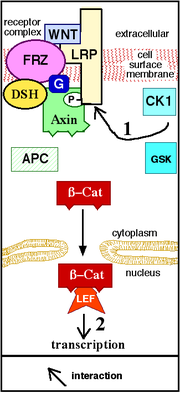
Extracellular
In cell biology, molecular biology and related fields, the word extracellular means "outside the cell". This space is usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid...
Wnt ligands
Ligand (biochemistry)
In biochemistry and pharmacology, a ligand is a substance that forms a complex with a biomolecule to serve a biological purpose. In a narrower sense, it is a signal triggering molecule, binding to a site on a target protein.The binding occurs by intermolecular forces, such as ionic bonds, hydrogen...
. Although the presence and strength of any given effect depends on the Wnt ligand, cell type, and organism, some components of the signaling pathway are remarkably conserved in a wide variety of organisms, from Caenorhabditis elegans
Caenorhabditis elegans
Caenorhabditis elegans is a free-living, transparent nematode , about 1 mm in length, which lives in temperate soil environments. Research into the molecular and developmental biology of C. elegans was begun in 1974 by Sydney Brenner and it has since been used extensively as a model...
to human
Human
Humans are the only living species in the Homo genus...
s. Protein homology suggests that several distinct Wnt ligands were present in the common ancestor of all bilaterian life, and certain aspects of Wnt signaling are present in sponge
Sea sponge
Sponges are animals of the phylum Porifera . Their bodies consist of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells. While all animals have unspecialized cells that can transform into specialized cells, sponges are unique in having some specialized cells, but can also have...
s and even in slime molds.
The canonical Wnt pathway describes a series of events that occur when Wnt proteins bind to cell-surface receptors of the Frizzled
Frizzled
Frizzled is a family of G protein-coupled receptor proteins that serve as receptors in the Wnt signaling pathway and other signaling pathways. When activated, Frizzled leads to activation of Dishevelled in the cytosol.-Species distribution:...
family, causing the receptors to activate Dishevelled family proteins and ultimately resulting in a change in the amount of β-catenin
Beta-catenin
Beta-catenin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CTNNB1 gene. In Drosophila, the homologous protein is called armadillo...
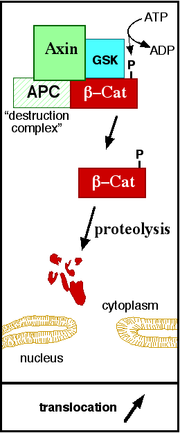
that reaches the nucleus (Figure 2). Dishevelled (DSH) is a key component of a membrane-associated Wnt receptor complex (Figure 2), which, when activated by Wnt binding, inhibits a second complex of proteins that includes axin, GSK-3
GSK-3
Glycogen synthase kinase 3 is a serine/threonine protein kinase that mediates the addition of phosphate molecules on certain serine and threonine amino acids in particular cellular substrates...
, and the protein APC
APC (gene)
Adenomatous polyposis coli also known as deleted in polyposis 2.5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the APC gene. Mutations in the APC gene may result in colorectal cancer....
(Figure 1). The axin/GSK-3/APC complex normally promotes the proteolytic degradation of the β-catenin intracellular signaling molecule. After this "β-catenin destruction complex" is inhibited, a pool of cytoplasmic β-catenin stabilizes, and some β-catenin, is able to enter the nucleus and interact with TCF/LEF family
TCF/LEF family
The TCF/LEF family is a group of transcription factors which bind to DNA through a high mobility group domain. They are involved in the Wnt signaling pathway, where they recruit the coactivator beta-catenin to enhancer elements of genes they target. They can also recruit members of the Groucho...
transcription factors to promote specific gene expression (interaction 2, Figure 2).
Cell surface Frizzled (FRZ) proteins usually interact with a transmembrane protein called LRP (Figure 2). LRP binds Frizzled, Wnt and axin and may stabilize a Wnt/Frizzled/LRP/Dishevelled/axin complex at the cell surface ("receptor complex" in Figure 2).
In vertebrates, several secreted proteins have been described that can modulate Wnt signaling by either binding to Wnts or binding to a Wnt receptor protein. For example, Sclerostin (not shown in a figure) can bind to LRP and inhibit Wnt signaling.
The part of the pathway linking the cell surface Wnt-activated Wnt receptor complex to the prevention of β-catenin degradation is still under investigation. There is evidence that trimeric G proteins (G in Figure 2) can function downstream from Frizzled. It has been suggested that Wnt-activated G proteins participate in the disassembly of the axin/GSK3 complex.
Several protein kinases and protein phosphatases have been associated with the ability of the cell surface Wnt-activated Wnt receptor complex to bind axin and disassemble the axin/GSK3 complex. Phosphorylation of the cytoplasmic domain of LRP by CK1
Casein kinase 1
The Casein kinase 1 family of protein kinases are serine/threonine-selective enzymes that function as regulators of signal transduction pathways in most eukaryotic cell types...
and GSK3 can regulate axin binding to LRP (interaction 1 in Figure 2). The protein kinase activity of GSK3 appears to be important for both the formation of the membrane-associated Wnt/FRZ/LRP/DSH/Axin complex and the function of the Axin/APC/GSK3/β-catenin complex. Phosphorylation of β-catenin by GSK3 leads to the destruction of β-catenin (Figure 1).
Feedback regulation of canonical Wnt signaling occurs via a variety of mechanisms, including induction or repression of Wnt signaling components themselves, including AXIN2
AXIN2
Axin-2 also known as axin-like protein or axis inhibition protein 2 or conductin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AXIN2 gene.- Function :...
and Naked cuticle.
Ligands that act on Wnt signaling
- 2-amino-4-[3,4-(methylenedioxy)benzyl-amino]-6-(3-methoxyphenyl)pyrimidine as an agonist of Wnt signaling.
- The signaling molecule Cerberus inhibits Wnt, thus repressing the inhibition of β-Catenin on SoxB1 family members. This enables the specification of Neuroepithelium in Drosophila neural induction.
Wnt-induced cell responses
Several important effects of the canonical Wnt pathway include:- Cancers. Alterations of Wnts, APC, axin, and TCFs are all associated with carcinogenesis.
- Body axis specification. Ectopic placement of Wnt in Xenopus eggs during early gastrulation gives rise to a secondary body axis and head, while inhibition of Wnt signaling results in a lack of dorsal structures in the frog embryo. Wnt is extensively involved in the formation of dorsal structures and the nervous system in early frog development and is found in high concentrations in the region known as Spemann's Organizer.
- Morphogenic signaling. Wnts produced from specific sites, such as the edge of the developing fly wing or the dorsal region of the neural tube of the developing vertebrate, are distributed throughout adjacent tissues in a gradient fashion. The Wnt pathway becomes activated to different degrees in cells of these tissues depending on how close they are to the production site, leading to subtle but crucial differences in the level of genes regulated by the Wnt pathway.
Wnt and patterning the neural tube
In vertebrates, dorso-ventral patterning of the developing neural tube is achieved by the counteracting activities of morphogenetic signaling gradients set up by Sonic HedgehogSonic hedgehog
Sonic hedgehog homolog is one of three proteins in the mammalian signaling pathway family called hedgehog, the others being desert hedgehog and Indian hedgehog . SHH is the best studied ligand of the hedgehog signaling pathway. It plays a key role in regulating vertebrate organogenesis, such as...
(Shh) in the ventral floor plate and notochord, and the canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway acting in the roof plate, the dorsal most region of the neural tube. While evidence that Wnt and Sonic hedgehog are direct antagonists of one another remains to be seen, the role of Wnt in patterning the neural tube is thought to work in an indirectly inhibitory manner towards Sonic Hedgehog via the canonical Wnt pathway.
Studies in early neural tube development have shown that the Wnt/β-catenin pathway is largely responsible for regulating Shh expression in the dorsal region of the neural tube. Addition of the GSK3 inhibitor LiCl, which stabilizes β-catenin by preventing its destruction, has been shown to attenuate Sonic Hedgehog response in neural tube explants in chicks. Chick electroporation assays have shown that ectopic activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway components results in an expansion of dorsal genes, Pax7 and Pax6
PAX6
Paired box protein Pax-6 also known as aniridia type II protein or oculorhombin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PAX6 gene.- Function :PAX6 is a member of the Pax gene family...
, into more ventral regions of the neural tube. These regions become dorsalized due to the ectopic presence of the active Wnt components, which are thought to inhibit the expression of genes such as Oligo2 and Nkx2.2 that are normally found there. Furthermore, misexpression of activated canonical Wnt pathway components β-catenin and TCF-lef results in complete dorsalization of the neural tube. Inhibition of Wnt signaling in the neural tube by introduction of a dominant-negative inactive form of TCF, the transcription factor activated by the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, results in shift of ventral genes into more dorsal regions of the neural tube.
Wnt signaling in the dorsal region of the neural tube also controls the expression of a transcription factor Gli3
Gli3
Zinc finger protein GLI3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GLI3 gene.This gene encodes a protein that belongs to the C2H2-type zinc finger proteins subclass of the Gli family. They are characterized as DNA-binding transcription factors and are mediators of Sonic hedgehog signaling...
, one of the main inhibitors of the Shh/Gli pathway. It is by signaling through the canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway that Wnt is able to activate and control the expression of the Gli3 transcription factor to repress transcriptional activity of Shh/Gli in the dorsal region of the neural tube and elicit dorsal cell fates.
In addition to Wnt and Shh signaling, studies have shown that Bone Morphogenetic Protein
Bone morphogenetic protein
Bone morphogenetic proteins are a group of growth factors also known as cytokines and as metabologens . Originally discovered by their ability to induce the formation of bone and cartilage, BMPs are now considered to constitute a group of pivotal morphogenetic signals, orchestrating tissue...
s (Bmp) are also necessary for Shh regulation in the dorsal neural tube, and, because of cross-talk between the Bmp and Wnt pathways, it was thought that Bmps were regulating the activities of Wnt. Recent studies have shown that Wnt may not be mediated by Bmps, but rather that Bmps may be mediated by Wnts. However, The interactions of the Wnt and Bmp pathways remain unclear and further research needs to be done to identify exactly how Bmps and Wnts work together to elicit dorsal cell fates in the developing neural tube.
Non-canonical Wnt signaling
There are many non-canonical pathways, but the two best-studied pathways are the Planar Cell Polarity (PCP) and Wnt/Calcium Pathways. The most distinctive differences between the canonical and non-canonical pathways include the specific ligands activating each pathway, ß-CateninBeta-catenin
Beta-catenin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CTNNB1 gene. In Drosophila, the homologous protein is called armadillo...
, LRP5
LRP5
Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LRP5 gene.- Function :LRP5 is a transmembrane low-density lipoprotein receptor that binds and internalizes ligands in the process of receptor-mediated endocytosis...
/6 co-receptor, and Dsh-DEP domain
DEP domain
In molecular biology, the DEP domain is a globular protein domain of about 80 amino acids that is found in over 50 proteins involved in G-protein signalling pathways...
independence, and the ability of the non-canonical pathway to inhibit the canonical pathway. Ligands that activate the non-canonical pathways are Wnt4, Wnt5a, and Wnt11. Expression of Wnt5a was shown to be increased in prostate cancer ; the mechanism of this increase in Wnt5a protein expression was proposed to be increase in Wnt5a gene transcription due to hypomethylation of Wnt5a promotor region.
In the PCP pathway, ligand binding to the receptor recruits Dishevelled
Dishevelled
Dishevelled is a family of proteins involved in canonical and non-canonical Wnt signalling pathways. Dsh is a cytoplasmic phosphoprotein that acts directly downstream of frizzled receptors...
(Dsh), which forms a complex with Daam1
DAAM1
Disheveled-associated activator of morphogenesis 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DAAM1 gene.-Further reading:...
. Daam1 then activates the small G-protein Rho
Rho family of GTPases
The Rho family of GTPases is a family of small signaling G protein , and is a subfamily of the Ras superfamily. The members of the Rho GTPase family have been shown to regulate many aspects of intracellular actin dynamics, and are found in all eukaryotic organisms including yeasts and some plants...
through guanine exchange factor. Rho activates ROCK ( Rho-associated kinase), which is one of the major regulators of the cytoskeleton
Cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a cellular "scaffolding" or "skeleton" contained within a cell's cytoplasm and is made out of protein. The cytoskeleton is present in all cells; it was once thought to be unique to eukaryotes, but recent research has identified the prokaryotic cytoskeleton...
. Dsh also forms a complex with rac1
RAC1
Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 also known as Rac1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAC1 gene. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene have been described, but the full-length nature of some of these variants has not been determined.- Function :Rac1 is...
and mediates profilin
Profilin
Profilin is an actin-binding protein involved in the dynamic turnover and restructuring of the actin cytoskeleton. It is found in all eukaryotic organisms in most cells. Profilin is important for spatially and temporally controlled growth of actin microfilaments, which is an essential process in...
binding to actin
Actin
Actin is a globular, roughly 42-kDa moonlighting protein found in all eukaryotic cells where it may be present at concentrations of over 100 μM. It is also one of the most highly-conserved proteins, differing by no more than 20% in species as diverse as algae and humans...
. Rac1 activates JNK
C-Jun N-terminal kinases
c-Jun N-terminal kinases , were originally identified as kinases that bind and phosphorylate c-Jun on Ser-63 and Ser-73 within its transcriptional activation domain. They belong to the mitogen-activated protein kinase family, and are responsive to stress stimuli, such as cytokines, ultraviolet...
and can also lead to actin polymerization. Profilin binding to actin can result in restructuring of the cytoskeleton.
In the Wnt/Calcium pathway, Wnt5a and Frizzled
Frizzled
Frizzled is a family of G protein-coupled receptor proteins that serve as receptors in the Wnt signaling pathway and other signaling pathways. When activated, Frizzled leads to activation of Dishevelled in the cytosol.-Species distribution:...
regulate intracellular calcium levels. Ligand binding causes the coupled G-protein to activate PLC
Phospholipase C
Phosphoinositide phospholipase C is a family of eukaryotic intracellular enzymes that play an important role in signal transduction processes. In general, this enzyme is denoted as Phospholipase C, although three other families of phospholipase C enzymes have been identified in bacteria and in...
, leading to the generation of DAG
Diglyceride
A diglyceride, or a diacylglycerol , is a glyceride consisting of two fatty acid chains covalently bonded to a glycerol molecule through ester linkages....
and IP3. When IP3 binds to its receptor on the ER, intracellular calcium concentration increases. Ligand binding also activates cGMP-specific phosphodiesterase
Phosphodiesterase
A phosphodiesterase is any enzyme that breaks a phosphodiester bond. Usually, people speaking of phosphodiesterase are referring to cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases, which have great clinical significance and are described below...
(PDE), which depletes cGMP and further increases calcium concentration. Increased concentrations of calcium and DAG can activate Cdc42
CDC42
Cell division control protein 42 homolog also known as CDC42 is a protein involved in regulation of the cell cycle. In humans, CDC42 is encoded by the CDC42 gene.- Function :...
(cell division control protein 42) through PKC
Protein kinase C
Protein kinase C also known as PKC is a family of enzymes that are involved in controlling the function of other proteins through the phosphorylation of hydroxyl groups of serine and threonine amino acid residues on these proteins. PKC enzymes in turn are activated by signals such as increases in...
. Cdc42 is an important regulator of cell adhesion, migration, and tissue separation. Increased calcium also activates calcineurin
Calcineurin
Calcineurin is a protein phosphatase also known as protein phosphatase 3, PPP3CA, and calcium-dependent serine-threonine phosphatase, and formerly known as protein phosphatase 2B . It activates the T cells of the immune system and can be blocked by drugs...
and CamKII
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase
/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases II or CaM kinases II are serine/threonine-specific protein kinases that are regulated by the /calmodulin complex...
(calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase). Calcineurin induces activation of transcription factor NFAT
NFAT
Nuclear factor of activated T-cells is a general name applied to a family of transcription factors shown to be important in immune response. One or more members of the NFAT family is expressed in most cells of the immune system...
, which regulates ventral patterning. CamKII activates TAK1 and NLK
NLK
Serine/threonine protein kinase NLK is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NLK gene.-Further reading:...
kinase, which can interfere with TCF/ß-Catenin signaling in the canonical pathway.
Planar cell polarity
An example of the control of planar cell polarity in insects like Drosophila is determining which direction the tiny hairs on the wings of a fly are aligned. Planar cell polarity is distinct from and perpendicular to apical/basal polarity. The signaling pathway that is involved in planar cell polarity includes frizzledFrizzled
Frizzled is a family of G protein-coupled receptor proteins that serve as receptors in the Wnt signaling pathway and other signaling pathways. When activated, Frizzled leads to activation of Dishevelled in the cytosol.-Species distribution:...
and dishevelled
Dishevelled
Dishevelled is a family of proteins involved in canonical and non-canonical Wnt signalling pathways. Dsh is a cytoplasmic phosphoprotein that acts directly downstream of frizzled receptors...
but not the axin complex proteins. The non-classical cadherin
Cadherin
Cadherins are a class of type-1 transmembrane proteins. They play important roles in cell adhesion, ensuring that cells within tissues are bound together. They are dependent on calcium ions to function, hence their name.The cadherin superfamily includes cadherins, protocadherins, desmogleins, and...
s Fat, Dachsous, and Flamingo
Flamingo (protein)
Flamingo is a member of the adhesion-GPCR family of proteins. Flamingo has sequence homology to cadherins and G protein-coupled receptors . Flamingo was originally identified as a Drosophila protein involved in planar cell polarity. Mammals have three flamingo homologs, CELSR1, CELSR2, CELSR3...
appear to modulate frizzled function. Other proteins including prickle
Prickle (protein)
The first prickle protein was identified in Drosophila as a planar cell polarity protein. Vertebrate prickle-1 was first found as a rat protein that binds to a transcription factor, neuron-restrictive silencer factor . It was then recognized that other vertebrates including mice and humans have two...
, strabismus
Strabismus (protein)
Strabismus was originally identified as a Drosophila protein involved in planar cell polarity. Flies with mutated stranismus genes have altered development of omatidia in their eyes...
, rhoA
RHOA
Ras homolog gene family, member A is a small GTPase protein known to regulate the actin cytoskeleton in the formation of stress fibers. In humans, it is encoded by the gene RHOA....
, and rho-kinase act downstream of frizzled and dishevelled to regulate the cytoskeleton and planar cell polarity.
Some of the proteins involved in planar cell patterning of the Drosophila wing are used in vertebrates during regulation of cell movements during events such as gastrulation
Gastrulation
Gastrulation is a phase early in the embryonic development of most animals, during which the single-layered blastula is reorganized into a trilaminar structure known as the gastrula. These three germ layers are known as the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.Gastrulation takes place after cleavage...
. A common feature of both hair patterning in Drosophila and cell movements such as vertebrate gastrulation is control of actin
Actin
Actin is a globular, roughly 42-kDa moonlighting protein found in all eukaryotic cells where it may be present at concentrations of over 100 μM. It is also one of the most highly-conserved proteins, differing by no more than 20% in species as diverse as algae and humans...
filaments by G proteins
Small GTPase
Small GTPases are a family of hydrolase enzymes that can bind and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate . They are a form of G-proteins found in the cytosol which are homologous to the alpha subunit of heterotrimeric G-proteins, but unlike the alpha subunit of G proteins, a small GTPase can function...
such as Rho and Rac.
Axon guidance
Wnt has some diverse roles in axon guidance. For example, the Wnt receptor Ryk is required for Wnt mediated axon guidance on the contralateral side of the corpus callosumCorpus callosum
The corpus callosum , also known as the colossal commissure, is a wide, flat bundle of neural fibers beneath the cortex in the eutherian brain at the longitudinal fissure. It connects the left and right cerebral hemispheres and facilitates interhemispheric communication...
. Another example is in the growing spinal cord commissural neurons: after their extending axons cross the midplate of the spinal cord, they are guided by a Wnt gradient , which is active through the Frizzled receptors in this case.
Stem cells
Traditionally, it is assumed that Wnt proteins can act as Stem Cell Growth Factors, promoting the maintenance and proliferation of stem cells.However, a recent study conducted by the Stanford University School of Medicine
Stanford University School of Medicine
Stanford University School of Medicine is a leading medical school located at Stanford University Medical Center in Stanford, California. Originally based in San Francisco, California as Cooper Medical College, it is the oldest continuously running medical school in the western United States...
revealed that Wnt appears to block proper communication, with the Wnt signaling pathway having a negative effect on stem cell function. Thus, in the case of muscle tissue, the misdirected stem cells, instead of generating new muscle cells (myoblasts), differentiated into scar-tissue-producing cells called fibroblasts. The stem cells failed to respond to instructions, actually creating wrong cell types.
Understanding the mechanisms by which pluripotency, self-renewal, and subsequent differentiation are controlled in embryonic stem cells is crucial to utilizing them therapeutically. In addition, control of Wnt signaling may allow for minimizing the use of animal products, which can introduce unwanted pathogens, in stem cell cultures. Wnt signaling was first identified as a potential component to differentiation because of its established role in development. Recent research has supported this hypothesis. There are data to suggest that Wnt signaling induces differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into mesoderm and endoderm progenitor cells.
There are several pieces of evidence to suggest that Wnt signaling is important in stem cell differentiation. TCF3, a transcription factor regulated by Wnt signaling, has been shown to repress nanog
NANOG
The North American Network Operators' Group is an educational and operational forum for the coordination and dissemination of technical information related to backbone/enterprise networking technologies and operational practices. It runs meetings, talks, surveys, and an influential mailing list...
, a gene required for stem cell pluripotency and self-renewal. Over expression of another gene associated with pluripotency, OCT4 leads to increased beta-catenin activity, suggesting Wnt involvement.
Studies of embryoid bodies (see embryoid body
Embryoid body
Embryoid bodies are aggregates of cells derived from embryonic stem cells, and have been studied for years with mouse embryonic stem cells. Cell aggregation is imposed by hanging drop, plating upon non-tissue culture treated plates or spinner flasks; either method prevents cells from adhering to a...
) have led to new insights regarding the role of Wnt signaling in human embryonic stem cells. Researchers at Stanford School of Medicine observed that embryoid bodies spontaneously begin gastrulation
Gastrulation
Gastrulation is a phase early in the embryonic development of most animals, during which the single-layered blastula is reorganized into a trilaminar structure known as the gastrula. These three germ layers are known as the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.Gastrulation takes place after cleavage...
. They determined that gastrulation in embryoid bodies mimics the in vivo process in human embryos; in vivo gastrulation has been previously linked to the Wnt pathway. Formation of the primitive streak in particular was associated with localized Wnt activation in the embryoid bodies. Once the Wnt pathway is activated, it is self-reinforcing. It is unclear, however, what induces the initial Wnt signaling that begins gastrulation.
Research published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry has suggested that activation of the Wnt pathway in mouse embryonic stem cells induces differentiation into multipotent mesoderm and endoderm cells. This study showed that upon inducing Wnt signaling in mono-layer embryonic stem cell cultures, the cells express high levels of markers associated with mesoderm development, particularly T-brachyury
Brachyury
Brachyury is a protein that in humans is encoded by the T gene. Brachyury is a transcription factor within the T-box complex of genes. It has been found in all bilaterian animals that have been screened, and is also present in the cnidaria.-History:...
and Flk-1. The cells also expressed high levels of Foxa2, Lhx1, and AFP
Alpha-fetoprotein
Alpha-fetoprotein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AFP gene....
, which are associated with endoderm development. The progenitor cells created via Wnt activation seemed to have particularly high potential to differentiate into bone and cartilage. The researchers suggested that beta-catenin plays an important role in skeletal development. They demonstrated that the progenitor cells could also develop into endothelial, cardiac, and vascular smooth muscle lineages.
A publication from the American Society of Hematology extended the previous study to human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) by demonstrating that Wnt signaling can induce hematoendothelial cell development from hESCs. This study showed that Wnt3 leads to mesoderm committed cells with hematopoietic potential. Overexpression of Wnt1 led to faster, more efficient hematoendothelial differentiation than Wnt3 overexpression. Wnt1 has also been shown to antagonize neural differentiation; this observation suggests a variety of roles for the Wnt pathway in stem cell activity. In contrast to Wnt3, which is associated with mesoderm and endoderm differentiation, Wnt1 serves the opposite function in neural stem cells. Wnt1 appears to be a major factor in self-renewal of neural stem cells. Wnt stimulation is also associated with regeneration of nervous system cells, which is further evidence of a role in promoting neural stem cell proliferation.
Environmental enrichment
Changes in Wnt signaling mimic in adult mice the effects of environmental enrichmentEnvironmental enrichment (neural)
Environmental enrichment concerns how the brain is affected by the stimulation of its information processing provided by its surroundings . Brains in richer, more stimulating environments, have increased numbers of synapses, and the dendrite arbors upon which they reside are more complex...
upon synapse
Synapse
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another cell...
s in the hippocampus
Hippocampus
The hippocampus is a major component of the brains of humans and other vertebrates. It belongs to the limbic system and plays important roles in the consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory and spatial navigation. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in...
with regard to reversible increase in their numbers, and spine
Dendritic spine
A dendritic spine is a small membranous protrusion from a neuron's dendrite that typically receives input from a single synapse of an axon. Dendritic spines serve as a storage site for synaptic strength and help transmit electrical signals to the neuron's cell body...
plus synapse densities at large mossy fiber
Mossy fiber (hippocampus)
In the hippocampus, granule cells of the dentate gyrus form distinctive unmyelinated axons that project along the mossy fiber pathway to the CA3 region. The axons emerge from the basal portions of the granule cells and pass through the hilus of the dentate gyrus before entering the stratum...
terminals It seems that Wnt signaling might be part of the means by which experience regulates synapse numbers and hippocampal network structure.
Wnt pathway in cancer stem cells
The canonical and non-canonical pathways show that the Wnt pathway is strictly regulated by many different elements. Thus, it can be expected that misregulation of these various components can have drastic effects throughout an organism. One interesting aspect of the Wnt pathway in particular is its involvement in the fate of stem cells and its role as a regulator of stem cell choice to proliferate or self-renew. Given these properties, it is not surprising that a strong correlation between Wnt signaling and the onset of cancer exists. In the normal pathway, APCAPC
-Biology:* Adenomatous polyposis coli, a type of colon cancer caused by a defect APC-protein due to mutations in the APC-gene* Antigen-presenting cell in medicine/immunology* Activated protein C, an anti-coagulant and anti-inflammatory protein...
and Axin
AXIN1
Axin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AXIN1 gene.-Interactions:AXIN1 has been shown to interact with Beta-catenin, GSK3B, TSC2, APC, LRP5, DVL1, MAP3K1, CSNK1E, Casein kinase 1, alpha 1 and PPP2R5A.-Further reading:...
prevent β-catenin
Beta-catenin
Beta-catenin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CTNNB1 gene. In Drosophila, the homologous protein is called armadillo...
from traveling to the nucleus by engaging it in the destruction complex. However, an APC deficiency or mutations to β-catenin that prevent its degradation can lead to excessive stem cell renewal and proliferation, predisposing the cells to the formation of tumors. Alteration of Wnt5a, a tumor suppressor gene
Tumor suppressor gene
A tumor suppressor gene, or anti-oncogene, is a gene that protects a cell from one step on the path to cancer. When this gene is mutated to cause a loss or reduction in its function, the cell can progress to cancer, usually in combination with other genetic changes.-Two-hit hypothesis:Unlike...
, could also lead to tumor formation.
One of the potential ways to treat cancer is to affect β-catenin, a central component of the canonical Wnt pathway. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, usually abbreviated to NSAIDs or NAIDs, but also referred to as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents/analgesics or nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory medicines , are drugs with analgesic and antipyretic effects and which have, in higher doses, anti-inflammatory...
) that interfere β-catenin signaling have been shown to be promising for the prevention of colorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer, commonly known as bowel cancer, is a cancer caused by uncontrolled cell growth , in the colon, rectum, or vermiform appendix. Colorectal cancer is clinically distinct from anal cancer, which affects the anus....
. NSAIDs inhibit prostaglandin
Prostaglandin
A prostaglandin is any member of a group of lipid compounds that are derived enzymatically from fatty acids and have important functions in the animal body. Every prostaglandin contains 20 carbon atoms, including a 5-carbon ring....
production, which interferes with β-catenin/TCF-dependent transcription. Another suggested method of treatment is to use natural antagonists of the Wnt pathway, such as secreted frizzled-related proteins (sFRPs
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 also known as SFRP1 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the SFRP1 gene.- Function :Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 is a member of the SFRP family that contains a cysteine-rich domain homologous to the putative Wnt-binding site of Frizzled proteins....
) or Dkk. Furthermore, using small molecules to block the interaction between β-catenin and TCF could stop the proliferation of cancer. Researchers have also developed a recombinant adenovirus (Ad-CBR) that constitutively expresses the β-catenin binding domain of APC. This enables the tumor suppressor activity of APC, thus preventing β-catenin translocation to the nucleus. Scientists are also using monoclonal antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies are monospecific antibodies that are the same because they are made by identical immune cells that are all clones of a unique parent cell....
against Wnt proteins to induce apoptosis
Apoptosis
Apoptosis is the process of programmed cell death that may occur in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, and chromosomal DNA fragmentation...
in cancer cells. Currently, there are many investigations underway to target various components of the Wnt pathway as a means of finding more effective treatments for cancer.
See also
- Signal transductionSignal transductionSignal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a cell surface receptor. In turn, this receptor alters intracellular molecules creating a response...
- MorphogenesisMorphogenesisMorphogenesis , is the biological process that causes an organism to develop its shape...
- Developmental biologyDevelopmental biologyDevelopmental biology is the study of the process by which organisms grow and develop. Modern developmental biology studies the genetic control of cell growth, differentiation and "morphogenesis", which is the process that gives rise to tissues, organs and anatomy.- Related fields of study...
- EmbryogenesisEmbryogenesisEmbryogenesis is the process by which the embryo is formed and develops, until it develops into a fetus.Embryogenesis starts with the fertilization of the ovum by sperm. The fertilized ovum is referred to as a zygote...
- CancerCancerCancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
- CateninCateninCatenins are proteins found in complexes with cadherin cell adhesion molecules of animal cells. The first two catenins that were identified became known as alpha-catenin and beta-catenin. Alpha-catenin can bind to beta-catenin and can also bind actin. Beta-catenin binds the cytoplasmic domain of...
- GSK-3GSK-3Glycogen synthase kinase 3 is a serine/threonine protein kinase that mediates the addition of phosphate molecules on certain serine and threonine amino acids in particular cellular substrates...
- FrzbFrzbFrzb is a Wnt-binding protein especially important in embryonic development. It is a competitor for the cell-surface G-protein receptor Frizzled....
- Wingless localisation element 3 (WLE3)Wingless localisation element 3 (WLE3)The WL3 Wingless localisation element 3 is an RNA structure that localises the wingless mRNA in flies.The structure consists of a stem, a bulge region, another stem and a loop.The published structure was determined and refined through experiments....
- Baldness treatmentsBaldness treatmentsBaldness treatment is a US $1 billion per year industry. In males past their early 20s, the incidence of balding is roughly equivalent to chronological age. Thus, by age 50, roughly half of men experience male pattern baldness . Beginning in the 1980s, drug therapy has increasingly become a...
External links
- Wnt site from Nusse Lab, Stanford
- Wnt pathways, their relationship, disease, and therapies by healthvalue.net
- Drosophila Wnt pathway from KEGG
- mouse Wnt pathway from KEGG
- humanα Wnt pathway from KEGG
- Homo sapiens (human) Wnt pathway from KEGG
- NetpathNetpathNetPath is a manually curated resource of human signal transduction pathways. It is a joint effort between Pandey Lab at the Johns Hopkins University and the Institute of Bioinformatics , Bangalore, India, and is also worked on by other parties....
- A curated resource of signal transduction pathways in humans

